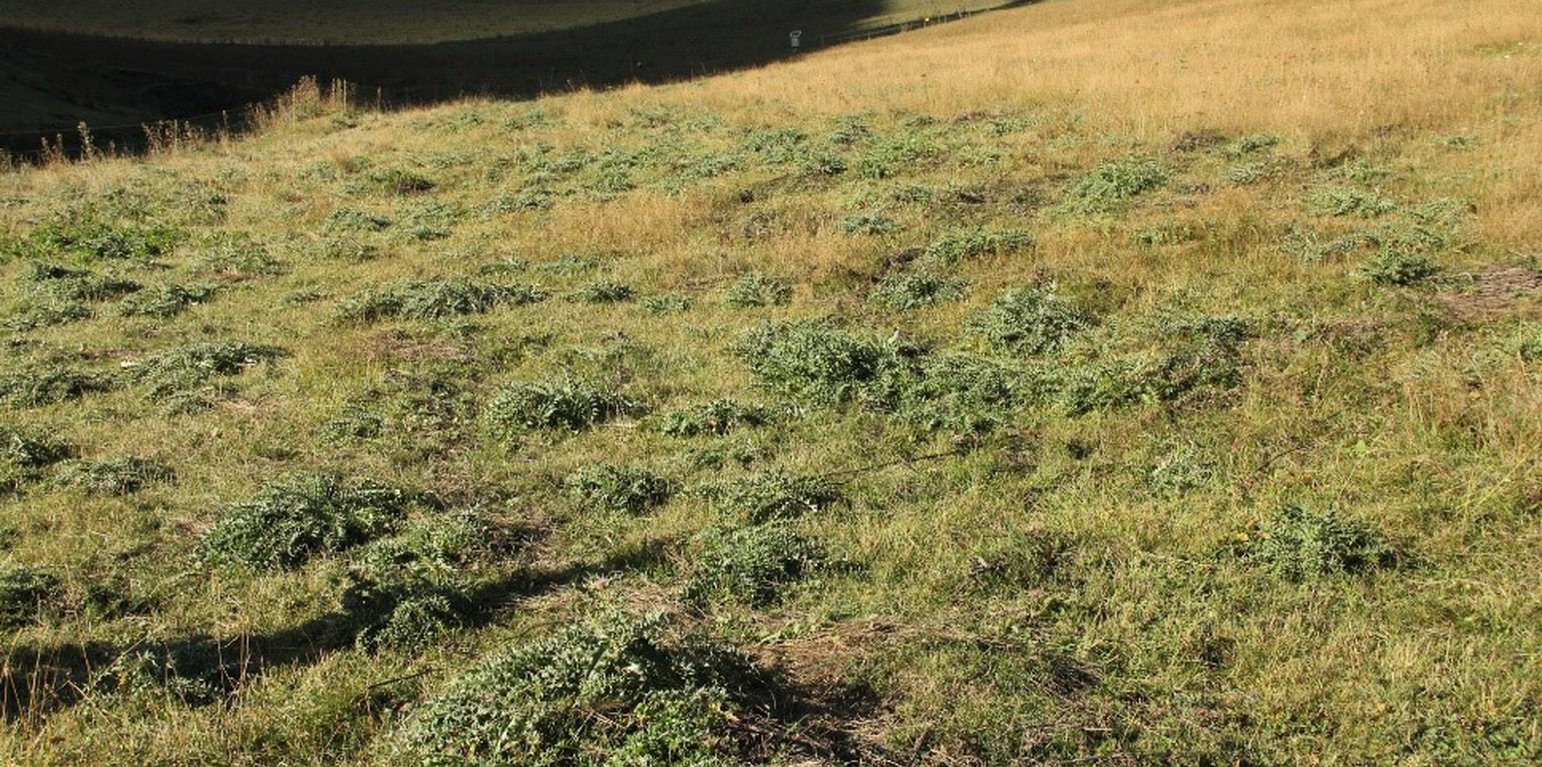
Pasture-weed control by thistle cutting
(Geórgia)
Descrição
Thistles invaded massively into village pasture land at 1800m elevation in the Caucasus. By cutting the thistles with a motor-cutter the cover of thistles have been reduced.
The technology was applied in flat sub-alpine pasture land at an elevation of about 1800 m in the village of Shenako in the Tusheti Protected Landscape, Georgia. Precipitation is 750-900mm and mean annual temperature is 2-4°C. Thistles (Cirsium sp.) were invading especially in those sections of the pasture that are rich in nutrients and have medium soil water content. This site conditions can be found mainly at the valley bottom.
There are no big machines available in this mountain villages. So the removal was done by motor-cutters. In this particular case STIHL petrol brush cutters were used with a 3 blade bush knife.
The removal of the thistles, which were covering up to 20% of the pasture land will increase the productivity of valuable fodder grass and herbs. The thistles are growing up to 1m height and taking up significant amount of nutrients from the soil and are shading other grass and herbs in their neighborhood. Because of their spices they are not eaten by cows or sheep, while the grazing pressure is increasing on the remaining grass and herb species. This leads to positive selection of thistles and a permanent increase of the thistles number and biomass in comparison to the high quality fodder plants.
The thistles have been cut in mid-June/beginning of July just at the begin of blossom. At this stage, the thistles mobilized most of the nutrients from their root system and spent them in leaf and blossom biomass. By cutting the thistles at this time, the highest impact on the nutrient balance can be reached and no new seeds will be produced in this year. It was observed, that the thistles have been eaten by the livestock when it was cut and dried up.
The motor brush cutter increases significantly the speed of cutting the thistles compared to hand scythe. The thistle has a powerful root system and is re-sprouting from the roots within the same summer. So it is important to repeat the cutting 2-3 times a year and to continue several years until the amount of thistles is permanently reduced.
The reduction of thistles will give more space, nutrients and moisture to other fodder plants and increase the productivity of the pasture land.
The challenge is the coordination of the work load within the users of the community pasture land. It needs a (written) agreement to share the workload for pasture maintenance between the families according to their number of livestock.
Localização
Localização: Shenako, Kakheti, Geórgia
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: 2-10 locais
Geo-referência de locais selecionados
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (0.02 km²)
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Sim
Data da implementação: 2018
Tipo de introdução
-
atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
-
Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
-
durante experiências/ pesquisa
-
através de projetos/intervenções externas
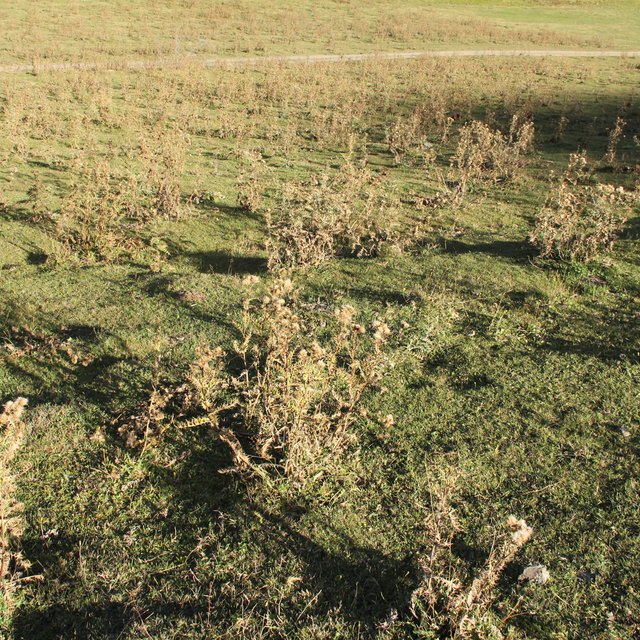

Dense population of thistle on pasture land (Hanns Kirchmeir)
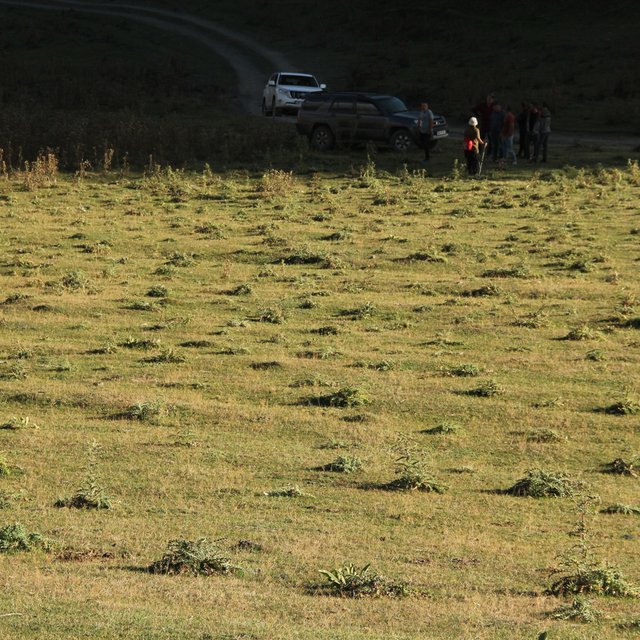

Thistles cut at begin of July (Hanns Kirchmeir)
Classificação da Tecnologia
Objetivo principal
-
Melhora a produção
-
Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
-
Preserva ecossistema
-
Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
-
Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
-
Reduzir riscos de desastre
-
Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
-
Atenuar a mudanças climáticas e seus impactos
-
Criar impacto econômico benéfico
-
Cria impacto social benéfico
Uso da terra
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra: Não
-
Pastagem
Tipo de animal: gado - lácteo, cavalos, ovelhas
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária? Não
Produtos e serviços: carne, leite
| Espécie | Contagem |
| gado - lácteo | 70 |
| ovelhas | 400 |
| cavalos | 30 |
| gado - carne bovina não-láctea | 35 |
Abastecimento de água
-
Precipitação natural
-
Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
-
Irrigação completa
Objetivo relacionado à degradação da terra
-
Prevenir degradação do solo
-
Reduzir a degradação do solo
-
Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
-
Adaptar à degradação do solo
-
Não aplicável
Degradação abordada
-
Degradação biológica - Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Grupo de GST
-
Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
Medidas de GST
-
Medidas de gestão - M5: Controle/mudança de composição de espécies
Desenho técnico
Especificações técnicas
The activity was applied on two plots. Plot 6 is 0.7 ha of size and located in the unfenced area. Plot 7 is 1.3 ha of size and located inside an electric fence. The hatched area (8) is indicating the fenced area.
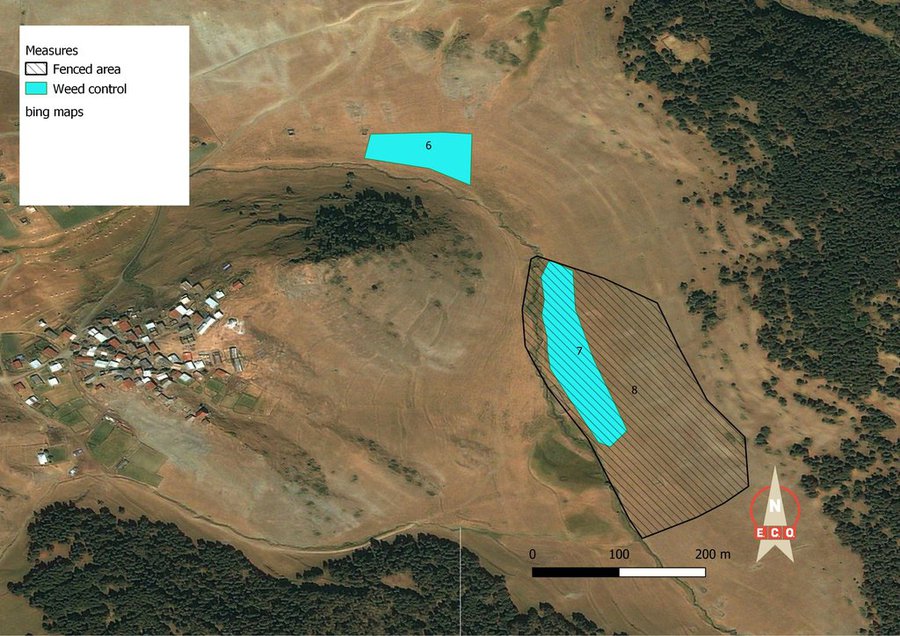
Author: Hanns Kirchmeir
Estabelecimento e manutenção: atividades, insumos e custos
Cálculo de insumos e custos
- Os custos são calculados: por área de tecnologia (tamanho e unidade de área: 2 ha)
- Moeda utilizada para o cálculo de custos: USD
- Taxa de câmbio (para USD): 1 USD = n.a
- Custo salarial médio da mão-de-obra contratada por dia: n.a
Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
The investment in the brush cutter will only pay off if large parts of pastures are managed.
Atividades de implantação
-
Prepare machinery and organize people (Periodicidade/frequência: June)
-
Select pasture plots were the measure will be applied (Periodicidade/frequência: June)
-
Cut the thistles on the selected pasture plots (Periodicidade/frequência: End of June - Mid of July)
Estabelecer insumos e custos (per 2 ha)
| Especifique a entrada |
Unidade |
Quantidade |
Custos por unidade (USD) |
Custos totais por entrada (USD) |
% dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
|
Mão-de-obra
|
| Selection of sites, preparation of materials and people |
person-days |
3,0 |
37,0 |
111,0 |
|
| Labour for cutting thistles on 2 ha |
person-days |
10,0 |
20,0 |
200,0 |
|
|
Equipamento
|
| High quality brush cutter |
pieces |
1,0 |
800,0 |
800,0 |
|
| Patrol (20l) and diesel (30l) for brush cutter (6 days, 8h/day, 1l/h) |
liter |
50,0 |
1,0 |
50,0 |
|
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia |
1'161.0 |
|
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD |
1'161.0 |
|
Atividades de manutenção
-
Repeat cutting of thistles 2x per year (Periodicidade/frequência: June/July and September)
Insumos e custos de manutenção (per 2 ha)
| Especifique a entrada |
Unidade |
Quantidade |
Custos por unidade (USD) |
Custos totais por entrada (USD) |
% dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
|
Mão-de-obra
|
| labour for cutting thistles (2ha) |
person-days |
6,0 |
20,0 |
120,0 |
100,0 |
|
Equipamento
|
| Patrol for brush cutter |
liter |
96,0 |
1,0 |
96,0 |
|
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia |
216.0 |
|
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD |
216.0 |
|
Ambiente natural
Média pluviométrica anual
-
<250 mm
-
251-500 mm
-
501-750 mm
-
751-1.000 mm
-
1.001-1.500 mm
-
1.501-2.000 mm
-
2.001-3.000 mm
-
3.001-4.000 mm
-
> 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
-
úmido
-
Subúmido
-
Semiárido
-
Árido
Especificações sobre o clima
Pluviosidade média anual em mm: 850.0
Main rainfall in spring and autumn, July and August is the dry season.
Nome da estação meteorológica: Data from CHELSA.ORG
Because of low annual temperature (2-4°C) the evapotranspiration is low and most of the year there is no water shortage. But in August and September drought can occur.
Inclinação
-
Plano (0-2%)
-
Suave ondulado (3-5%)
-
Ondulado (6-10%)
-
Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
-
Forte ondulado (16-30%)
-
Montanhoso (31-60%)
-
Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo
-
Planalto/planície
-
Cumes
-
Encosta de serra
-
Encosta de morro
-
Sopés
-
Fundos de vale
Altitude
-
0-100 m s.n.m.
-
101-500 m s.n.m.
-
501-1.000 m s.n.m.
-
1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
-
1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
-
2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
-
2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
-
3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
-
> 4.000 m s.n.m.
