Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard) [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Erik Bühlmann
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1001 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard): 20 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard): 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard): 19 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard): 17 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard): 10 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
17/07/2005
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Establishment of an orchard intercropping system on severely degraded cropland.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
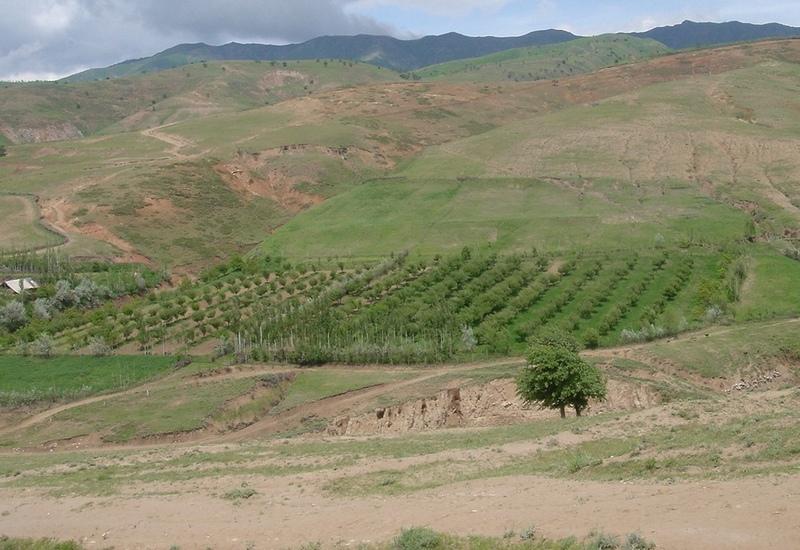
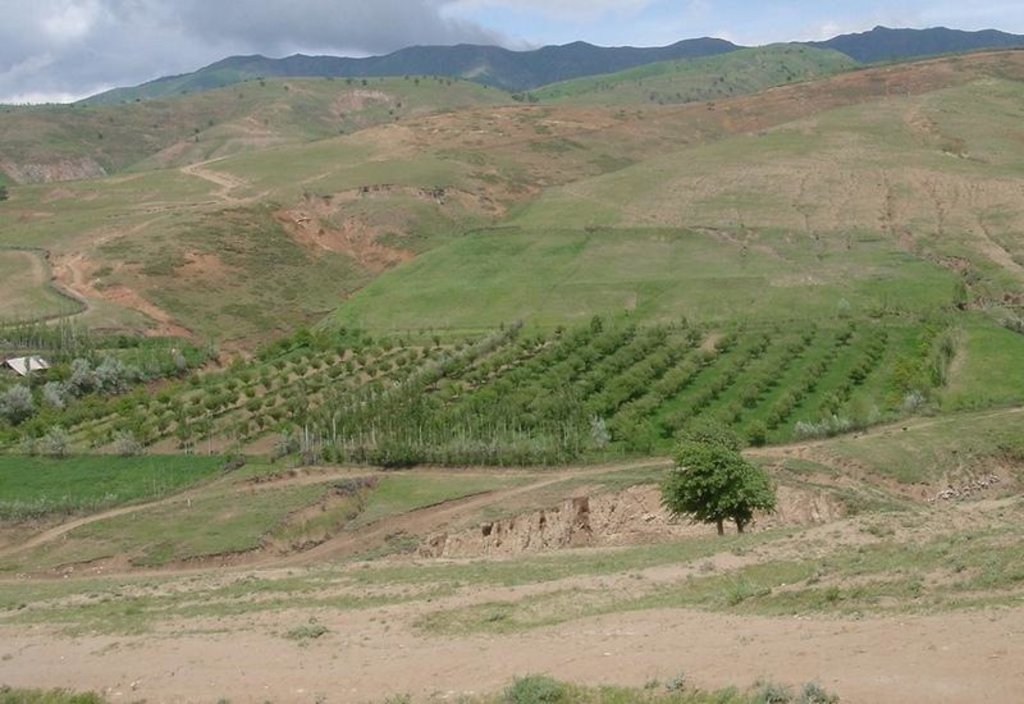
A fruit orchard (consisting of apples, apricots, cherries, pears and nut trees) was established on degraded cropland. Intercropping of annual crops such as wheat, flax, chick peas and vegetables as well as perennial herbaceous fodder plants (alfa-alfa and esparzet) were planted after the first year of the establishment of the orchard. Only the onion plot is rotated systematically since the farmer states that fertility declines due to heavy soil losses result from over-irrigation. Spacing of tree rows varies between 8-10m, the intercropping system is cultivated using a tractor. Fruit trees are aligned in the direction of the slope to facilitate irrigation. At the top of the field an irrigation channel (40cm wide, 15cm deep) stabilised with aligned poplar trees directs water onto the orchard system. During the rainy season the channel serves as a cut-off drain, protecting the land from water running on. Along the trees, a 2.5 m wide grass strip protects the ground from splash erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: The orchard system was established to increase farm production by integrating different resources, while simultaneously conserving soil and water resources and preventing development of gullies. Prior to tree planting, the area had been levelled with a bulldozer to restore the severely degraded cropland. The bought seedlings were planted in hand-dug pits. During summer, the orchard system is watered three days per week; manure is applied around the fruit trees on an annual basis. Pruning of the trees is done in early spring. Due to irrigation, the grass strips can be harvested twice a year for haymaking. Farming two crops at a time means gross farm production could be considerably increased, which is the reaon why the farmer considered the technology successful. However, establishment and maintenance of the technology is cost intensive and, in this case study, was only affordable due to the farmers off-farm income. Since the tree rows are aligned up and down the slope, soil erosion is solely reduced by the capability of the irrigation channel (and aligned tree barrier) to prevent the system from runon. Planting tree rows on the gradient would increase the technologies potential to reduce soil loss.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
RRS
Especificação adicional de localização:
Faizabad Rayon
Map
×2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: vegetables
major food crop: wheat
other: chickpeas, flax

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agrofloresta
Principais produtos/serviços:
major cash crop: fruit, vegetables
major food crop: wheat
other: chickpeas, flax, alfa alfa, esparzet
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe water erosion (gullies and rills) and subsequent decline in fertility on cropland and on overgrazed pastures.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: If the land is irrigated, then after the harvest of annual crops (mid-July until beginning of August), and there is immediate sowing/planting of vegetables (maize, tomatoes, cucumbers, melon among others), then the harvest of vegetables in late August and September is possible.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Comentários:
Water supply also rainfed
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: March - August
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V5: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
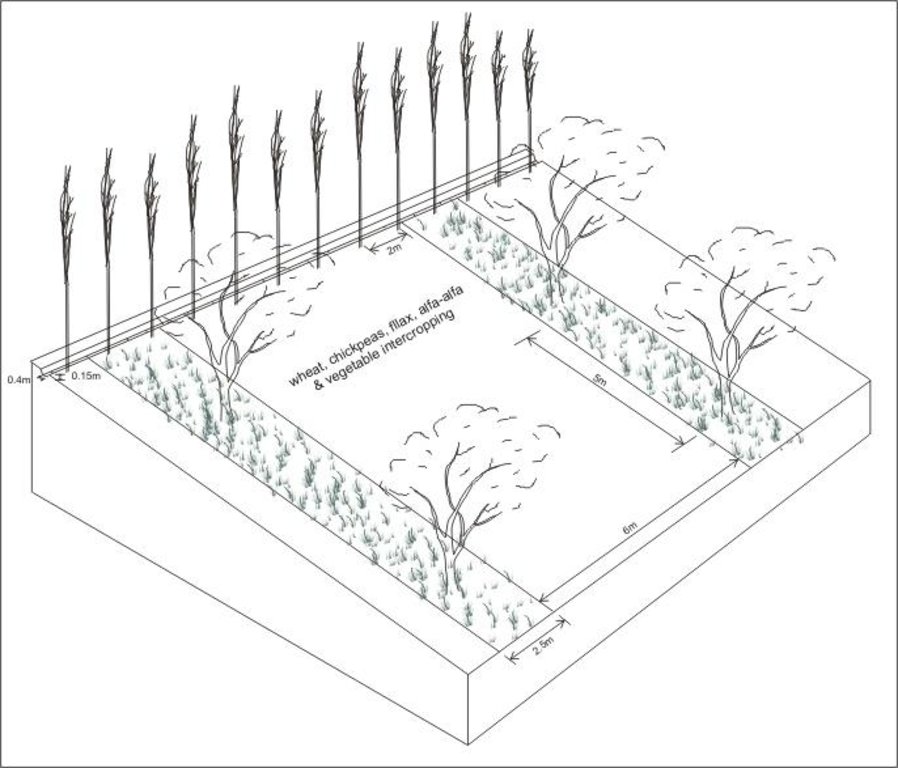
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Irrigated orchard system with intercropping; irrigation channel (stabilised by aligned poplar trees) also acts as a cut-off drain to prevent runon.
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Date: 18.07.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat, chickpeas, flax, vegetables, alfa-alfa, esparzet
Remarks: between tree rows
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure
Quantity/ density: 20kg/tree
Remarks: spreading around fruit trees
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: silitra and/or superphosphate
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: only if wheat is intercropped
Vegetative measure: aligned: slope direction
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vegetative measure: aligned: slope direction
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: aligned: along irigation channel on contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 50
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: poplar trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, pear, cherry, apricot, peach and nut trees
Grass species: grass cover with esparzet and alfa alfa (sown to improve grass cover)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 17.00%
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Construction material (earth): earth was moved to fill gullies and large rills
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 17%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | land levelling and filling up of gullies | Estrutural | winter/early spring |
| 2. | digging of irrigation channel | Estrutural | spring |
| 3. | acquiring tree seedlings on market or at sovkhoze | Vegetativo | |
| 4. | digging of pits | Vegetativo | early spring |
| 5. | planting seedlings in pits | Vegetativo | early spring |
| 6. | sowing of esparzet and alfa alfa (grass strips) to get intact grass cover | Vegetativo | spring |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | land levelling | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | tools | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | machine for land levelling | ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 470,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing of irigation channel/cut-off drain from washed in soil | Estrutural | rainy season/weekly |
| 2. | periodical irrigation (3x a week) | Vegetativo | summer /three days/week |
| 3. | periodical irrigation (3x a week) | Vegetativo | summer /three days/week |
| 4. | application of manure | Vegetativo | early spring /annual |
| 5. | application of manure | Vegetativo | early spring /annual |
| 6. | application of pesticides | Vegetativo | spring /annual |
| 7. | application of pesticides | Vegetativo | spring /annual |
| 8. | pruning of fruit trees | Vegetativo | winter/early spring /annual |
| 9. | pruning of fruit trees | Vegetativo | winter/early spring /annual |
| 10. | cutting of grass (haymaking) | Vegetativo | summer /twice a cropping season |
| 11. | cutting of grass (haymaking) | Vegetativo | summer /twice a cropping season |
| 12. | ploughing of area between tree rows (disc plough) | Agronômico | depending on crop / annual |
| 13. | applying of mineral fertilisers | Agronômico | spring / annual (only for intercropped wheat) |
| 14. | weeding | Agronômico | spring / regularly |
| 15. | applying manure around fruit trees | Agronômico | winter/spring /annual |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | ploughing of area | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | sowing and weeding | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | pruning of fruit trees | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | spraying trees with biocides | ha | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | 1,0 | |||||
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 210,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs were calculated for a 100x100 m field plot (with a projected 200 fruit trees/ha).
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Number of trees planted: since the establishment and maintainance require considerable financial and labour inputs; expenditures for tree seedlings bought from the market: N.B. if nursing the trees is completed by land user himself, establishment costs can be halved.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
growing period between 180-210 days
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm incomes, which in most cases are earned in Russia, either by themselves or by their relatives.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Subsistence, only surpluses sold
Level of mechanization: Ploughing is carried out by tractor whenever possible, but also animal traction is existent.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Households with 1-2 ha are depending on available working force, labour is limiting factor.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
loss of land for wheat production
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
machines used for land cultivation cannot operate so easily
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
fruit yields
Comentários/especificar:
due to lack of fertilisers and biocides
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
disputes on land use rights with other villagers, since orchards are in great demand
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
Outros impactos ecológicos
prevention of land from gullies and large rills
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
20 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| increase in overall farm income |
| prevention of gully and large rill erosion |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| orchard system is protected from runon |
| effectively prevents formation of gullies and large rills |
| significant increases in gross farm production |
| effective way of rehabilitating bad lands |
|
increases soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? consequent mulching would increase the organic matter content of the soil, and hence soil fertility |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| fruit trees vulnerable to pests, frost and strong winds |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| high establishment and maintainance costs | if nursing of tree seedlings is carried out by the land user himself, establishment costs can be reduced |
| does not prevent soil erosion, soil losses especially where irrigated | By planting tree rows on gradient (not up and down the slope) |
| management of orchard systems requires considerable inputs which often cannot be afforded by poor people |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos