



Farmyard manure is the most common form of organic fertiliser applied to crops in the midhills of Nepal. Farmyard manure has a high proportion of organic material which nurtures soil organisms and is essential for maintaining an active soil life. Typically, only about half of the nutrient content of farmyard manure becomes available for crop growth during the first year after it is applied to the soil. The rest of the nutrients are channelled through soil biotic processes and are released in the following years. The high organic matter content and the more active soil life improve or maintain a friable soil structure, increase the cation exchange capacity, the water holding capacity, and the infiltration rate, and reducing the risk of soil pests.
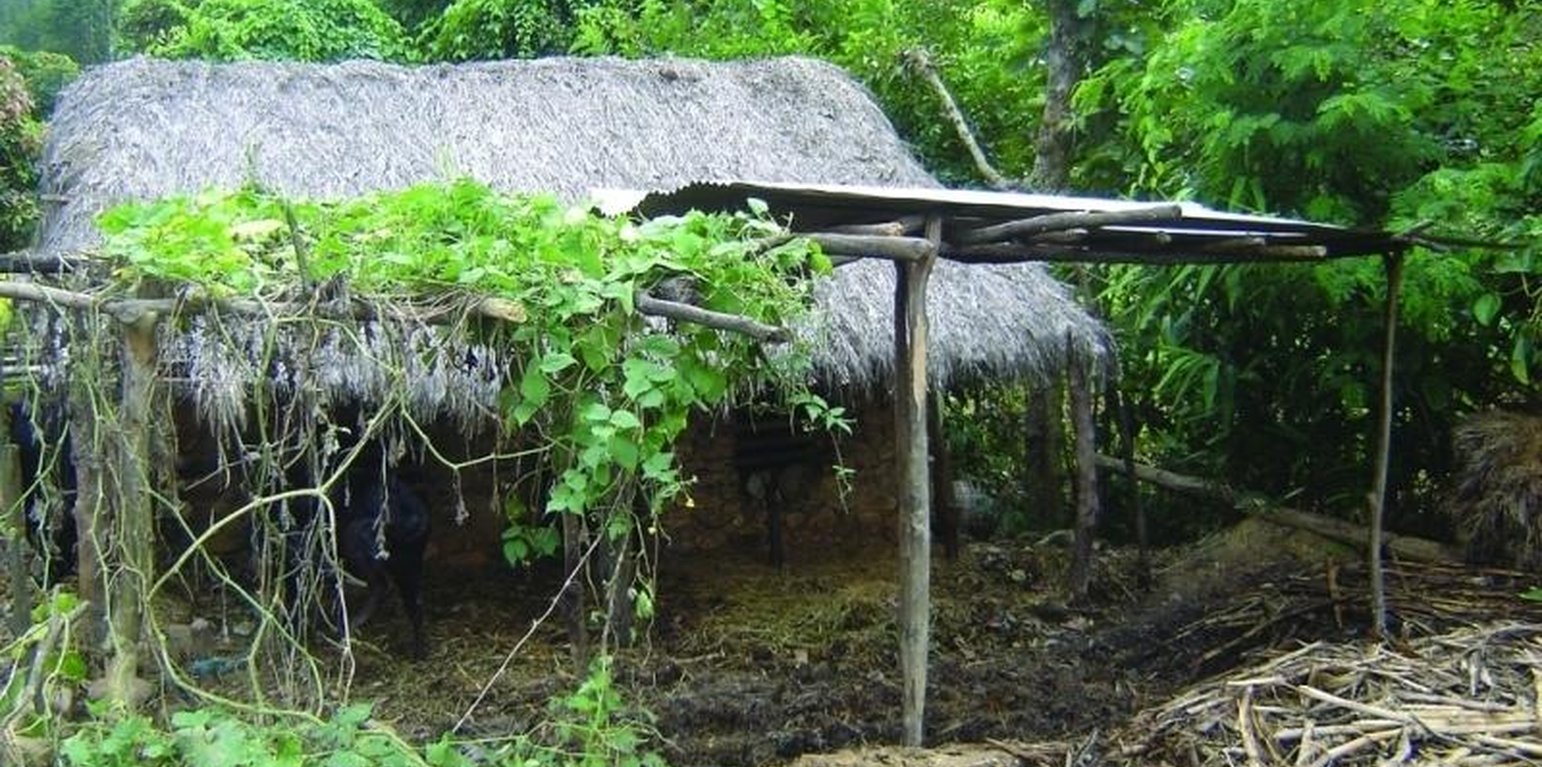
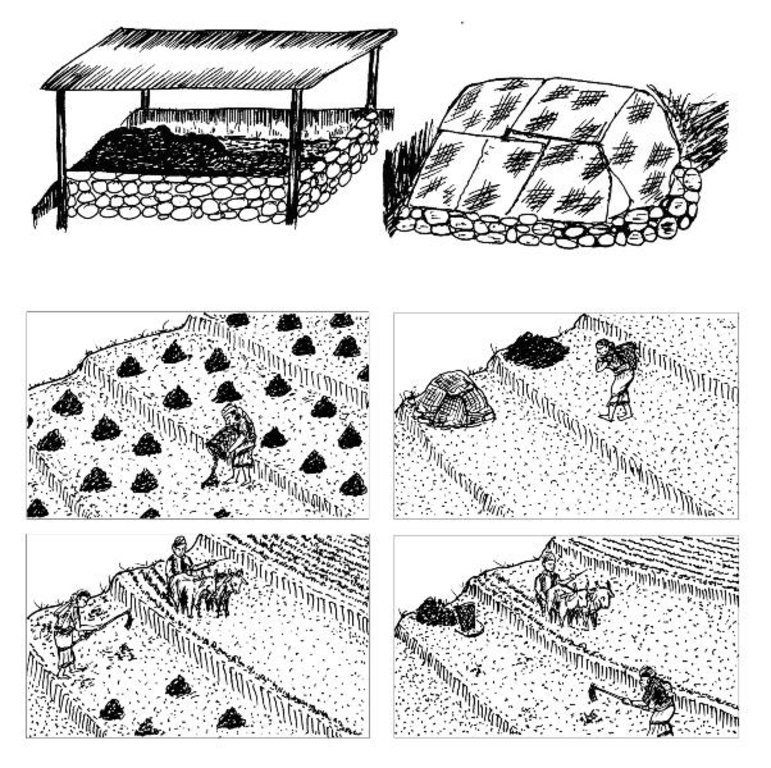
Indigenous methods of preparing and using farmyard manure vary depending on the ecological zone, access to bedding material from crop or forest land and to crop residues and fodder, the availability of labour, and other factors. Traditionally, Nepali farmers take the manure out of their sheds to dry it for 2-3 days and then carry it to the field where it is left in small heaps for a number of days before being spread and incorporated into the soil.
Farmers rate the quality of manure according to which livestock species it comes from. These ratings have been confirmed by nutrient analysis as cattle manure (NPK%: 0.6, 0.13, 0.66) is considered to be better than buffalo manure (0.33, 0.25, 0.10), and horse manure; while pig (0.5, 0.18, 0.42), goat (0.6, 0.13, 0.99), and sheep manure (0.6, 0.13, 0.99) are considered better than cattle manure. Chicken manure (1.46, 0.51, 0.51) is considered the best of all.
It has however been shown that considerable nutrient losses occur if the manure is inappropriately handled or stored. Drying of the manure leads to loss of nutrients through volatilisation, and rainfall and runoff leads to leaching or washing out of nutrients. In addition, the common disposal of urine - the part of the excreta with the highest nutrient concentration - further reduces the level of nutrients in manure.
To reduce nutrient losses farmyard manure needs to be protected from direct sunlight; protected from rainfall or run-on; and protected from runoff. This can be achieved in a variety of ways using a variety of inputs. It is most important to protect the manure during storage and just before it is applied in the field to make the best use of this valuable local resource.
ទីតាំង: Midhills districts of Nepal, ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស: អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត:
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖



| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា (ដុល្លារ) | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប (ដុល្លារ) | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | |||||
| Building manure pit and shelter | Persons/day | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | |||||
| Material | unit | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 27.0 | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 27.0 | ||||
Reduced expenditure on mineral fertilisers
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies