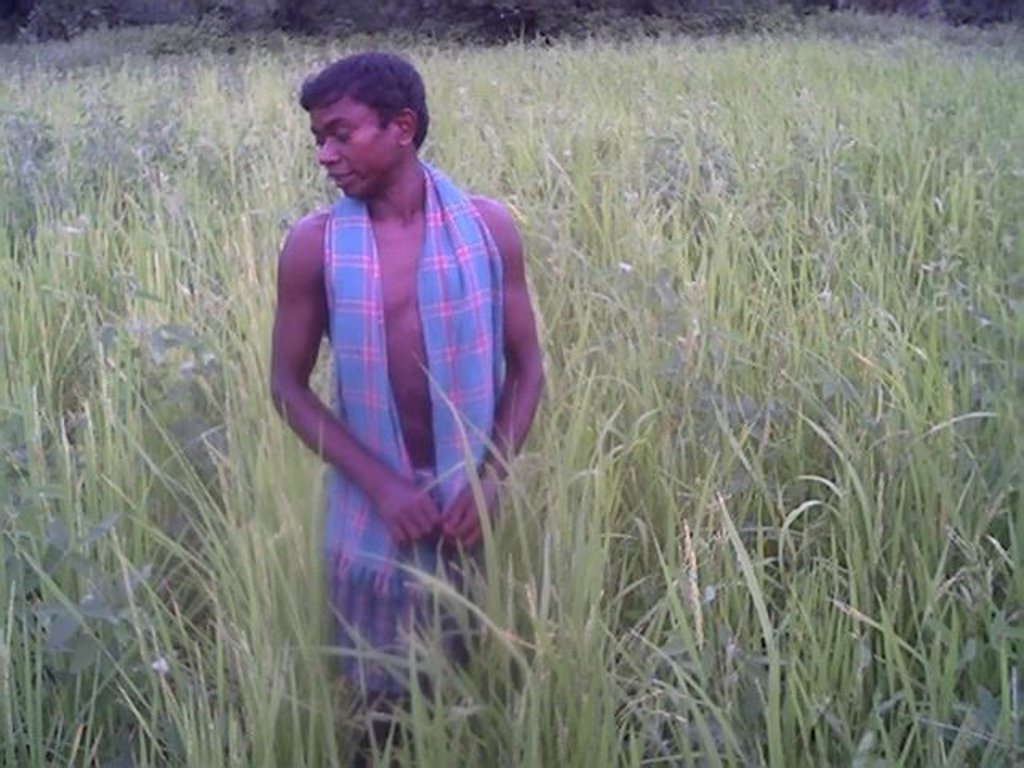
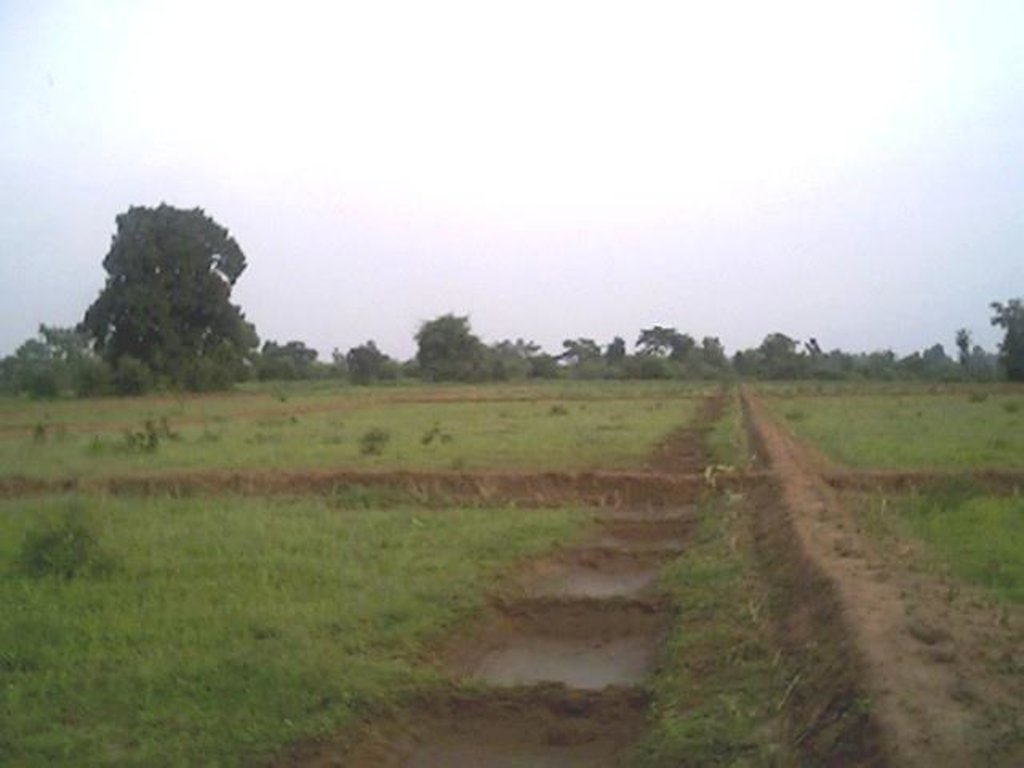
Dug-out sunken pond cum countour bund [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Buda Gata with Adibandha
technologies_1086 - Índia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Mohanty Rajib Kumar
Índia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
17/12/2004
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Community based sustainable livelihoods [Índia]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
It can be defined as combination of structural & vegetative measures where contour bunds are constructed from the excavated sandy loam soil of cultivated wastelands in semi-arid climatic(?) zone with moderate slope in medium soil depth conditions in order to link with self-subsistance & market oriented production systems from private lands.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The area is located at the foot-slopes & hill slopes area where run-off is at peaks very often at the time of rainy season. Therefore, sand casting came as a first order priorities by the farmers of this patch. At the outset, a livelihood focused micro-plan had been prepared by the villagers stating the details of the base-line data along with problems & alternative solutions. The patch was identified to be the worst affected, concentraton of poor people (defined by villagers), people of this patch ready to contibute at least 20% of the cost. In the mean time project sent the PIA to BAIF, Bangalore to study the linking of farm ponds & its relevance in this context of our situation. As a demonstration, PIA & other technical team facilitated the villagers. One water harvesting structure was constructed by line deptt of soil conservation just at the down hills to harvest rain water & protect the lands below from sand casting. But there were no alternatives for the land users of that patch about the optimum utilisation recharged water. The surrounding area was totally unbunded with sandy loam soil. Therefore, land users are of opinion to go fo field bunding. Earlier the practice was to dig a trench at upper gadient & put a bund below it out of the excavated soil from trench. But the requirement of land users was to get some water in each farmers land to protect the Kharif & some early rabi crop.(june-dec). By which the lands where, farmers take up only minor millets for their subsistance, that too less production & land So the main purpose of this technology was to convert the land into bunded lands along with to fetch some water at the time of dry spell in between the monsoon period. A four days in field training was conducted by the project to community link workers(SWC), particularly on patch treatment, use of levelling instruments like A-frame, proper planning, design, lay-out of different type of structure in a map & ground. After many rounds of discussion with the land users, one of them ( rich farmers with more land) was ready to do it in his own land. But, the SWC specialist did a detail transact along with land users, although results of first round tansact was mentioned in the micro-plan. The main pupose was to looking at problems & demarkating on the map. After that estimate was prepared & lay-out of key contour was done by SWC specialist with the help of community link workers & land users. The work was implemented by by the labourers with the supervision of the respective User's group leade & monitoring was done by the SWC specialist. The prioty ranking by the land users vegetaive measures like vertiver & Sabai (grass plantation on the bund along the side of the bund. For that, the necessary requirement like nursery, seedling collection was done by agriculture specialist. Training was conducted on the probable alternatives of agronomic measures like taking of crop which is of little longer duration, intercrops & cash crops etc. The vegetaive & structructural measures are subsidised by the project & the agronomic measures was taken up on loan basis. The development fund was also generated out of contribution from the land users which was deposited in a separate account for future maintainance cost.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
Orissa
Especificação adicional de localização:
Khaparakhol
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
A group of SWC proffessionals were sent to BAIF Karnatka to study the replication of ' Linking of farm ponds models. After a detail study we concluded that the climate in particular & rainfall in general of our area is not fit for that technolgy. When SWC specialist share their experience to land users, some of the farmers agreed to have a experimentation of the technology. Therefore, modification has been done by the SWC specialists as per the suitability & requirement of the land users.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major cash crop: Ground nut
Major food crop: Paddy/minormillets
Major other crop: Cotton

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agropecuária
- Agrossilvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
Major cash crop: Fruit like mango/Custard apple
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This patch of the land is poor in the nutrient status in comparison to other lands of the village, with high concentration of marginal farmer. Heavy top soil erosion over the years yields to decreasing of productivity of land. The main requirement of water is in the dry spell in between the monsoon period.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Run-off was severe at the time of rainy season which causes heavy soil erosion. 2. Sand casting on down below lands . 3. Long duration crops is not possible, ex- Ground nut, paddy, cotton etc. 3. Lands was not levelled for smoothening of ploughing operation. 4. The uncultivated wasteland(according the record of rights) was distributed to some landless persons who are unable to take up any productive cultivation in these lands.
Ranching: Although technolgy is not directly applied, but indirect effect is there on grazing.
Grazingland comments: The major cause of loss in livestock is that there is no option for the villagers for stall feeding. Example- in summer no availability of green fodder or less availabity.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Minor Millets/ Paddy(june-Sept)- Black gram or pulses(Sep-Dec) or cotton as the sole crop for nine months.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - SepSecond longest growing period in days: 75Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Dec
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Coleta de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 km2.
The concerned watershed is a subsidiary system of the Suktel river drainage sytem. The area of operation is micro watershed , i.e. 500 hac as a unit of the tributary of the Suktel river.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Suitable alternatives which will yield more benefit with less investments.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Knowledge sustainable livelihoods framework)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Maintainance & responsibility sharing for protection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Particularly vegetation which yields non-timber forest produce.), overgrazing (Uncontrolled & free grazing at the period Dec-June restricts the land users to go for second crop.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Frequent drought occurs in every alternative 3rd year.), poverty / wealth (Initiation of any activities for sustainance of livelihoods need some capital)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Better crop cover
Material/ species: paddy, minor millets, groundnut, vegetables
Quantity/ density: Average
Relay cropping
Material/ species: pulses after minor millets or short duration paddy
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ground nut, green gram & fibre crop(Jute)
Remarks: Line sowing- 5 lines of green gram with one line of green gram & jute on the fence of the land.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Cotton as a demonstation practice.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: The silt deposits in the sunken pond is used in the nearby land.
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: After paddy the land is used for pulse
Minimum tillage
Remarks: Previously unbunded, now bunded upland rquires minimum tillage.
Pits
Remarks: Thecontour bunds & field bunds constructed out the excavated soil from the pits.
Agronomic measure: Soil moisture condition
Remarks: It is enhanced due to the technology
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20 ft
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1250
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 inches
Trees/ shrubs species: Teak
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Custard Apple
Grass species: Vertiver & Sabai
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Spacing between structures (m): 50 ft
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6 ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25 ft
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2 ft
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50ft
Construction material (earth): The earth from the dug-out sunken pond is used for the construction of contour bunding
Construction material (stone): Stone is used at the weak point for stabilisation
Change of land use type: Minor millets, long duration upland paddy, Grount nut, pulses after paddy/millets or cotton etc.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: After harvest of first crop like minor millets/ paddy, next crop is taken up by land users along with some vegetables(Horticulture crop).
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Grazing was restricted in these areas & land was optimally used, like bund cultivation.
Major change in timing of activities: Tthese lands were last option for the land users.But now the activities like summer plough has changed the time.
Control / change of species composition: Earlier sole crop, like only minor millets/Upland paddy. But now land users have started intercropping systems.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Rupee
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
50,0
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey & alignment of key Contour & lay-out of tanks | Vegetativo | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Digging of pits for grass, fruit plants & timber | Vegetativo | June |
| 3. | Collection of Vertiver & Sabai grass from external source | Vegetativo | july |
| 4. | Collection of seedling of Trees/Plants | Vegetativo | July |
| 5. | Survey & contour demarkation | Estrutural | April-May |
| 6. | Demarkation on map | Estrutural | April-May |
| 7. | Estimate & lay-Out | Estrutural | April-May |
| 8. | Implementation of work | Estrutural | June |
| 9. | Survey & Key Contour line demarkation at 75 ft interval | Gestão | June |
| 10. | Digging of Sunken ponds | Gestão | July |
| 11. | Top level dressing of bund | Gestão | July |
| 12. | Water-way with connection Dug-out sunken ponds | Gestão | August |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 20,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 120,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | Agronômico | April-May / annual |
| 2. | Intercultural operation with manure application | Agronômico | June / annual |
| 3. | Sowing | Agronômico | July & sep for two crops / each cropping season |
| 4. | weeding & intercultural operation, if required. | Agronômico | July / annual |
| 5. | Harvesting of paddy or minor millets or ground nut | Agronômico | Aug-sep / annual |
| 6. | Sowing of pulses as relay crop | Agronômico | Aug-sep / each cropping season |
| 7. | Harvesting of pulses | Agronômico | Nov-Dec / each cropping season |
| 8. | Collapsing of bunds may damage th evegetation | Vegetativo | Rainy Season /annual |
| 9. | Checking against free grazing | Vegetativo | Jan-June / |
| 10. | Watering to plants | Vegetativo | Dec-May /annual |
| 11. | Management of surplus water | Estrutural | Rainy Season/Once in Year |
| 12. | Collapsing of bund | Estrutural | |
| 13. | Tanks must be desilted | Estrutural | Dry season/Once in Year |
| 14. | Control of surplus water-flow | Gestão | Rainy season / once a year |
| 15. | Stabilisation of bund at weak points | Gestão | August / once a year |
| 16. | Desiltation of ponds | Gestão |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 7,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: in a typical area of 5 hac, around 30,000 has been spent in which 20% of the establishment cost is borned by the land users.
There are two types of dug-out sunken pits of specifications. The sunken pit was dug & the earth from the sunken pit was put on a contour bund. So the earth-work was calculated as per cubic ft. The seedlings were bought from nursery & planted with 20% contribution of labour.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Soil depth is very less, hard soil with slope variation because of undulating lands. The labour was also not sufficiently available at the time of establishment, because the work was implemented at time of main growing season. At that time land users are busy in their own field because of cultivation work.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
1000-1500 mm: Ranked 1, Avg rainfall from liz kiff report. The study of 20 years of rainfall data shows that, drought comes in every alternative 3 years. The rainfall varies from a minimum of 715.6 mm to maximum of 1863 mm
500-750 mm: Ranked 2
1500-2000 mm: Ranked 3
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (as per the record in the topo-sheet No-64 P/1 with scale1:50,000)
Slopes on average: Gentle (As the stretch of land is at the hill slopes. The slope firstly from 5-8% where as the land where dug-out sunken ponds were dug is of slope 2-5%, ranked 1) and moderate (ranked 2)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, due to continuos soil erosion the topsoil eroded completely which resulted into varied soil depth where only deep rooted crops & plants are possible) and moderately deep
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Ranked 1, the soil is basically reddish in colour with sandy loam texture) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, the soil fertility of uplands is very low where the said technology is established. But the lands near to it some what medium land with medium soil fertility) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (the watershed map from the topo-sheet shows that there only one drainage line where two contributaries are there. That is the perinneal stream where water from the lands drain out to main drainage lei, ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (the soil texture being the sandy loam category, the storage capacity is very low. Therefore, after monsoon rainfall the soil is unable to maintain the water requirement at the dry spell to high percol, ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are very rich (1-2 farmers having more than 10-15 acre of land).
30% of the land users are average wealthy (land users having upto 5 acres(Little less in comparison to first categ).
50% of the land users are poor (land users having only0-2 acres(more in No. in this patch)).
Off-farm income specification: Others have also activities like NTFP collection, keeping small ruminants like goats, chicks etc.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, wooden plough) and manual labour (ranked 2)
Market orientation cropland: subsistence (self-supply, minor millets/paddy/pulses, ranked 1) and mixed (ground nut & vegetables, ranked 2)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (micro-plan)
Grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (130 Households with 25 hac of grazing lands)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Per hac production/economic cost.
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Vertiver as fodder on bund.
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
Teak plants has been planted this year. The yeild is yet to come.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Land users believe that some land is wastage due the structure.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Ploughing operation.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Resource rich & resource poor land users accrued double benefit by changing the crop.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Farm employment at lean period. Income through labour
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Field Demonstration- living institution
Comentários/especificar:
Alternatives to mitigate drought.
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Contribution labour from land users because of convincing benefit from the technology. The women also contributed in plantation activities.
Instituições nacionais
Comentários/especificar:
Members from other areas of district also learnt the technology through exposure visit.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Some of the land users of other patch of the village decided to take up similar activity.
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Transparency: The details of activity is shared amongst all the villagers.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Land users having land below 1 hac are getting more benefit out this technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Earthen hume pipes.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
This condition help the land users to take up second crop.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Particularly top-soil.
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
30
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Diversidade de habitat
Outros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
Comentários/especificar:
Production/ Economic benefit becomes double.
Water availability in dry spell
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
19
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Many farmers & SWC specialists visited the spot for the learning purpose. All we cannot say that it is a spontaneous adoption, but they have started taking up this technology in their own area.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Maintainance is very less How can they be sustained / enhanced? Only timely care is needed. |
|
Land users can have water in their field other than rain water to be used for different purpose. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some demos agriculture was done in this patch which has to be repeated for the second year for confidence building of the land users. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Water availability in the dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land users will desilt the pond timely & care to plants grass on the bund. |
|
The land where only one crop is possible, vegetable & pulse crop can be taken up as second crop How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some methodology is to be applied to keep water in the pond for longer duration. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Ploughing operation will be difficult. | This is although difficult but th benefit is more, therefore land users will compromise with this type of difficulty. |
| Water availability in dry period & desiltaion process. | This can be overcomed by planting vertiver on the sides of the pond & low cost polythene can be used for prolonging percolation rate of water in sandy loam soil. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The farmers started taking up cotton & paddy in stead of minor millets | Improved variety of minor millets is supplied to farmers for better yield in comparison to country variety. |
| Diversion of surplus water | The land users have to dig atleast one more feet & earthen pipes will be used for the diversion of surplus water. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Community based sustainable livelihoods [Índia]
Sustainable livelihoods enhanced through people's organisations by linking with other resource organisations prticularly for resource poor.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
Módulos
Não há módulos