Conversion of conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest [Israël]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Tom Cohen
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
technologies_7674 - Israël
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Brook Anna
University of Haifa
Israël
exploitant des terres:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
Israël
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
University of Haifa (uhaifa)1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
This intervention is explicitly designed to reverse and restore previously degraded soils (monoculture exhaustion, fertility decline, low biodiversity).
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Converting conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest-based agroforestry system restores soil health, increases vegetation cover, enhances biodiversity while diversifying production. The intervention improves soil organic matter and ecological resilience through multi-storey planting, reduced soil disturbance, and nature-based land management.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
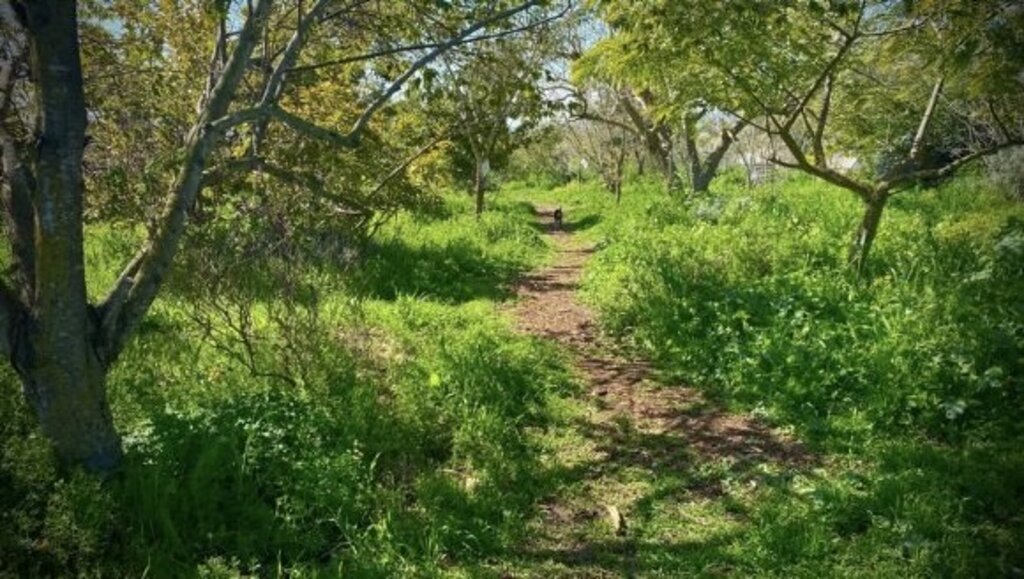
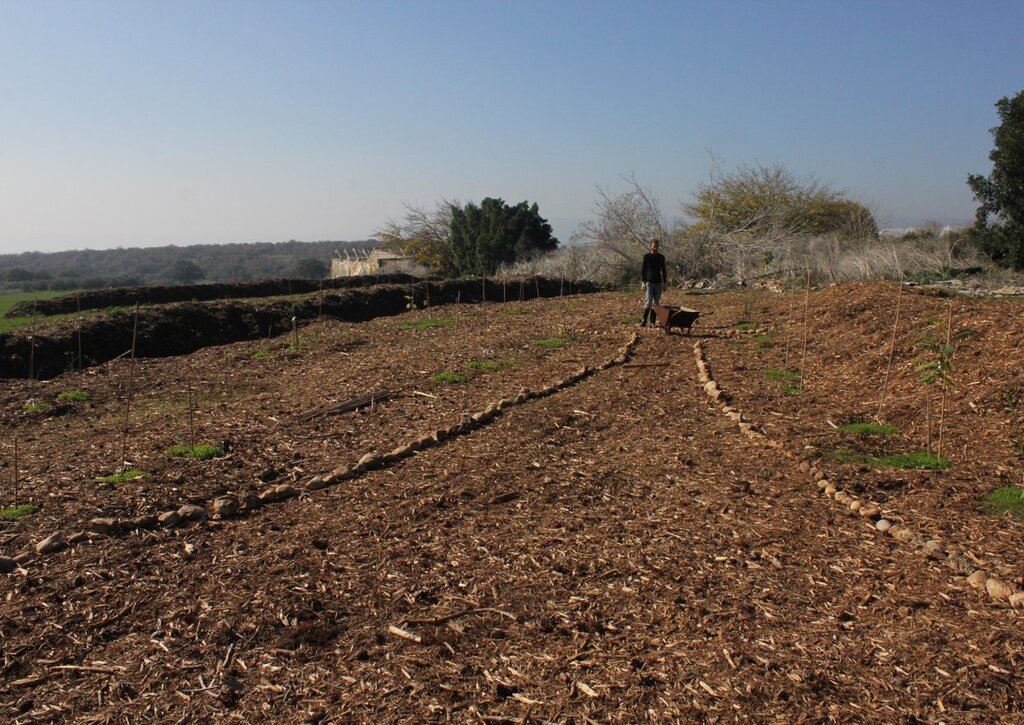
The development of a “food forest” was in response to visible soil degradation caused by years of wheat-based monoculture in Bethlehem of Galilee. The previous land use consisted of annual wheat production, tractor-powered deep ploughing, and routine use of herbicides and pesticides. Over time, these practices depleted soil organic matter, reduced microbial activity, and increased vulnerability to erosion, compaction, and moisture loss. The current food forest, covering approximately 1.5 acres (0.6 hectare), represents a transformative shift from this intensive, extractive system toward a sustainable, perennial, multi-strata agroforestry model.
The primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
The site has been under continuous restoration for approximately eight years, during which it has gradually developed into a multi-layered food forest. The upper canopy includes species such as ficus, tipa, mulberry, pecan, plane trees, and nitrogen-fixing “ice-cream bean” (Inga edulis), which together generate shade, biomass, and structural diversity. The productive mid-storey contains fruit-bearing species including lemon, plum, pomegranate, avocado, and additional deciduous trees. Beneath these layers, aromatic shrubs such as lavender and rosemary provide perennial cover, habitat complexity, and year-round biomass production. A dedicated lower layer supports seasonal vegetables: carrots, radishes, turnips, lettuces and other greens, interplanted within tree alleys and cultivated using organic methods.
