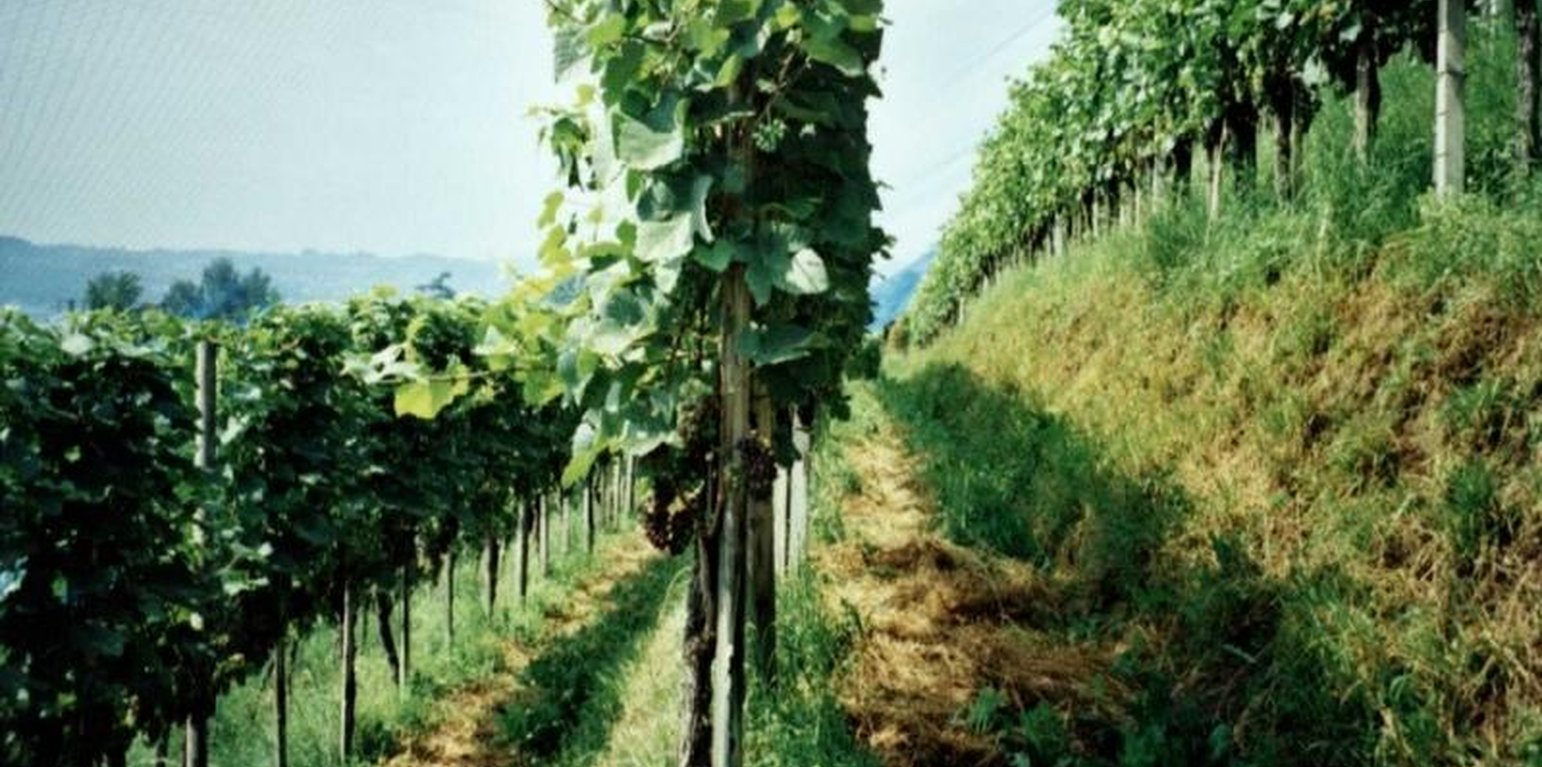




Description: The vineyards of the region are all, for micro-climatc reasons, more or less sloped. The technology is applied on steep to very steep slopes. It ist characterised by two elements: 1) small bench terrace with one contour-oriented vine row per terrace and 2) an initially sown all-year green cover of the soil surface for stabilisation reasons (green cover is also used between vine rows which are oriented up and down the slope, eg not terraced, see SWI01).
Purpose: Main purpose of the terrace construction is a possible mechanisation on steep to very steep slopes. Direct purpose of the green cover is the stabilisation of the small terraces, indirect but important purpose is the prevention of soil degradation, especially soil erosion by water and - secondary - to protect soil surface from compactation when using mechanised equipment.
Establishment: The terraces are constructed by external specialists and heavy machinery (walking excavator, type "Menzi Muck") and are considered to serve for a whole life cycle of the vine (20-40 years). The green cover is sown since stabilisation is needed from the very beginning on. The duration of the establishment is 3 years. Because of insufficient root length of young vines agronomic and vegetative measures differ from the "normal" measures: For reasons of competition the space around the freshly planted vines is kept free from vegetation with a hoe.
Maintenance: the topsoil is ripped from time to time with fuel driven machine (spade machine tracked by tractor). Cover vegetation is either cut or chopped and serves as mulching . Herbicides are applied around the vines. Minimum tillage and cutting / mulching may additionally serve to mobilise nutrients and to increase organic matter content or to eliminate competition of cover vegetation.
Natural environment: the vineyards are mainly placed on mountain or hill slopes, below 600 m a.s.l., annual rainfall is around 1000 mm with at least one erosive storm per year. The geological underground is limy, locally layered by Molasse (type of conglomerate). Soil properties are strongly influenced by anthropogenic activities (viticulture). Main degradation problem without green cover is erosion by water.
Human environment / land use: the region has a strong wine growing tradition (several centuries), belongs to the important Swiss wine growing regions and is not very densly populated.
First experiments with green cover in Switzerland were done in the 70ies around Zürich on contour small bench terraces, in the region of the lake of Biel contour small bench terraces with green cover started to be implemented in the 80ies
ទីតាំង: Lake of Biel, Canton of Berne, ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ចំនួនទីកន្លែងបច្ចេកទេស ដែលវិភាគ:
ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
តើស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ការពារអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍?:
កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត: តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
ប្រភេទនៃការណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តន៍៖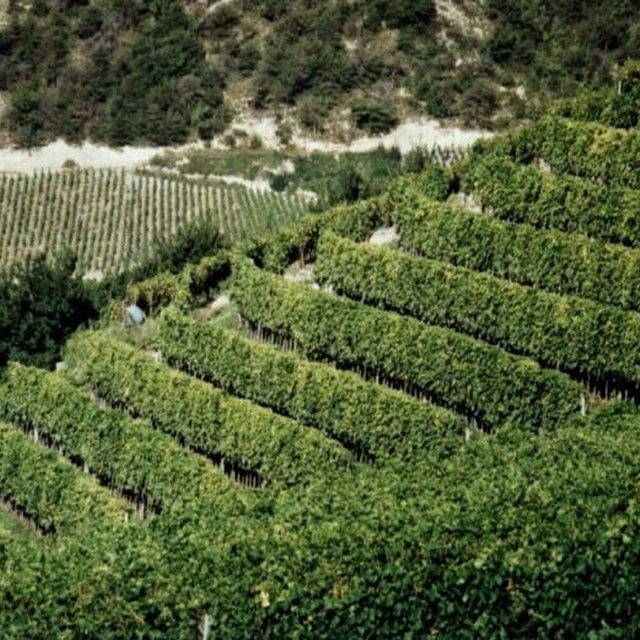




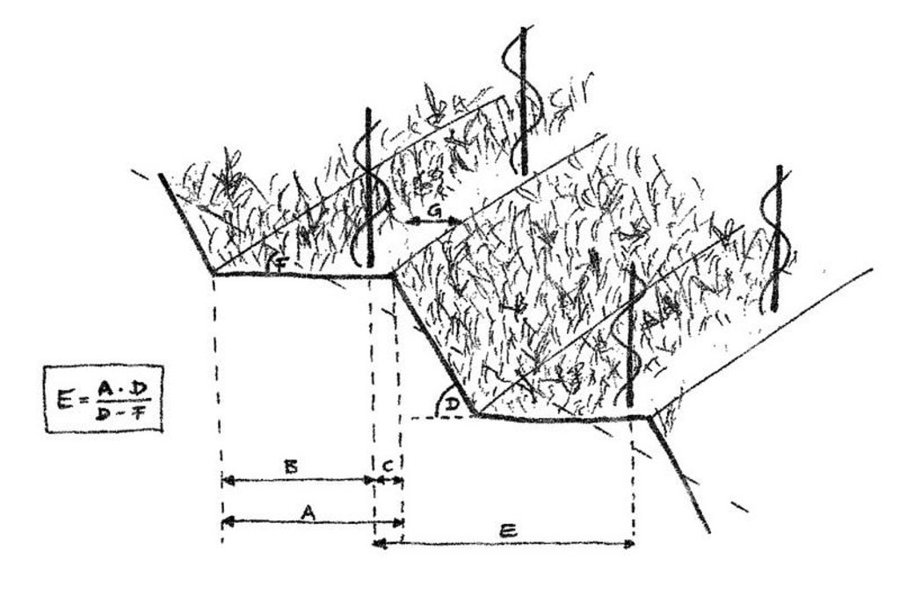
maximum production capacity is reduced due to 1. Plantation density is smaller and 2. Capacity per vine is reduced due to slight competition of water and nutrients, intensified in the terrace riser under dry conditions
Reduced quality of wine occurs when strong competition of water and nutrients happen and nothing is done against it.
Higher susceptibility to fungal decay due to higher evapotranspiration rate with green cover and therefore humid microclimatic conditions. Other problems are competition over water and nutrients or danger of frost - negligible - only in depressions or plains (due to higher evapotranspiration rate)
Primarily due to less costs, especially resulting from less erosion damages in the long term (because of green cover). Secondary due to marketing argument "ecological agricultural production", subsidies related to green cover (direct payment which is only
More and specific knowledge necessary
Special machines needed, mechanisation is almost a must to be economically successful in the long term
Healthier than without SWC, less application of biocides and more comfortable and healty posture of body.
Increased exchange of knowledge and contacts in winegrowers society
Research stations gained new knowledge and attention
Among winegrowers, but perhaps also slightly among consumers (through an ecological marketing argument) or walkers (walking through a green vineyard may arise interest in green cover).
Between generations or between farmers applying green cover and others. Reason: farmers are differently attached to traditional values and norms (i.e.: traditionally every plant was seen as unuseful weed and fought with a hoe).
Many farmers apply green cover see green cover as a personal satisfaction or challenge for an ecologically and economically sustainable viticulture
Landscape and appearance of Landscape & appearance of vineyard as cultural heritage. Different values an norms of "how a vineyard should look like". Traditionally vines were planted very dense with no vegetation cover in between. Contour small bench terraces are quite new to the area (20-30 years)
Especially through improved water retention capacity (due to improved soil structure)
Mainly due to green cover (rather than terraces)
Through beneficial animals
High diversity due to different habitats (extensively managed terrace riser and terrace)