Drought-resistant crops [Suisse]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Seraina Lerf
- Rédacteurs : Tatenda Lemann, Maria Eliza Turek, Joana Eichenberger
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6272 - Suisse
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Brunner Stefan
Brunner Eichhof
Suisse
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suisse1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The technology described covers one such response in Switzerland.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The key is the improved adaptation of the crops to heat and drought. These adaptations are based on plant physiological and morphological characteristics that confer increased drought tolerance, as well as phenology, which can also affect the plants' water requirements. The goal is to reduce production losses and promote a regional, plant-based food system in Switzerland. To introduce and maintain drought-resistant crops requires specific activities and inputs, such as selecting suitable seeds and ensuring long-term profitable cultivation. This technology is applied to cropland in Switzerland, especially in the Swiss Plateau, where climate change is causing increasingly warmer and drier summers, as well as more intense precipitation in the winter months. These climatic changes favour the cultivation of crops that can better cope with drought periods, allowing for the replacement of crops that require irrigation in the same growing areas.
The main purpose is to adapt agricultural production to the effects of climate change while simultaneously reducing the emissions caused by farming. By cultivating drought-resistant crops, the risk of production losses during drought periods can be minimized, and a transformation towards more diverse, plant-based, and regional food production systems can be promoted. A major advantage of this technology lies in the adaptability of the selected crops to climate change. Since they are better adapted to tolerating drought periods, no additional irrigation is needed: this saves labour and other resources. Moreover, growing drought tolerant crops enables the production of regional, plant-based, and protein-rich foods (especially legumes) that are appreciated by certain consumer groups and can be better marketed.
However, there are also challenges and disadvantages that are not yet appreciated by land users. The lack of knowledge about non-traditional crops in Switzerland is a significant problem. Both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in cultivation are lacking, leading to high risk for farmers who must experiment with cultivation. Additionally, despite climate scenarios predicting drier summers, there is still the risk of cool and wet summers with increased precipitation. Besides the biophysical challenges, there are also socio-economic obstacles, as the demand from wholesalers is often focused on traditional crops, and niche crops like millet are commonly not popular.
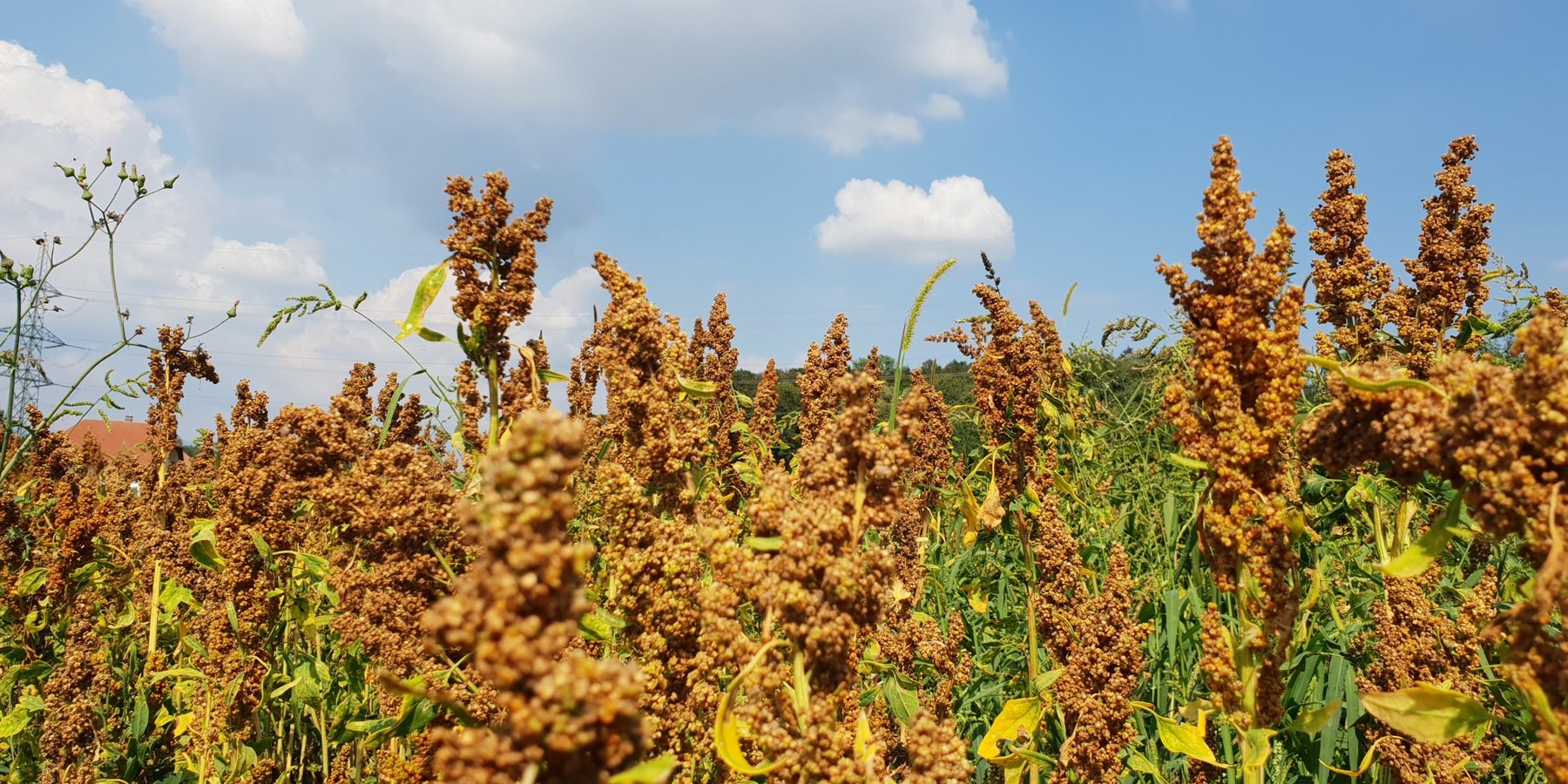
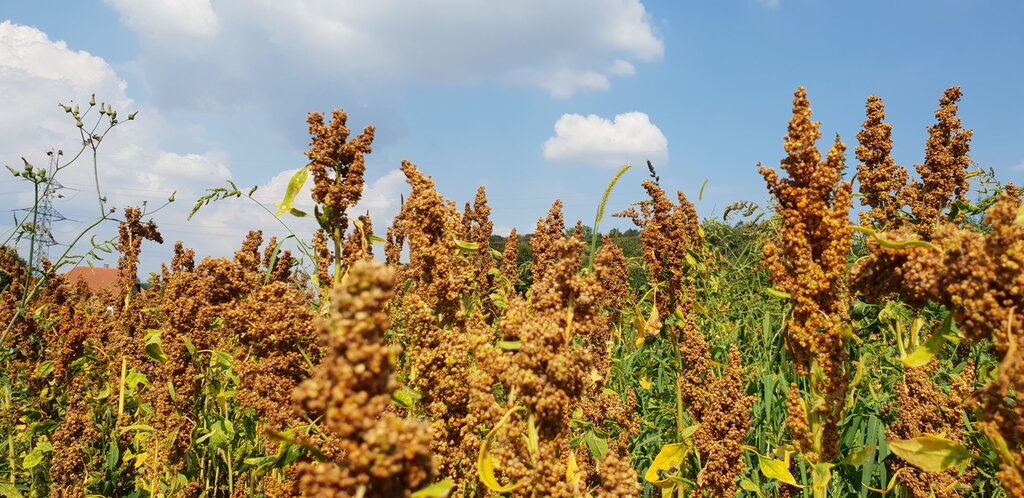
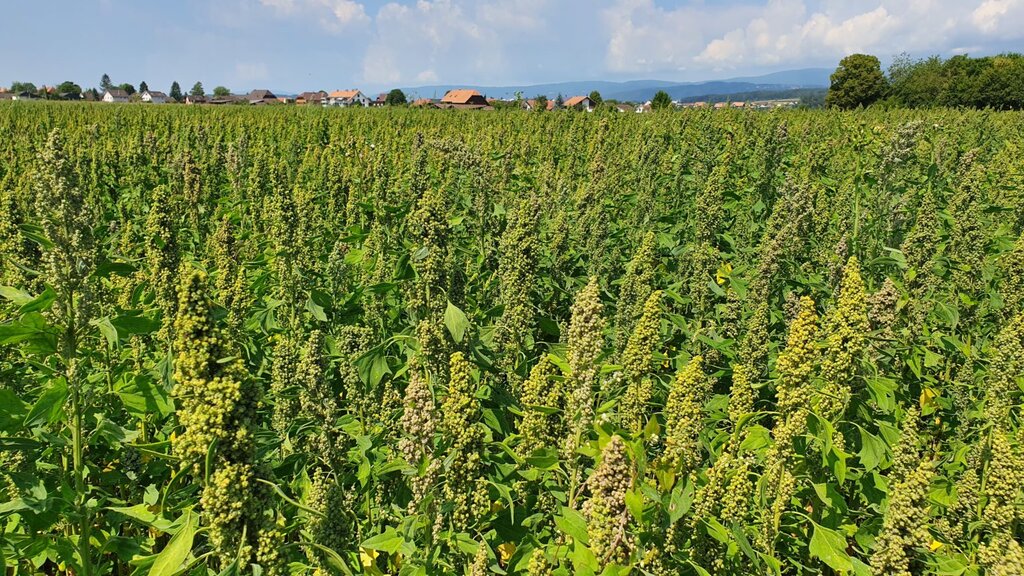
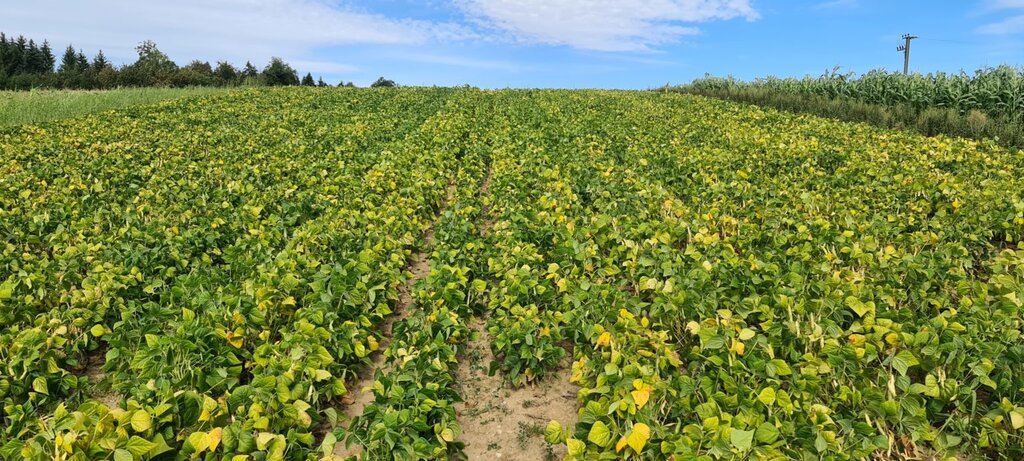
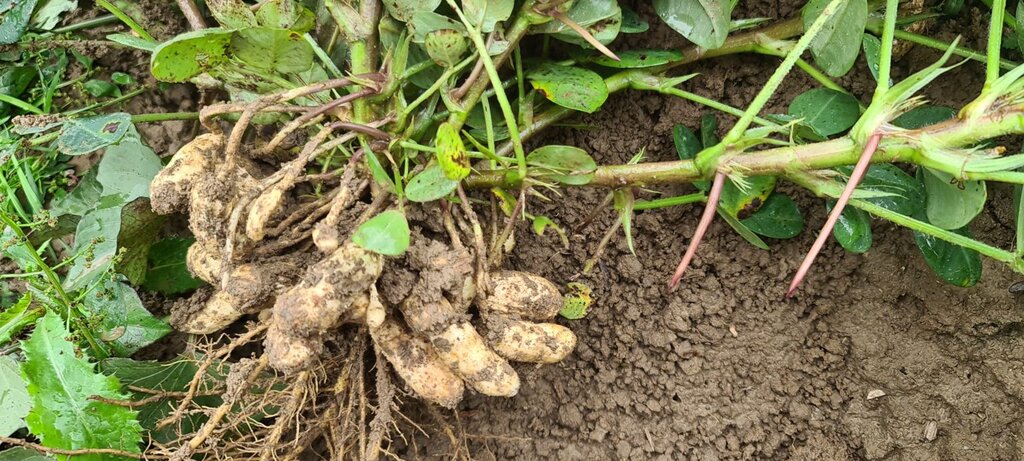
This documentation focuses on an example of an innovative farmer in Spins, Switzerland. Stefan Brunner has been testing a wide variety of drought-resistant legumes such as lentils, lupins and black runner beans on his Eichhof farm since 2017. In addition to the large-scale cultivation of these drought-resistant crops, he also cultivates quinoa, peanuts, chia, sorghum, millet and rice in a demonstration plot. Stefan Brunner simultaneously attaches great importance to sustainable cultivation methods which include surface tillage and mulching.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
All pictures were taken on the agricultural land of Stefan Brunner in Spins near Aarberg. The pictures of the quinoa field, the bean cultivation and the peanut harvest were taken from the website of the Brunner family's Eichhof farm:
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Suisse
Région/ Etat/ Province:
western midlands of switzerland
Autres spécifications du lieu:
western midlands of switzerland (Broye catchment area), example farm in the canton of berne in Spins (near Aarberg)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 0,1-1 km2
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The regions in which the technology is used are located in the agricultural zone of Switzerland
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2017
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - quinoa ou amarante
- céréales - sorgho
- céréales - blé d'hiver
- cultures fourragères - graminées
- legumes and pulses - lentils
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
The number of growing seasons depends on the crops grown. With a crop rotation of 6 years, winter cereals, winter lentils/winter legumes and lupins are grown overlapping after three years of permanent grassland (grass production). Brunner also uses green manure between the different crops and therefore has around 2 growing seasons per year
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
6 years crop rotation:
3 years grass
Winter cereals
Winter lentil (winter legumes)
Lupin

Pâturages
Pâturage intensif/ production fourragère :
- Affouragement en vert/ zéro-pâturage
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pleine irrigation
Commentaires:
Stefan Brunner is able to irrigate all his fields in Spins near Aarberg. He owes this to the nearby location of the "Alte Aare" river, which gives him the privilege of having sufficient water available even during the summer.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A5: Gestion des semences, amélioration des variétés
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Brunner sees soil degradation as an unavoidable consequence of all agricultural tillage. However, this can vary greatly depending on the type of tillage. Brunner does not see a direct improvement in soil degradation through the cultivation of drought-resistant plants. However, in combination with soil-conserving forms of cultivation. Brunner attaches particular importance to shallow tillage (maximum depth of 5 cm). Accordingly, crops that can be sown at this depth are suitable. Brunner strives for permanent rooting of the soil and prefers crops that can be sown in the fall so that the soil is rooted over the winter or can handle green manure. These measures (shallow cultivation and root penetration) keep the soil looser. The roots form flow paths, which increases the water storage capacity of the soil. The shallow tillage with small machines, which Brunner uses for his drought resistent crops, also reduces the physical pressure on the soil compaction.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
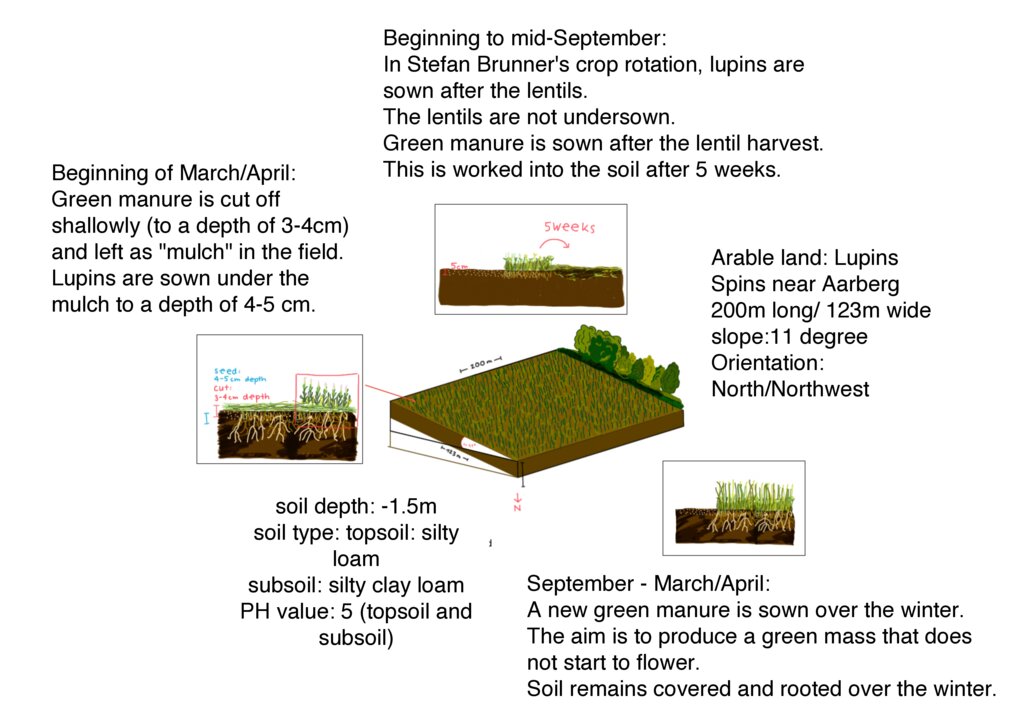
The depicted technical drawing shows the farmland of Stefan Brunner, where lupins were sown in the spring of 2024. This field is representative of all the arable land, totaling 14 hectares of crop rotation areas managed by Brunner. The cultivation areas are situated at an altitude of 487 meters above sea level on flat or slightly sloping terrain on a hill range in the Bernese Mittelland. The depicted field is 200 meters long and 100 meters wide, with a slope of approximately 11° and an orientation towards the north/northwest. The soil is classified as silty loam based on the finger roll test, with the subsoil containing more clay compared to the topsoil. The pH value is 5, which is in the slightly acidic range.
The fields in Spins are located near the river "Alte Aare." Due to the proximity to the water, the farmer has the privilege of having irrigation available for all his fields. Since the implementation of large-scale cultivation of drought-resistant crops in 2017, Brunner has been growing a variety of crops on his land. According to Brunner, the following crops that he cultivates can cope well with drought: lentils, lupins, sorghum, corn, peanuts, millet, and cabbage. In combination with the method of surface rotting and mulching, the soil is protected against drying out and erosion and can retain moisture for longer. The cultivation of various crops can be combined with this farming method, leading to better drought resistance.The graphic illustrates the cultivation of lupins using a green manure cultivation method.
Auteur:
Seraina Lerf
Date:
21/06/2024
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
18 ha
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage: and sowing | (once per cultivation period) |
| 2. | maintenance: weeding (recurring work step, but less labor-intensive than tillage) | (Recurring work throughout the year) |
| 3. | harvesting: threshing | (once a year for grain legumes) |
| 4. | Threshing the previous crop. Before the lupins, lentils were grown in Stefan Brunner's crop rotation. | summer (july-september) |
| 5. | If there is no undersowing (as with the lentils), the soil must be tilled. This is very shallow, i.e. no more than 5 cm deep. | summer (july-september) |
| 6. | A varied green manure is sown in the cultivated soil. The aim of this is to keep the soil rooted and to incorporate nutrients into the soil | summer (july-september) |
| 7. | After 6-7 weeks, the green manure is worked back into the soil. When the plants are still young, they have the highest nutrient input before they extract the nutrients from the soil again if they continue to grow. As a result, the nutrients are mineral-bound in the soil, i.e. stored so that they are available to the plants. | autumn (early/mid-September) |
| 8. | Another green manure is sown, which produces a lot of mass but freezes off in winter before it starts to flower. The aim is to keep the soil covered and rooted throughout the winter. | autumn |
| 9. | In spring, the soil is again worked shallowly. This means a maximum depth of 3-4 cm. The winter green manure is "planed". This means cutting it to a depth of 3-4 cm and leaving the plant material on the ground. | spring |
| 10. | The lupins are sown under the plant material to a depth of 4-5 cm, so that the soil remains moist and the plant material protects the soil from drying out. | spring (beginning of March/April) |
Commentaires:
The first three information does not refer to a specific crop, but describes general maintenance activities that Brunner takes into account when cultivating his crops.
Stefan Brunner's crop rotation also includes 3 years of grassland. This cultivation reduces the workload, as no maintenance work has to be taken into account in addition to the harvest.
The activities 4-10 described relate to the cultivation of lupins. This crop was cultivated at the time of documentation in spring 2024.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Si vous n'êtes pas en mesure de décomposer les coûts dans le tableau précédent, donnez une estimation du coût total de l'entretien de la Technologie:
22575,0
Commentaires:
The costs of cultivating drought-resistant plants cannot be precisely quantified. Based on the interview results, it is therefore not possible to make any general statements about the costs of cultivation.
Nevertheless, in order to be able to make a rough estimate of the input costs required to implement the technology (Example based on the cultivation of lupins), information from REFLEX 2024 (AGRIDEA's business database) and FiBL (Research Institute of Organic Agriculture) was used. According to REFLEX 2024, the target price for lupins in 2023 and 2024 is 144Fr./dt. A FiBL leaflet also states a requirement of 130-170kg seed/ha (blue lupins).
According to the results collected, the documented farm uses a disk coulter seed drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm, sows approx. 3-4 cm deep and requires 200 kg/ha of seed.
With a field size of the documented farm of approx. 2 ha, the costs for the required lupin seed amount to CHF 576 according to the data from REFLEX 2024.
Then there are the labor costs and the machines. Depending on which machines are required and whether the required machines are already available or whether a new investment or rental would be necessary.
The estimate only refers to the seed required. Additional recurring costs include maintenance/ rental costs for machinery and labour. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more precise information on this. It depends on the machines and labor costs used.
However, according to the interview results with a farmer who grows drought-resistant crops, there are no significant additional costs if the drought-resistant crops can be grown with the same machinery as for conventional crops.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The greatest difficulty in terms of costs lies in the lack of knowledge in the cultivation of these crops. The fact that very little scientific and practical knowledge and experience is available means that farmers take a greater risk in cultivating these crops. If cultivation is not carried out correctly and the farmer suffers production losses as a result, he bears the consequences. This is why they have to look for inventive solutions.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
865,00
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Payerne
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Production losses during periods of drought can be minimised
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Product diversity can be increased by growing alternative drought-resistant crops
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By improving the soil's ability to cope with weather extremes (drought/heavy rainfall), land management in cultivation is simplified through greater flexibility.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau potable
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Gentle tillage without the use of pesticides in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops (good groundwater quality)
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Drought-resistant crops require less irrigation. In addition, the tillage method (surface rotting) also prevents the soil from drying out.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Gentle soil cultivation with minimal use of machinery (and application of surface rotting) requires more labour, even if the cultivation of drought-resistant crops does not mean additional work compared to conventional crops
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Less water required for irrigation
qualité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Avoiding the use of pesticides leads to improved water and soil quality
Harvesting/collection of water
récolte/ collecte de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods) can lead to improved groundwater recharge
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Surface runoff can be minimised by improving the water absorption capacity of the soil (permanent root penetration).
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods), less excess water is formed
nappes phréatiques/ aquifères
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil can lead to improved groundwater recharge
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Permanent ground cover can reduce soil drying out
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The permanent ground cover reduces drying out and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This can improve the soil water balance.
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The ground should be permanently covered. The permanent ground cover reduces drying out.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The permanent covering and rooting of the soil prevents surface run-off. This can prevent soil loss.
accumulation de sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Green manuring can ensure an improved hummus structure.
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The permanent ground cover reduces dehydration and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This prevents soil sealing.
compaction du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The soil should remain permanently rooted and covered and be worked with as few and light machines as possible. This minimises soil compaction.
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By applying green manure, the soil can be enriched with nutrients (nutrient cycle of the soil).
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
greater plant diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts de la sécheresse
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the improved ability of plants to cope with drought. to deal with drought. In combination with good water storage capacity of the soil, the effects of drought on the harvest can be minimised.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
Information in this chapter on practical experience in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops is based on interview results from Stefan Brunner. He cultivates drought-resistant crops in combination with surface cultivation and mulching. As a result the effects of the two technologies cannot be considered entirely separately.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
flux des cours d'eau fiables et stables en saison sèche
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
pollution des rivières/ nappes phréatiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The use of herbicides and fungicides was avoided in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, thus preventing contamination
capacité tampon/de filtration
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
improved water absorption capacity (through soil cultivation methods) of the soil
Stability of production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the improved adaptability to climatic conditions, production remains more stable
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. Annelie Holzkämper
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | modérément | |
| températures saisonnières | été | augmente | modérément |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| canicule | modérément |
| vague de froid | pas connu |
| conditions hivernales extrêmes | pas connu |
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes biologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| maladies épidémiques | pas connu |
Commentaires:
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. rer. nat. Annelie Holzkämper
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
The more equipment has to be used in cultivation, the more expensive the maintenance costs become. As Brunner is able to cultivate drought-resistant crops such as lupins and lentils with the existing equipment, he did not incur any additional costs. Even if a new machine for gentle soil cultivation in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, such as a “planer”, had to be purchased, a plow could be sold in return. As long as the same mechanization can be used as Brunner was already using for conventional crops, the costs remain the same. As a result, Brunner's cost-benefit ratio was assessed as positive, even in the short term.
In the long term (over a period of 10 years), Brunner also sees an increased positive cost/benefit ratio. Consistently good soil cultivation regenerates the soil so well that it is able to absorb much more water. The amount of work required to implement this form of cultivation increases in the short term. However, the improved soil conditions in connection with the cultivation of drought-resistant crops have a positive effect on the workload and yield in the long term, as the crops on healthy soil are more flexible in the face of extreme weather conditions such as increasingly frequent droughts. Brunner also emphasizes that, from his perspective, it is worth incurring higher start-up costs for careful cultivation in order to generate long-term benefits.
The start-up costs are often relatively high, but the long-term benefits are all the more valuable. Start-up capital is therefore essential to be able to generate long-term benefits.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
Information based on the experience of Stefan Brunner (Spins)
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
autre (précisez):
breeding
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Continuous adaptation in the context of breeding
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| No Irrigation Needed: These crops do not require irrigation, thus saving water and reducing labor. |
| Promotion of Soil Health: The cultivation of these crops is beneficial for the soil, as as the tillage is shallow and legumes do not require additional nutrient inputs through fertilization. |
| Benefits in Direct Marketing: These crops are niche products produced in limited quantities in Switzerland. Conscious consumers who value regional food products appreciate these items and understand the higher costs due to the high labor requirements. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Reduced Irrigation Needs: If the crops can tolerate more drought, less irrigation is needed. |
| Minimized Economic Risk: Drought tolerance reduces the risk of crop failure during dry periods. |
| Crop Rotation Benefits: Better adaptation through diverse crop cultivation. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| High Labour Requirements: initial labour requirements are significantly higher due to limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation, but with time this reduces - as less and less work is required on healthy and nutrient rich soils. | More practical knowledge should be gathered by encouraging more farmers to cultivate these crops and facilitating knowledge exchange. |
| Lack of Mechanization: Available market machines are not suited for the desired cultivation methods. | Alternative machines are needed, which are smaller and lighter and only minimally till the soil. New approaches and inventions in machinery are required. |
| The wholesale market is not particularly interested in domestically produced alternative foods. Wholesalers are profit-oriented and primarily offer what is consumed in Switzerland. | A reorientation of dietary habits is necessary. Millet, for example, is ideally suited to the climatic conditions in the Seeland region. Increased consumption could lead to more extensive cultivation. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge: limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation | More research should be carried out in this area and practical experience in cultivation should be gained through practical implementation. Inovative farmers are in demand. |
| Weather Variability: There is no guarantee that heavy rains won't occur, potentially ruining the harvest. | The extent to which crops are affected by severe weather events depends on when they occur. Severe weather events have an impact on every crop, but of course you don't know when they will occur. A useful strategy is therefore to build a highly diverse production system at farm and landscape level. |
| Practical and Socioeconomic Challenges: Market preferences and practical issues, such as livestock not favoring sorghum feed, can be obstacles. | No answer given. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
On June 10, 2024, an interview was conducted with farmer Stefan Brunner on his farm in Spins near Aarberg. Additionally, the cultivated area was inspected
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
On June 20, 2024, an interview was conducted with PD Dr. Annelie Holzkämper.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
10/06/2024
Commentaires:
Inspection of the cultivation aera
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve et al. (2023): How to find alternative crops for climate-resilient regional food production, in: Agricultural Systems, Bd. 213, S. 103793, doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103793.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Wuyts, Nathalie et al. (2023): Klimaresilienter Ackerbau 2035, Agrarforschung Schweiz, doi:10.34776/afs13-135.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve. (2021): Prospects of cultivating alternative crops in a changing climate in Switzerland, Master’s Thesis, University of Bern.
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Internet platform of the Eichhof of the Brunner family from Spins near Aarberg
URL:
https://www.brunnereichhof.ch
7.4 Observations d'ordre général
The information used to complete this documentation is mainly based on the experience reports of Stefan Brunner from an interview on June 10, 2024
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé