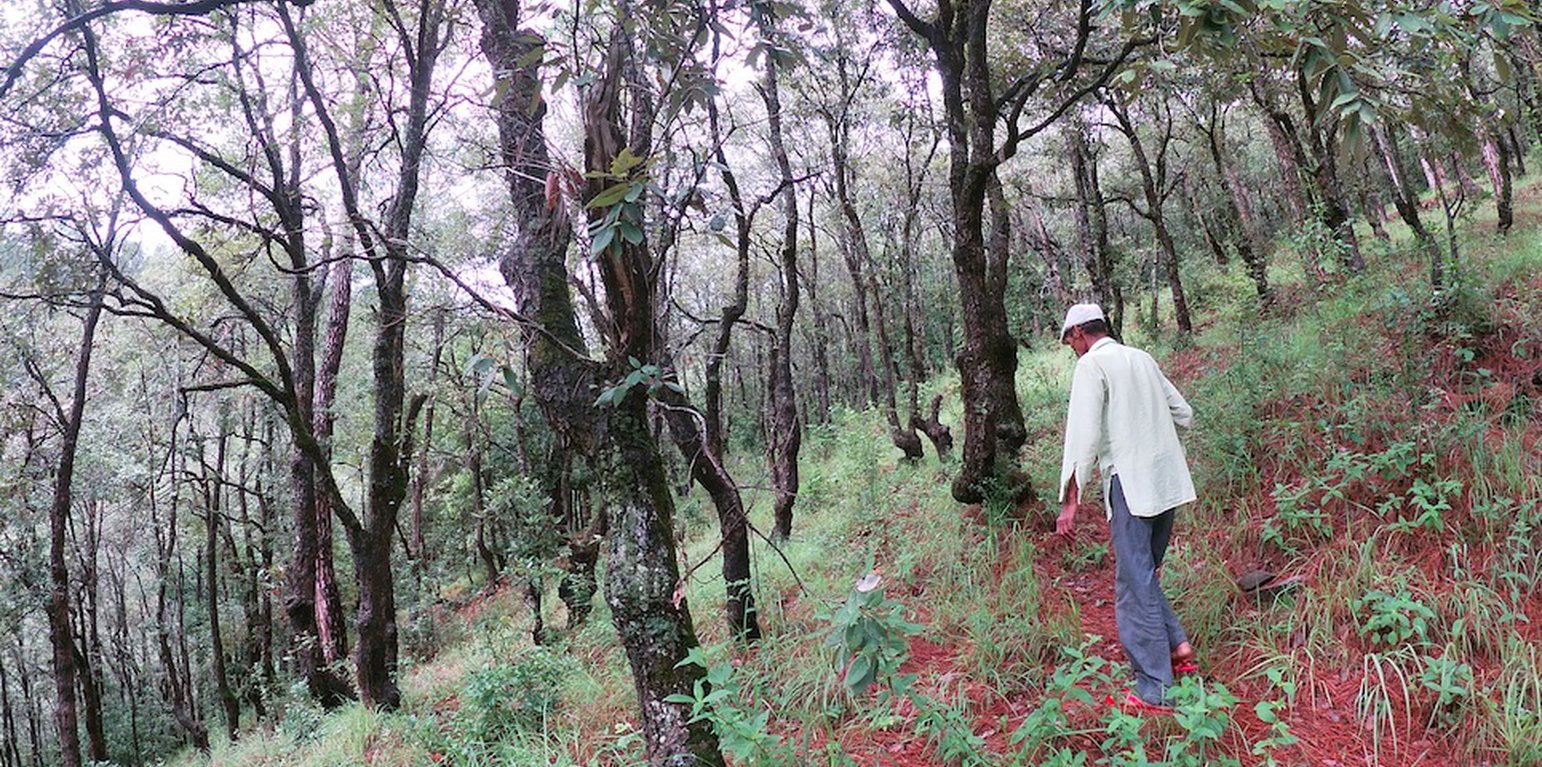




1. The technology is applied in a natural environment and is located about 1km away from the settlement and the agriculture land of Nakina Village. The village has access to its own forest, which covers a geographical area of 114 hectare. Of this, 94 hectares come under the Village Forest Council, locally referred to as the Van Panchayat.
2. Characteristics of Technology:
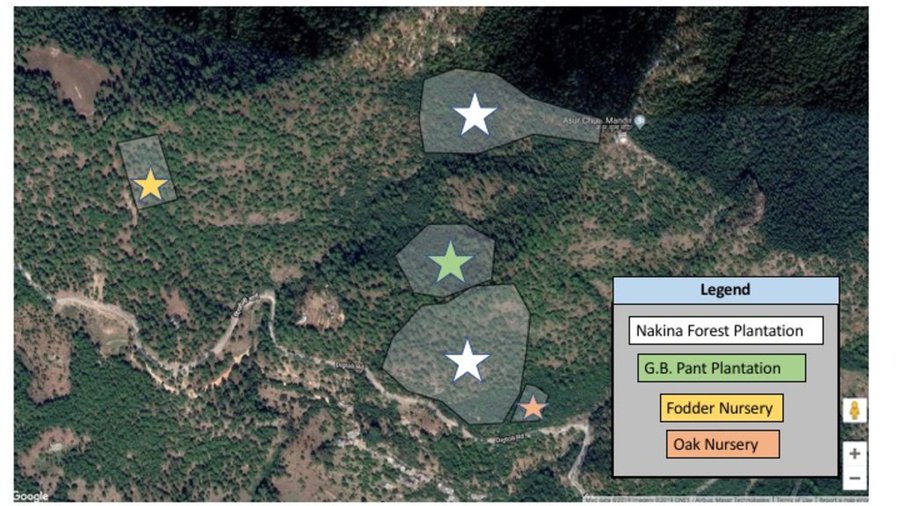
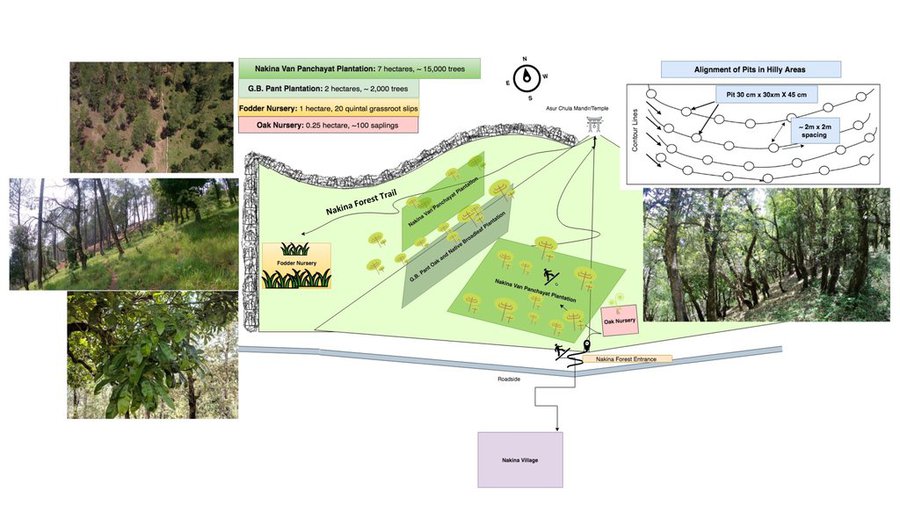
a. Broadleaf species have been established over 7 hectares through natural assisted tree regeneration methods. These include Banj Oak (Quercus leucotrichophora), Falyaat (Quercus glauca), Koeraal (Bauhinia verigata), Bhimal (Grewia optiva), Padam Paaya (Prunus cerasoides), Haradh (Terminalia chebula), Reetha (Sapindus Mukorossi), Utees (Alnus napalensis), Ainyar (Lyonia ovalifolia), Khadik (Celtis australis).
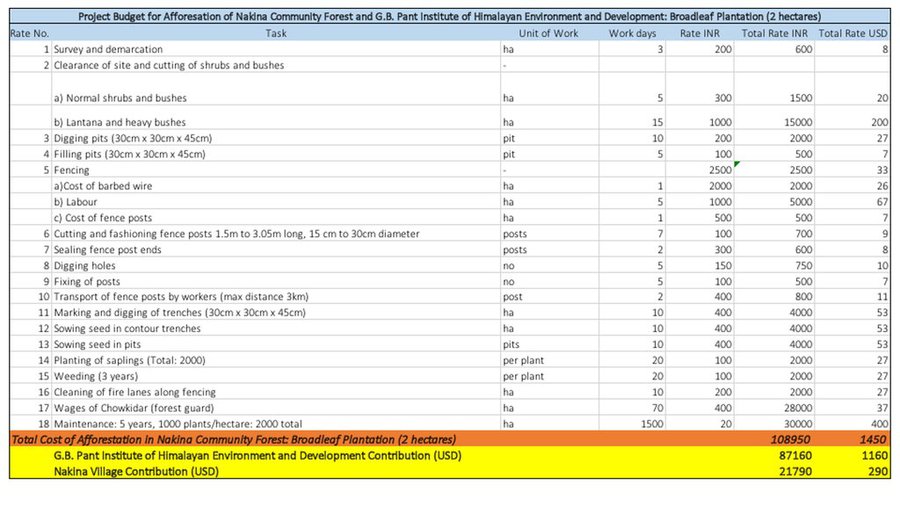
b. Nakina Van Panchayat has made an oak plantation site of 2 hectares in collaboration with G.B. Pant Research Institute.
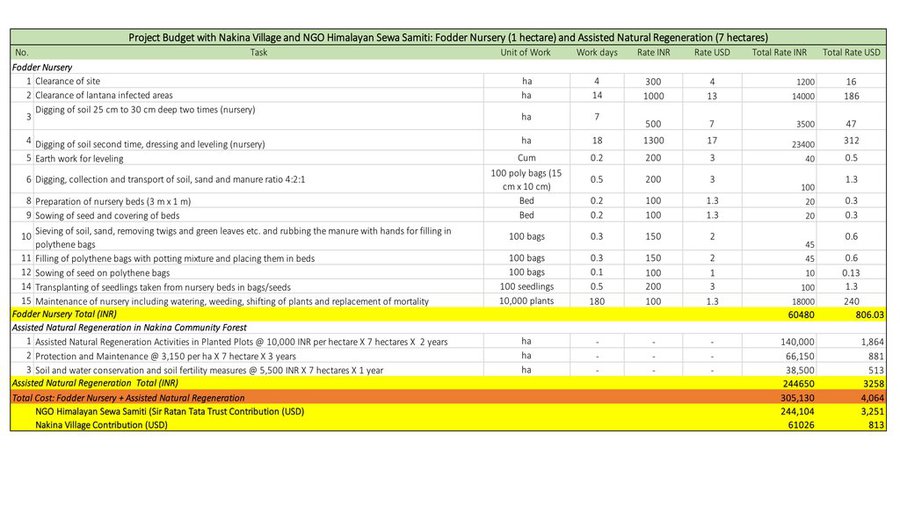
c. A fodder nursery covering 1 hectare hosts a variety of subtropical (Napier: Pennisetum purpureum, Aus, Ginni) and temperate grasses (Guchhi, Dolni, Italian rye: Lolium multiflorum). It was established with the assistance of the NGOs Swati Gramodyog Sansthan and the Himalayan Sewa Samiti. Extraction of fodder leaves and timber are restricted and regulations managed by the Van Panchayat (community forest council).
Purposes/functions:
-Increase trees and grasses to improve availability of fuel and fodder for community, as well as enrich biodiversity.
-Plantation is on a mountain slope (+25% slope), so it will help in preventing soil erosion and landslides.
-Improve soil and water conservation, prevention of surface run-off, support groundwater recharge and spring rejuvenation.
Major activities/Inputs needed to establish and maintain technology:
1. Activities for Assisted Natural Regeneration: protect and facilitate the growth of parent trees inherently present in the area and their regenerations, rather than establishment of entire plantation
2.Activities for the oak plantation: Selection and seed provision of appropriate tree species, clearing of vegetation and preparation of forest top soil, leveling of soil, digging of plantation pits, sowing weeding, watering, occasional pruning, propagation of trees from cuttings, dead sapling replacement, establishment of barrier/fencing for protection from fire.
