Incentive-based catchment treatment [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2404 - Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
GEOTEST AG (GEOTEST AG) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre tecnologias da GST

Diques de piedras [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Se trata de diques de piedras que se ubican en el lecho de los arroyos, acompañados por plantaciones alrededor de las construcciones.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User

Zanjas de Coronación [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Las zanjas de coronación impiden la entrada del escurrimiento superficial a las cárcavas
- Compilador/a: Unknown User

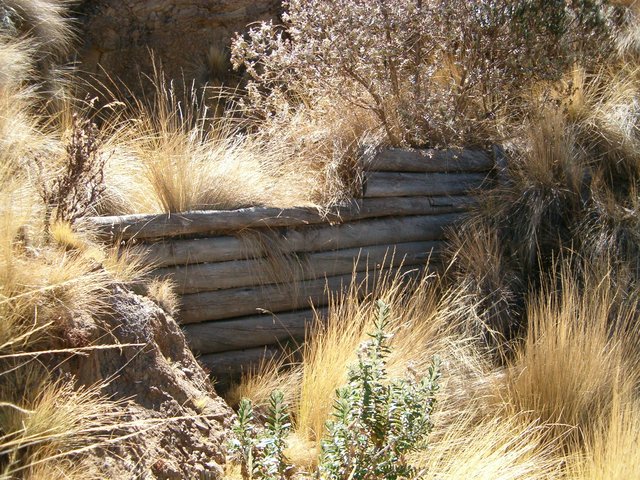
Estabilización de taludes (biotrampas) [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
La tecnología consiste en la práctica de reforestación en combinación con el establecimiento de trampas de sedimentos (biotrampas) para consolidar los taludes.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim
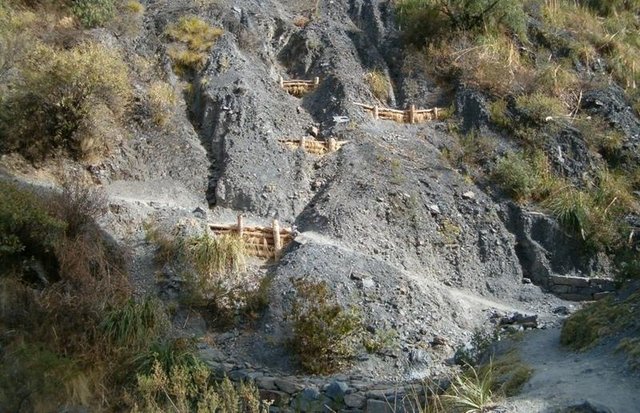

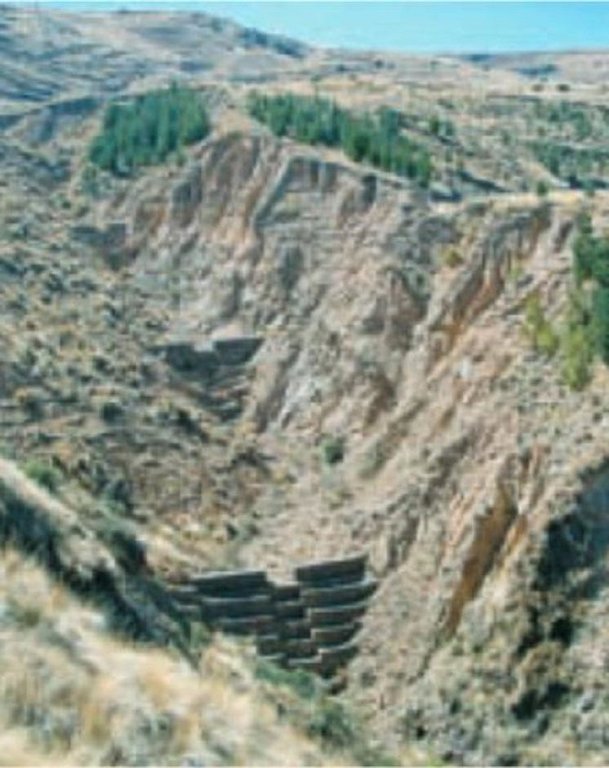
Gully control and catchment protection [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Integrated gully treatment consisting of several simple practices including stone and wooden check dams, cut-off drains and reforestation in sediment traps (biotrampas).
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim
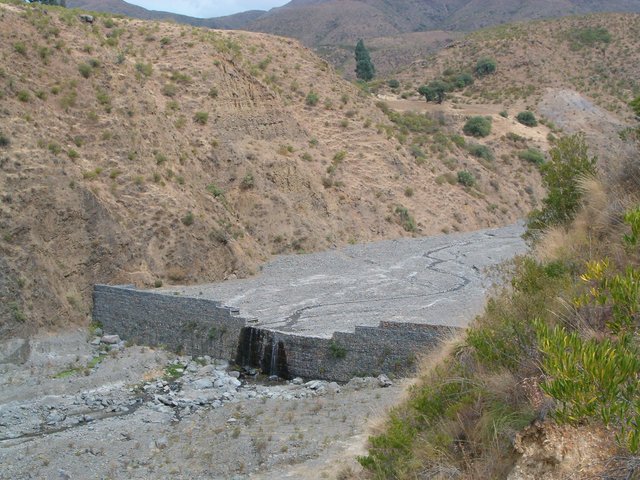

Obras Hidráulicas - Gaviones de Piedras [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Mampostería gavionada (= gaviones puestos en el cauce). Se trata de paquetes de piedras encajadas en malla de alambre que forman una represa de sedimentos.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim

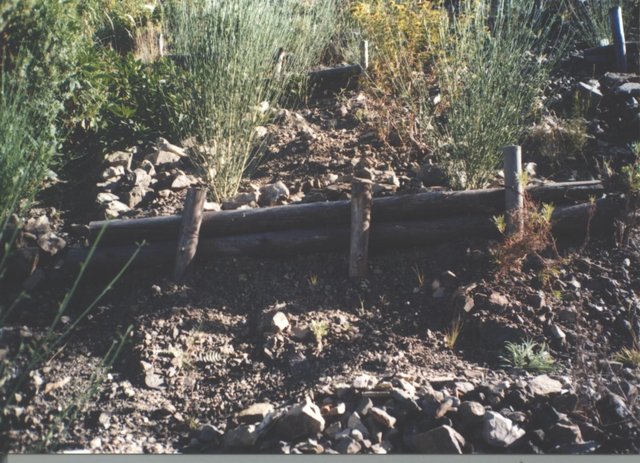
Diques de madera (tipo Krainer) [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Se trata de diques de madera que se ubican en el lecho de los arroyos, acompañados por plantaciones alrededor de las construcciones.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
A project supported, incentive-based approach: farmers are sensitised about erosion, and involved in gully control and other measures to protect catchments.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
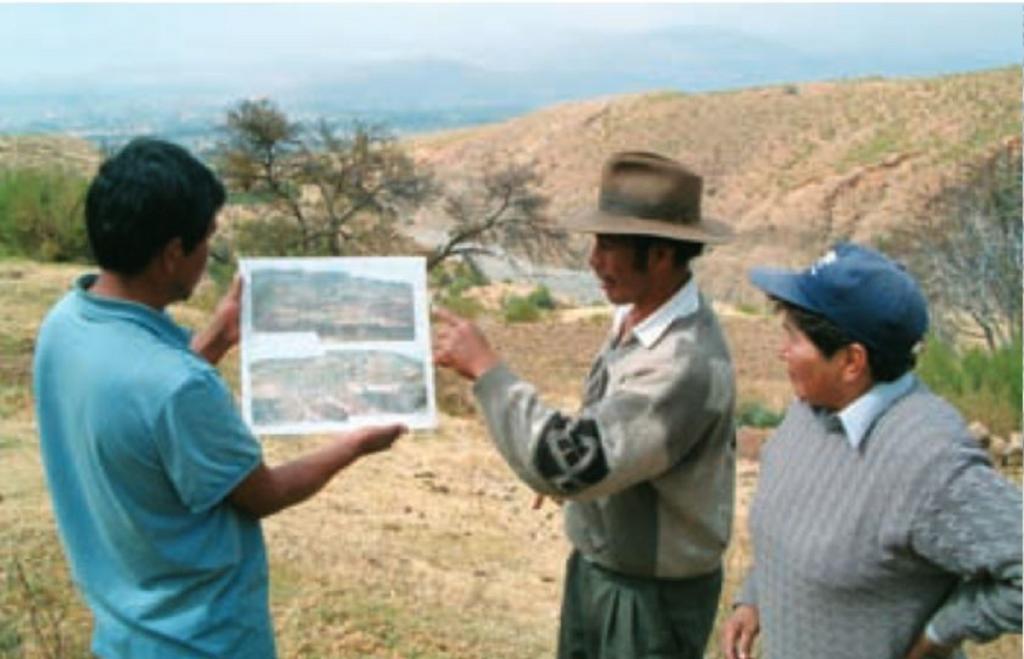
Aims / objectives: The objective of the locally-based organisation Programa de Manejo Integral de Cuencas (PROMIC) is to involve land users in the control of soil erosion in the catchments above Cochabamba city. While erosion here is largely a natural process, it is aggravated by inappropriate agricultural practices. PROMIC receives funds from national and international governments, and works in an interactive manner. Together with local farmers, erosion processes in the context of the human environment were analysed to identify the needs of the agriculture population - and to plan a conservation and development programme. The aim was to convince farmers of the necessity to protect their agricultural land and stabilise the gullies below, and of the overall importance of implementing technologies to combat erosion.
Role of stakeholders: The farmers were involved in the process through regular community meetings organised by PROMIC, in which they could adjust PROMIC's catchment intervention plans to their own requirements through an interactive process. PROMIC considered that the sensitisation work and the interactive process were essential to ensure long-term sustainable land use. In the short term, however, it will be mainly the city downstream - Cochabamba - that benefits from the implementation of the erosion control technologies. For that reason, the farmers were paid to carry out construction of the measures (through 'cash-for-work'). The farmers should, however, profit from the technologies in the long term. They were taught how to build and maintain check dams, cut-off drains and biotrampas. The implementation in the watershed started in 1996 and took six years: when the implementation phase was over, farmers no longer received financial subsidies. The long period of sensitisation should help to ensure that farmers incorporate erosion prevention technologies into their cropland above the gullies. PROMIC still monitors the state of the structures from time to time, but most of the maintenance is left to the farmers themselves. PROMIC continues, however, to provide technical support and some transport of materials. Both internal and external evaluation followed the end of the implementation phase.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia
Região/Estado/Província:
Cochabamba district
Map
×2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Indique o ano de início:
1996
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
- teach farmers about sustainable land use, - build up skills amongst farmers to enable them to treat gullies without outside help, - reduce flooding and sedimentation in the valley of Cochabamba and general soil loss in the area through collaboration with farmers in the watershed, - improve traditional agriculture with a package of conservation-related practices, - indirectly support farmers by cash-for-work incentives which enables them to implement SWC technologies on their own fields
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - lack of knowledge about damage caused by erosion and benefits of various possible conservation technologies, - lack of financial resources: shortage of funds prevents farmers investing in technologies, even if these bring benefits to them (as well as to the downstream population), - persistence of detrimental traditional agricultural practices, leading to accelerated degradation
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Inibitivo
Few direct short-term profits from SWC technologies in gullies for the farmers in the watershed (the main beneficiary is the city of Cochabamba downstream).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Search for national and international subsidies to help the farmers to implement the technologies during the initial period.
Quadro institucional
- Inibitivo
The local farmers' association is insufficiently organised to ensure the independent continuation of activities post-project.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Local farmers' association should be included in the sensitisation and implementation process.
Outro
- Inibitivo
Climate: Climatic extremes such as strong winds and excess or deficit of rain.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Plant trees at close spacing, and plant trees/ shrubs that can tolerate climatic extremes.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
There were no women working in the gully rehabilitation. The reason is a cultural taboo against women working with heavy materials; women are responsible for looking after cattle, and for the household.
- Organizações comunitárias
Local farmers association
- Specialised engineers of PROMIC
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Passivo | interviews/questionnaires, information during regular meetings, entrevistas / cuestionarios |
| Planejamento | Participativo | results of the socio-economic diagnosis defined the planning; farmers were involved through regular meetings: interactive planning at individual and community level |
| Implementação | Apoio externo | None |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Passivo | interviews/questionnaires; internal and external evaluations where farmers were interviewed |
| Research | Passivo | socio-economic diagnosis; collection and analysis of bio-physical baseline data |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
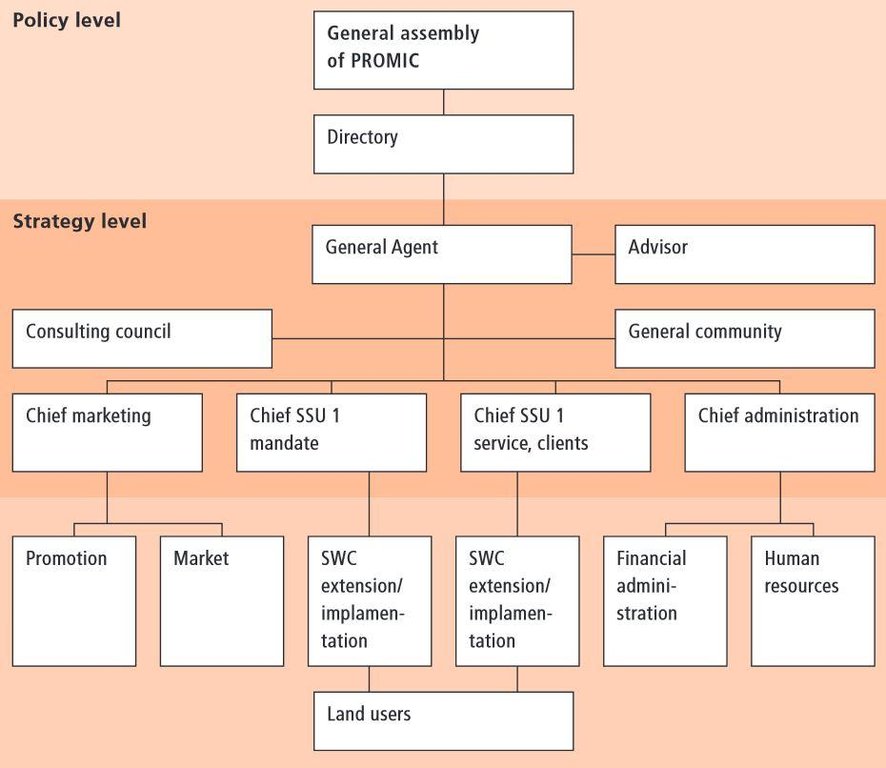
Descrição:
General assembly: National and international public and private institutions, members, foundation
Directory: Prefecture, general agent, Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), Belgian Technical Cooperation (BTC), private enterpreneurs
Consulting council: Municipalities, projects, universities
Advisors: General agent, marketing, SSU1, SSU2 (see below), administration
SSU: Strategic service unit
Services: Executive body for technology extension and implementation: PROMIC field technicians
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Foram tomadas decisões quanto à seleção de tecnologia(s):
- Made by specialised engineers of PROMIC
Explique:
farmers were involved by modifying initially proposed technologies.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by Made by specialised engineers of PROMIC
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Tipo de formação:
- Em exercício
Assuntos abordados:
The approach included training on technical aspects and on long-term planning for sustainable land use. Some farmers were trained to become foremen - who in turn instructed other farmers. During the construction period PROMIC project staff trained farmers on the job in soil conservation practices.
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
Descreva/comentários:
Name of method used for advisory service: participatory planning of gully treatment; Key elements: making farmers aware of the environmental and economic necessity for the technology, interactive planning of technology implementation at individual and community levels
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, moderadamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Local
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/ formação
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach was to initially target groups. Later, individuals were included (with individual farmer-family visits) to improve the effectiveness of the awareness raising and the implementation.
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Especifique os tópicos:
- Sociologia
- Ecologia
- Tecnologia
- S
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
Research was done on 1)SWC (testing different measures), 2)various soil parameters, and 3) a socio-economic survey. Research was an important part, not only for planning (based on biophysical and socio-economic data), but also to stay in contact with the rural population and to obtain their confidence. Thanks to the research, the technology is well adapted to the biophysical conditions.
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 20.0%; international non-government: 80.0%
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Mão-de-obra
| Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|
| Totalmente financiado | labour for the rehabilitation of the gully area |
- Equipamento
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Maquinário | Totalmente financiado | |
| Ferramentas | Totalmente financiado | |
- Agrícola
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| seedlings | Totalmente financiado | |
- Infraestrutura
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Estradas | Totalmente financiado | community infrastructure |
| technical support | Totalmente financiado | |
- Outro
| Outros (especifique) | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| transport for further technology implementation | Totalmente financiado |
Se a mão-de-obra pelos usuários da terra foi uma entrada substancial, isso foi:
- Pago em dinheiro
Comentários:
100% of the implementation was subsidised. Farmers were contracted to build the structures
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
The approach resulted in a considerable improvement in SWC. However, despite new knowledge about erosion, the farmers themselves hardly carry out any new gully conservation work without payment, and in the long term maintenance is not ensured.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Some other projects in Bolivia have copied parts of PROMIC's approach.
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Incerto
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Good technical support during and after conclusion of the implementation phase (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Technical support not enough on its own - needs to be complemented by further sensitisation.) |
| Sensitisation of the farmers to erosion and degradation processes, and awareness creation about the impact and necessity of SWC in the hills to protect the valleys (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued sensitisation work after the implementation phase.) |
| Transparent process during research, planning and implementation phases; incorporation of farmers' ideas (thus: good acceptance of PROMIC by the rural population). |
| Integration of farmers in the process of implementation of soil conservation. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Farmers need to be even more integrated in the process of monitoring to guarantee the maintenance of the soil conservation achieved.) |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Farmers implementing SWC are not those benefiting most from the impact in the short term; even though the city of Cochabamba benefits considerably, financial support for implementation has stopped | Seek financial support from Cochabamba; implement a system of payment for environmental services |
| Lack of money for replication and long-term maintenance of SWC measures | Guarantee financial support in the threatened area, by the local government and international organisations. |
| Sensitisation phase (for farmers and government) was too short to ensure sustained application of the technology without external support and supply. Established structures are often neglected and thus deteriorate | Find new donors to continue the training/awareness raising on SWC technologies. Include the farmers in the monitoring visits and demonstrate examples of successful SWC (positive stimuli). |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
PROMIC documentation
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Mooseggstrasse 9, 3550 Langnau, Switzerland; geoheim@bluewin.ch
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Diques de piedras [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Se trata de diques de piedras que se ubican en el lecho de los arroyos, acompañados por plantaciones alrededor de las construcciones.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User

Zanjas de Coronación [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Las zanjas de coronación impiden la entrada del escurrimiento superficial a las cárcavas
- Compilador/a: Unknown User

Estabilización de taludes (biotrampas) [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
La tecnología consiste en la práctica de reforestación en combinación con el establecimiento de trampas de sedimentos (biotrampas) para consolidar los taludes.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim

Gully control and catchment protection [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Integrated gully treatment consisting of several simple practices including stone and wooden check dams, cut-off drains and reforestation in sediment traps (biotrampas).
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim

Obras Hidráulicas - Gaviones de Piedras [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Mampostería gavionada (= gaviones puestos en el cauce). Se trata de paquetes de piedras encajadas en malla de alambre que forman una represa de sedimentos.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim

Diques de madera (tipo Krainer) [Estado Plurinacional da Bolívia]
Se trata de diques de madera que se ubican en el lecho de los arroyos, acompañados por plantaciones alrededor de las construcciones.
- Compilador/a: Georg Heim
Módulos
Não há módulos