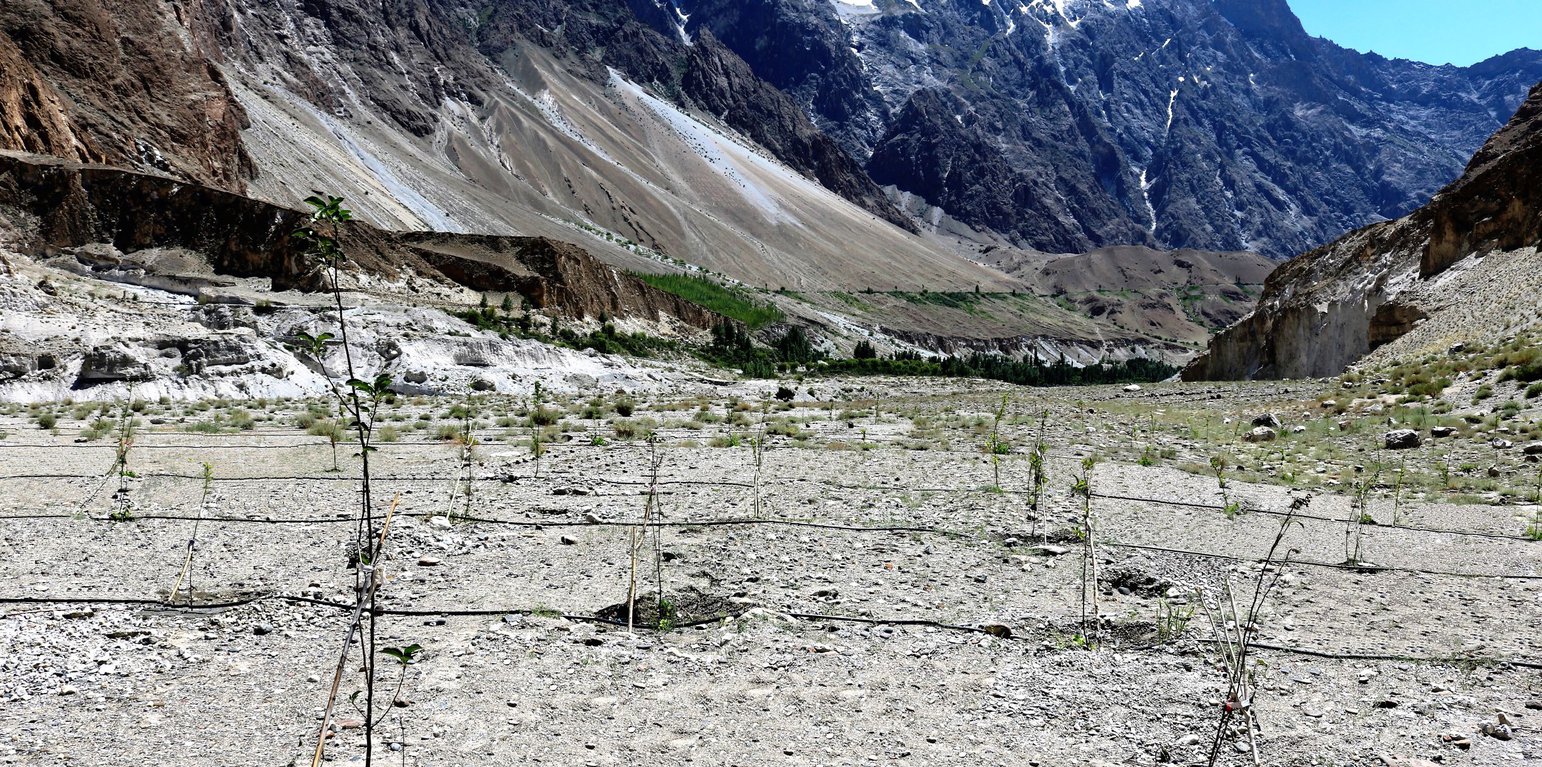




The fragile rouged mountains prone to the effect of climate change makes the mountain com-munities in Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan more vulnerable. Agriculture is the major source of their livelihoods and it purely dependents on glacier meltwater which makes the community more susceptible due to the unstable behaviour of the glaciers. Irrigation is practised with traditional irrigation canals, intake of which is located at glacier terminus. On one hand lowering of glacier surface disconnects many irrigation canals. Uncertain glacier behaviour has resulted in the decline of water availability and even forced some communities to abandon their agricultural land. On the other hand, only 2% of land in Gilgit-Baltistan is used for agriculture purposes whereas a huge chunk of barren land lays above the Hunza River, which cannot be cultivated through the traditional irrigation system hence it remains unutilized.