Production follows a diversified model typical of food forests. Tree crops currently yield modest but consistent quantities of lemons, plums, mulberries, pomegranates, and herbs, primarily for consumption by visitors, volunteers, and workers on site rather than large-scale commercial sale. The adjoining vegetable-growing area produces additional crops for small-scale marketing, providing a modest revenue stream while maintaining ecological integrity. As the system is still maturing, productive output is expected to increase over the coming years.
The project is privately managed by a couple in their thirties, who own and oversee all aspects of the site. Labour requirements were most intensive during the establishment phase of planting, mulching, earth-shaping, and infrastructure setup. As the food forest enters a more stable successional stage, labour demands have gradually decreased, with current activities centred on pruning, biomass recycling, vegetable cultivation, and occasional enrichment planting. No chemical inputs are applied at any stage.
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
Overall, this food forest demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for Mediterranean environments, showcasing how degraded wheat monoculture fields can be restored into resilient, biodiverse, and ecologically functional agroforestry systems. The long-term transition highlights substantial gains in soil health, water retention, and landscape diversity, while supporting small-scale production and community-oriented engagement.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Israël
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Galilee
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Bethlehem of Galilee
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
0,01
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2017
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The landowners developed the site as part of a holistic environmental vision and continue to refine it through ongoing learning, experimentation, and renewal. They actively initiate collaborations with research institutions in Israel and abroad to support long-term monitoring of the site and to advance the food-forest practice within a scientific and evidence-based framework.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- légumineuses et légumes secs - pois
- plantes et herbes médicinales/ aromatiques/ pesticides
- légumes - légumes à feuilles (laitues, choux, épinards, autres)
- légumes - légumes-racines (carotte, oignon, betterave, autres)
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- citron
- figue
- fruits à pépins (pommes, poires, coings, etc.)
- fruits à noyaux (pêche, abricot, cerise, prune)
- fruits à coque (noix du Brésil, pistaches, noyers de bancoule, amandes)
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 3
Précisez:
Up to three for the fastest growing crops
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
The whole farm forest embodies intercropping throughout its multi-strata structure
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Various annual crops as described above - and an adaptive succession strategy

Forêts/ bois
- Plantations d'arbres, boisements
Plantation d'arbres, afforestation: Précisez l'origine et la composition des espèces. :
- Variétés mixtes
Type de plantation d'arbres, d'afforestation:
- plantations forestières des zones de climat continental tempéré
- Ficus, Tipu (Tipuana tipu), Plane tree (Platanus spp.), Sissoo (Dalbergia sissoo), Ice-cream bean
Est-ce que les espèces d’arbres précisées ci-dessus sont des espèces d'arbre arbres à feuilles caduques ou à feuilles persistantes ?
- forêt mixte décidue/ à feuillage persistant
Produits et services:
- Fruits et noix
- Autres produits forestiers
- Conservation/ protection de la nature
- Loisirs/ tourisme
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - blé de printemps
Système de cultures annuelles :
Blé ou rotation similaire de foin/pâturage
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Occasionally (see above)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
Commentaires:
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- perturbation minimale du sol
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
- V2: Herbes et plantes herbacées pérennes

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M2: Changement du niveau de gestion / d'intensification
- M5: Contrôle/ changement de la composition des espèces
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)
- Cs: salinisation/ alcalinisation

dégradation physique des sols
- Pc: compaction
- Pi: imperméabilisation des sols
- Ps: affaissement des sols organiques, tassement des sols

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bh: perte d’habitats
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
For this pilot, the technology primarily addresses soil degradation (chemical + physical + biological) that resulted from long-term monoculture and herbicide-based management.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
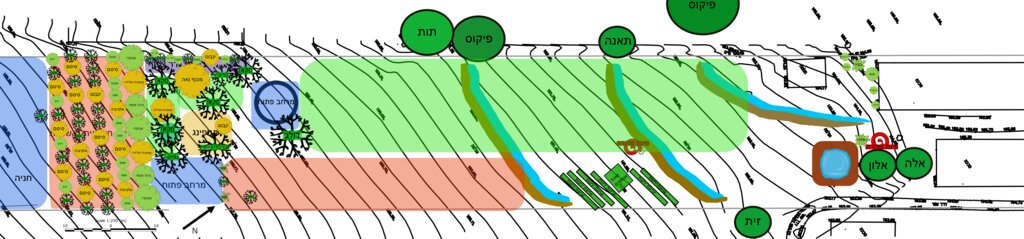
The general site plan (above) illustrates the full spatial organization of the food forest, structured into clearly defined functional zones that together create a balanced ecological and productive landscape (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). The outer perimeter consists of a protective tree belt designed to provide wind buffering, habitat continuity, and microclimate regulation. Inside this perimeter lies a series of densely planted clusters of mixed-species trees and support plants, forming the core forested zones of the design. These clusters contain a combination of canopy species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing support species, and understory elements arranged to promote ecological interactions and long-term resilience. Several open areas are intentionally integrated throughout the site, providing space for circulation, light penetration, future expansion, and community activities. The plan also includes a designated agricultural strip for annual vegetable production, strategically placed to benefit from the moderated microclimate created by the surrounding tree layers. Additional functional elements such as a compost area, shaded seating or gathering points, and access paths appear throughout the design, supporting both maintenance and educational use. Overall, the plan demonstrates a holistic integration of productive, ecological, and social spaces, emphasizing diversity, spatial layering, and regenerative land-use principles.
Auteur:
Nitzan Betzer
Date:
01/06/2017
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
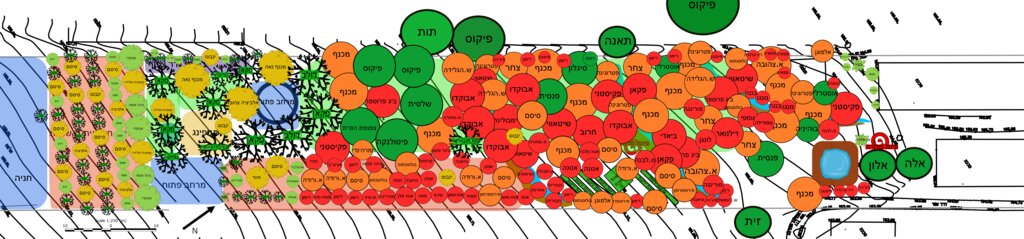
The planting plan (below) illustrates the full structural design of the food forest, showing a diverse mixture of perennial species arranged according to ecological function and spatial layout (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). Each color on the map represents a different botanical or functional category. The green circles indicate the major canopy and shade-providing trees that form the upper layer of the system. The red circles mark the fruit-bearing species distributed across the plot, including pomegranate, avocado, fig, loquat, mango, mulberry and others, representing the primary productive component of the mid-storey. The orange circles correspond to nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs, strategically positioned to enrich soil fertility and support surrounding species through natural nutrient cycling. The yellow circles mark ornamental or habitat-supporting species that enhance biodiversity, microclimate regulation and ecological resilience. Together, these categories create a multi-layered mosaic in which canopy, fruit, support species and habitat elements interweave across the site. The design also includes designated open areas, compost space, perimeter rows and an agricultural strip for annual vegetables, demonstrating an intentional balance between ecological restoration, food production and functional zoning.
Auteur:
Nitzan Betzer
Date:
01/06/2017
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
1.5 acres
Si vous utilisez une unité de superficie locale, indiquez le facteur de conversion vers un hectare (p.ex. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha = :
1 acre = 0.4 hectares
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars américains
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
158.2
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial site assessment and mapping of soil condition and exposure | Late winter / early spring |
| 2. | Discontinuation of tillage and herbicide applications | Immediately prior to establishment |
| 3. | Soil preparation without deep tillage (light loosening, mulching base layer) | Early spring |
| 4. | Planting of trees in primary layout (skeleton layer) | Spring |
| 5. | Planting of shrubs and understory companion species | Late spring / early summer |
| 6. | Installation of organic mulch cover to protect soil and retain moisture | After planting (early summer) |
| 7. | Enrichment planting / filling gaps with additional groundcover species | Late summer / following spring |
| 8. | Protection of young trees/shrubs if needed (guards, shading, temporary watering) | First growing season |
| 9. | Establishment of biomass cycling (chop-and-drop, composting on-site) | After vegetation takes root |
| 10. | Transition into maintenance phase (reduced intervention, natural succession) | Once canopy begins forming |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Manual labour | Person-days | 139,0 | 158,2 | 21989,8 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tools and maintenance equipment | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Equipements | Tractor (for construction) | 1,0 | 7200,0 | 7200,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Seedlings, cuttings, and seeds | 1,0 | 14000,0 | 14000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Compost | 1,0 | 10500,0 | 10500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Irrigation system | 1,0 | 14500,0 | 14500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Pruned biomass mulch | 1,0 | 6500,0 | 6500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 79689,8 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 79689,8 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Land user bore all costs: but note the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
Commentaires:
No chemical fertilizers or pesticides are used; fertilization is based solely on compost
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching with organic biomass (leaf litter, pruning residues, woodchips, etc.) | 2–3 times per year, mainly after rainy season and mid-summer |
| 2. | Selective pruning of trees and shrubs to maintain structure and light balance | Annually / as needed (late winter or autumn) |
| 3. | Enrichment planting and succession planting of understorey species | Seasonally, as ecosystem matures or gaps appear |
| 4. | Weeding by ecological suppression (groundcover strengthening) rather than removal | Continuous, low-intensity maintenance |
| 5. | Soil moisture conservation (biomass renewal / occasional supportive watering in drought years) | Seasonally during dry periods (as needed) |
| 6. | Monitoring soil condition and vegetation health | Ongoing, at least once per season |
| 7. | Replacement of failed or weak young plants | Annually during early growth seasons |
| 8. | Maintenance of biodiversity guilds / companion planting structure | Continuous, adaptive to natural succession |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Manual labour | Person-days | 110,0 | 158,2 | 17402,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Equipment renewal and maintenance | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Cuttings and seeds | 1,0 | 4000,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Autre | Water bills | 1,0 | 5500,0 | 5500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Autre | Products selling kits | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 33902,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 33902,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The establishment costs refer to the initial food forest area of approximately 1.5 acres, while the annual maintenance costs refer to the forest in its current state, covering about 3 acres. Land user bore all costs: but note that the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
The most significant cost factor, both during establishment and ongoing maintenance, is labour. All work is carried out manually using hand tools, and apart from the initial establishment phase, no heavy machinery is used
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
The climatic information for the food forest site was obtained from two sources: official data provided by the Israel Meteorological Service (IMS) and on-site measurements collected through a dedicated rain gauge installed as part of the research infrastructure. Together, these sources provide accurate local rainfall and climate monitoring for the plot.
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Both species diversity and habitat diversity have transformed due to the establishment of the food forest, and are now both high. This is a very agrobiodiverse system.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- subsistance (auto-approvisionnement)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- > 50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
The land user manages approximately 2–5 hectares in total, of which a portion is undergoing transition into a food forest system; this is considered small-scale in the local agricultural context
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- individuel
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Agricultural input expenses are very limited in this system. Since the site operates as a food forest rather than a conventional agricultural plot, nearly no external inputs are purchased. The management relies on ecological processes, on-site biomass, mulching, and manual care. Inputs are therefore minimal and do not reflect commercial-scale agricultural expenditure.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The plot was originally managed as a monoculture field that depended economically on agricultural production. Today, the food forest operates on a completely different model: its income is derived primarily from research activities, educational programs, workshops, and community engagement. Economic sustainability is no longer based on agricultural yield, as crop production is not the financial foundation of the site anymore.
Impacts socioculturels
opportunités culturelles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
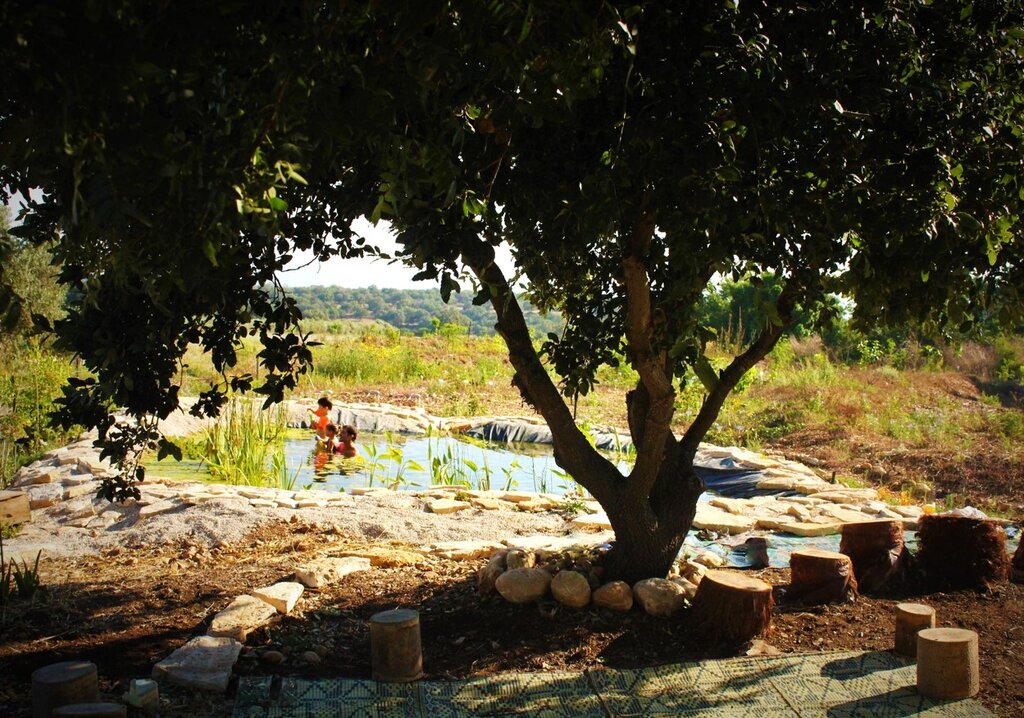
The food forest contributes significantly to cultural opportunities in the area. It serves as a community-oriented space that hosts educational events, workshops, volunteer activities, and gatherings focused on sustainability and ecological awareness. The site fosters cultural exchange, strengthens community cohesion, and provides a shared environment for learning, creativity, and connection to nature.
institutions communautaires
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Note: The food forest strengthens community institutions by collaborating with local educational programs, volunteer groups, and research initiatives. It provides a stable platform for schools, community organizations, and environmental groups to conduct activities, thereby reinforcing their role in community life and expanding their capacity for outreach and engagement.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest contributes to improved SLM and land-degradation knowledge by serving as a living demonstration site where restoration practices can be observed, tested, and monitored over time. It provides real-world evidence on soil recovery, biodiversity enhancement, and regenerative management, supporting both scientific research and practical learning for land users, students, and professionals.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest reduces surface runoff through continuous vegetative cover, increased soil organic matter, and improved infiltration. The multi-layered perennial structure slows water movement, stabilizes the soil, and enhances water absorption, thereby decreasing erosion risk and minimizing overland flow during rainfall events.
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest reduces soil surface evaporation through dense vegetative cover, shading from the multi-layered canopy, and increased soil organic matter. Mulching and groundcover plants further protect the soil surface, lowering temperatures at ground level and limiting direct exposure to sun and wind, which significantly decreases soil surface evaporative water loss.
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest increases soil moisture by improving infiltration, enhancing organic matter content, and maintaining continuous groundcover. The multi-layered canopy moderates temperature and reduces evaporation, while mulch and living groundcovers retain water in the upper soil layers. Together, these features create a cooler, moister soil environment that supports long-term ecological function.
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest improves ground cover through the establishment of multi-layered perennial vegetation, including trees, shrubs, and living groundcovers. Mulch application and natural leaf litter further protect the soil surface, ensuring year-round coverage that reduces erosion, enhances soil health, and supports ecological stability.
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest reduces soil crusting and surface sealing by increasing organic matter, maintaining continuous vegetative cover, and enhancing biological activity in the upper soil layers. Leaf litter, mulch, and root penetration prevent the formation of hard surface layers, while improved soil structure allows better infiltration and aeration, minimizing the risk of crust development.
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest enhances nutrient cycling and soil nutrient recharge through continuous biomass production, leaf litter accumulation, and root turnover. Nitrogen-fixing species, mulch, and on-site organic matter decomposition replenish soil nutrients naturally, while diverse plant strata promote active microbial communities that accelerate nutrient transformation and availability.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest increases soil organic matter and below-ground carbon through continuous inputs of leaf litter, root biomass, and decomposing mulch. The perennial, multi-layered vegetation system supports sustained carbon incorporation into the soil, while reduced disturbance and enhanced microbial activity further promote long-term carbon storage and soil organic matter accumulation.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest substantially increases vegetation cover by establishing multiple perennial layers - canopy trees, mid-storey species, shrubs, and groundcovers - that provide continuous, year-round biomass. This expanded plant cover protects the soil, supports ecological processes, and creates a more resilient and biodiverse landscape compared to the former monoculture field.
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest increases above-ground biomass and carbon storage through the establishment of diverse perennial vegetation, including canopy trees, fruit species, shrubs, and herbaceous layers. As these plants grow, they accumulate significant living biomass, sequester carbon, and contribute to long-term ecological stability through continuous organic matter production and structural complexity.
diversité végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest greatly increases plant diversity by integrating a wide range of tree species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing plants, shrubs, herbs, and groundcovers. This multi-strata design replaces the former single-crop system with a complex, species-rich community that enhances ecological resilience, supports wildlife, and promotes functional biodiversity across the site.
diversité des habitats
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest increases habitat diversity by creating a multi-layered structure that supports varied ecological niches. The combination of canopy trees, understory species, shrubs, groundcovers, open areas, and water features provides habitats for a wide range of insects, birds, and small wildlife. This structural and functional diversity replaces the uniform habitat of the former monoculture and greatly enhances overall ecosystem complexity.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The food forest helps reduce carbon and greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing external inputs, eliminating chemical fertilizers, and avoiding soil disturbance that would otherwise release stored carbon. The perennial vegetation continuously sequesters carbon in both biomass and soil, while the system’s low-energy, regenerative management reduces emissions associated with conventional agricultural practices.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
The assessment of on-site impacts combines both social-cultural learning processes and quantitative biophysical measurements. On the social, cultural, and economic side, the site hosts workshops, guided learning sessions, and community activities designed to understand the meaning, role, and value of the food forest for local stakeholders. These engagements provide qualitative insights into cultural benefits, community strengthening, and the educational function of the place. For the more tangible biophysical parameters – soil health, vegetation condition, biodiversity, and ecological recovery – the monitoring relies on analytical laboratory tests and systematic long-term sampling. Soil samples collected at different stages of the establishment process were analyzed for organic matter, nutrients, structure, and biological activity, providing a clear picture of soil improvement over time. In addition, the site is monitored through remote-sensing-based indicators developed in collaboration with the University of Haifa, which track temporal changes in vegetation cover, biomass, soil moisture proxies, and overall ecological function. Together, these qualitative and quantitative assessments offer a comprehensive understanding of the site’s development, documenting both the ecological restoration underway and the parallel social and educational impacts generated by the food forest.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Using IPCC Tier-1 methods (2006 Guidelines with the 2019 Refinement), we estimate annual removals from (i) mineral soil organic carbon (SOC) gains after conversion from tilled wheat to multistrata agroforestry, and (ii) incremental woody biomass growth. Mediterranean evidence suggests SOC increases on managed woody systems of ~0.2–1.0 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, while biomass increments in multistrata/silvo-arable agroforestry typically add ~0.8–2.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ in the establishment decades; together this yields ~1.0–3.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, i.e., ≈ 3.7–13 tCO₂e ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ (3.67 conversion). For reporting we adopt the conservative lower bound until our paired soil cores (baseline vs. years 2/5/8) and tree allometry—supported by Sentinel-2 time-series—finish quantifying site-specific change. Sources: IPCC 2006/2019 AFOLU guidance; AR6 WGIII (AFOLU); Mediterranean meta-analyses of SOC/biomass in woody systems and agroforestry.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
Off-site impacts were assessed through a combination of qualitative and quantitative indicators that capture how the food-forest system influences the surrounding landscape and community beyond the plot boundaries. Hydrological effects were inferred from reduced surface runoff and improved infiltration within the site, which collectively lower downstream sedimentation and erosion risks; these implications were evaluated using rainfall records, soil-moisture trends, and comparison of runoff behavior between the restored area and adjacent conventionally managed fields. Vegetation development and canopy expansion – monitored through Sentinel-2 time-series and UAV imagery – provide additional evidence of landscape-scale improvements such as enhanced microclimatic buffering and habitat connectivity. Social and cultural off-site impacts were evaluated through participation in workshops, educational programs, and community events, which extend ecological knowledge and stewardship beyond the site itself. Together, these measurements and observations offer a coherent picture of how the food forest contributes to broader environmental and community benefits outside its physical boundaries.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | modérément | |
| précipitations annuelles | décroît | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | modérément |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| canicule | bien |
| sécheresse | bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
The slightly negative short-term balance does not reflect external subsidies but rather the intentional design and purpose of the site. The food forest is not a commercial enterprise and was never intended to generate profit from agricultural production. Its primary function is research, education, and community engagement, and therefore its revenues come from workshops, collaborations, and research grants rather than crop sales. The short-term financial deficit simply reflects the fact that the landowners invest in a long-term ecological and educational project whose value is measured in environmental and social outcomes rather than immediate economic returns. It should not be interpreted as dependence on agricultural subsidies or market-based support.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
One household: 1.5 acres
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
The design and composition of the food forest are continuously adapted as the system matures and as new insights emerge from ongoing learning by the landowners and collaborating researchers. Species selection, spatial arrangement, and management practices have been refined over time in response to observed ecological dynamics - such as canopy development, soil improvement, microclimatic changes, and species performance. Additional trees, shrubs, and groundcovers have been introduced to enhance diversity, strengthen ecological functions, and address emerging needs such as shade regulation, soil enrichment, or habitat creation. This adaptive approach reflects the core principle of the technology: the food forest is a living system that evolves through observation, experimentation, and evidence-based adjustments informed by both practical experience and scientific collaboration.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| Restores soil fertility and structure without relying on chemicals and reduces weed pressure naturally through permanent groundcover |
| Improves moisture retention and reduces drought stress over time and supports biodiversity and creates a healthier farm ecosystem |
| Transformational: turns degraded land into a productive long-term asset |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for restoring degraded agricultural soils in Mediterranean climates |
| Increases soil organic matter and biological activity, improving long-term soil function and carbon sequestration |
| Serves as a living demonstration site with high educational and upscaling potential for regenerative farming in the region |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Slow establishment phase before benefits become visible | Patience + phased planting; choose fast-growing pioneer species to accelerate canopy formation |
| Requires knowledge and ecological management skills | Ongoing guidance from experts / capacity building / training |
| Young plants vulnerable to drought during first summers | Supplemental irrigation in the first years and thicker mulching to reduce evaporation |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Long ecological recovery timeline before system reaches full functionality | Use succession planning and pioneer/perennial nurse species to accelerate canopy closure and soil regeneration |
| Success depends on appropriate species selection for local microclimate and soil | Improve site-specific design using adaptive planting trials, monitoring, and locally adapted cultivars |
| Knowledge-intensive management compared to conventional systems | Provide technical training, extension support, and farmer-to-farmer learning |
| Restoration outcomes may vary with drought years and extreme heat events | Increase biomass cover, soil shading, and water retention strategies in early establishment years |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
Field visits and surveys were conducted once every season on-site with the primary land user (one key informant), supplemented by technical assessments from the research team
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
One-on-one interviews were conducted with the primary land user (one key informant) at least once a year, focusing on management decisions, perceived benefits and challenges, and changes observed since the start of the transition
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
The expert input was provided by specialists involved in the University of Haifa restoration pilot
- compilation à partir de rapports et d'autres documents existants
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Zbedat, G., & Brook, A. (2025). Land Restoration Effectiveness Assessed by Satellite-Based Remote Sensing Technologies as A New Monitoring Approach. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 48, 149-155.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Google Scholar
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
T. A. Cohen, A. Brook and G. Zbedat, "Long-Term Land Restoration Assessment Using Remote Sensing in Mediterranean Ecosystems," 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Padua, Italy, 2024, pp. 179-183, doi: 10.1109/MetroAgriFor63043.2024.10948855.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Google Scholar
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
React4Med site
URL:
https://react4med.eu
Titre/ description:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest Collection
URL:
https://haifa.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/discovery/collectionDiscovery?vid=972HAI_MAIN:HAU&inst=972HAI_MAIN&collectionId=81263109080002791
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé