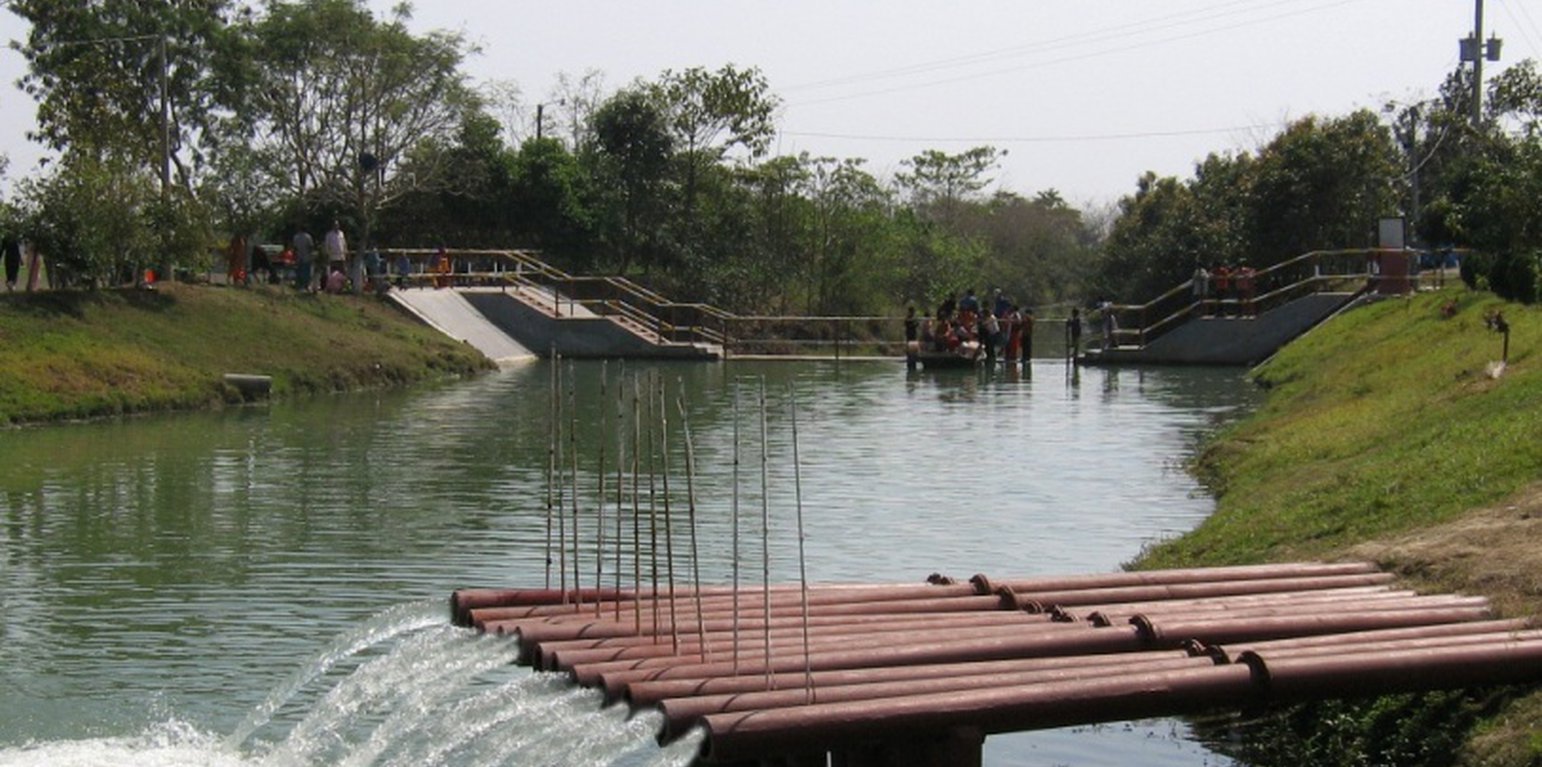




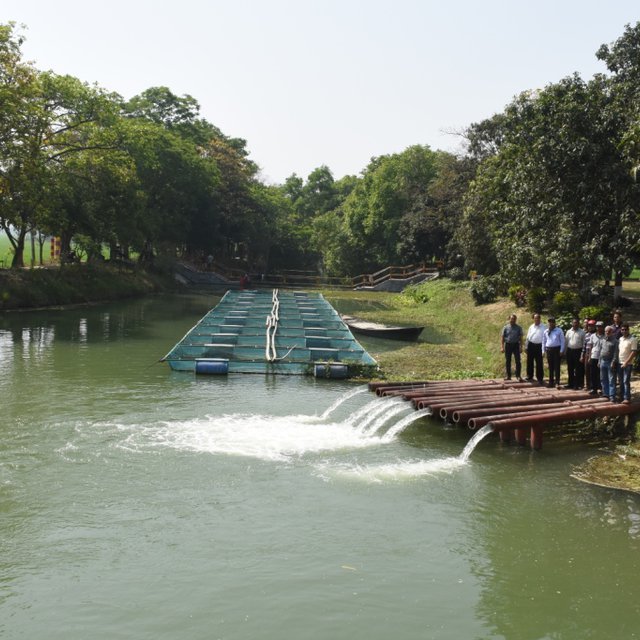
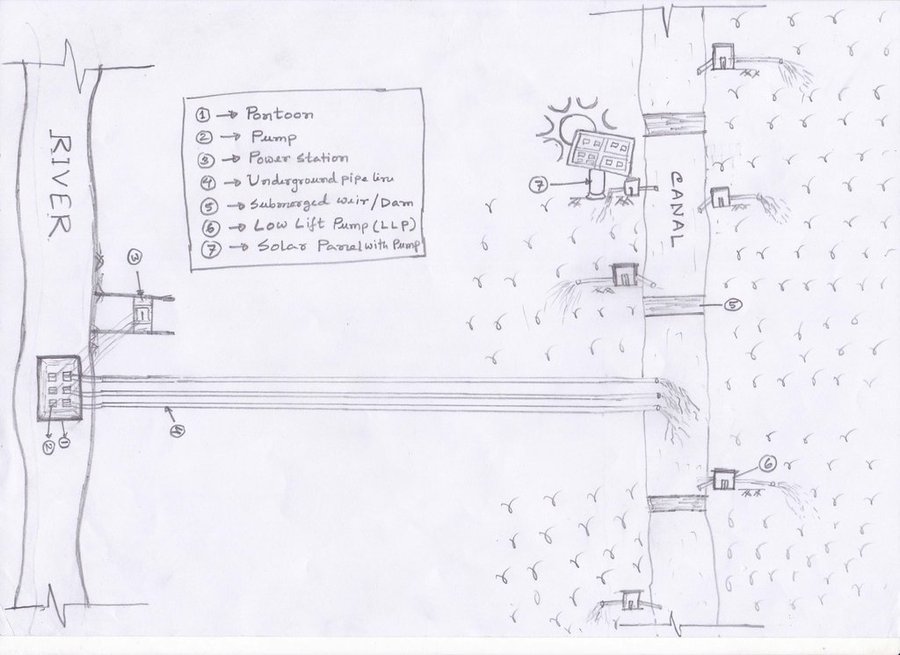
The project is sited at Sharmongla under Godagari Upazilla of Rajshahi district. The Sharmongla canal is located about 3.5 km away from the Padma river. Its total length is 29.0 km. Under this technology, water is lifted from the Padma river by pumps set on a pontoon. The lifted water is then discharged to a canal through underground pipelines. The water so discharged is lifted to the crop fields (delivery points) for irrigation. The elevation difference between the delivery points and the sourcing river is about 21 m. There are numbers of submerged weirs/dams constructed across the canal at different locations for conserving water: the water then helps regenerate the ecosystem along its banks and enriches the habitat.
Pontoon at a glance:
•Year of construction: 2004
•No. of centrifugal pumps at pontoon: 12
•Pump capacity: 50 m lifting height.
•Power of each pump: 60 HP
•Capacity of each pump: 2.5 cusec
•Total capacity of pump sets: 30 cusec
•Capacity of electric sub-station: 750 KW
•No. of discharge pipelines: 12
Sharmongla canal at a glance:
•Length of the canal: 29 km
•Average width of the canal: 15 m
•Average depth from ground level: 5 m
•No. of submerged weirs and dams within the canal: 14
•No. of LLP (low lift pump): 27 electrified and 6 solar pumps
•Total irrigated area: 1850 ha
•Benefiting farmers: 5330
•Harvest yield of rice per year: 20,500 metric tonnes (approx.)
•Afforestation on the canal bank: 65,500 trees
Purposes/objectives of the technology:
•The main purpose of the said technology is to provide water for irrigation. This prevents abstracting of groundwater, which has adverse effects on the environment: therefore this system is environment friendly.
• Enhancing groundwater recharge thereby supports ecosystem function.
•The storing of river water in irrigation canals supports the enrichment of the habitat.
Approach for implementing the technology:
There was no irrigation facility for crop production in this drought-prone area. Government officials came to the locality, discussed with the local community, elites, as well as the farmers. Finally, the local community was convinced about the technology. Then the irrigation system could be implemented in the area. On seeing the success of the technology, the same has been replicated on approx. 9400 ha. in Barind area, benefitting approx. 32,200 farmers.
Maintenance of the technology:
In case of problems, the respective mechanic of that area informs the Assistant Engineer through the Sub-Assistant Engineer. Thus the problem is solved by their own initiative. It is also monitored by the Executive Engineer of the respective District, and finally by the Executive Director from the headquarters if needed.
Crop cultivation:
Due to the application of the technology, previously fallow land has come under cultivation/irrigation facilities, mono-cropped land has been converted into multi-cropped land. Different crops, like rice, wheat, maize, mustard, pulses, potato, tomato, spices and other vegetables are cultivated.
Farmers’ acceptance:
The technology has been well accepted by the farmers, as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation and different crops are now being cultivated year-round.
ສະຖານທີ່: ບັງລາເດດ
ຈໍານວນ ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ວິເຄາະ: 2-10 ພຶ້ນທີ່
ການແຜ່ກະຈາຍຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຢູ່ໃນເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນທີ່ບໍ?: ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ວັນທີຂອງການປະຕິບັດ: 10-50 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ
ປະເພດຂອງການນໍາສະເໜີ





| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (BDT) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (BDT) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 1 | 1.0 | 5000000.0 | 5000000.0 | |
| Construction of underground water distribution line | 1 | 1.0 | 27800000.0 | 27800000.0 | |
| Construction of submerged weir / dam | 1 | 14.0 | 1600000.0 | 22400000.0 | |
| Re-excavation of derelict canal | 1 | 1.0 | 29000000.0 | 29000000.0 | |
| ອື່ນໆ | |||||
| Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges | 1 | 33.0 | 243000.0 | 8019000.0 | |
| Solar pump installation | 1 | 6.0 | 2000000.0 | 12000000.0 | |
| LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 1 | 8.0 | 2700000.0 | 21600000.0 | |
| Pumps installation on the pontoon | 1 | 12.0 | 1833000.0 | 21996000.0 | |
| Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 1 | 1.0 | 23100000.0 | 23100000.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 170'915'000.0 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 2'010'764.71 | ||||
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ (BDT) | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ (BDT) | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ |
| ອຸປະກອນ | |||||
| Prepaid meter repair | 1 | 0.2 | 100000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | |||||
| Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| ອື່ນໆ | |||||
| Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 500000.0 | 500000.0 | |
| Pump repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| Distribution line maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 75000.0 | 75000.0 | |
| Power station repair and maintenance | 1 | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 200000.0 | 200000.0 | |
| LLP repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 915'000.05 | ||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 10'764.71 | ||||
At present land users are used to grow high water demanding crops. For example Boro paddy and potato both crops require large volume of water and the irrigated area slowly increasing, that situation demand of irrigation water increasing.
The supply of agricultural inputs increased and channelized through deploying dealers etc. Hence expenses relatively decreased
Basically in this area could be grouped in to two. One group has almost no land and previously they have to migrate beyond barind area as labor and they were poor. At present they have job (agri-labor or otherwise) in their area and become more solvent then past 90's. On other hand the second group cultivate the land of their own or leased, which they could not in 90's. They also in handicap because of poor crop and no option to cultivate in two seasons. Hence apparently both groups as of their status are in well shape. The peoples those who have no land for cultivation now can engage them in many other entrepreneurship (e.g. farm product marketing, livestock/poultry raring, carpentering, grocery, etc etc) emerged.
Along with the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) other national institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension, Livestock, Fisheries, Bangladesh Rural Development Board (BRDB), Financial institutions- Rajshahi Agricultural Development Bank and others (NGO) are operating more effectively in the Barind in multiple dimensions. In addition students from Rajshahi University also engaged in their research on various issues. BMDA also improving its capacity and skill to develop more effective approach for Barind area.
This comment was done comparing between conveying water by open drainage and through pipeline. Definitely there are almost no run-off from pipe line distribution. On the hand land users have to confirm their field bunds to protect run-off. Prepaid metering system also restricted land users not to allow excess water to over flow from their field. In-spite of that there may be small amount run-off, but the detachment of top soils is within tolerable limit and accumulate within field bunds.
It is reported that ground water slowly recharged, As a results shallow tube wells are also working , which were about to abandoned before.
Vegetation coverage increased,
Increased land cover-Reduced drought
In 90's the lands were bare and in monsoon after heavy downpour a large amount of water going to downstream as run-off with detached top soil. At present land is covered, field bunds are strengthen, restrict run-off as a result soil loss decreased.
Field bunds enhance soil accumulation by limiting run-off water by field bunds/dykes.
Mechanized cultivation and usage of farm machinery however enhance soil compaction.
Emission of carbon decreased as vegetation cover round the year increased.
Reduced dusty wind, temperature cooler then before.
Usage of surface water reduces groundwater abstraction and improves groundwater (GW) recharge
As the land cover has increased, that has a substantial impact on limiting polluted surface water to flow up to river.