Sweet Potato Ridge [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Daniel Danano
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1068 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Itália1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
05/12/2008
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
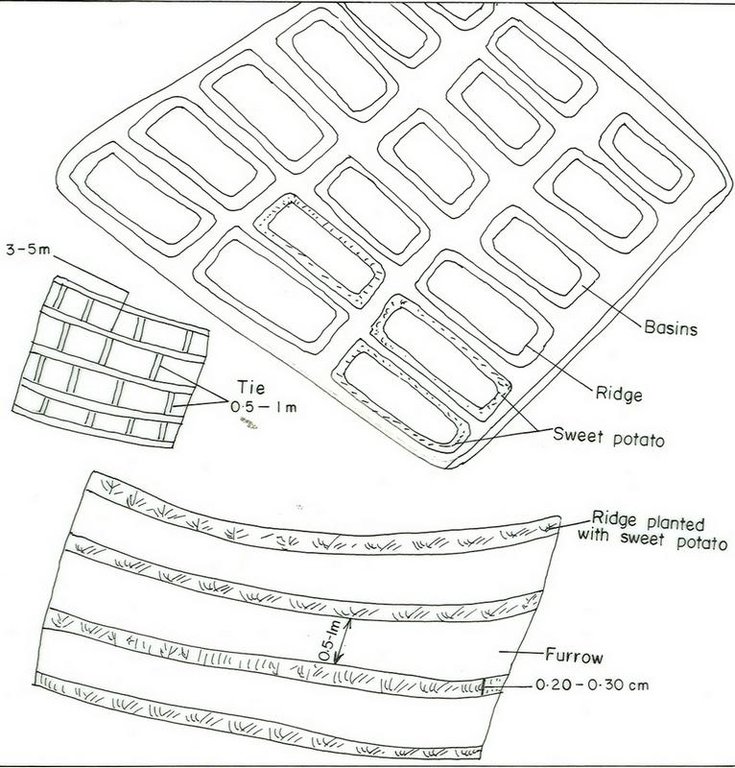
Earth embankment formed by digging a channel and pile the soil to form a ridge on which potato is planted.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Sweet potato ridge are constructed from the soil dug out of the furrow. Farmers make the furrow and ridge by dengora and a hoe. In some cases oxen scoop are used to move the soil and form the embankment. Sweet potato is planted by cuttings. It is often planted during the end of the main rainy season. There are different methods employed in making ridge and furrows. The furrows are meant to collect rain water and the cuttings of sweet potato planted on the ridge. The plant benefits from the soil water stored by the farrows. It has deep roots that go deep insearch of soil water. Water could also move up by capillary movement. Forming the ridges and basin is quite labours. The ridges are frequently made new and in some cases the former ridges and furrows are maintained. The technology suits to sub-humid and semi arid agro-ecological zones having sandy loam soils.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Originated locally from long term experiences and improvments
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major food crop annual cropping: Sorghum, sweet potato
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Chat
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil mositure stress, erosion and over population.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Shortage of rains, lack of finance for purchasing improved seeds and fertilizers.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Sorghum-Sweet Potato-Maize-Legumes
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 21 0Longest growing period from month to month: May - Nov
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 100-1.000 km2
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Oromia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope length, increase in soil fertility
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Sweet potato
Quantity/ density: 20000-2500
Remarks: along the contour
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize, sorghum, chat
Remarks: row and broadcast
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Sorghum, chat
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Sorghum, chat, maize
Green manure
Material/ species: Sweet potato
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 1500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Trees/ shrubs species: some accacia trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, mango
Perennial crops species: chat
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 1.5-2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5-1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-70
Structural measure: Ridge and furrows
Spacing between structures (m): 2-3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.51
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-70
Construction material (earth): Soil dug is embanked to form the ridge
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Birr
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
8,6
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
0.81
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seed bed preparation | Vegetativo | dry season |
| 2. | Pitting | Vegetativo | after rain |
| 3. | Manuring | Vegetativo | all season |
| 4. | Planting | Vegetativo | during rains |
| 5. | Cultivation | Vegetativo | during rains |
| 6. | Excavation (furrow formation) | Estrutural | dry period |
| 7. | Embankment (ridge forming) | Estrutural | |
| 8. | Planting sweet potato | Estrutural | rainy season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 73,0 | 73,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 35,0 | 35,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 183,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Agronômico | dry season / each cropping season |
| 2. | Harrowing | Agronômico | dry season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Contour ridging | Agronômico | dry season / each cropping season |
| 4. | Planting | Agronômico | rainy season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Cultivation | Agronômico | rainy season / 2-3 |
| 6. | Reconstructing basins, ridges and tie | Vegetativo | dry eason / |
| 7. | Applying more manure | Vegetativo | all season / |
| 8. | Repair of ridges and furrows | Estrutural | before planting/1 |
| 9. | Placing of fertile soil on the ridges | Estrutural | before planting/2 |
| 10. | Applying manure during cultivation | Estrutural | after planting/1 |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Total labour expended to till the land, pulverize it, harrow and making of the ridges. The cost further include the monetary estimate of manuring the land and purchasing of the sweet potato cuttings, assuming these are purchased from market.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Soil dryness and texture-light soils are very simple for opration and the least cost is incurred. Loam soils are good soils with moderate cost of investment.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (ranked 1), 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (ranked 2) and 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (ranked 3)
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and moderate (ranked 3)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Also Deep and shallow (both ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Comercial/mercado
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
25% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (sweet potato is mostly planted on level and gentle slopes and hence land preparation is made largely by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, most part consumed at home) and mixed (ranked 2, small portion of the sweet potato is sold at market)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Due to population pressure land shortage is a critical problem humpering production and productivity
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
sweet potato leaves are used for fodder
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
sweet potato leaves are used for fodder
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
85% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: more farmers are practicing the technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Improve production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of high yielding varieties and fertilizers |
|
Reduces risk of crop failure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage more crop type |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Efficiently controls soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? The ridges retard surface flow and the furrow provide space for rain water storage |
| Allows maximum storage of rain water |
|
Improves water storage capacity of soils How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato improves the soil structure by initiating microbial activities |
|
Reduces evapotranspiration rate of soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato provide dense ground cover and hence reduce evapotranspiration losses |
|
Improves soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato is naturally a soil fertility enhancing crop. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos