Mobile cultivation beds [Allemagne]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Peter Kirch
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1678 - Allemagne
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Shaw Robert
Nomadisch Grün gemeinnützige GmbH
Allemagne
Bärich Christian
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Nomadisch grün GmbH - AllemagneNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) - Allemagne1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Mobile vegetable cultivation system for urban areas with "baker boxes" as main elements.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
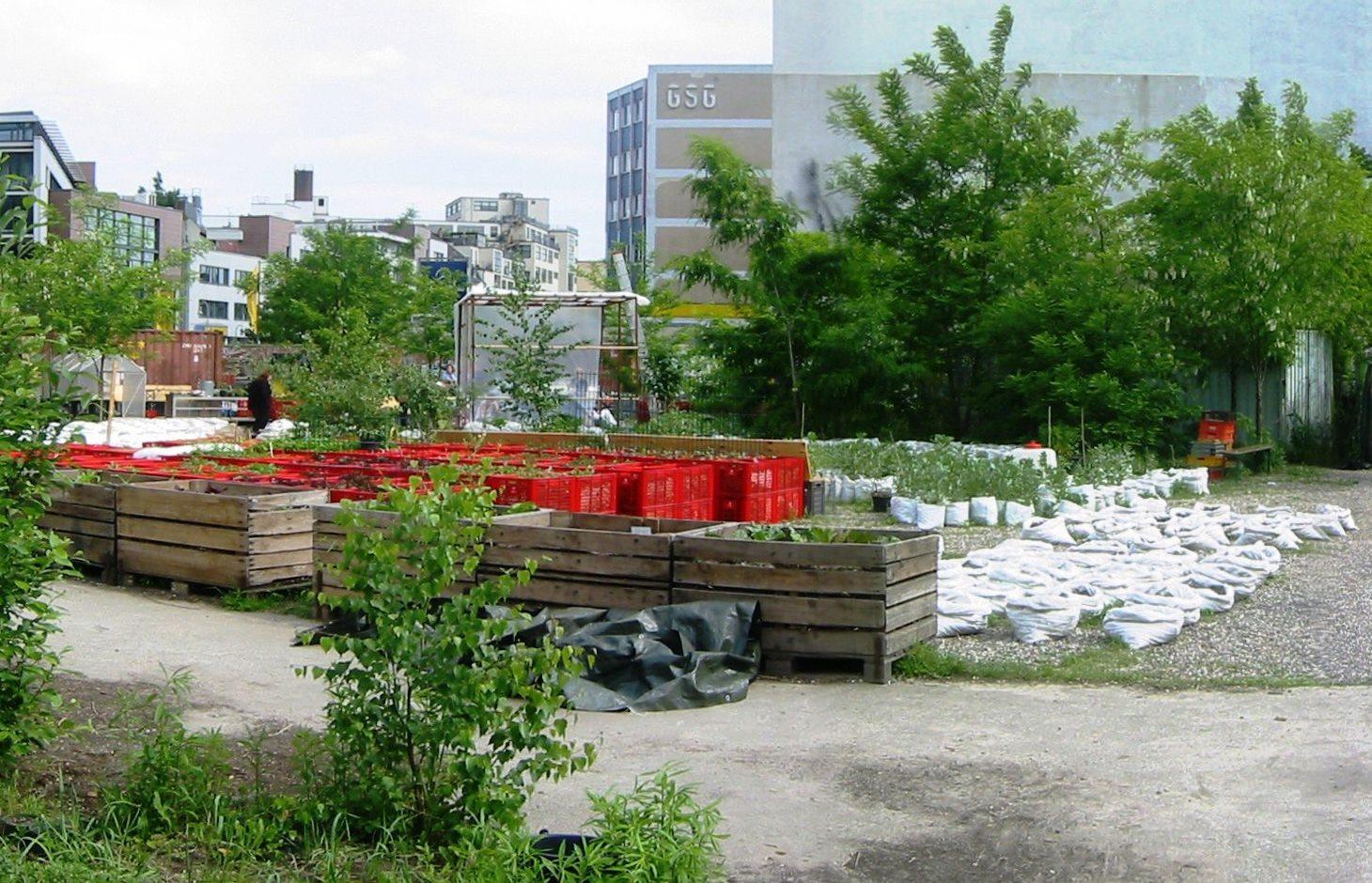
The main technology applied in the urban gardening project "Princess gardens" can be described as mobile vegetable culitivation system based on the use of "baker boxes".
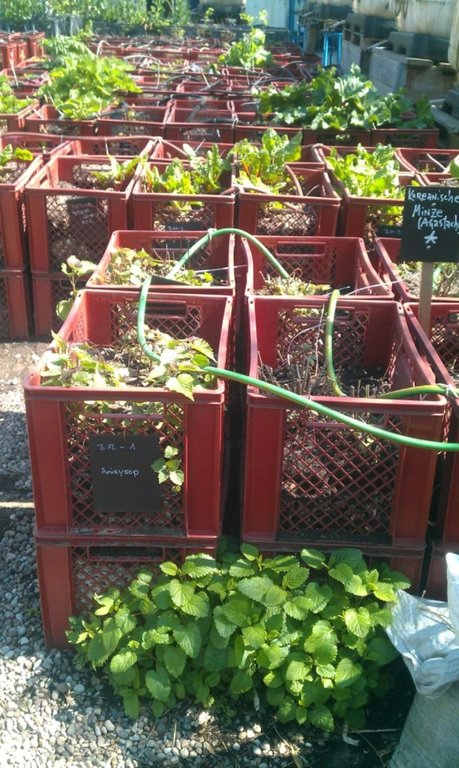
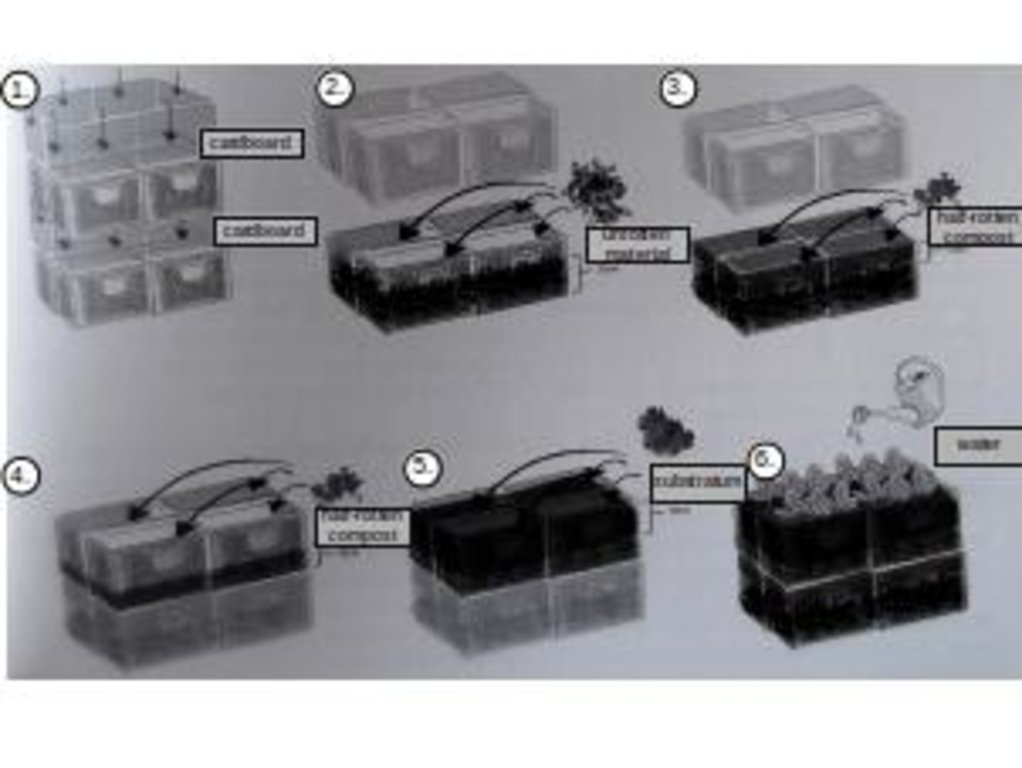
"Baker boxes" are plastic boxes (size: average area of 40 cm x 60 cm x 35 cm) made out of heat-resistant materials, which do not contain softeners. The bottom part as well as the side parts are formed in a grid pattern (holes of 1cm³ size).
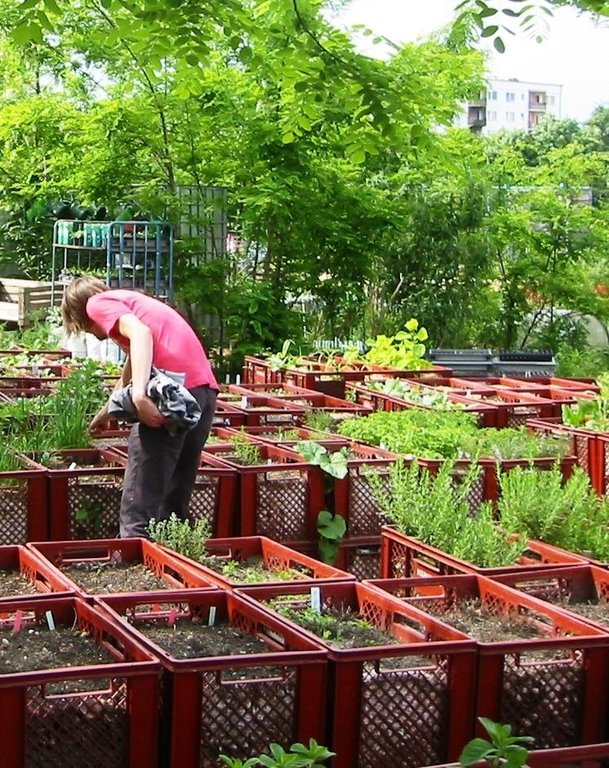
For the vegetable production, cultivation units ("box towers" ) are built out of two boxes by placing them on top of each other. The lower box is filled with organic material (composition of the material like in a compost) and the upper box is filled with garden mould (or other earth material suitable for cultivation). To prevent the washing out of earth material through the grid pattern, carton is put on the bottom as well as on the side walls of the upper box.
During a period of time (length can vary from 1 to 3 years) the upper box can be cultivated according to the principles of "good practise" (e.g. crop rotation). During this time, the lower box serves as compost. In the course of each year this box is checked if the ongoing decomposition processes have lead to the creation of free space in the box. In this case, organic material needs to be refilled.
In the end of the 1-3 years-cultivation period the upper box is emptied and the contained earth material can be used for purposes such as landscaping. The box is then filled with organic material and switched with the lower box, which should contain "ready to cultivate"-compost material. The cultivation can then be restarted.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to allow cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils. Through the use of the box towers as cultivation units the roots of the plants never get in touch with the soil. While the main rooting zone is to be found in the upper box, deeper rooting plants can grow down to 70 cm into the lower box without reaching the soil in place.
Another purpose of the technology is to create a mobile cultivation system. If needed, the boxes can be easily moved away even during the vegeation period.
Last but not least, the technology has the purpose to create a space, where knowledge sharing on a practical basis regarding the topics e.g. agriculture, sustainability and health can take place.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the technology first and foremost a sufficient number (depending on the size of the gardening area) of "baker boxes" is needed.
Maintenance activities consist of refilling the lower box with organic material.
This is also true for the required inputs.
Natural / human environment: The environment is strongly influenced by humans, as the first urban structures in this area already were established about 200 years ago. Regarding the topic soil this led to the conversion of the natural soils in place to Technosols.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Allemagne
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Berlin
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,006
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,006 km2.
Map
×3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Implantations, infrastructures
- Habitats, buildings
- Trafic: routes, réseaux ferroviaires
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem can be addressed as a lack of cultivation plots within the urban areas. This is due to the fact that the soils are to a great extent sealed or contaminated.
As a result in the urban area there is also a lack of pratical learning areas which relate to the topics agriculture and soils.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As major land use problems the cultivation circumstances are regarded. This inculdes the topics of destroyed natural soil fertility and a lack of water infiltration into the ground.
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 200Longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- Cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S11: Autres

modes de gestion
- M6: Gestion des déchets (recyclage, réutilisation ou réduction)
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
Specification of other structural measures: creation of cultivation plots
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation physique des sols
- Pk: scellage et encroûtement
- Pu: perte de la fonction de bio-production en raison d’autres activités
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (1 sealing (foundations of buildings were constructed in the area))
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (as a main cause for urbanisation), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (need for public services in the city), governance / institutional (urban planning in the city)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Commentaires:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
edited by Peter Kirch on the basis of Daniel Müller/dkmnews in „Prinzessinengärten- Anders gärtnern in der Stadt“, Nomadisch Grün (Hg.),Dumont Buchverlag, Köln, 2012, page. 115
Location: Berlin. Germany
Date: 08.10.2015
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Structural measure: boxes
Spacing between structures (m): various
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,35
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,6
Construction material (other): plastic (food-safe)
Change of land use type: urban area to urban gardening area
Layout change according to natural and human environment: area is limited through infrastructure elements (roads) and buildings.
Auteur:
Peter Kirch
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Euro
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
0,9
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | putting boxes in place |
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Costs are affected by the wages for the employees and the rent of the plot
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water sotrage capacity is very low
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Seasonality of water quality and source of pollution: for agricultural use only (rainwater)
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2%
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, very poor
1% of the land users are very rich.
5% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
4% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- communauté/ village
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
100
diversité des produits
surface de production
Revenus et coûts
revenus agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
100
diversité des sources de revenus
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
institutions communautaires
institutions nationales
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The "Prinzessinnengarten" is more than just a place to grow vegetables in the city. It is a space for diverse activities. Through the opportunity to contribute and to participate in open workshops, through the garden café and a variety of cultural events, the "Prinzessinnengarten" has become a lively meeting place far beyond the neighborhood.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
ruissellement de surface
Sols
humidité du sol
couverture du sol
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
diversité végétale
diversité animale
diversité des habitats
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | pas connu |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de vent locale | pas connu |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas connu |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Commentaires:
An economic analysis is hard to make, as the main goal of the project is not economical profit. In the interviews it was stated, that each year about 50.000 people visit the garden. To have an outreach to such a high number of people with a budget of about 500.000 € is regarded as "benefical" by the project members.
Only looking at the financing part it was stated in the interview that the garden is one of the very few urban gardening projects that can provide for its recurrent costs itself.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Comments on adoption trend: The members of the "Prinzessinnengarten" are supporting other land users to implement urban gardening projects through giving them advise. Up to 100 urban gardening projects were supported this way. The support is often funded by foundations. How to receive such funding is communicated by the Prinzessinnengarten to the ones seeking their advise.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| light and long-lasting production units |
| a great part of the needed material has been recylced |
| standardized format of the production units (fitting even to international cargo norms) |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| mobile, flexible cultivation system |
| allows cultivation on sealed or polluted soils |
| open access technology |
| knowledge sharing as key priority |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| limited productivity | |
| are highly dependent on irrigation, as the boxes dry-out fast (high evaporation/ surface area) | |
| Soil can be easily lost/washed out throught the grid pattern (especially in the long term, when the erosion measures are reduced (decomposition of carton) | |
| The spacing in between the boxes serves as habitat for snails. | |
| The carton sometimes rots away in the course of the cultivation period. This leads to a loss of soil material out of the boxes. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| dependent on a high supply of "baker boxes" | |
| dependent on external inputs (especially organic material) | |
| allows only for hand labour |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Urban Gardening. Über die Rückkehr der Gärten in die Stadt. Christa Müller, 2011.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
ISBN 3-86581-244-9
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Prinzessinnengärten. Anders gärtnern in der Stadt. Marco Clausen, 2012
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
DuMont,ISBN 3-8321-9436-3
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé