Halting seasonal drought in Barind through efficient water resource management [Bangladesh]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Barendra elakay Khara proshaman
approaches_6143 - Bangladesh
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Establishing National Land Use and Land Degradation Profile toward Mainstreaming SLM Practices in Sector Policies (ENALULDEP/SLM)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Department of Environment (DoE) - Bangladesh1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
08/04/2020
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
Introduction of sustainable water usage to prevent impacts of seasonal droughts in Barind region, Bangladesh
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Barind is a drought-affected area of Bangladesh. It covers about 7,770 sq. km, that is 41% of the North Western part of Bangladesh, spreading over 16 districts of Rajshahi and Rangpur Division. It is one of the driest areas in Bangladesh with comparatively high temperatures - though cooler in the wet season from mid-June to October. Rainfall in the area varies from about 1500 mm to 2000 mm per annum. Temperature ranges from 4 degree Celsius to 44 degree Celsius. The area is at a comparatively higher elevation than the adjoining floodplains. There are two main terrace levels - one at 40m and the other between 19.8 and 22.9 m above mean sea level. The total cultivable area of Barind is about 583,000 ha, of which 34% is loamy, 10% is sandy, and 49% is clay: the remaining 7% is of other composition.
In the 1980s, the area was predominantly single cropped, and yields were poor and subject to seasonal drought, from late February to early May (up to the onset of pre-monsoon). No crops could be grown during the "rabi" season (November to May). The impacts of drought were severe and affected food insecurity and livelihoods. To address the situation, the Bangladesh Agricultural Development Corporation (BADC) under the Ministry of Agriculture (MoA) initiated two projects. One in 1985: The Barind Integrated Area Development Project and subsequently in 1992, the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) as a separate institutional entity. Both the projects focused on a new approach to water extraction, distribution and management practices at institutional level. Deep tubewells were installed and maintained by BMDA, rather than privately (which is often practiced in other parts of the country).
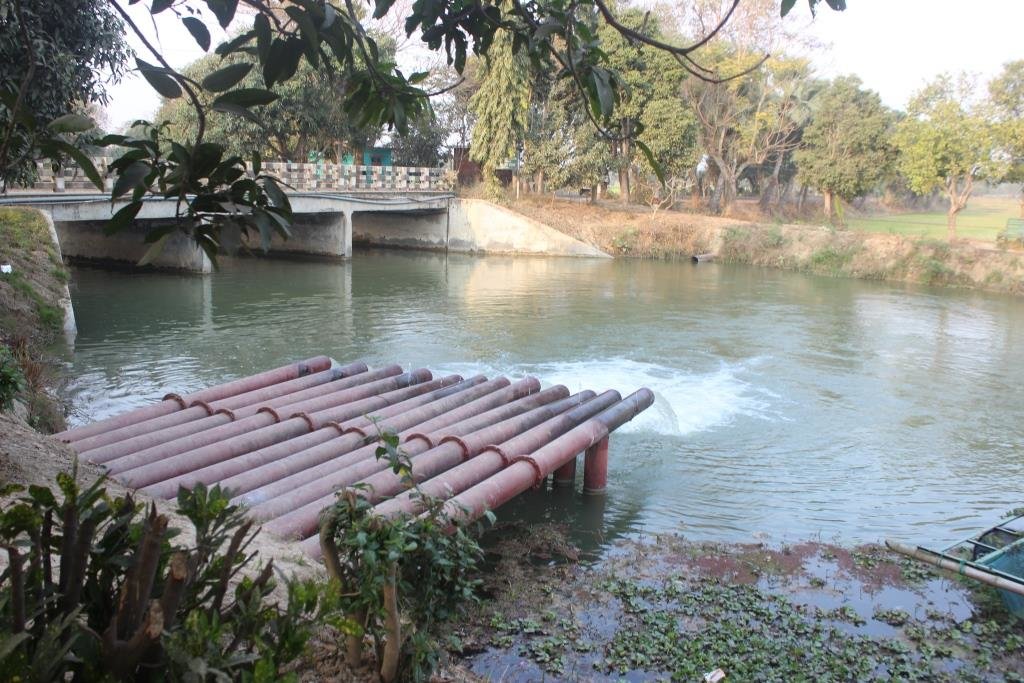
Deep tubewells (DTWs) were installed to abstract water from 15-20 meters, and water was initially distributed through open channels. Later, these were fitted with smart card–operated electric/solar pumps to develop a drought-resilient irrigation system Both projects have helped the Barind region reduce poverty and achieve self-sufficiency in rice. Without supplementary irrigation, there would be crop failure.
Since it was established, BMDA has focused on halting seasonal drought in Barind, and increased cropping intensity by providing irrigation through 15,800 DTWs in different districts. That reduced the cost of irrigation water for one bigha (0.1ha) from about $40 to <$20. On the other hand initiation of smart cards and buried pipelines for water distribution increased the efficiency of water use and facilitated revenue collection by the BMDA. However abstraction of groundwater (GW) for irrigation triggered another issue - drawdown of GW in the area, which even led to abandoning shallow tubewells (STW) used for drinking water.
In 2004 BMDA initiated another project, to lift surface water from the Padma river to ponds/canals/rivers in the main land after re-excavation. These sources are used as reservoirs and at the same time contribute to GW recharge generally. At the same time, usage of solar power instead of electricity is another means of reducing the cost of pumping water.
BMDA again installed 490 dugwells where STW or DTW could not be constructed. These dug wells are used for safe drinking water and small-scale irrigation. These measures have meant that, at present, the area avoids seasonal drought in most of the locations. Potatoes, "boro" and transplanted "aman" occupy more than 50% of the cultivable land. In addition, provision of safe drinking water and improved communications have boosted the local economy. The approach embraces various technologies including (1) tapping river water (from the Ganges, Mahananda and Tangan rivers0; (2) storing water in creeks or ponds; (3) distribution to farm land through subsurface irrigation pipes (buried pipelines); (4) use of low lift pumps (LLP) with solar energy support ; (5) prepaid water metering - usage of smart cards; (6) conversion of derelict water bodies to become effective water reservoirs ; (7) dug wells with solar power for water abstraction; (8) orchard plantations where both surface or groundwater are limited; (9) plantations of trees and horticultural crops along road and channels to change the land cover; (10) usage of compost to improve soil health. All of these contribute to land degradation neutrality (LDN) in one way or another.
Finally BMDA's approach is to boost productivity in the drought affected Barind through its projects, and encouraged communities to adopt diversified land use: previously much land remained fallow during most of the year outside the monsoon. Institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) and many NGOs promote a variety of seasonal, annual and perennial crops in the area, the use of balanced fertilizer, plantation of high density fruit crops. The impact of the BMDA approach has greatly changed the drought-affected Barind.
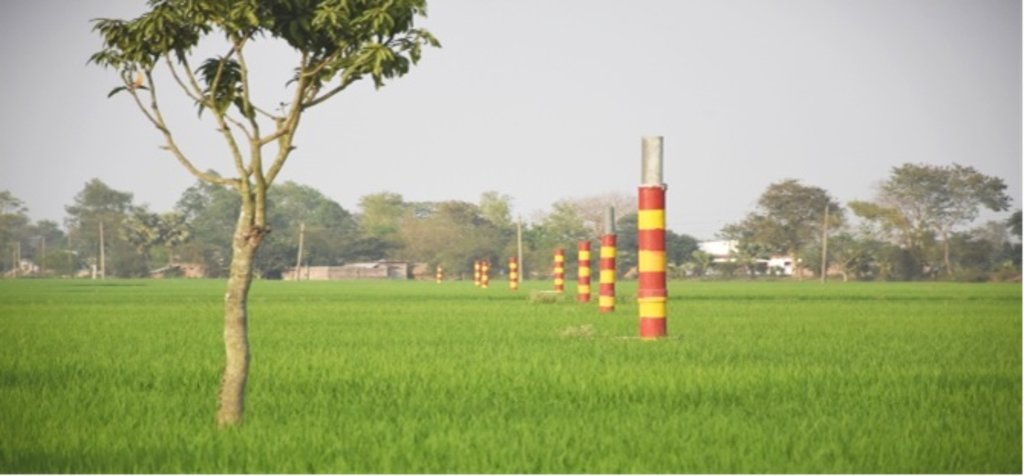
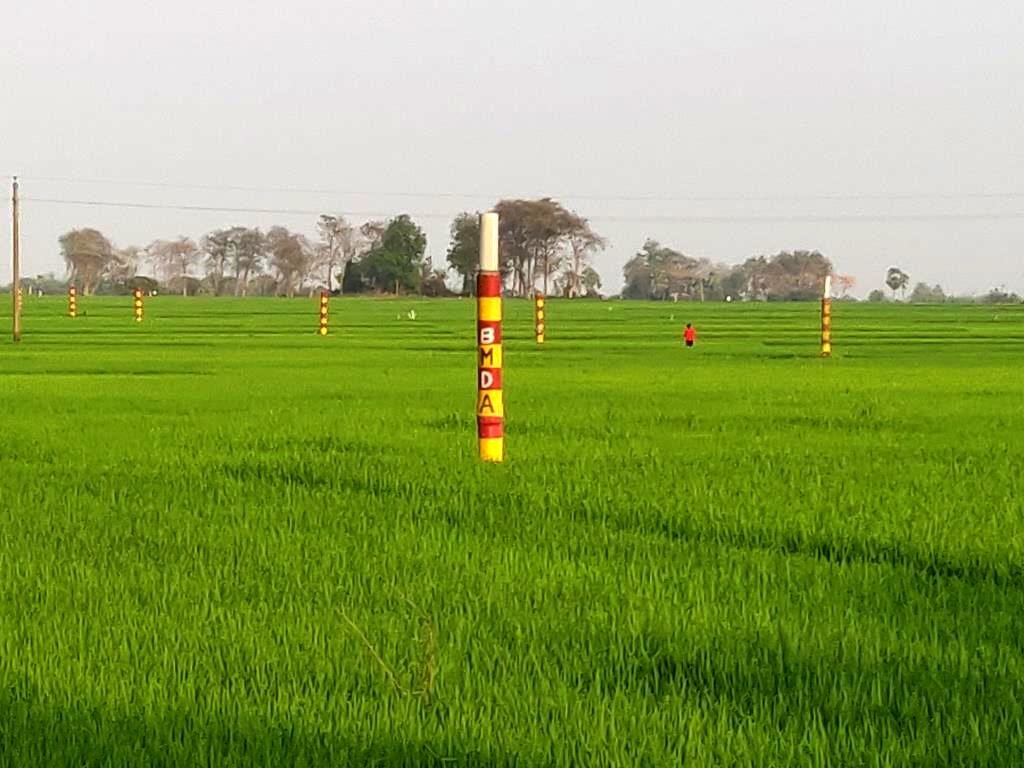
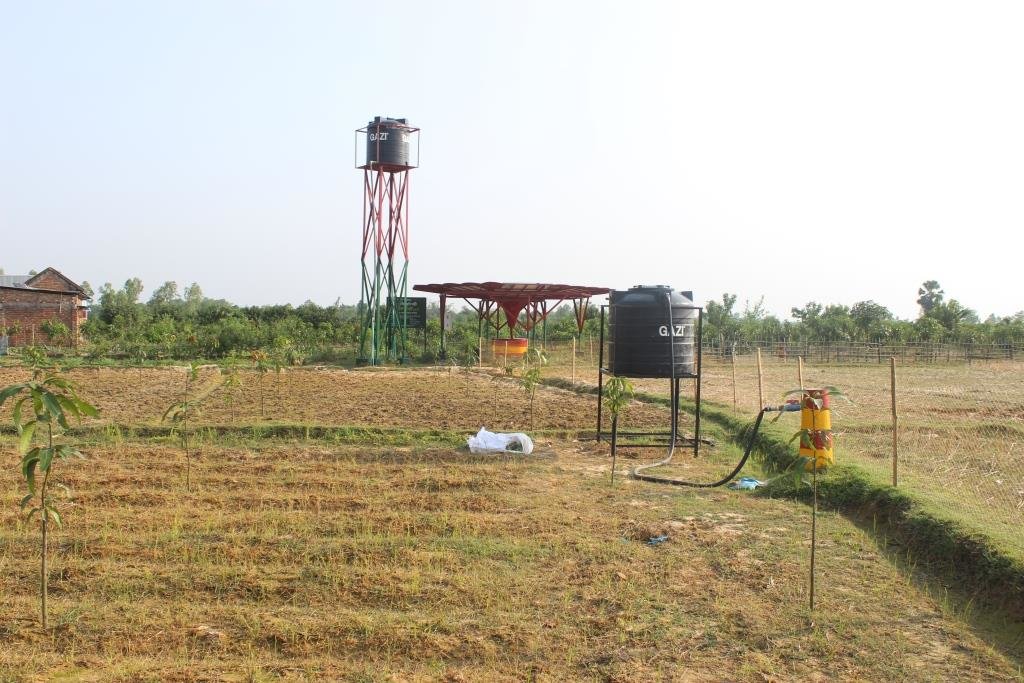
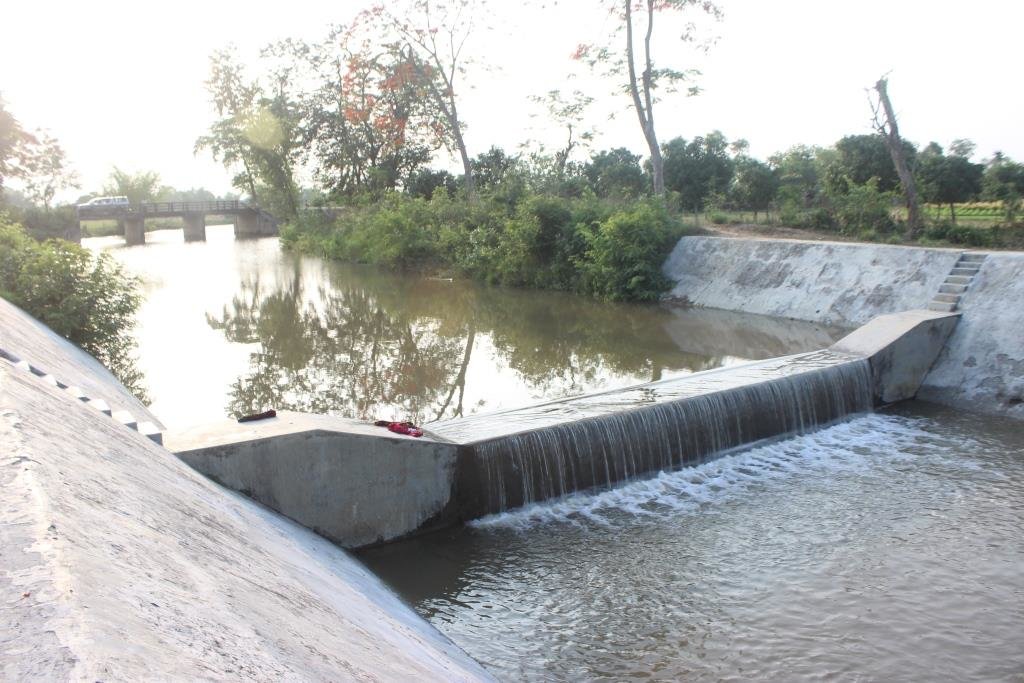
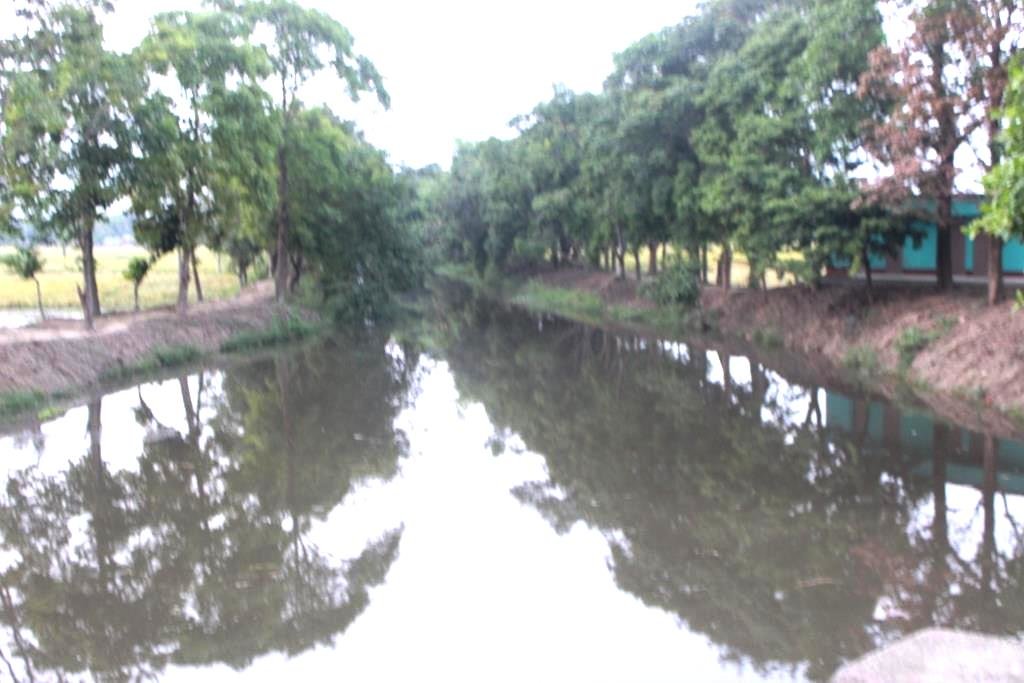
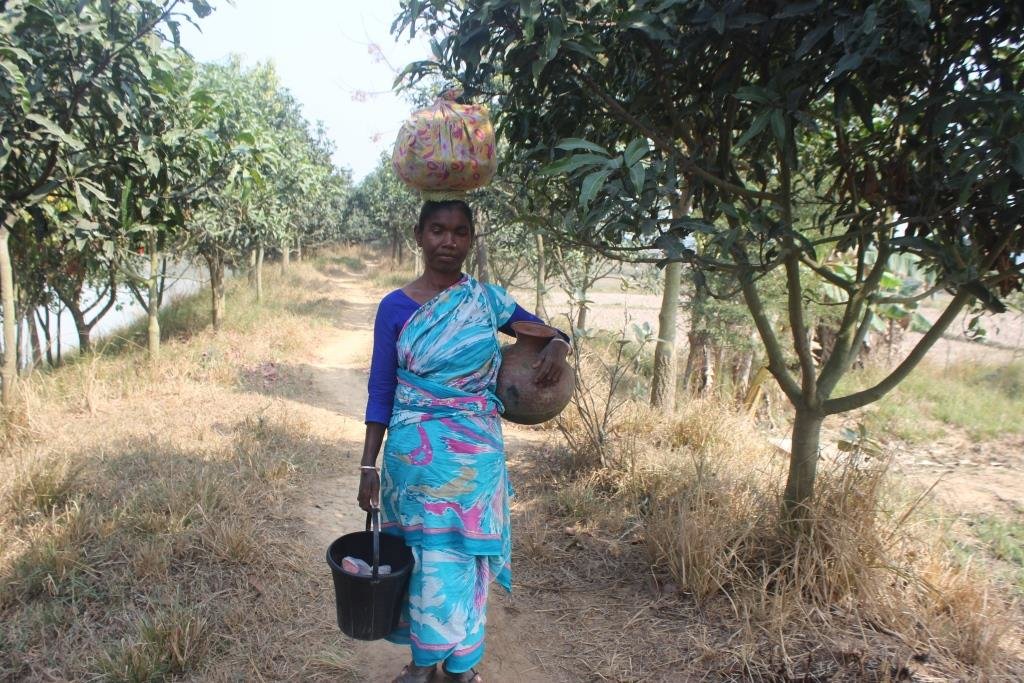
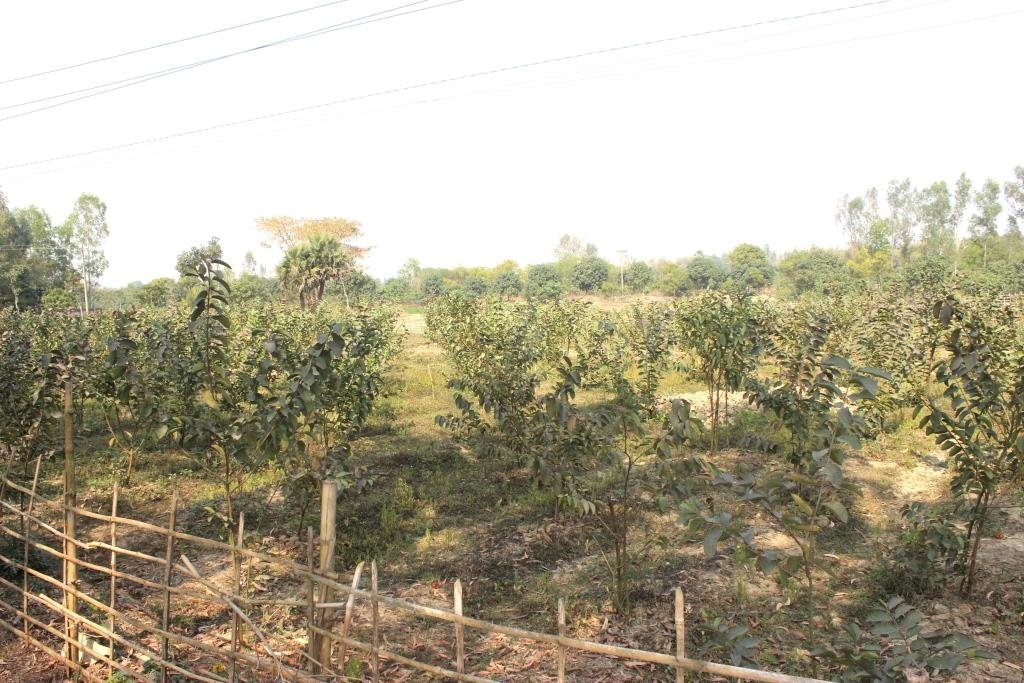
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
All these pictures demonstrate the usage of surface water for irrigation and livelihoods in Barind.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Bangladesh
Região/Estado/Província:
Rajshahi
Comentários:
Barind which was the driest area of Bangladesh, has now changed its landscape to green.
Map
×2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Indique o ano de início:
1992
Comentários:
Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) is continuing with more development projects to provide irrigation facilities with more options. Cropping intensity has increased, and most of the single cropped land has been transformed to double and triple cropped land.
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
To provide irrigation water for cropping in dry season.
To increase cropping intensity in drought affected areas of Barind.
To manage land use or land cover in Barind.
To mobilize community on rational usage of soil and water resources.
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Normas e valores sociais/culturais/religiosos
- Propício
Increased livelihood options and access to education, marketing, health services.
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Propício
Increased access to financial institution.
Quadro institucional
- Propício
All technical support provided by BMDA.
Colaboração/coordenção de atores
- Propício
BMDA supports all action in related to irrigation, maintenance, water supply etc.
Quadro jurídico (posse de terra, direitos de uso da terra e da água)
- Propício
Lands owned by land users
Políticas
- Propício
Land users are in the line of BMDA policies.
Governança da terra (tomada de decisões, implementação e aplicação)
- Propício
Traditional approach.
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Propício
Community has access to technical support.
Mercados (para comprar entradas, vender produtos) e preços
- Propício
All inputs are available in the area.
Carga de trabalho, disponibilidade de força de trabalho
- Propício
Available, people are getting work now.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
Men and women are involved in the process
Growing crops as of their choice, for example: rice, fruits, vegetables or orchard trees.
- Organizações comunitárias
Farmers have societies,
Influenced in choice of crops, etc.
- Organização não governamental
Several NGO s are functional in the area.
Most of them are supporting credit and marketing facilities
- Governo local
Local institutions involved in the process
Capacity building, advisory services on fertilizer usage, crop selection etc.
Caso várias partes interessadas foram envolvidas, indique a agência líder:
BMDA is working as lead agency
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Passivo | Farmers are using irrigation water for their crops supplied by BMDA and they pay revenue |
| Planejamento | Passivo | Farmer nor the community are involved in the planning process |
| Implementação | Passivo | Land users allow to set buried pipelines under their fields. |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Passivo | Land users are not involved in the M&E but they participate in the events organized. |
| Nenhum | Land users only choose their crops to be grown |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
Descrição:
Barind Multipurpose Development Authoroty (BMDA) is the symbol of development in Barind area also of the Tista floodplain and the Old Himalayan piedmont plain.
Autor:
ShoaibJU
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente usuários da terra, apoiados por especialistas em GST
Especifique em que base foram tomadas as decisões:
- Avaliação de conhecimento bem documentado de GST (tomada de decisão baseada em evidências)
- Resultados de pesquisa
- Experiência pessoal e opiniões (não documentado)
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Usuários de terra
- Equipe de campo/consultores
Caso seja relevante, especifique gênero, idade, status, etnia, etc.
BMDA has trained staff to care for the system by and large. There are both male and female staff.
Tipo de formação:
- Em exercício
- Áreas de demonstração
Assuntos abordados:
Buried pipeline maitenance, good seed production, marketing etc.
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- Em centros permanentes
Descreva/comentários:
BMDA has field offices at each upazila to look after the system
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, significativamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Local
- Regional
Descreva instituição, papéis e responsabilidades, membros, etc.
BMDA has it headquarters at Rajshai city and sub-offices at all "upazila" to where the pipeline extended.
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/formação
- Equipamento
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
BMDA monitors groundwater levels regularly, and also the pipelines and other operational activities.
Caso afirmativo, esta documentação é destinada a ser utilizada para monitoramento e avaliação?
Sim
Comentários:
During the documentation of the SLM best practices of the Barind area intensive conversations, meetings and workshops were organized with all officials of headquarter and filed offices.
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Não
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Caso o orçamento exato seja desconhecido, indique a faixa:
- 10.000-100.000
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique tipo(s) de apoio, condições e fornecedor(es):
All infrastructural establishment cost were born by BMDA
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Equipamento
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Maquinário | Totalmente financiado | |
| Ferramentas | Totalmente financiado | |
- Construção
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Pedra | Totalmente financiado | |
- Infraestrutura
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Estradas | Totalmente financiado | |
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
5.5 Outros incentivos ou instrumentos
Foram utilizados outros incentivos ou instrumentos para promover a implementação das tecnologias de GST?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Installation and maintenance cost borne by BMDA, but farmers have to pay for water through smart cards (Pre-paid).
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos usuários locais de terra, melhorou a participação das partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Farmers are using irrigation water for their crops
A abordagem propiciou a tomada de decisão baseada em evidências?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
As of now buried pipe lines for irrigation water supply are being adopting in many areas of the country.
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Usage of water rationally: BMDA installs control meters for each of the land user.
A abordagem melhorou a coordenação e a implementação economicamente eficiente da GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
The approach has changed the Barind ecosystem at large.
A abordagem aprimorou o conhecimento e as capacidades dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Land users enable to use irrigation water for growing crops of their choice
A abordagem aprimorou o conhecimento e as capacidades de outras partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Other local institutions in Barind area are involved in the system.
A abordagem construiu/fortaleceu instituições, colaboração entre partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Adoption of the irrigation system at all areas of the Barind.
A abordagem atenuou conflitos?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Stakeholders are enable to use water as they like.
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
The area was resource poor before the 1990s. Now livelihoods of the community improved largely.
A abordagem melhorou a igualdade de gêneros e concedeu autonomia a mulheres e meninas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Man and women are engaged themselves in their land and crops.
A abordagem encorajou os jovens/as próximas gerações de usuários de terra a se envolverem na GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Interventions with new crops, specially high value fruits etc in the area.
A abordagem melhorou as questões de posse de terra/diretos do usuário que inibiam a implementação das tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Land tenure system is traditional, where large areas are sublet or leased to the individuals or groups by the land owners.
A abordagem resultou em segurança alimentar aprimorada/nutrição melhorada?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
The area produces a large amount of cereals, potatoes, vegetables, fruits etc.
A abordagem melhorou o acesso aos mercados?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Fruits and paddy rice have good markets.
A abordagem resultou em acesso melhorado à água e ao saneamento?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Safe drinking water where tubewells do not function, and sanitation also developed as the system.
A abordagem resultou em uso/fontes de energia mais sustentável?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Using solar power to abstract dug well water greatly facilitates the community.
A abordagem aprimorou a capacidade dos usuários da terra de adaptar-se a mudanças climáticas/extremos e atenuar os desastres relacionados com o clima?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Vegetative cover in the Barind has changed the ecosystem at large.
A abordagem resultou em emprego, oportunidades de renda?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Local people are having work everywhere of the Barind.
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Produção aumentada
Cropping intensity increased
- Lucro (lucrabilidade) aumentado, melhora da relação custo-benefício
Low cost of irrigation water contributes to benefits for the land users.
- Degradação do solo reduzida
Halts or reduces seasonal drought
- Riscos de desastre reduzido
Less climate extremes, no crop loss due to drought. Temperature relatively cooler than before.
- normas e regulamentos (multas)/aplicação
No social unrest
- Prestígio, pressão social/coesão social
Livehood improved greatly.
- Consciência ambiental
Local people are now aware of the environment. They grow trees around their homesteads, preserve water in their ponds etc.
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
Buried pipeline irrigation has changed the Barind area greatly.
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| More crops could be grown throughout the year, |
| Crop diversity is possible, annual, perenial or seasonal |
| Secure crop production |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Minimum loss of irrigation water |
| Surface (river) water usage minimize stress on ground water usage |
| Improved ground water recharge |
| Safe drinking water where tubewell is not available. |
| Usage of solar power for lifting water from dug well or for lifting water to buried pipeline |
| Introduction of water meters reduces misuse of irrigation water |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The system could be implemented at single farmer level | Developing community approach with the support of the government |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Very high pressure on land and soil resources | Lower water consumptive crops could be introduced |
| Severe soil nutrient depletion may develop | Use of manure/ compost or organic matter or crop rotation to enrich soil |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Intensive field visit with responsible officers (5) from BMDA and interview with beneficiaries (30) .
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Especially the farmers (5) who used to grow very high density fruits crops and of solar powered dugwell (3)
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
10 officers from different institutions, like BMDA, DAE, University of Rajshahi, SRDI, NGO, Fishries etc.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Few official docments of design and plan of pipelines, dugwell etc.
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
Baring Multipupose Development Authority
URL:
http://www.bmda.gov.bd/site/page/2ea693ba-ac10-4ada-b304-111d72a72105/-#
Título/ descrição:
Pro-Poor Groundwater Development
URL:
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/33246/Pro-Poor-Groundwater-Development-The-Case-of-the-Barind-Experiment-in-Bangladesh.pdf?sequence=5
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos