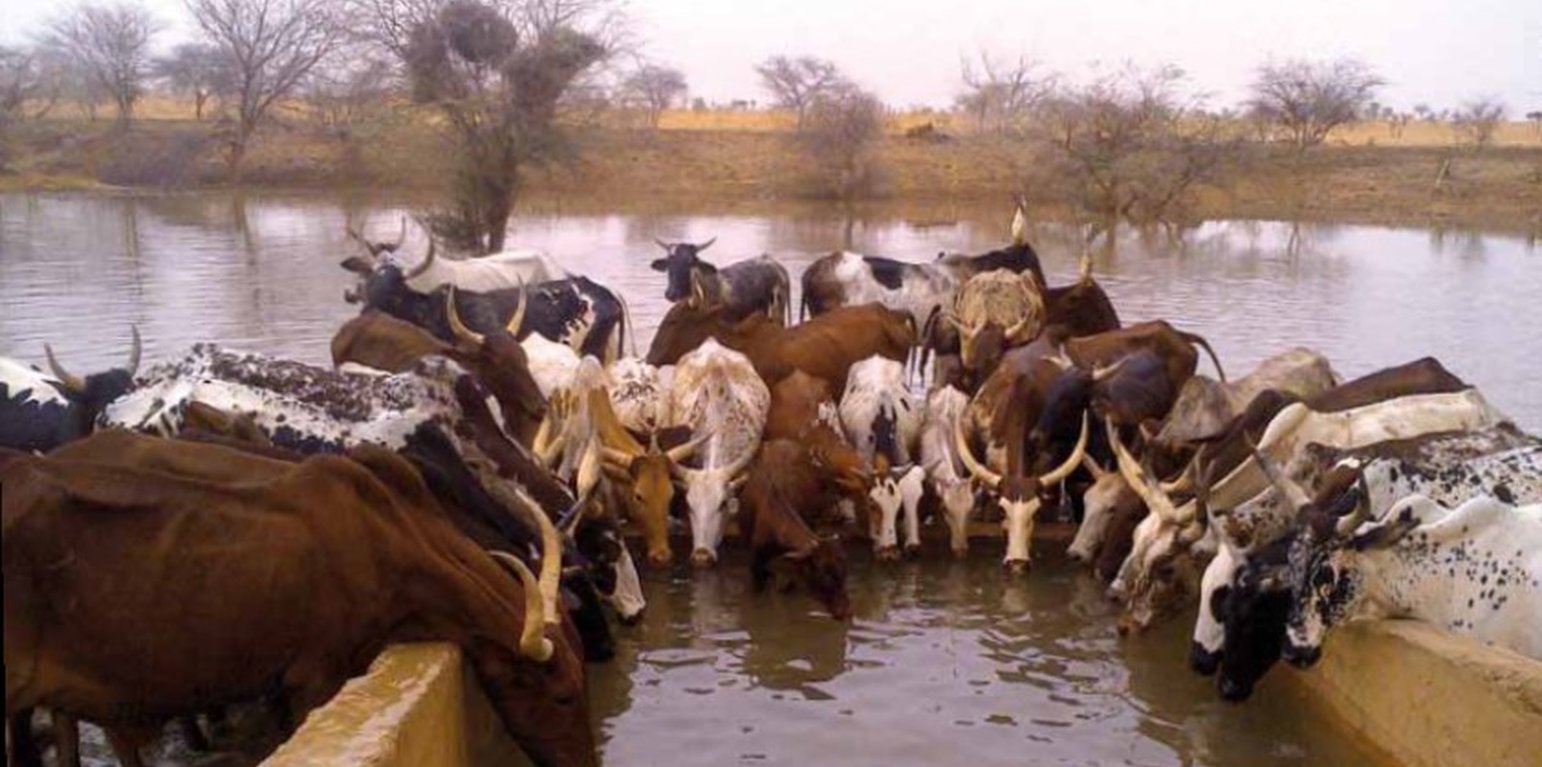




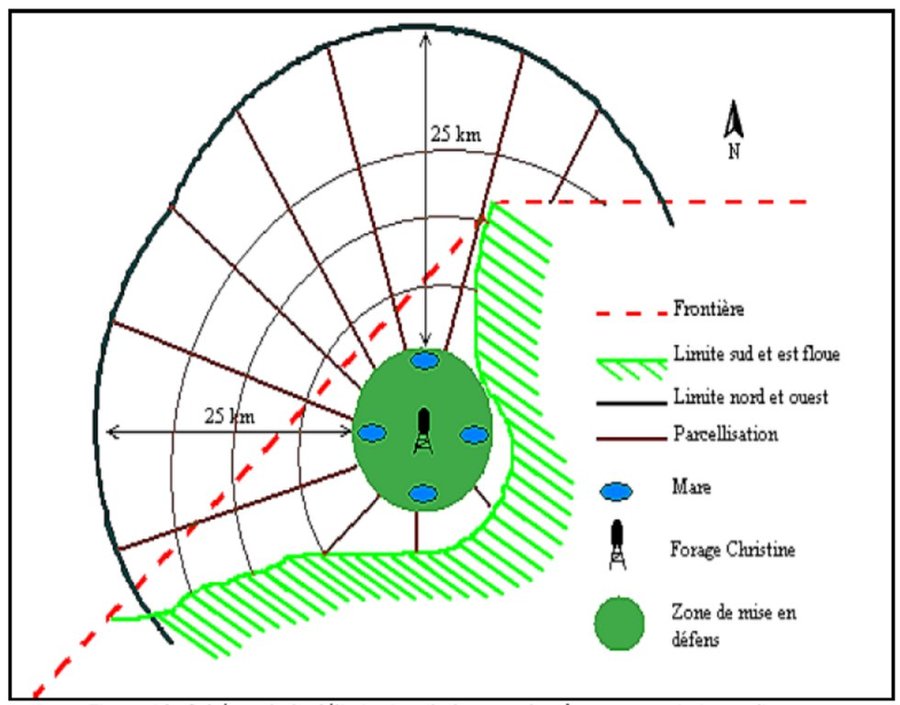
The well called 'Forage Christine' was constructed in 1971 by a French engineer, which named it after his wife, and opened it for the first time in 1972. Due to conflicts between Burkina and Mali it was ruined in 1976, and then again in 1985. In 1996 the National Office for Wells and Boreholes (ONFP), a government agency, rehabilitated the well and made two supplementary boreholes. The complex consists of a main well with an operating flow rate of 120 m3/h, having a submersible pump of brand KSB, type OPA 150s-65/8, and a pump capacity of 60 m3/h. Next to the main well there is a secondary well, which is equipped with a hand-operated pump with a capacity of 18 m3/h.
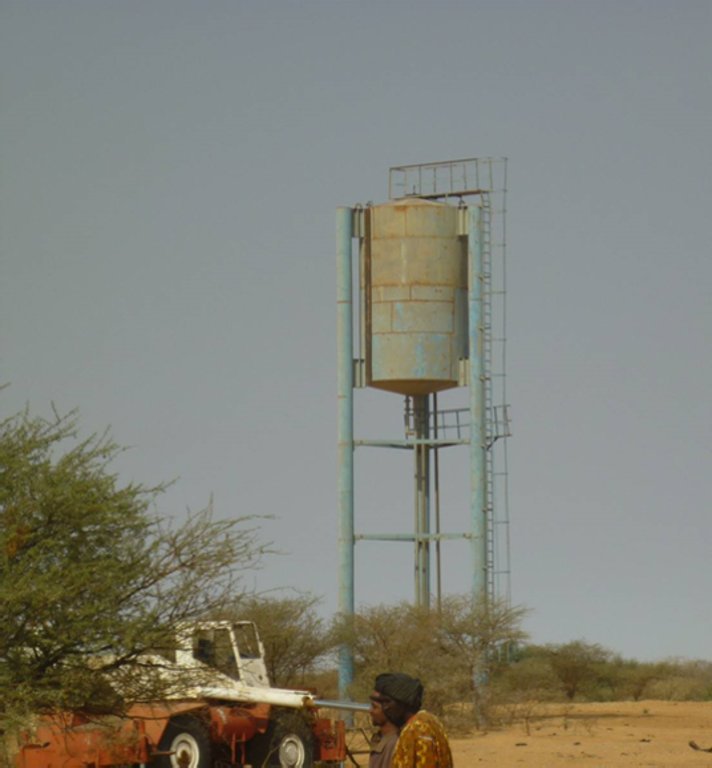
The energy for pumping water from the wells is provided by a generator with an engine of brand DEUTZ (type: F3 - 6L 912) and a switch of brand LEROY SOMER – Type LSA 42.1 L8L C1/4, a voltage of 400 V and continuous power of 50 kW. The generator has a switch and a battery. A diesel tank with a volume of approximately 9 m3 was installed for the power supply to the generator. The pumped water is stored in an elevated water tank, which is located at a distance of about 200 m from the well, and has a volume of 50 m3. The water from the elevated water tank is distributed to four artificial ponds with a dimension of 50 m x 50 m x 1.5 m at equal distances on all sides of the central reservoir. The water is conducted to the artificial ponds through PVC piping, which is buried underground over a distance of 8 km, or 2 km for each pond. The water flow is controlled by nine valves of type Nr. 4000, Reg. Nr. W 1.129, installed on the pipes. The hydraulic complex was installed in 1996 by the National Agency for Water and Sanitation (ONEA). The complex is managed by the livestock keepers through the User Association of 'Forage Christine' (AUFC). The statutes of this organisation were adopted on 2 May 2014. The well is managed according to a set of requirements which specify the terms for access to water: date of opening and closure of the well, the amount to be paid per animal and the management of the cash money provided.
'Forage Christine' is a major water infrastructure, established in the northern part of the Sahel region in Burkina Faso between longitude 0°45’W and latitude 14°48’N, providing drinking water to herds within an area of 100 to 300 km from its central location between Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger. It was established in 1971 in the context of major droughts that had affected the Sahel, and it was opened for the first time in 1972. It is located in the middle of the Sahel region of Burkina Faso, at two km from the pond of Tin-Arkachen in the department of Déou, at approximately 45 km from the capital of the department, and 85 km from Gorom-Gorom. At the sub-regional level, the well is a around ten km from the border with Mali, and at 100 km from the border with Niger. The climate is of Sahelian type, and has a rainy season of 3 to 4 months (from June-July to September), which is subject to strong temporal and spatial variations in precipitation, and a dry season of 8 to 9 months. The climatic conditions are characterized by highly irregular winds, precipitation, evapotranspiration and moisture due to fluctuations in atmospheric circulation patterns. Annual precipitation is around 500 mm on average, with roughly 30 rainy days, and is marked by significant inter-annual variations. The stream network of the region consists of several streams, with one permanent river: Béli. To this river, ponds and many depressions are connected, which disappear after the month of January. The soils are very diverse in general, and mostly of sandy texture. They do not provide a good medium for plant growth due to the low permeability, which reduces water infiltration. Therefore water availability appears to be one of the major limitations for rainfed agriculture, in addition to the limited retention and availability of nutrients. According to the phytogeographic division of Burkina Faso (Fontes and Guinko, 1995), the area of 'Forage Christine' is situated in the northern or strict Sahelian phytogeographic sector. This sector is characterized by a set of typical Saharan and Sahelian vegetation species which mainly occur in shrub and woody steppes (48.85%) and grassy steppes (24.37%), which form the larger part of the rangelands (***). This vegetation provides the most important natural grazing land to livestock.
With regard to the human environment, the last General Population and Housing Census mentions a population of 25321 inhabitants for the municipality of Déou. Yet this number varies significantly due to the seasonal migration of people from other regions to use water and forage resources. The ethnic groups in the region are mainly Fulbé, Kurumba, Songhai, Tuareg, Mossi and Hausa people.
Economic activities in the region are livestock keeping, farming, craftmanship, fishing, trade, tourism and hunting. Several socio-economic groups are guiding these activities. Some 60 farmer groups, 53 groups of livestock keepers, six of which for female livestock keepers, and three organisations for environmental protection. With regard to infrastructure for education, sanitation and socio-economical conditions, the municipality of Déou has three markets, 18 schools, one middle school, 47 permanent functional literacy centers (CPAF), one recreation center, six cereal banks, three healthcare and welfare centers (CSPS), three medical stores, one tourist camp and one financial institution.
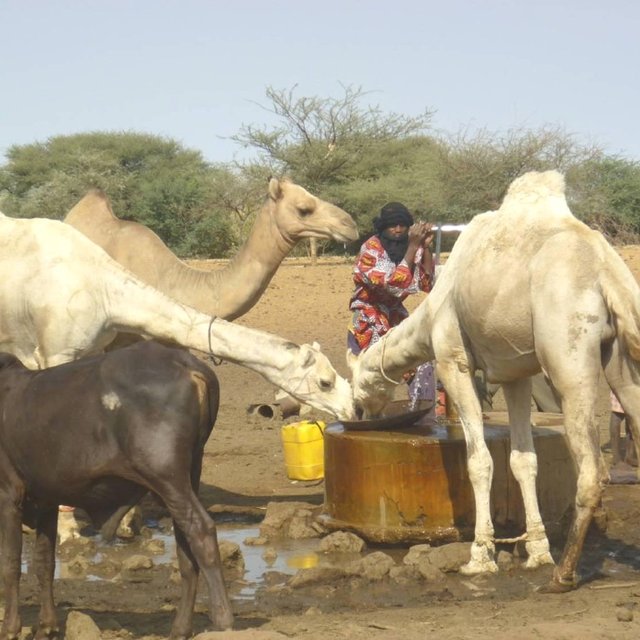
Farming and livestock keeping continue to be the most important socio-economic activities. The agricultural crops produced include millet, sorghum, maize, cowpea, rice and groundnut. In 2009, a total area of 345.5 ha was sown for these crops. The Sahel region in Burkina Faso has excellent conditions for livestock keeping. The animal species found in the region are mainly cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, camels, donkeys and horses and poultry. Several facilities and installations for water supply to pastoral areas are available in the region, as well as storage facilities for agricultural and agro-industrial by-products (SPAI) and infrastructure for trade and animal health care. The municipality of Déou disposes of one reservoir, five artificial ponds, 43 firm wells, ten vaccination centers, one store for agricultural and agro-industrial by-products (SPAI), one animal shelter, a facility for slaughtering and a livestock market.
Localização: Déou, Sahel/Oudalan, Burkina Faso
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: Local único
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: 1971
Tipo de introdução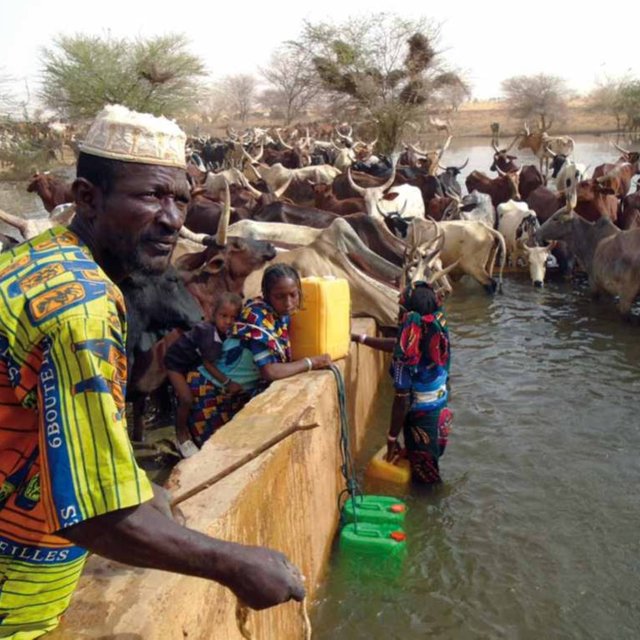







| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (FCFA) | Custos totais por entrada (FCFA) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Periodic maintenance of the generator | season | 1,0 | 150000,0 | 150000,0 | |
| Compensation of the GE manager | person-month | 12,0 | 37500,0 | 450000,0 | |
| Charges for accounting | person-month | 12,0 | 175,0 | 2100,0 | |
| Wage of the guard | person-month | 12,0 | 50000,0 | 600000,0 | |
| Outros | |||||
| Use of diesel | season | 1,0 | 2921000,0 | 2921000,0 | |
| Use of oil, filters | season | 1,0 | 68000,0 | 68000,0 | |
| Reparations to the hydraulic complex | season | ||||
| Fuel delivery | season | 1,0 | 125000,0 | 125000,0 | |
| Transport costs of maintenance operator | season | 1,0 | 60000,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 4'376'100.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 7'956.55 | ||||