Lessons learned from the "Mind the Gap" project: Improving Dissemination Strategies [Tunísia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Joren Verbist
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_7123 - Tunísia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Innovation specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Tunísia
Gender specialist:
Najjar Dina
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Marrocos
Natural Resource Economist:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Tunísia
Werner Jutta
German Ministry of Agriculture
Derbel Sondos
AVFA (National Agricultural Training and Extension Service)
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management InitiativeNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Líbano1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
2019
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre tecnologias da GST

ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services … [Tunísia]
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
- Compilador/a: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [Tunísia]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- Compilador/a: Joren Verbist
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
The “Mind the Gap” project researched the adoption gap between agricultural research and women and men farmers. Its objective was to determine most effective and cost-efficient technology transfer strategies and give recommendations to national extension institutes and development partners to adapt their scaling strategy
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Research into innovative agricultural technologies for the livestock-barley system in semi-arid Tunisia has yielded success. However, adoption of these has remained low for decades, not only in Tunisia but across developing countries (Noltze et al. 2012; DFID 2014; Syngenta Foundation 2015). Bridging this 'adoption gap' has proved to be a challenge, and there has been limited emphasis on improving agricultural extension methods. In this context, the International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) together with partners set up the "Mind the Gap" project, funded by the BMZ and GIZ.
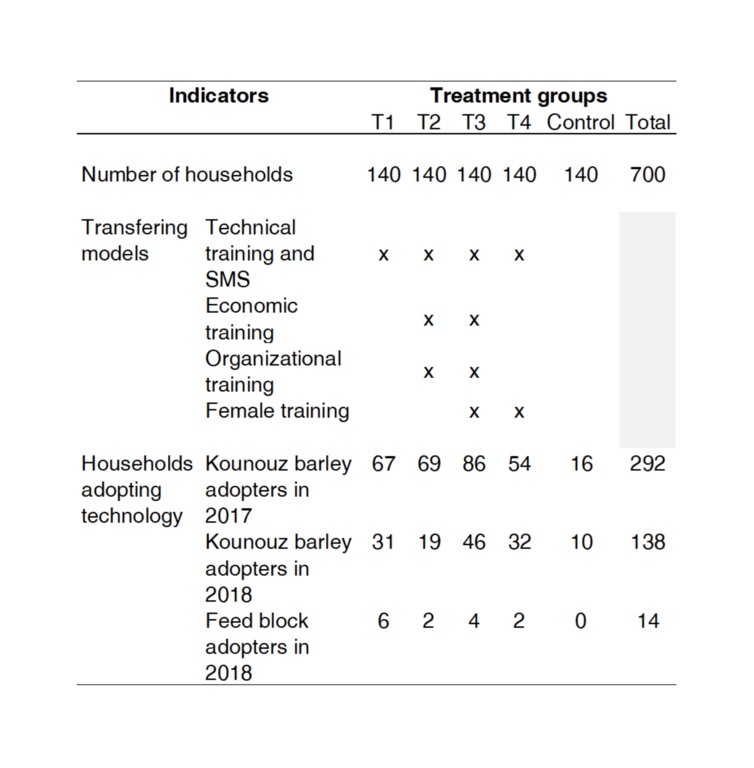
This project aimed to fill this gap by developing and testing new models for transferring sustainable technology packages to smallholder farmers. Four transfer models were implemented across four test groups:
T1: Technical training and SMS.
T2: Technical training, SMS, economic, and organizational training.
T3: Technical training, SMS, economic and organizational training, with a focus on female empowerment.
T4: Technical training, SMS, and female empowerment.
The transferring models are thus (a) Technical training and SMS; (b) Economic training; (c) Organization training; (d) Female empowerment.
Technical training and SMS involved sending weekly text messages containing technical and organizational information to 560 farmer households from August 2017. Workshops were conducted in 2017 and 2018 to develop these messages in collaboration with regional extension services and other stakeholders.
Economic training included one-day sessions in 2017 to demonstrate the economic benefits of innovations. In 2018, a Farmer Business School (FBS) approach was adopted to enhance farmers' entrepreneurial skills, with a tailored curriculum and seven five-day courses delivered to 280 farmer households.
The organizational training aimed to enhance farmers' understanding cooperative management. Through classroom sessions and visits to existing cooperatives, farmers received insights into cooperative creation, management challenges, and the benefits of collective action.
Female empowerment activities engaged women from 280 farmer households, focusing on visits to female cooperatives and sensitization events to encourage their participation in agricultural activities and access to credit.
The adoption of two innovations was evaluated through this methodology. The first innovation, "Kounouz," is an improved barley variety designed to better withstand drought conditions. The second innovation involves feedblocks, also known as nutrient-dense pellets, which serve as an alternative livestock feed made from by-products.
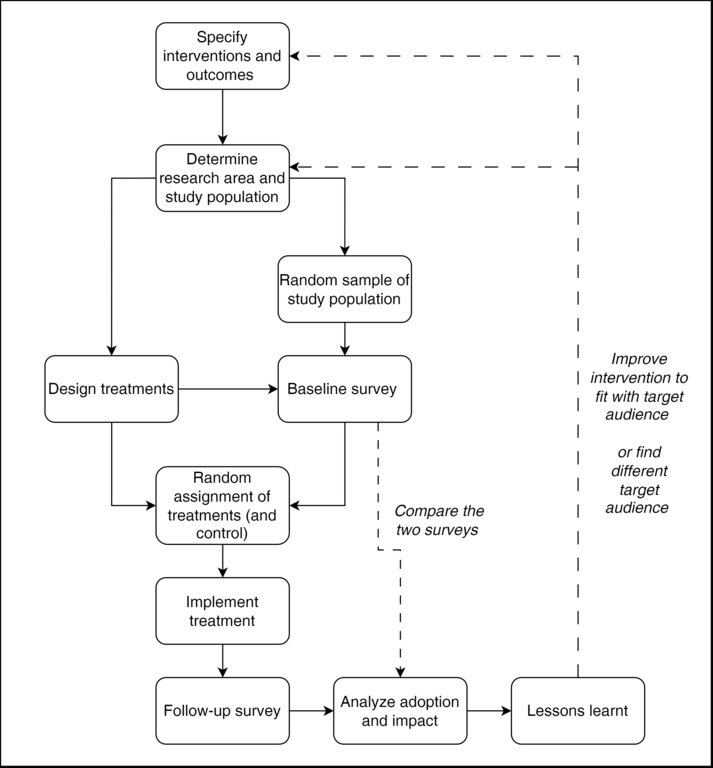
The project rigorously evaluated these transfer models through randomized controlled trials, focusing on their impact on innovation adoption rates and cost-efficiency. The combined approach, carried out under T3, showed the highest adoption rates, particularly among female-headed households. Field visits were identified as a significant contributor to technology adoption, while SMS proved most cost-effective.
Most importantly, it showed that the four transferring models should be used in combination for the highest adoption.
In conclusion, the research underscores that addressing the 'adoption gap' in agricultural innovation requires comprehensive approaches encompassing technical, economic, organizational, and gender empowerment training. By combining these elements significant strides can be made in cost-efficiently enhancing technology adoption rates among smallholder farmers, offering valuable insights for agricultural extension efforts not only in Tunisia but also across the MENA region and potentially beyond.
Acknowledgement:
We would like to thank BMZ/ GIZ who supported this innovative research through their contributions to the “Mind the Gap” project as well as Tunisian NARES (INRAT, AVFA, OEP, CRDA) for co-implementing project activities.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Tunísia
Map
×2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Indique o ano de início:
2016
Ano de término (caso a abordagem não seja mais aplicada):
2019
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
To better understand the adoption gap of new sustainable farming technologies, and discover cost-efficient and effective approaches to improve adoption of these technologies.
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Normas e valores sociais/culturais/religiosos
- Inibitivo
Participation of women at trainings was sometimes low (no availability to due household tasks)
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Propício
Access to financial resources allowed purchase of technologies (Kounouz seeds or feed blocks)
Quadro institucional
- Propício
The right institutions were selected (OEP, INRAT, AVFA) to implement MtG project activities
Colaboração/coordenção de atores
- Propício
Collaboration between the partners (NARES) was good and important; eg INRAT multiplied Kounouz seeds ; OEP and CRDA distributed Kounouz seeds and AVFA trained farmers on Kounouz production
Políticas
- Inibitivo
Feed block production has strict regulations
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Propício
Technical support to practice the technology (eg feed block composition) is important and was guaranteed by OEP
Mercados (para comprar entradas, vender produtos) e preços
- Inibitivo
Prices of substitute feed like subsidized wheat bran and barley hinder the adoption of feed blocks.
Carga de trabalho, disponibilidade de força de trabalho
- Inibitivo
Workload for feedblock production is high and manpower not always available.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
No communities but individual farmers
Inviting farmers to trainings,
Organization of baseline and follow up survey with OEP
- Especialistas em GST/ consultor agrícola
AVFA (National Agricultural Training and Extension Service)
CTV (Local Extension Service)
OEP (Livestock and Pasture Office)
AVFA:
Organizational and economic trainings (FBS, BUS, cooperatives, etc) to 280 HH
Organized logistics (transport, restoration, training room)
OEP:
Technical training on feed blocks to 560 HH
Distribution of inputs to CTV, selection of cooperatives.
- Pesquisadores
University of Goettingen
INRAT (National Agricultural Research Institute)
University of Goettingen:
Project development, PhD students, data collection for baseline and follow up survey
INRAT:
Development of new barley variety (Kounouz) in collaboration with ICARDA
Technical training on barley with OEP to 560 HH
- Organização internacional
ICARDA
GIZ
ICARDA: Overall technical and administrative coordination
GIZ: Trained AVFA trainers on FBS and BUS
Caso várias partes interessadas foram envolvidas, indique a agência líder:
ICARDA
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Passivo | The experiments were designed and set up by the research agency. |
| Planejamento | Passivo | Methodology was also determined by the research agency. |
| Implementação | Participativo | The approach to dissemination that proved successful was interactive. |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Passivo | The experiment was monitored by the research agency. |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente especialistas em GST, após consulta com usuários da terra
Explique:
There was a strong focus on research rather than implementation, which required scientific expertise rather than land user knowledge.
Especifique em que base foram tomadas as decisões:
- Avaliação de conhecimento bem documentado de GST (tomada de decisão baseada em evidências)
- Resultados de pesquisa
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Usuários de terra
Caso seja relevante, especifique gênero, idade, status, etnia, etc.
Land user, with a strong focus on females for two treatment groups.
Tipo de formação:
- Agricultor para agricultor
- Áreas de demonstração
- Reuniões públicas
- Cursos
Assuntos abordados:
The four main trainings were given:
-Technical with SMS
-Economic (e.g., better farm management)
-Organizational (e.g., setting up farmer cooperatives)
-Female empowerment
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
- Em centros permanentes
Descreva/comentários:
Advice was given through the training which included both on-site (e.g., demonstration fields) and meetings
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, moderadamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Local
Descreva instituição, papéis e responsabilidades, membros, etc.
Training sessions regarding cooperation can be organized.
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/ formação
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
Four treatment groups were made based on different combinations of training, they were evaluated for their adoption of Kounouz barley and feed blocks.
Caso afirmativo, esta documentação é destinada a ser utilizada para monitoramento e avaliação?
Sim
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Especifique os tópicos:
- Sociologia
- Economia/Marketing
- Tecnologia
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
Several research papers were published with authors from different partners.
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Indique o orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem em US$:
400000,00
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
GIZ/BMZ
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Não
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Nenhum
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
5.5 Outros incentivos ou instrumentos
Foram utilizados outros incentivos ou instrumentos para promover a implementação das tecnologias de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos usuários locais de terra, melhorou a participação das partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A abordagem mobilizou/melhorou o acesso aos recursos financeiros para implementação da GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A abordagem melhorou a igualdade de gêneros e concedeu autonomia a mulheres e meninas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A abordagem resultou em segurança alimentar aprimorada/nutrição melhorada?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Produção aumentada
- Lucro (lucrabilidade) aumentado, melhora da relação custo-benefício
- Riscos de desastre reduzido
- Afiliação a movimento/projeto/grupo/rede
- melhoria dos conhecimentos e aptidões de GST
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Highest adoption rate for Kounouz was in T3 (61% in 2017 and 33% in 2018) where the whole package of extension was provided (technical training, SMS + economic and organizational training +female empowerment + access to input). This indicates that different adoption models should be combined rather than singled out. |
| The treatment groups T3 and T4 which received the female empowerment training have the highest Kounouz variety adoption rates in 2018 (T3 = 33%, T4 =24%). The implication of women in the project has a positive influence on the adoption of innovative technologies. The gender dimension should be considered as a vector of adoption of new technologies especially in Tunisian agriculture. |
|
In terms of cost, the government can choose according to the available budgetary resources: i) Highest level of technology adoption with the highest cost of trainings 34% in T3 with a total cost of trainings estimated at 900 TND per person ii) Medium technology adoption rate with a lower cost of trainings 22% in T1 with a total cost of trainings estimated to 230 TND per person). T3 is most effective but T1 is more cost efficient. |
| The strong collaboration between four public research and extension institutions (OEP, INRAT, AVFA and CTV) and one international agricultural institution (ICARDA) is one of the important factors for adoption and transfer of knowledge |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Concerning the technical extension methods, the field visit (with an intermediate cost) especially done in the similar areas is more efficient than the training (with a high cost) and the SMS text message (with a very low cost). | However, these extension methods are complementary and encourage the project’s farmers to adopt innovative technologies. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Udo Rudiger, Aymen Frija, Jutta Werner, Liza Straussberger, Barbara Rischkowsky. (13/4/2022). Impact of improved agricultural extension approaches on technology adoption: Evidence from a randomised controlled trial in rural Tunisia. Experimental Agriculture, 58, pp. 1-16.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/67344
Título/ descrição:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger. (24/12/2019). Synthesis Mind the Gap.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10505
Título/ descrição:
Udo Rudiger. (16/12/2019). Mind the Gap: Improving Dissemination Strategies to Increase Technology Adoption by Smallholders. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10471
Título/ descrição:
Samar Zaidi, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Mohamed Arbi Abdeladhim. (22/3/2023). Résilience des ménages face à l’insécurité alimentaire et au changement climatique dans les régions du centre et du nord-est de la Tunisie: Une analyse empirique. New Medit, 22 (1), pp. 19-34.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68229
Título/ descrição:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Jutta Werner, Matin Qaim. (7/3/2018). Designing and Conducting Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) for Impact Evaluations of Agricultural Development Research: A Case Study from ICARDA’s ‘Mind the Gap’ Project in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8209
Título/ descrição:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Jutta Werner, Hloniphani Moyo. (18/9/2018). Developing a policy framework for agricultural extension systems in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/8390
Título/ descrição:
Quang Bao Le, Jutta Werner, Boubaker Dhehibi, Mounir Louhaichi, Chandrashekhar Biradar. (10/11/2019). Functionally context socio-ecological type (fCSET) approach to support outscaling of agricultural innovation options.
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10801
Título/ descrição:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger, Mohamed Zied Dhraief. (9/9/2019). Factors Influencing Farmers’ Decisions to Adopt Improved Technologies in Semi-Arid Farming Systems: A case study of the barley variety Kounouz and feed blocks technology in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10223
Título/ descrição:
Hloniphani Moyo, Jutta Werner, Boubaker Dhehibi, Udo Rudiger, Cherifa Saidi. (14/4/2019). Improving dissemination strategies to increase technology adoption by smallholder farmers in Tunisia. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9813
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services … [Tunísia]
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
- Compilador/a: Joren Verbist

Small-Scale Nutrient-Dense Pellet Production [Tunísia]
Compressing agro-industrial by-products produces nutrient-dense livestock feed pellets that can compete with expensive and imported alternatives. This innovation consists of a small-scale compressor or "pelletizer" and formulae to create feed pellets of sufficient quality with locally available inputs.
- Compilador/a: Joren Verbist
Módulos
Não há módulos