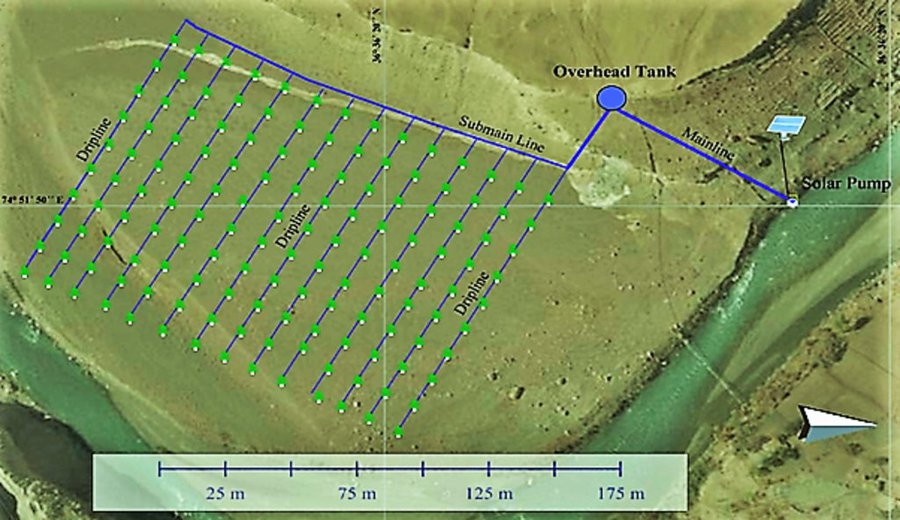
To address both issues, ICIMOD together with a local level partner’s consortia piloted solar water lifting to irrigate barren land for establishing apple orchards along Hunza River at Passu and Morkhun Villages. These two villages are located far from each other. In each village, orchards of 2.5 hectare area were established and the drip irrigation system installed was efficiently used to irrigate apple plants. Similar technological packages (solar pump, drip irrigation and mulch) were applied in both the villages.
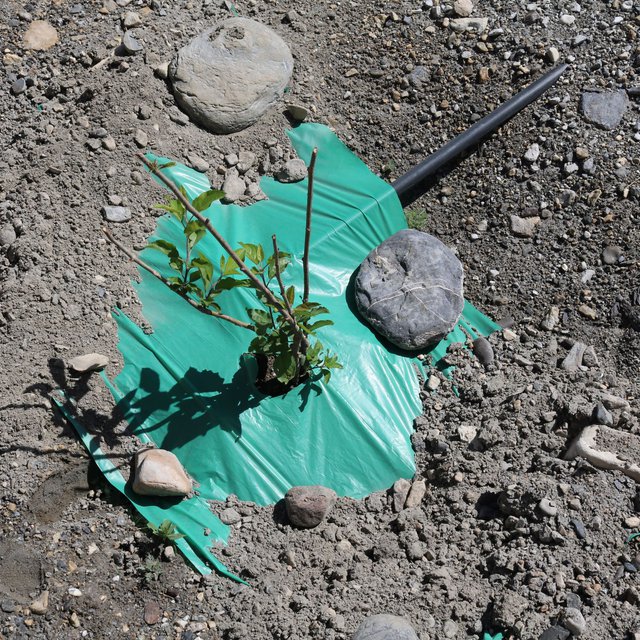
The pumping system comprises a submersible pump (Lorentz, Germany 1 HP) powered by 500 watts solar panels to carry the water to storage tanks (500 litres) made up of plastic that has been placed upslope at 100 feet vertical height from the river. The water from the storage tanks was routed/led to the apple saplings through the surface and pressure compensating drip irrigation system. The pumping capacity of the pump is 7.5 litres/minute, which is irrigating around 3300 apple plants at Passu and Morkhun. The storage tank was kept 60 feet vertical height from the orchard field to be irrigated. Tree to tree distance and row to row distance of apple was maintained at 15 feet in Passu and 10 feet in Morkhun. Drip irrigation (surface and pressure compensating) system was established to irrigate each apple plant, the emitter of the drip system was adjusted according to the plant to plant distance of apple seedlings to be irrigated. Pits were constructed for planting apples and later they also served as water harvesting pits /check basins. Plastic mulch was applied to each apple plants covering a radius around the trunk to minimize soil moisture losses, reduce weed and reduce soil erosion by water and wind.
