Mechanical Bench Terracing [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : ONGPO LEPCHA
- Rédacteur : Tashi Wangdi
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Thruel Chhey Lag Len Thap Tey Aring Chey Ni (འཕྲུལ་ཆས་ཐོག་ཨ་རིང་བཅད་ནི།)
technologies_6836 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Penjor Tenzin
Bemji village
Bhoutan
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology is not problematic with regard to land degradation. Indeed, the terraces helps in avoiding and reversing land degradation by reducing surface erosion, retaining soil moisture and improve soil fertility.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
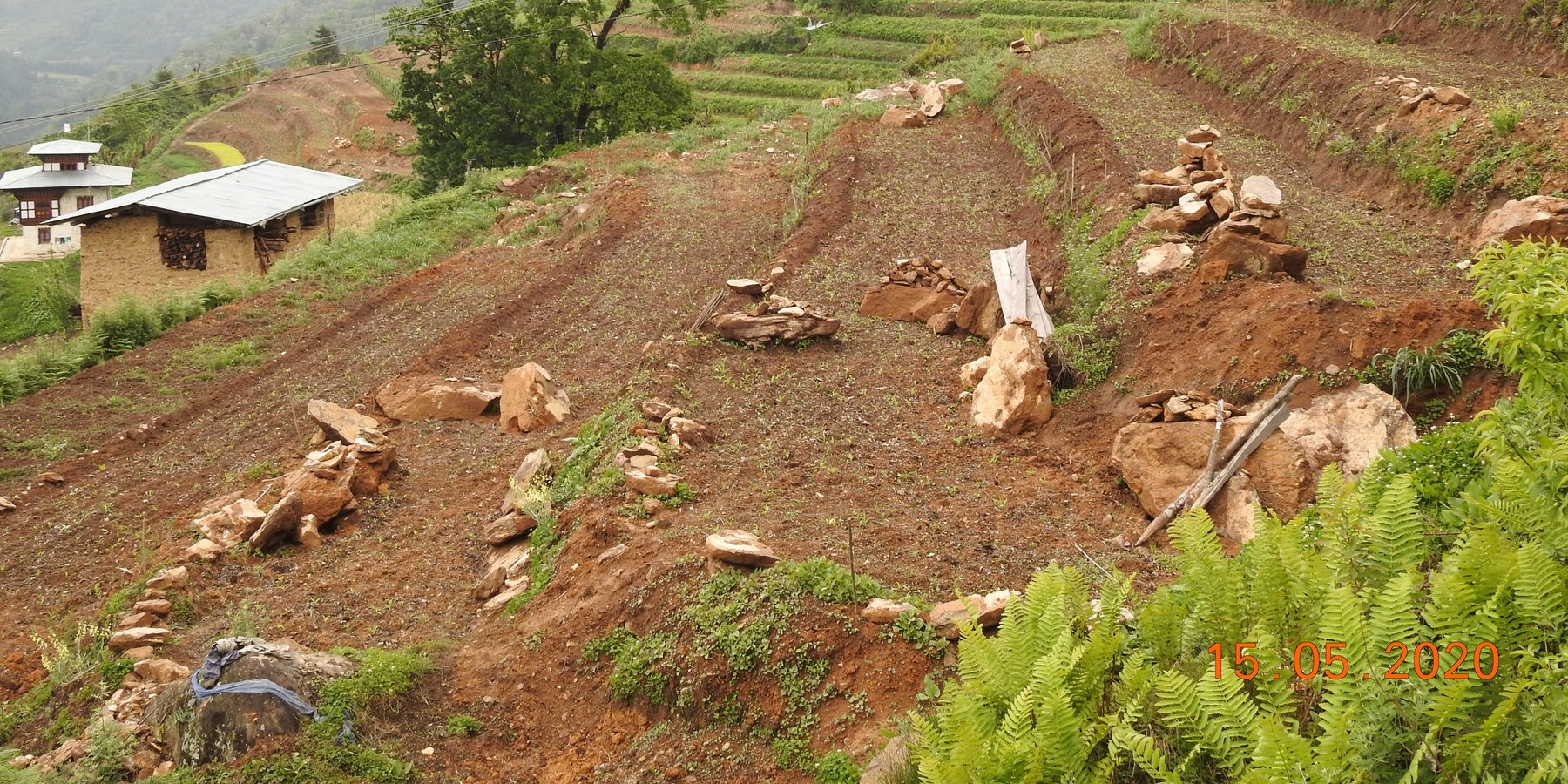
Soil erosion by water is one of the major problems in hilly or mountainous countries like Bhutan. In such areas, effective erosion control measures are required to reduce the slope gradient and minimize surface runoff. Among many SLM interventions, mechanical bench terracing is one of the most widely promoted and popular technologies in Bhutan.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
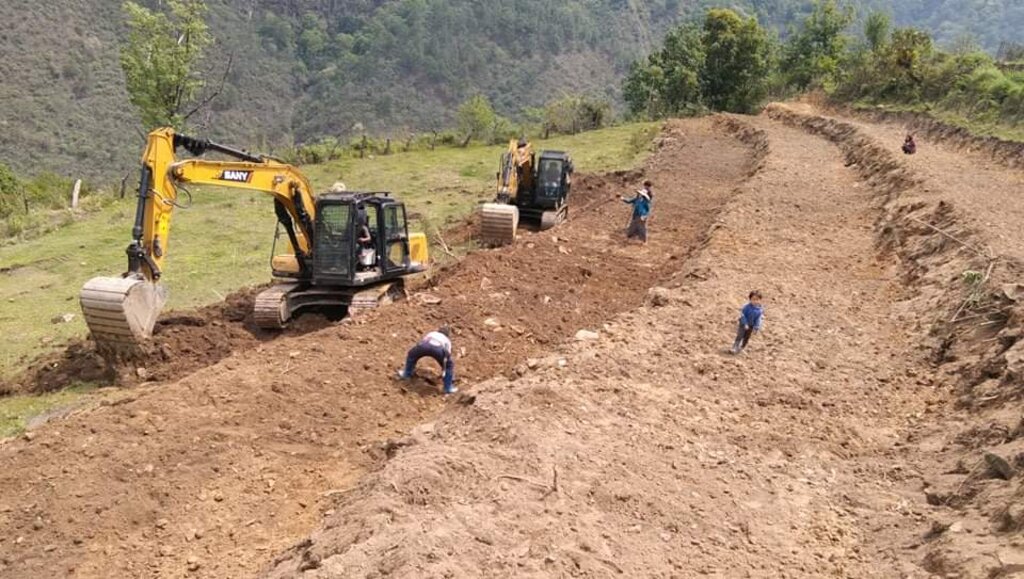
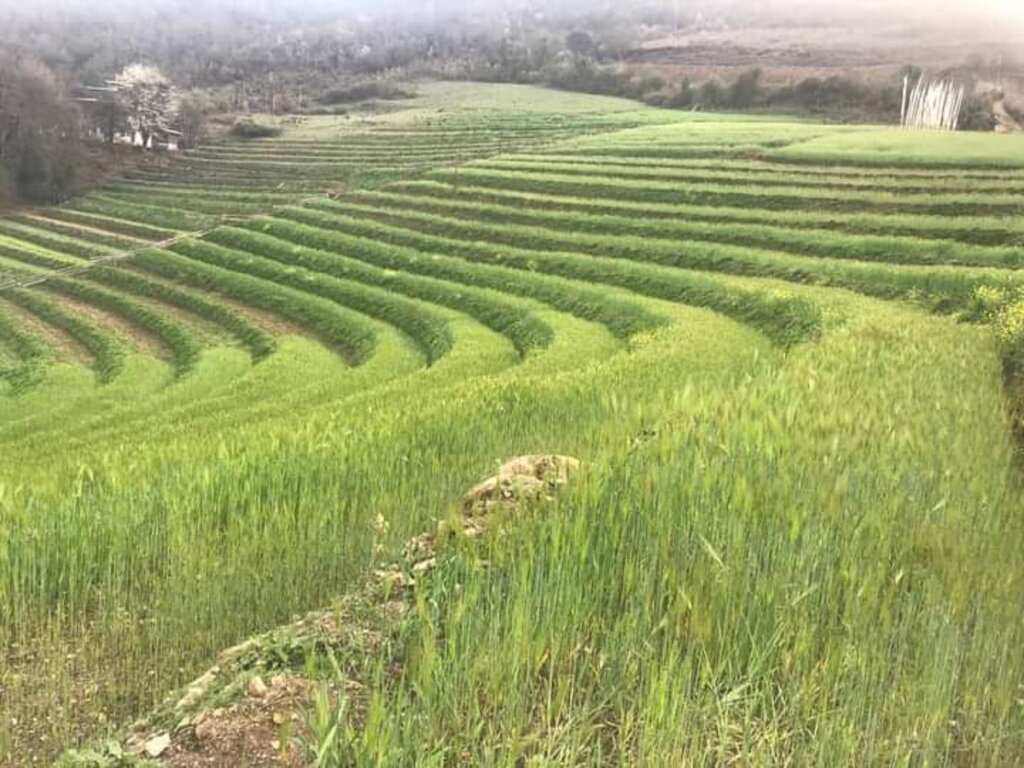
Bhutan is one of the most mountainous countries in the world and agricultural activities are carried out on slopes up to 35 degrees (70 percent). Erosion by water is one of the major causes of land degradation. In such areas, effective erosion control measures include reducing slope gradients to minimize runoff by creating a series of level platforms or “bench terraces” along the contour. Current bench terracing is made using small to medium-sized earthmoving machines called excavators, and thus the technology is called Mechanical Bench Terracing. This is one of the main SLM measures promoted widely and most preferred by landowners who claim that it reduces soil erosion, improves soil fertility, conserves soil moisture, and eases field operations. Bench terraces create impact by 1) helping minimize the risk of soil erosion caused by surface runoff, 2) effectively regulating water flow, and 3) preventing soil saturation by allowing better drainage. Additionally, bench terracing transforms previously unusable or less productive land into cultivable areas, maximizing the utilization of limited land resources. A typical bench terrace on a 20-25 degree slope has a terrace bed of 2-5 m meters and a riser of 0.75 to 1 metre high. The risers are made of earth and the terrace is made flat most of the time to prevent runoff of rainwater.
Establishing and maintaining bench terracing involves a feasibility study of the sites, participatory planning, hands-on training of the landowners, and surveying of contour lines using A-frames. There is also procurement of construction materials, arranging labour and machines and training machine operators. Once constructed, proper water management, soil fertility, and nutrient management practices are crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability and productivity of the terraced land. Furthermore, knowledge and training on crop cultivation techniques, field management, and maintenance are vital to optimize the benefits.
In summary, bench terracing offers numerous benefits. These include:
1) Overall reduction in land degradation
2) Soil conservation by prevention of erosion by runoff
3) Conservation of soil fertility
3) Increase arable land available for cultivation
4) Ease of mechanized field operations with level terrace beds
5) Water conservation and drainage6) Improved crop production
Land users like the fact that bench terracing provides land that is easier to work. The land is better utilized for cultivation, resulting in improved productivity. Land users generally appreciate its numerous benefits in terms of land productivity, soil conservation, and water management. What they dislike are the expense and labour input if expenditure has to be borne by the land owners and neither machine operators nor small to medium-sized machines are readily available in the market for hire.
