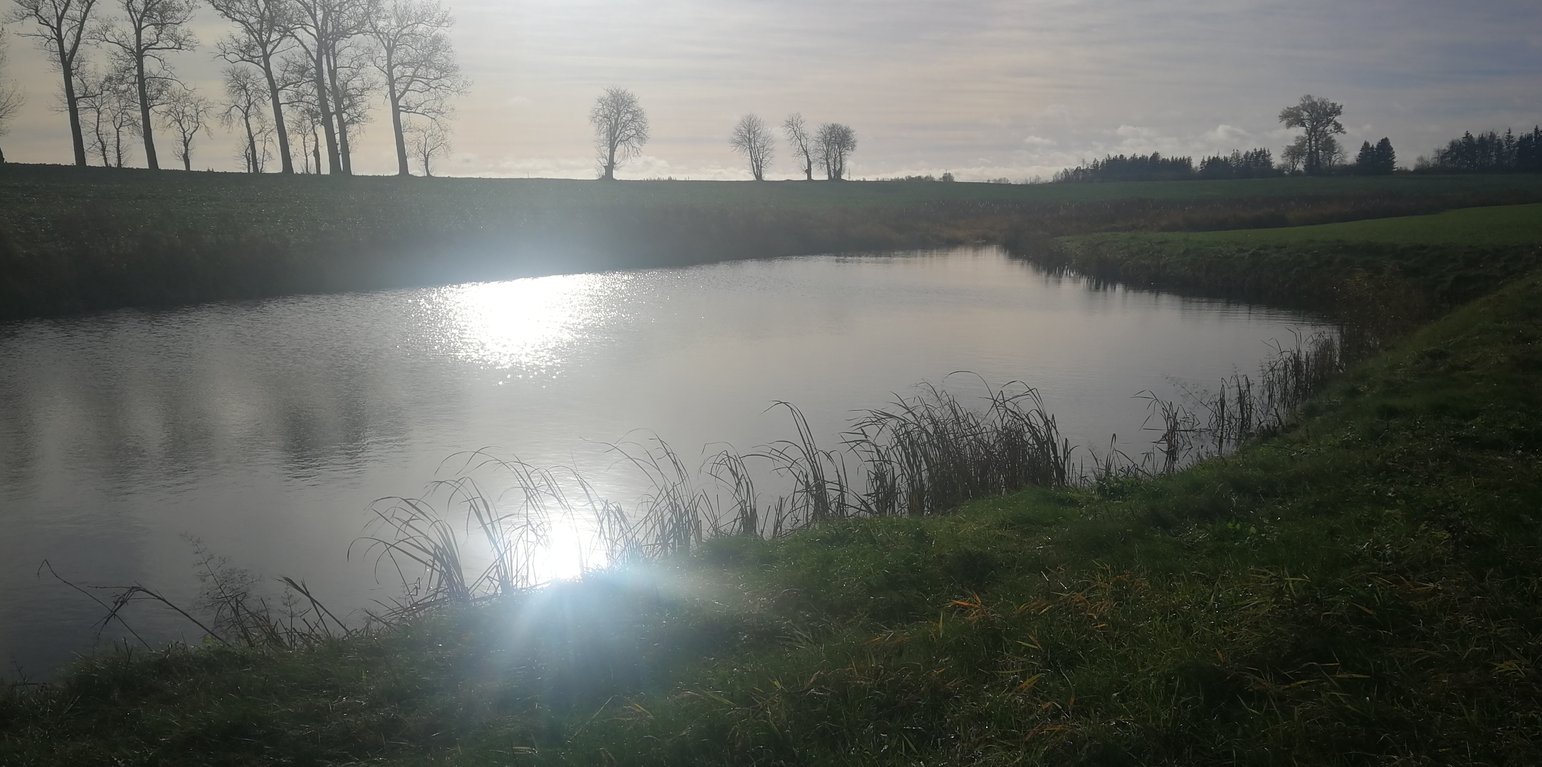
Wetland in the Stabė River
(Lituânia)
Šlapynė at Stabės Terespolis
Descrição
The installation of this wetland contributes to reducing the ecological debt to nature by restoring natural complexes, reaching a balance between environmental and economic interests, and promoting sustainable farming conditions in one of the most important and valuable natural areas of central Lithuania.
In the lower part of the river Stabė, 1.8 km from its mouth, a wetland of 2.38 ha has been installed. The wetland was constructed by artificially flooding the valley. Corrugated metal plating was used at the inlet and outlet of the wetland to protect the stream banks. While most Lithuanian wetlands are peaty, this one is not. Over time, the surface layer of the wetland has been altered by the hydrophytic wetland-specific plants, their species composition, and the degree of decomposition of these plants. Sediments washed down from the fields accumulate here. The organic matter in these sediments creates the typical habitats of saturated organic soils, which are effective in terms of nitrogen - and especially phosphorus - retention.
The wetland has four main sections. The deepest part covers 0.21 ha and is up to 2.0 m deep. Sediments are deposited here. When there is a decrease in flow, these sediments can then be removed mechanically and transported to fertilize the adjacent fields. The next section covers 0.94 ha and its depth is less than 0.5 m. It is covered with wetland vegetation. The third section works as a filter and the water is aerated. It is protected by a dyke, 6 metres in length, perpendicular to the direction of flow. The dyke is formed from soil and pitched with stone and gravel. The maximum depth of the water in this section is 0.1 metres. The fourth and final section is where the surface water is treated by macropytic vegetation. It covers 1.2 ha and is from 0.2 to 0.5 m deep. Barriers help prolong the period that the water is held.
The wetland was designed to retain nutrients in the spring and reduce their concentrations downstream. Through an ongoing research programme, the impact of the wetland has been monitored from the start. In the first year, vegetation had not become established so there were no impacts. However in 2020 and 2021 there were very positive results in terms of nutrient capture.
Localização
Localização: Terespolis village, Kėdainiai district, Lituânia
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: Local único
Geo-referência de locais selecionados
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Não
Data da implementação: 2015; menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução
-
atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
-
Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
-
durante experiências/ pesquisa
-
através de projetos/intervenções externas
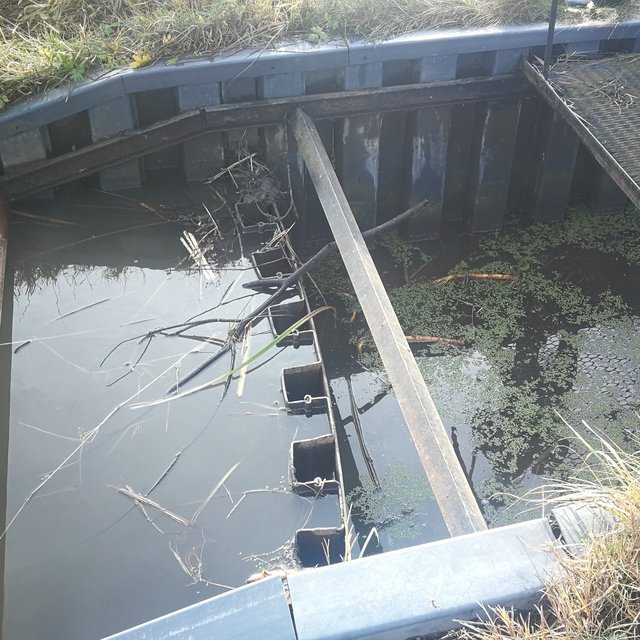

Outlet of the wetland (Jovita Mėžinė)
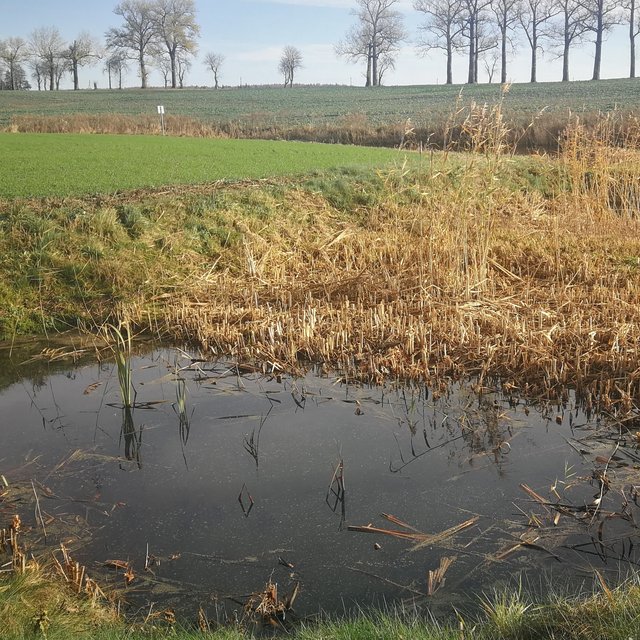

Sedimentation pond (Jovita Mėžinė)
Classificação da Tecnologia
Objetivo principal
-
Melhora a produção
-
Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
-
Preserva ecossistema
-
Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
-
Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
-
Reduzir riscos de desastre
-
Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
-
Atenuar a mudanças climáticas e seus impactos
-
Criar impacto econômico benéfico
-
Cria impacto social benéfico
Uso da terra
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra: Não
-
Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas - Pântanos, zonas úmidas
-
Outros - Especifique: Land not used for agricultural purposes for a long time
Abastecimento de água
-
Precipitação natural
-
Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
-
Irrigação completa
Objetivo relacionado à degradação da terra
-
Prevenir degradação do solo
-
Reduzir a degradação do solo
-
Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
-
Adaptar à degradação do solo
-
Não aplicável
Degradação abordada
-
Degradação biológica - Bh: perda dos habitats
-
Degradação da água - Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
Grupo de GST
-
Gestão/proteção de zonas úmidas
-
New wetlands establishment
Medidas de GST
-
Medidas estruturais - S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis, S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Desenho técnico
Especificações técnicas
The wetland is designed from four main parts. The deep part is where sediments are deposited in the event of a sudden decrease in water flow rates. These sediments can then be removed mechanically and transported to appropriate locations.
The shallow part with barriers increases the residence time of surface water in the wetland. In this part, only the artificially induced water level and the loaded strips of field stones that direct the flow of water is loaded, thus increasing the residence time of the surface water.
Completely shallow part up to a depth of 0.1 m. It is a 6.0 m wide underwater embankment with an anti-erosion coating and fieldstone layer, through which the water is aerated and cleared.
The fourth shallow part is where the surface water is treated by macrophyte vegetation.
More technical pictures and detailed description of the technology can be found in the report "Šlapynės įrengimas Terespolio k., Kėdainių rajone (Implementation of wetland in Terespolis village, Kedainiai district) " on https://old.gamta.lt/files/%C5%A1lapyn%C4%97s%20projektas1550671582565.pdf
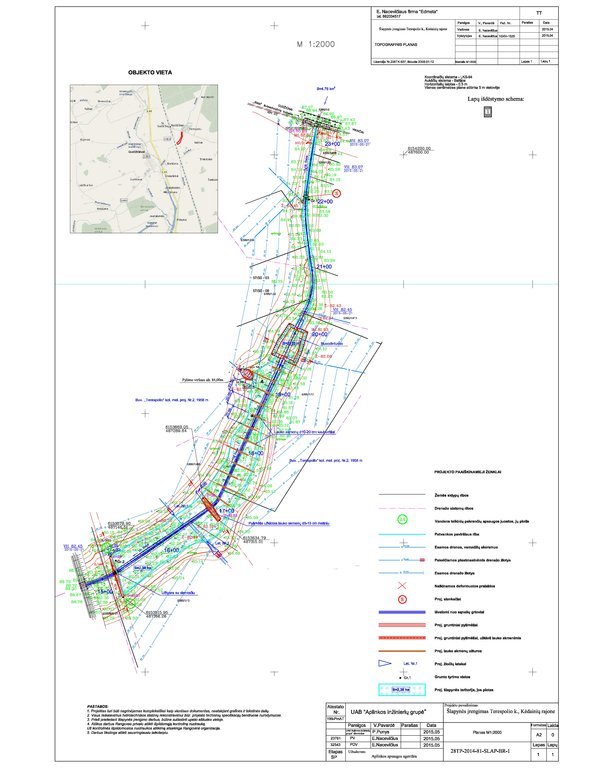
Author: E. Nacevičiaus firma "Edmeta" and UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė"
Estabelecimento e manutenção: atividades, insumos e custos
Cálculo de insumos e custos
- Os custos são calculados: Por unidade de tecnologia (unidade:wetland volume, length: 2.38 ha)
- Moeda utilizada para o cálculo de custos: EURO
- Taxa de câmbio (para USD): 1 USD = n.a EURO
- Custo salarial médio da mão-de-obra contratada por dia: n.a
Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Inflation is one of the most affecting factors. The real costs of the last years are not publicly available.
Atividades de implantação
-
Preparation of the river part (Periodicidade/frequência: autumn)
-
Bank establishment (Periodicidade/frequência: autumn)
-
Construction of the deep part (Periodicidade/frequência: autumn)
-
Construction of the shallow parts (Periodicidade/frequência: autumn)
-
Lower barrier works (Periodicidade/frequência: autumn)
Estabelecer insumos e custos (per wetland)
| Especifique a entrada |
Unidade |
Quantidade |
Custos por unidade (EURO) |
Custos totais por entrada (EURO) |
% dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
|
Mão-de-obra
|
| Preparation of the river part |
total costs |
1,0 |
2038,0 |
2038,0 |
|
| Bank establishment |
total costs |
1,0 |
2340,0 |
2340,0 |
|
| Construction of the deep part |
total costs |
1,0 |
2776,0 |
2776,0 |
|
| Construction of the shallow parts |
total costs |
1,0 |
9135,0 |
9135,0 |
|
|
Equipamento
|
| Lower barrier works |
total costs |
1,0 |
1053,0 |
1053,0 |
|
| Preparation of the river part |
total costs |
1,0 |
2300,0 |
2300,0 |
|
| Bank establishment |
total costs |
1,0 |
3228,0 |
3228,0 |
|
| Construction of the deep part |
total costs |
1,0 |
11833,0 |
11833,0 |
|
| Construction of the shallow parts |
total costs |
1,0 |
3750,0 |
3750,0 |
|
|
Material vegetal
|
| Lower barrier works |
total costs |
1,0 |
3655,0 |
3655,0 |
|
|
Material de construção
|
| Preparation of the river part |
total costs |
1,0 |
258,0 |
258,0 |
|
| Bank establishment |
total costs |
1,0 |
7336,0 |
7336,0 |
|
| Construction of the deep part |
total costs |
1,0 |
44,0 |
44,0 |
|
| Construction of the shallow parts |
total costs |
1,0 |
34363,0 |
34363,0 |
|
|
Outros
|
| Lower barrier works |
total costs |
1,0 |
5482,0 |
5482,0 |
|
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia |
89'591.0 |
|
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD |
89'591.0 |
|
Atividades de manutenção
-
Vegetation observations and removal of excess vegetation (Periodicidade/frequência: once a year)
-
Measurements of sediments and their removal (Periodicidade/frequência: once a year)
-
N and P measurements and removal of priming (Periodicidade/frequência: depending on the measurements after fertilization)
-
Animal regulation and removal of damage (Periodicidade/frequência: depending on the needs and season)
-
Other activities (after floods, vandalism) (Periodicidade/frequência: after events)
Custos totais de manutenção (estimativa)
5000,0
Ambiente natural
Média pluviométrica anual
-
<250 mm
-
251-500 mm
-
501-750 mm
-
751-1.000 mm
-
1.001-1.500 mm
-
1.501-2.000 mm
-
2.001-3.000 mm
-
3.001-4.000 mm
-
> 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
-
úmido
-
Subúmido
-
Semiárido
-
Árido
Especificações sobre o clima
n.a.
Inclinação
-
Plano (0-2%)
-
Suave ondulado (3-5%)
-
Ondulado (6-10%)
-
Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
-
Forte ondulado (16-30%)
-
Montanhoso (31-60%)
-
Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo
-
Planalto/planície
-
Cumes
-
Encosta de serra
-
Encosta de morro
-
Sopés
-
Fundos de vale
Altitude
-
0-100 m s.n.m.
-
101-500 m s.n.m.
-
501-1.000 m s.n.m.
-
1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
-
1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
-
2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
-
2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
-
3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
-
> 4.000 m s.n.m.
A tecnologia é aplicada em
-
Posições convexas
-
Posições côncavas
-
Não relevante
Profundidade do solo
-
Muito raso (0-20 cm)
-
Raso (21-50 cm)
-
Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
-
Profundo (81-120 cm)
-
Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (superficial)
-
Grosso/fino (arenoso)
-
Médio (limoso, siltoso)
-
Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície)
-
Grosso/fino (arenoso)
-
Médio (limoso, siltoso)
-
Fino/pesado (argila)
Teor de matéria orgânica do solo superior
-
Alto (>3%)
-
Médio (1-3%)
-
Baixo (<1%)
Lençol freático
-
Na superfície
-
< 5 m
-
5-50 m
-
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície
-
Excesso
-
Bom
-
Médio
-
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada)
-
Água potável boa
-
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
-
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
-
Inutilizável
A qualidade da água refere-se a: tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade é um problema?
Ocorrência de enchentes
Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado
-
Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
-
misto (subsistência/comercial)
-
Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola
-
Menos de 10% de toda renda
-
10-50% de toda renda
-
>50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza
-
Muito pobre
-
Pobre
-
Média
-
Rico
-
Muito rico
Nível de mecanização
-
Trabalho manual
-
Tração animal
-
Mecanizado/motorizado
Sedentário ou nômade
-
Sedentário
-
Semi-nômade
-
Nômade
Indivíduos ou grupos
-
Indivíduo/unidade familiar
-
Grupos/comunidade
-
Cooperativa
-
Empregado (empresa, governo)
Idade
-
Crianças
-
Jovens
-
meia-idade
-
idosos
Área utilizada por residência
-
< 0,5 ha
-
0,5-1 ha
-
1-2 ha
-
2-5 ha
-
5-15 ha
-
15-50 ha
-
50-100 ha
-
100-500 ha
-
500-1.000 ha
-
1.000-10.000 ha
-
> 10.000 ha
Escala
-
Pequena escala
-
Média escala
-
Grande escala
Propriedade da terra
-
Estado
-
Empresa
-
Comunitário/rural
-
Grupo
-
Indivíduo, não intitulado
-
Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra
-
Acesso livre (não organizado)
-
Comunitário (organizado)
-
Arrendado
-
Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água
-
Acesso livre (não organizado)
-
Comunitário (organizado)
-
Arrendado
-
Indivíduo
Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola)
Água potável e saneamento
Impactos
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção agrícola
Production increased by drainage and return of sediment to the cropland.
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Impactos fora do local
disponibilidade de água (lençóis freáticos, nascentes)
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco (inclusive baixo caudal)
Análise do custo-benefício
Benefícios em relação aos custos de estabelecimento
Retornos a curto prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Benefícios em relação aos custos de manutenção
Retornos a curto prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo
muito negativo
muito positivo
Mudança climática
Mudança climática gradual
Temperatura anual aumento
não bem em absoluto
muito bem
Temperatura sazonal aumento
não bem em absoluto
muito bem
Precipitação pluviométrica anual aumento
não bem em absoluto
muito bem
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
não bem em absoluto
muito bem
não bem em absoluto
muito bem
Adoção e adaptação
Porcentagem de usuários de terras na área que adotaram a Tecnologia
-
casos isolados/experimental
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram sem receber incentivos materiais?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Número de residências e/ou área coberta
1
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
A quais condições de mudança?
-
Mudança climática/extremo
-
Mercados dinâmicos
-
Disponibilidade de mão-de-obra (p. ex. devido à migração)
Conclusões e experiências adquiridas
Pontos fortes: visão do usuário de terra
-
More even seasonality, land more suitable for agriculture.
Pontos fortes: a visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada
-
Biodiversity supported/ sediment capture/ nature-based sustainable solution.
Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos: visão do usuário de terracomo superar
-
More nutrients come out of the exit point of the wetland than enter in the entry point.
Accurate details of impact still under assessment
Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos: a visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitadacomo superar
Referências
Revisor
-
William Critchley
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
-
Joana Eichenberger
Data da documentação: 28 de Setembro de 2021
Última atualização: 31 de Janeiro de 2024
Pessoas capacitadas
-
Egle Baltranaite - co-compilador/a
-
Jovita Mėžinė - co-compilador/a
Descrição completa no banco de dados do WOCAT
A documentação foi facilitada por
Instituição
- Klaipeda University (KU) - Lituânia
Projeto
- OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)
Referências-chave
-
Report about installation of the technology - UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė", 2015. Šlapynės įrengimas Terespolio k., Kėdainių rajone [Installation of wetland in Terespolis village, Kedainiai district], Kaunas: https://old.gamta.lt/files/%C5%A1lapyn%C4%97s%20projektas1550671582565.pdf
-
Report about implementation of the technology - UAB "Aplinkos inžinierių grupė", 2016. Pasklidosios vandens taršos mažinimo priemonių įrengimo pilotiniame baseine darbai [The installation of diffuse water pollution abatement measures in pilot river basins], Kaunas: https://old.gamta.lt/files/Galutine%20ataskaita%20pakoreguota.pdf
Links para informação relevante que está disponível online