The cost of an integrated package including solar pumps with accessories, storage tanks, intake and distribution systems (i.e. from river to tank and tank to trees), drip irrigation, apple plants and operational expenses (manpower) for both the sites was US$ 42000 for 5 ha of land. Village Development Organizations (VDO) of both villages take care of maintenance of technological package through a maintenance fund, which is being raised by participating households (HHs). Benefit sharing mechanism has been agreed among the participating HHs. The total income would be divided equally among participating 72 HHs in Morkhun and 135 HHs in Passu.
The technological package was applied in arid climate at an elevation ranging from 2340m to 4877 m above sea level. Passu is located at 36.49o latitude and 74.90o longitude and Morkhun is located at 36.6o N latitudes and 74.86o E longitudes. The area receives 150-200 mm annual rain-fall. The temperature ranges from 11 degree Celsius to 29 degree Celsius. The population of Passu and Morkhun is 1168 and 653 persons respectively. Both villages are semi nomadic and depend mainly on livestock rearing.
Localização: Morkhun and Passu, Gilgit Baltistan Province, Paquistão
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: 2-10 locais
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Não
Data da implementação: 2016; menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução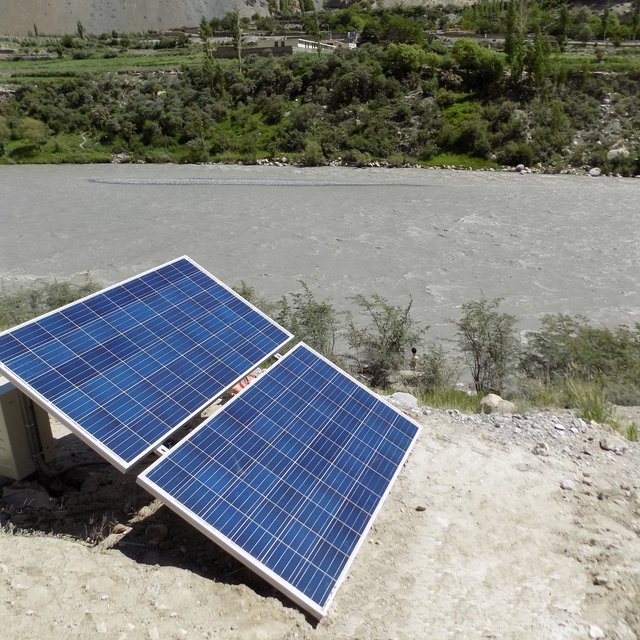








| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Skilled | Person days | 136,0 | 14,43 | 1962,48 | |
| Unskilled | Person days | 745,0 | 7,7 | 5736,5 | |
| Equipamento | |||||
| Spade | Number | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Shovel | Number | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Material vegetal | |||||
| Apple Plants | Number | 3300,0 | 0,087 | 287,1 | |
| Material de construção | |||||
| Solar panel, pump with all accessories | sites | 2,0 | 6490,0 | 12980,0 | |
| Water storage, intake, distribution pipes and mulch | sites | 2,0 | 6861,0 | 13722,0 | |
| Drip irrigation | sites | 2,0 | 4173,0 | 8346,0 | |
| -Check basin (pits) | number | 3300,0 | 0,466 | 1537,8 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 44'571.88 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 44'571.88 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Unskilled | Number | 26,0 | 7,7 | 200,2 | |
| Equipamento | |||||
| Spade | Number | 10,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Plumbing tool kit | Kit box | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Material vegetal | |||||
| Apple ( replacement of dead plants) | number | 330,0 | 0,087 | 28,71 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 228.91 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 228.91 | ||||
Quantidade anterior à GST: None
Quantidade posterior à GST: 5 ha
Production area increased as uncultivated land brought under cultivation, but crop production has not increased yet because orchard just established.
Use of renewable solar energy for fruit cultivation
Irrigation water availability increased with innovative technological packages.
Community institution (village development organizations) strengthened due to the approach of farming in a group.
Land management skills of community enhanced due to various training such as crop cultivation, operation and maintenance of water conservation and management technologies.
Improved soil moisture as a result of water harvesting pits, mulching and efficient drip irrigation.
improved soil cover due to mulch.
Reduced soil loss ( from wind and water erosion) due to application of mulch and also due to vegetation cover and above-ground biomass.
The technological package is climate change resilient as compared to the melt water dependant surface flood irrigation. Melt water of glacier and snow is very sensitive to climate change. Glaciers are dynamic, their depth and volume fluctuation happens each year.
Reduced risk of downstream flooding though the amount is very less.