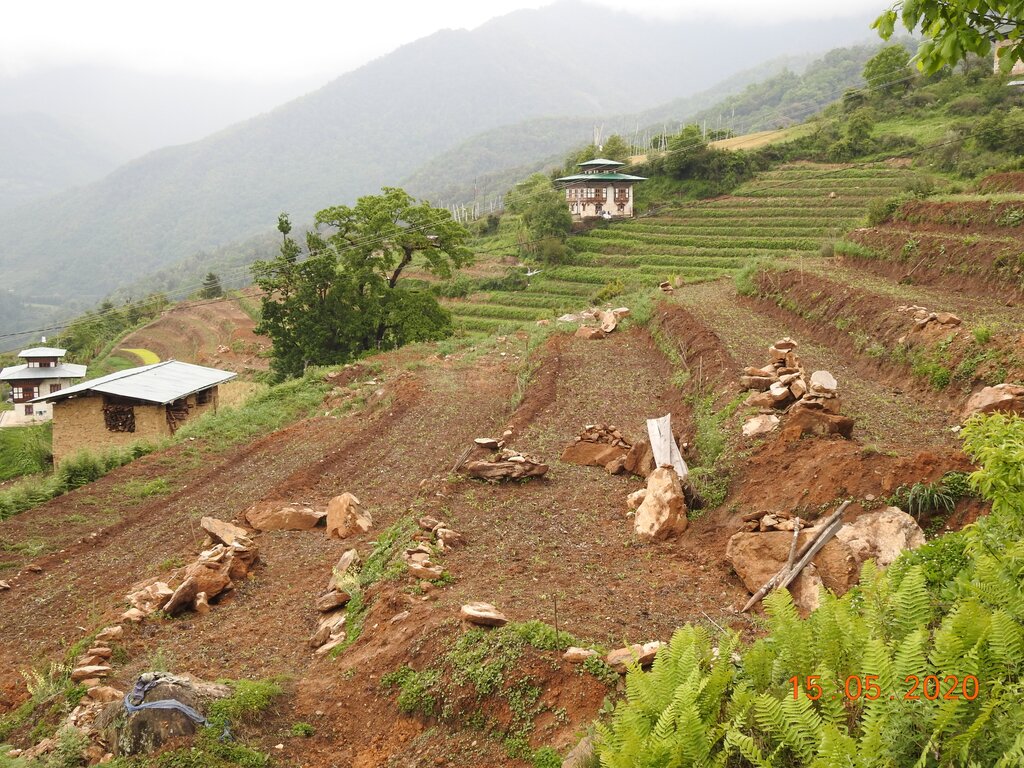
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Trongsa Dzongkhag (district)
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bemji Village, Nubi Gewog (block), Trongsa Dzongkhag (district)
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
1,0097
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2019
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Mechanical bench terracing in Bemji Village was implemented by Dzongkhag Agriculture Sector with technical support from the National Soil Services Center and funded by GEF-LDCF, UNDP
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- protéger un bassin versant/ des zones situées en aval - en combinaison avec d'autres technologies
- créer un impact économique positif
- Improve farm mechanization
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - riz (de terres humides)
- céréales - blé de printemps
- plantes à racines et à tubercules - pommes de terre
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Paddy followed by Wheat or barley
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Paddy followed by wheat or barley/vegetables
Commentaires:
The crops are grown mostly for self consumption, however, the surplus productions are sold at the weekly local market in Trongsa Dzongkhag (District).
