



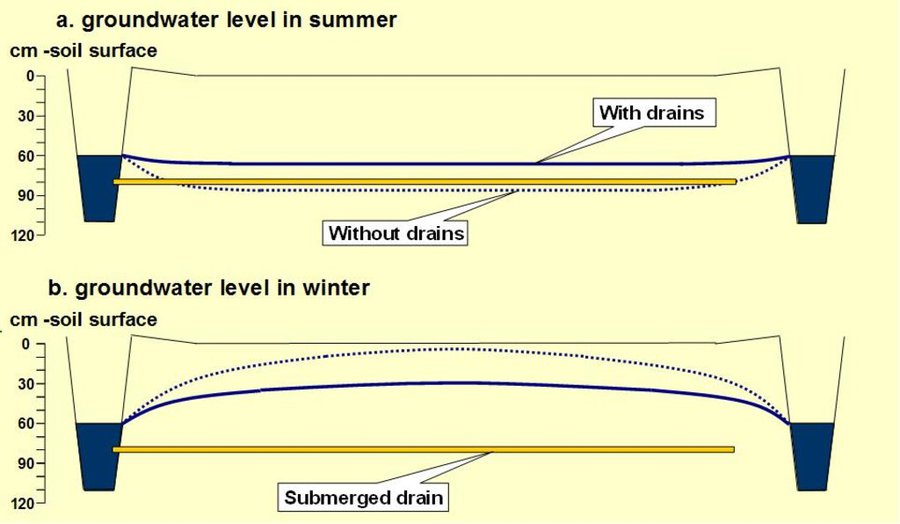
Contrary to usual drains, submerged drains are installed below ditchwater level. Submerged drains diminish the differences between ditch level and groundwater level in the fields by enabling the infiltration from ditch to field and the drainage from field to ditch.
In summer and dry periods the infiltration from ditch to field is much lower than the evapotranspiration of the grass, resulting in a lowering of the groundwater level some decimetres below ditch water level. With submerged drains the groundwater level is lowered less drastically because infiltration from ditch to field is improved. In winter and wet periods, fields are drained more quickly compared to conventional drainage.
Purpose of the Technology: Submerged drains diminish the differences between ditch level and groundwater level in the fields by enabling the infiltration from ditch to field and the drainage from field to ditch. Under peak rainfall events groundwater levels become less high and remain at high levels for shorter times than in fields without submerged drains.
Due to the increased groundwater level in summer the decomposition of the peat soil is reduced. As a result, the rate of soil subsidence is decreased and also the emission of greenhouse gases and of N and P released to the surface water.
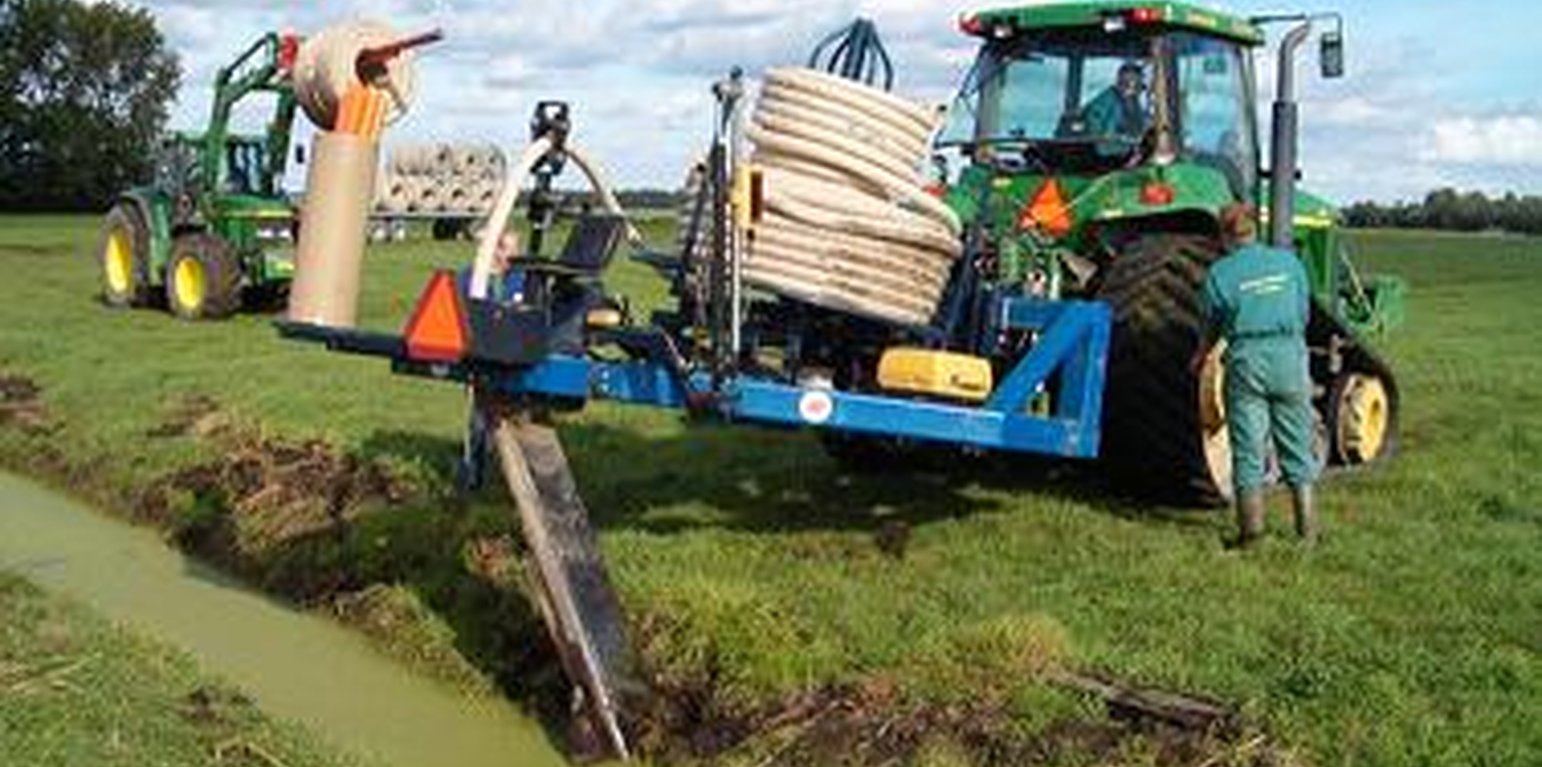
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The installation of submerged drains is done with common drainage installation machines. Submerged drains should be installed between 15 and 25 cm below the ditch water level, and between 45 and 75 cm below the soil surface. The drain pipes should have a diameter of at least 6 cm. The distance between drains is at most 6 m. Drain length is at most 300 m. Submerged drains can be installed in the length or width direction of a field. Drains must be installed level.
Natural / human environment: Submerged drains were designed for peat soils under permanent pasture for dairy farming. More than 70 % of Dutch peat soils are under this land use. Drainage of these peat soils results in subsidence, mainly by decomposition (oxidation) of the peat (partly by shrinkage and consolidation). This is an ongoing process, because every 10 to 15 year ditchwater levels are adapted to the lowered surface in order to enable dairy farming and to prevent the conversion to wetlands. Soil subsidence causes several problems: decreased suitability for grazing and grassland farming, increased flood risk, emission of greenhouse gases, damage to infrastructure (dikes, roads, foundations, sewerage networks) and increased cost of water management.
Submerged drains were tested with a network of practitioners and 10 dairy farmers in the Dutch peat soil area between 2011 and 2013 on an area of 20 ha.
Localização: Krimpenerwaard, The Netherlands/Province of Zuid-Holland, Países Baixos
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados:
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (0.054 km²)
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução






| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (euro) | Custos totais por entrada (euro) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| maintenance of drains and outlet in ditch | ha | 1,0 | 30,14 | 30,14 | 100,0 |
| installation of submerged drains | ha | 1,0 | 1980,0 | 1980,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2'010.14 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1'844.17 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (euro) | Custos totais por entrada (euro) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Outros | |||||
| Annual cost incl maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 127,0 | 127,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 127.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 116.51 | ||||
Quantidade anterior à GST: 10.7-12.4 tons DM/ha11575
Quantidade posterior à GST: 9.8-12.4 ton DM/ha10975
Net grass yields (DM) measured on experimental plots. May slightly decrease due to SMD, but less loss due to trampling, increased length of grazing season. This delivers 500 kg DM/ha extra fodder produced and 30 extra grazing days.
But also loss possible: From 11575 kg DM/ha to 10975 kg DM/ha Decrease in grass yield is possible between 3 and 9%. This does not take into account losses due to tramping in situation without drains and longer grazing season under SMD.
SMD enable a longer grazing season, increased bearing capacity and reduced risk of flooding of fields
reduced additional feedstock; benefits of extra grass yields and grazing days amount to 171 euro/ha
net benefits of installing SMD are approx. 54 euro per ha per year
trafficability and workability of fielfds improved due to drier topsoil conditions and increased bearing capacity
SMD require an increased inlet and drainage of water in the ditches by the water board, increased pumping hours: 10-22% in dry years; 7-12% in wet years.
Inlet: extra 36-86 mm/y in dry years, 19-45 mm in wet years
Drainage: 17-59 mm in dry years; 33-60 in wet year
Community of Practice on SMD in peat soils enabled knowledge transfer between land users, research insttitutes, farmer's association and authorities
The CoP has informed water boards and provinces in the part of The Netherlands with problems due to soil subsidence
The long-term experiments in The Netherlands, pilots and activities of the farmers organisation LO Nederland, the Veenweide Informatie Centrum and the Community of Practice Submerged Drainage on Peat soils have increased the understanding of participating farmers of submerged drainage, the water accounting of their land, soil and soil quality. Tjey acquired practical knowledge on the implementation of the technology. Participating farmers continue to exchange knowledge and intend to extend the area under SMD. As a result of the pilots and the activities of the Community of Practice, interest for submerged drainage was raised among other dairy farmers, policy makers and authorities.
slight decrease of export of N, P and SO4 to the surface water
SMD increased drainage by 20-65 mm per year in 2011 and 2012
SMD increased infiltration by 8-93 mm per year in 2011 and 2012
decreased soil subsidence to 50% (reductions of 3-6 and 5-8 mm/year)
no direct impact on breeding conditions for meadow birds
decreased GHG emissions in CO2 eq: 6.8-13.5 t/ha per year (pilot Keulevaart) and 11.3-18.1 (pilot Demmeriksekade)
quicker lowering of groundwater table after extreme rainfall events (1-5 days)
More easy water management in polders: Fewer sub-polders with fixed ditch water level; possibility to create areas with high and low surface levels
reduced costs of infrastructure protection (30% or 3.5 M€/year until 2100 in the Frisian peat meadow area)