3. Activities for fodder nursery:- Selection and seed provision of appropriate grass species and polypot materials, preparation of seedbeds; clearing of vegetation, removal of stones/large roots, ploughing/hoeing, mixing sand and compost on areas with poor soil, sowing seeds pre-monsoon, weeding and watering seedlings, propagation from seed or root cuttings, dead sapling replacement, establishment of barrier/fencing protection from fire.
Benefits/Impacts:
•Restores productivity and fodder/fuelwood availability
•Ecosystem stability
•Enhancement of biological diversity to degraded lands.
•Control landslide and soil erosion
•Control forest fire.
•Maintain wildlife habitat
•Increase livelihood of local people, decrease time spent collecting fodder
•Storage carbon on the forest help to reduce the CO2 in the atmosphere.
Likes:
This technology is properly functioning in the implementation area and local people have received many benefits from sustainable managing their natural resources rather than receiving incentives for institutional support, local people of the Nakina village are strongly active to protect the forest with their own coordination.
Dislikes:
1.Improve wildlife habitat, which may increase human wildlife conflicts as it is near to agriculture land and settlements.
2.Require regular maintenance activities, which require organization within the community and can increase periodic workload depending on level of participation
Байршил: Nakina Village, Pithoragarh Bloc, Uttarakhand, Энэтхэг
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо: 2-10 байршилд
Технологийн тархалт: тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?: Тийм
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо: 10-50 жилийн өмнө
Нутагшууллын төрөл











| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (INR) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (INR) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Plantation Community Manual labour | person-days | 400.0 | 400.0 | 160000.0 | 50.0 |
| Skilled labour (advisor, experts) | person-days | 7.0 | 2000.0 | 14000.0 | |
| Fodder Nursery Raising | Total Cost | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 25.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | |||||
| Axe, Crow bar, Wheel barrow | pieces | 10.0 | 1500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Digging forks, Hammers, Hoes, Spade | pieces | 10.0 | 1500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Scissors, Pruning knives/shears, Budding and Grafting Knives/Tape | pieces | 10.0 | 700.0 | 7000.0 | 50.0 |
| таримал материал | |||||
| Fodder Grass/20 Quintals of Grassroot slips | Total Cost | 1.0 | 45000.0 | 45000.0 | 50.0 |
| Plantation Material, 3.88 INR per Sapling x 1000 Sapling per hectare x 7 hectare | Total Cost | 1.0 | 27160.0 | 27160.0 | 50.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | |||||
| Soil/Water Conservation and Soil Fertility Measures: 5,500 INR per Hectare x 2 | Total Cost | 1.0 | 11000.0 | 11000.0 | 100.0 |
| Nakina Forest: Assisted Natural Regeneration preparation and composting | Total Cost | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fodder Nursery composting | Total Cost | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | |||||
| Plantation Transportation, Pitting, Planting: 6.9 INR per plant X 1000 sapling x 2 hectare | Total Cost | 1.0 | 13800.0 | 13800.0 | 50.0 |
| Fodder Nursery (Rootstock Purchase, Transportation) | Total Cost | 1.0 | 5500.0 | 5500.0 | 50.0 |
| Nakina Village: Assisted Natural Regeneration Activities in Planted Plots, 10,000 INR per hectare X 7 hectares x 3 years | Total Cost | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 371'460.0 | ||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 5'306.57 | ||||
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (INR) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (INR) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Maintenance of nursery | Total Cost/Year | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 25.0 |
| Maintenance of plantations | Total Cost/Year | 1.0 | 4000.0 | 4000.0 | 25.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 7'000.0 | ||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 100.0 | ||||
The situation of infrastructure is difficult and inconsistent in the hill regions because of the terrain. The major infrastructural issues are drinking water and irrigation facilities, electricity, transportation and communication facilities and social infrastructure (housing and education). As for financial services, only the State Bank of India (SBI) is active in the hill regions where it is trying to achieve the objective of 100% financial inclusion. Some villages mentioned buying into into agricultural insurance in the past, however this was a temporary enterprise and they were never compensated after extreme climatic events that occurred and damaged over 70% of their crop. Though infrastructure and education has generally improved over the years, institutional and marketing networks in the region aimed at supporting hill-farmers are lacking.
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ: 2 ton/ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ: 30 ton/hectare
Tree lopping for fodder was decreased by 15%
Decreased the amount of supplementary fodder required for livestock. The amount of grasses, fodder, and fuelwood has increased significantly.
Less time spent collecting forest resources, as the area where the technology is near the village and supports fodder/fuelwood growth (broadleaf forest/oak nursery area)
Improved self sufficiency of village, as the technology has helped increase animal productivity (more fodder, better quality) and increased water availability.
Water condition has improved and people spend less time spent collecting fodder in the forest.
There is less friction between the villages of Bhurimuni and Nakina. Nakina did not have to go ask for permission to access the Bhurimuni Naula for water during the dry season.
The improvements of forest resource security and resilience to disasters/climatic extremes have allowed the villagers have more free time to build up a communal gathering area for ceremonial events and festivals around the Vaishnavi Temple.
Recreation opportunities for villagers have increased. Particularly women, (some of whom are involved in a self help group and active Van Panchayat members), expressed that they saved approximately 1-2 hours/day in fodder collection time.
The partnerships formed between land-users, the Nakina Van Panchayat, the Forest Department and external institutions are leading examples of necessary cooperation between all levels of governance for project harmonization.
People are taking forest management seriously and making innovative plans for further SLM interventions, whether it be community-initiated or with the help of external institutions/agencies.
Conflict has decreased in the village do to increased availability of resources. The overall morale of the village is better and less frantic due to an improvement in dodder, fuel and water provision. This has further enhanced cooperation for interventions that require participation and effort in the community forest.
The technologies improve water holding capacity of the soil by decreasing runoff velocity and improve overall water storage.
Soil moisture of common land was increased by about 15%
Trees and other vegetation has helped mitigate displacement of soil from upstream areas to the lowlands
Vegetation growth and cover has improved due to more shade and water availability
Increased species diversity due to improved moisture availability, soil conditions and microclimate.
Provide more water and habitat for small animals/birds.
Healthy afforested areas provide more water, habitat, and protection for microorganisms and insect species. They support native grasses and vegetation.
Incidents of landslides decreased due to less surface flow velocity and soil destabilisation. Villagers also noted that there were that less displaced soil and sediment accumulation in the ravine that normally incurs damage from upstream debris flow in the monsoon season.
Drought impacts decreased due improved surface and subsurface hydrological functioning in the upper watershed catchment areas. This increased microwatershed/ springshed groundwater stores and enhanced stream and spring flows in the dry season.
Erosion impacts from extreme rain storms is reduced by decreasing flow velocity
Carbon storage is increased by the plantation. It has been previously studied that Uttarakhand Van Panchayat forests sequester carbon at the average rate of 3.5 t ha -1 yr-1. This varies depending on forest distribution, species and land management.
.
The forest intervention area is protected by the villagers from anthropogenic and wild fires, therefore the forest has rehabilitated more quickly and has a lower risk of burning due to improved green vegetation cover and less flammable pine needle accumulation. In the case of pine forests, pine needles are a major source of fuel for fire and the removal of buildup remains a major challenge for the land users.
Because of the interventions, vegetation/biomass, soil cover and water availability has improved and created a more suitable microclimate for microorganisms, plants, animals and people. The microclimate has improved due to decreased surface temperatures from exposed, bare soil or ground that is covered with pine needles. This improved microclimate is visible, as it has additionally allowed a wider range of species (grasses, shrubs, wildflowers, insects, birds) to inhabit the intervention site.
Improved spring discharge in the peak dry season
Bhind and Vaishnavi Naulas (springs) have improved discharge in the peak dry season. According to villagers, there was little to no water available in May/June, and since 10 years the flow has returned due to the plantation efforts combination with structural technologies.
Helped slow down sediment and runoff
No direct evidence, but statements from the locals indicate that there are less sediments in the spring water ( due to improved soil infiltration and buffering capacity)
Less damage from runoff
Decreased intensity of runoff on the roadside and settlement below