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - orge
- céréales - blé de printemps
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Paddy followed by Wheat/Barley/vegetables
Commentaires:
In the past when terracing was not done only flat land was used to grow cereals but sloppy ones were left as grazing land or kept uncultivated. After terracing land user were able to use most of their land for cropping.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
According to the land user, the water supply is mostly rainfed; however, water for irrigation is also readily available.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- mesures en travers de la pente
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S1: Terrasses
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Bench terracing is generally constructed to prevent and reduce land degradation due to surface runoff caused by water/rainfall.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
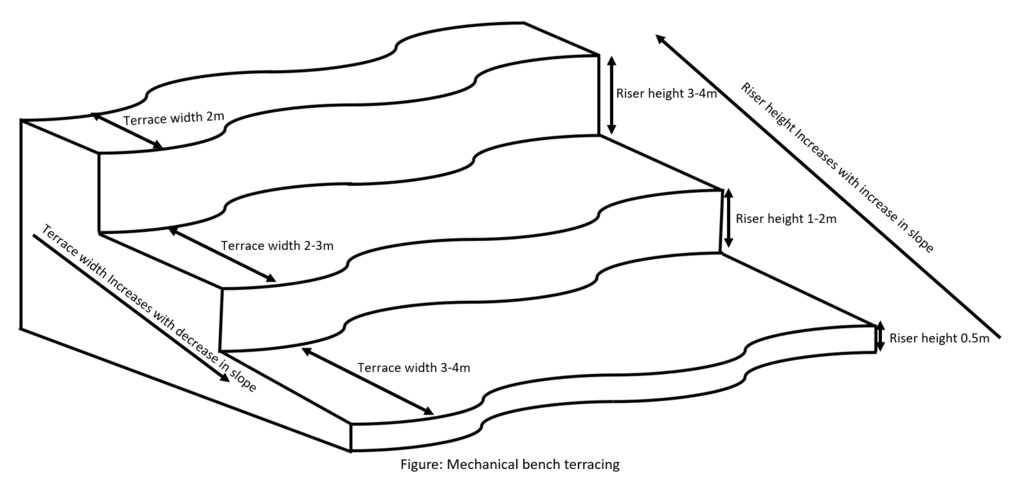
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Technical Drawing of bench which are made mechanically
Auteur:
Ongpo Lepcha
Date:
21/11/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
2.4 acres
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ngultrum
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
80,62
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Feasibility study | Based on land user and extension agents convenience |
| 2. | Participatory SLM Action planning | Based on land user and extension agent convenience |
| 3. | Hands on training for land owners and machine operator | Prior to actual implementation of the activity |
| 4. | Bench terracing by machine | When the land is fallow (Nov-Feb) |
| 5. | Leveling and removal of stones | Based on land user convenience |
Commentaires:
It take about three weeks to implement all the activities in 2.40 acres of land
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Labour | person-days | 98,0 | 500,0 | 49000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Excavator | nos | 1,0 | 40916,0 | 40916,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 89916,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1115,31 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
The land owner bore about 32% of the total cost while the remaining cost was covered by the GEF-LDCF Project
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of terrace bunds | When ever necessary |
Commentaires:
According to the land users, maintenance of the technology involved very little expense because once the terrace was formed the land became more stable.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Once the terraces are well established the maintenance costs are minimal.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The data used was from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Warm temperate zone
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
However, excess rain can cause flooding in the terrace but instances like this has never happened.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
As most of the terraced fields are properly fenced with electric fencing, the incidences of wild animal crop damage are minimal.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes âgées
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- grande dimension
Commentaires:
In total, land users have around 23 acres of land, however the technology was applied on 2.40 acres of land.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
Précisez:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the Land Act and the Land Rules and Regulations of the Kingdom of Bhutan, which dictate the overall land use in the country.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
Before 1,814 kgs/acre
Quantité après la GDT:
After bench terracing 1,971 kgs/acre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
According to the land user, there has been increased crop production.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
According to the land user, the quality has relatively improved but is unable to describe the changes, however, he observed changes in the size of the grain and enhanced grain filling ability.
diversité des produits
Quantité avant la GDT:
In the past, the land owner has been growing only wheat or barley
Quantité après la GDT:
Now the owner is growing paddy followed by wheat or barley in a year
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land user shared that the number of crops grown in the area has increased, and people also started commercial farming.
surface de production
Quantité avant la GDT:
23 acres of land
Quantité après la GDT:
2.4 acres of land are currently being cultivated after bench terracing
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This is probably due to the lack of labour and some of the farm lands located very far from the home/settlement.
gestion des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The land users shared that after bench terracing, the management of land has greatly improved. This is evident from the quality of crops that they grow on the terrace. Working on the land is also easy unlike working on slopes.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
Before bench terracing the owner used oxen for ploughing
Quantité après la GDT:
Now they use power tillers and cost have reduced for agriculture farming
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Other objective of promoting bench terracing is also to enable farm mechanization.