A tecnologia é aplicada em
-
Posições convexas
-
Posições côncavas
-
Não relevante
Profundidade do solo
-
Muito raso (0-20 cm)
-
Raso (21-50 cm)
-
Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
-
Profundo (81-120 cm)
-
Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (superficial)
-
Grosso/fino (arenoso)
-
Médio (limoso, siltoso)
-
Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície)
-
Grosso/fino (arenoso)
-
Médio (limoso, siltoso)
-
Fino/pesado (argila)
Teor de matéria orgânica do solo superior
-
Alto (>3%)
-
Médio (1-3%)
-
Baixo (<1%)
Lençol freático
-
Na superfície
-
< 5 m
-
5-50 m
-
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície
-
Excesso
-
Bom
-
Médio
-
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada)
-
Água potável boa
-
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
-
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
-
Inutilizável
A qualidade da água refere-se a: tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade é um problema?
Ocorrência de enchentes
Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado
-
Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
-
misto (subsistência/comercial)
-
Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola
-
Menos de 10% de toda renda
-
10-50% de toda renda
-
>50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza
-
Muito pobre
-
Pobre
-
Média
-
Rico
-
Muito rico
Nível de mecanização
-
Trabalho manual
-
Tração animal
-
Mecanizado/motorizado
Sedentário ou nômade
-
Sedentário
-
Semi-nômade
-
Nômade
Indivíduos ou grupos
-
Indivíduo/unidade familiar
-
Grupos/comunidade
-
Cooperativa
-
Empregado (empresa, governo)
Idade
-
Crianças
-
Jovens
-
meia-idade
-
idosos
Área utilizada por residência
-
< 0,5 ha
-
0,5-1 ha
-
1-2 ha
-
2-5 ha
-
5-15 ha
-
15-50 ha
-
50-100 ha
-
100-500 ha
-
500-1.000 ha
-
1.000-10.000 ha
-
> 10.000 ha
Escala
-
Pequena escala
-
Média escala
-
Grande escala
Propriedade da terra
-
Estado
-
Empresa
-
Comunitário/rural
-
Grupo
-
Indivíduo, não intitulado
-
Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra
-
Acesso livre (não organizado)
-
Comunitário (organizado)
-
Arrendado
-
Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água
-
Acesso livre (não organizado)
-
Comunitário (organizado)
-
Arrendado
-
Indivíduo
Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola)
Água potável e saneamento
Comentários
Most important of-farm income is tourism (guesthouses, crafts).
Impactos
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção de forragens
By reduction of thistles the space for other plant species has increased.
Análise do custo-benefício
Benefícios em relação aos custos de estabelecimento
Retornos a curto prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Benefícios em relação aos custos de manutenção
Retornos a curto prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Adoção e adaptação
Porcentagem de usuários de terras na área que adotaram a Tecnologia
-
casos isolados/experimental
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram sem receber incentivos materiais?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
A quais condições de mudança?
-
Mudança climática/extremo
-
Mercados dinâmicos
-
Disponibilidade de mão-de-obra (p. ex. devido à migração)
Conclusões e experiências adquiridas
Pontos fortes: visão do usuário de terra
-
Decreasing the cost for maintanace of cattle
-
Reducing the working hours
-
Improving the pastures via weed control
Pontos fortes: a visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada
-
Easy to apply, no specific skills needed
-
Visible impact within a few years
Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos: visão do usuário de terracomo superar
-
Irresponsibility of some members of the community during the maintenance of el-fence
Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos: a visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitadacomo superar
-
No responsibility within the community pasture land for maintenance of pasture land.
A new regulation on how to share the workload of pasture maintenance could be negotiated between villagers.
-
Machinery is expensive.
The investment will pay off when the measures are applied to the entire pasture land (100-200 ha).
Referências
Data da documentação: 18 de Dezembro de 2018
Última atualização: 7 de Agosto de 2019
Pessoas capacitadas
-
Hanns Kirchmeir - Especialista em GST
-
Kety Tsereteli - co-compilador/a
Descrição completa no banco de dados do WOCAT
A documentação foi facilitada por
Instituição
- Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Geórgia
Projeto
- Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)