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before bench terracing the land owners use the field for growing only wheat or barley. After bench terracing they grow two crops in a year, paddy followed by wheat or barley
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Since the land is on a sloping area there is surface and rill erosion in the past, but after the bench terracing, the incidences of surface and rill erosions are minimal
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
As the terraces field are used for paddy cultivation there is no excess water. Even if there is excess the land owner can easily drainage to water ways
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Erosion was easily observable in the past due to the agricultural land being on mountain slopes. However, now, due to the series of levelled land, water erosion and landslides are no longer observed.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before terracing rainwater is lost due to surface runoff however with terracing surface runoff is prevented as a result the amount of irrigation water required has reduced. Thus increasing water availability.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| orage local | très bien |
| averse de grêle locale | pas bien |
| tempête de neige locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| glissement de terrain | bien |
Catastrophes biologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| maladies épidémiques | pas bien |
| infestation par des insectes/ vers | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
légèrement positive
Commentaires:
The land users were not able to explain very clearly the benefits of the technology. This is because land users were supported by the government for the establishment of the terrace. They didn't have any idea how much would it cost if they had to do everything by themselves.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
16 hhs covering 19.50 acres of vulnerable land were brought under bench terracing in Bemje village
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Agronomic management and working have become relatively easier: with bench terracing working with animals or machinery for tillage activities becomes very easy unlike in slopes. |
| Land can be better utilized, despite decreased total cultivated land: Terrace provides land users the option to fully utilize the available land. If it was a slope, even if they have more land they cannot use them for farming. |
| Prevents the degradation of the land by rain: The main purpose of terracing is to reduce and prevent land degradation caused by surface runoff. |
| Irrigation water is better utilized and conserved: When the surface is properly leveled irrigation water is well distributed. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Prevents landslide: Since the surveyed area was located on the mountain slopes, there are chances of slides if measures were not taken and bench terraces were not made. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| It is a very expensive affair: If machinery and laborers have to be managed by individual land users it would be very expensive. | However, in Bhutan, the technology is mostly funded by the project and Government of Bhutan |
| Land users could not convert all available land into the terrace. | More support from the government so that they can convert all slopy areas into terraces. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Since bench terracing required huge expenditure it is difficult for the owners to bear the full cost | To implement the intervention through donars fund on cost sharing basis |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
One household
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
One individual
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
09/07/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Bizoza, A. R. (2011). Institutional Economic Analysis of Bench Terraces in The Highlands of Rwanda. Farmers, Institution and Land Conservation. Wageningen University
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/29235864.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Mesfin, A. (2016). A Field Guideline on Bench Terrace Design and Construction. Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://nrmdblog.files.wordpress.com/2016/04/bench-terrace-manual.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Dorji, S. (2017). Soil Conservation in Serthi Gewog: A Case Study. Samdrup Jongkhar Initiative.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.sji.bt/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Soil-Conservation-Pilot-Impact-Area.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
BTFEC. (2019). Evaluation of Sustainable Land and Management and Innovative Financing to Enhance Climate Resilience and Food Security in Bhutan. BTFEC.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.bhutantrustfund.bt/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/CIF-Report1.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management: Guidelines and Best Practices 2021
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.nssc.gov.bt
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Turning slopes, dry land into viable agricultural land in Trongsa
URL:
https://www.undp.org/bhutan/stories/turning-slopes-dry-land-viable-agricultural-land-trongsa
Titre/ description:
Bench Terraces: Classification and Maintenance | Soil Management
URL:
https://www.soilmanagementindia.com/soil-erosion/terracing/bench-terraces-classification-and-maintenance-soil-management/15307
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé