Usage of Gher boundary for cropping [Bangladesh]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Gherer bunder upar nana prokar shakshabjee uthpadon
technologies_1171 - Bangladesh
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Shaha Tapan Kuma
SRDI
Bangladesh
Especialista em GST:
Bhander Bidhan Kumar
SRDI
Bangladesh
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI) (Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI)) - Bangladesh1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
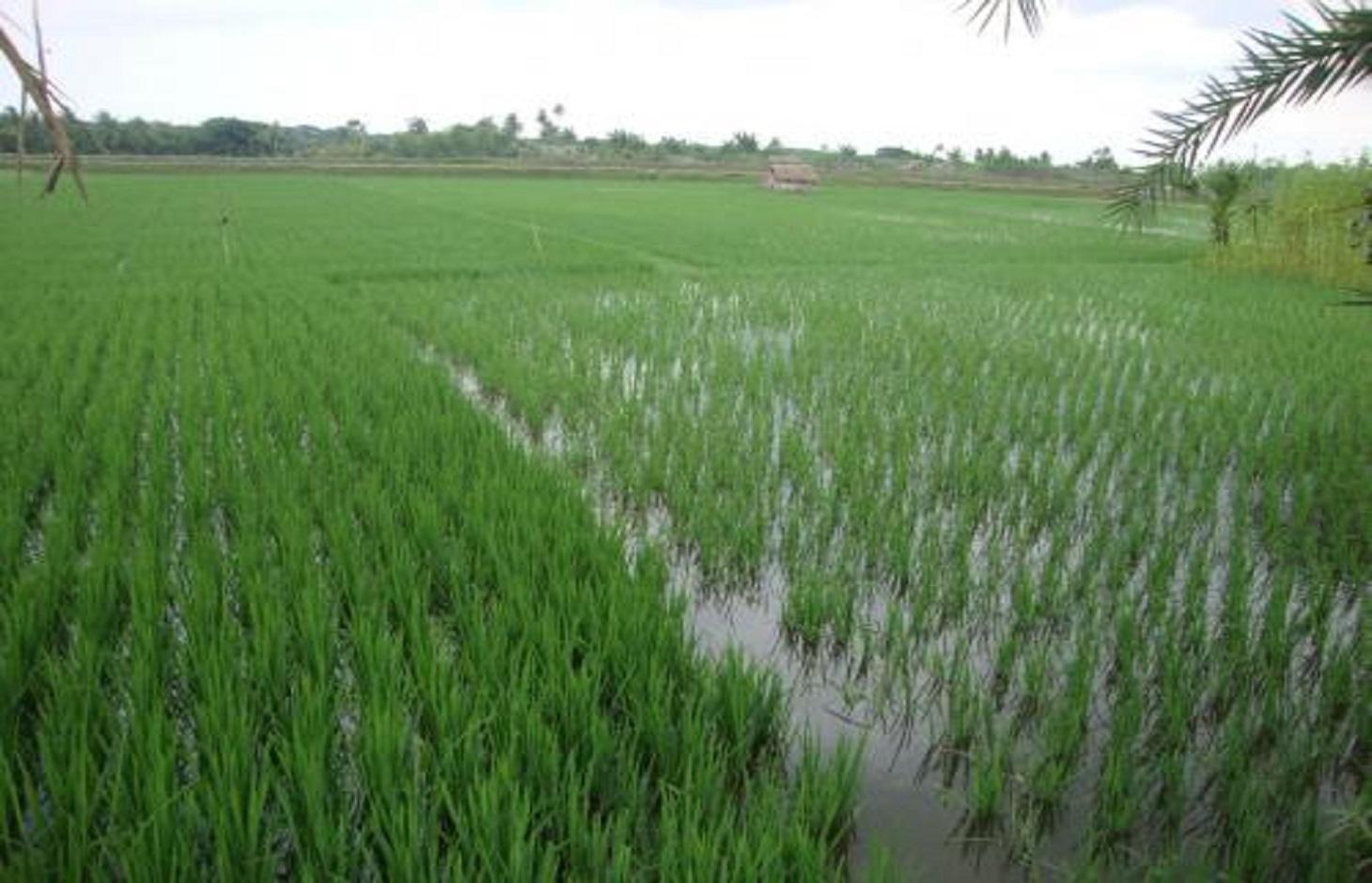
Gher (shrimp cultivation) boundary usage for multiple cropping.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
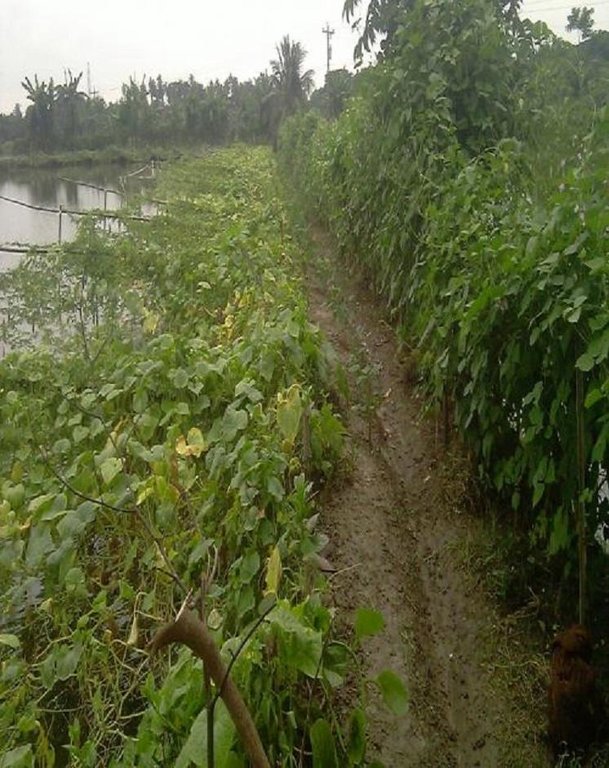
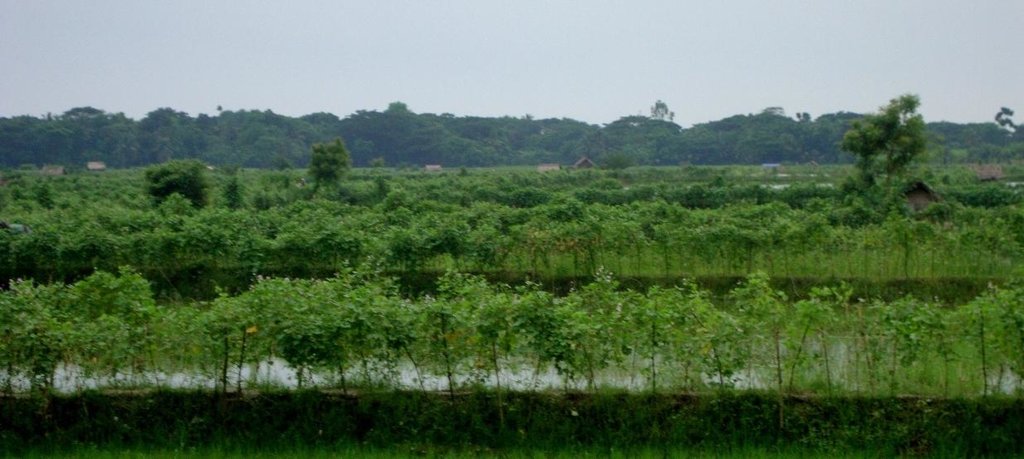
Gher is a local word used for shrimp cultivation plot. The boundaries of these ghers are nowadays raised and maintained to grow vegetables, fruits and also some tree species. In this case the boundary of the plot is raised at least 3 feet with grest width 1 feet plus depending on the height of the boundary (Bund/dyke). Within the gher the land is used for both sweet water prawn (Golda) or saline water prawn (Bagda) with other different types of fishes (locally called Sada Mach) if suitable depending on the salinity of water. Some of the gher lands are used for transplanted Aman with shrimp/fishes.
Farmers dug a ditch along the boundary or in any corner of the field or at the center of the plot to preserve water and fishes during the dry season. In some of the cases the farmers used shallow tube well water to sustain the fishes. In non-to slightly saline areas they used it even for boro (winter rice).
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is a boundary which is used for various types of crops, including year round vegetables and land for rice and fishes including shrimps.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The boundary is constructed above flood level (2-3 feet), the width is approx. 2-3 feet, the ditches are 2-3 feet deep along the boundary or at the corner or at the center.
To grow vegetables farmers used nylon nets for creeping supported by the bamboo or Dhaincha or strings.
Top soils kept on top of the bunds to avoid relatively less fertile soil on the bunds.
Main inputs are seeds of vegetables, nets, bamboo, strings, fingerlings of fish etc.
Natural / human environment: The salinity of the soils from the bunds is washed away by rainwater, which facilitates vegetable production: Rain water desolves salt and moves to the bottom of the bund, and soil becomes non-saline or slightly saline where vegetable could be grown.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bangladesh
Região/Estado/Província:
Bangladesh Southern region
Especificação adicional de localização:
Khulna
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Cropland and aquaculture
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water salinity during dry season; tidal surge; cyclones
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water salinity; tidal surge; sidre (name of a cyclone)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Gher use is very much variable. The main issue of using land is to adapt soil and water salinity. Some ghers are used for only shrimp, some are mixed with other fishes, some are mixed with transplanted Aman. But the boundary/bunds are used for year round vegetables, Banana, fruits (Kul, Guava, Mango) etc.
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Mixed: Mo: Other
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 160; Longest growing period from month to month: July to Sept
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- apicultura, aquacultura, avicultura, cunicultura, sericicultura, etc.
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
Gher (Shrimp cultivation) boundary used for multiple crops; vegetables, fruits, tree etc in southern coastal region of Bangladesh.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Salinization: salination of top soil is due to saline ground water coming in shallow depth), Salinization (The area under this issue is in coastal zone. Conflict of land use is prominent. The lands became saline as other stakeholders keep saline water for other uses (salt production, shrimp))
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
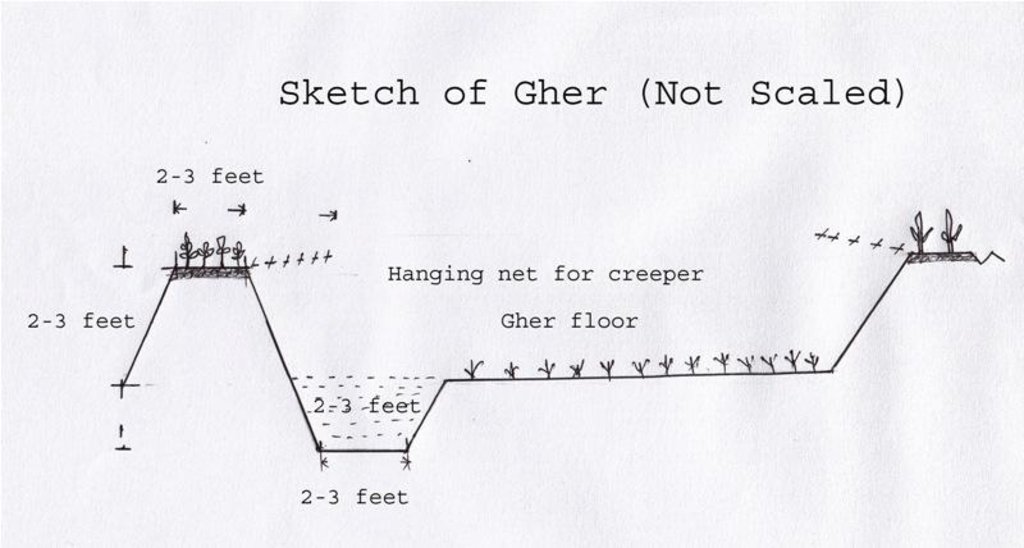
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The gher boundary is raised approximately 2-3 feet with a crest of 2-3 feet. A ditch also dug to store water and fish during dry season.
Location: Dumuria. Khulna
Date: 03-09-13
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It is only land manipulation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Previously farmer did not put the top soil on the top of the bunds. That impedes crop production on bunds.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Decrease of soil salinity, Increase of options for growing more crops
Agronomic measure: Top soil kept on top
Structural measure: Bunds
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-50
Construction material (earth): Bunds are raised by piling earth
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Bunds are used for year round cropping
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Taka
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
79,0
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | Estrutural | Nov-Dec |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | ha | 10,0 | 65,0 | 650,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 2,0 | 300,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Watch and ward | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Seeds, nets etc | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1605,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | Agronômico | July/Nov |
| 2. | Cultural practices | Agronômico | Aug-Oct/Dec-March |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 20,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Piling earth to construct gher bunds
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Availability of labour
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Most of the rainfall experienced in rainy season
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Coastal plain, narrow ridge with broad flat basin
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women casually worked during harvesting vegetables
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
70% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Power triller on hire.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
15-50 ha: Mainly owner of lands of this area
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Desalinized soil of the bund
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
Cash from vegetables
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Conflicts to use water resource
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Growing and marketing of year round vegetables help the farmer to get cash money throughout the year. That improves their livelihood and access to health care, education etc.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Ghers are ponded and no water can be drained
Solo
Salinidade
Comentários/especificar:
+ Soil salinity reduced as washed by rainwater -> found in soils of Gher bunds
- Due to ground water abstraction -> found in coastal regions, increasing trend
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Comentários:
Salinity is washed out from the bund by rainwater. Consequently year round vegetable can be grown on bunds of the gher besides fish in the main land or transplanted rice (depending on the salinity of soil and water and choice of farmers).
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Comentários:
Long term benefit is yet to be observed
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Leased land users are not capable to adopt the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Growing more crops will benefit the farmer with more return. As of now marketing of the goods are facilitated by local small entrepreneurs. Most of them have poor linkage with broader markets. How can they be sustained / enhanced? These entrepreneurs could be appropriately linked with bigger one at regional levels (Upazila/ Districts). At the same time road net works are to be alleviated to facilitate access of transport to carry farmers good with all securities. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Land could be used as farmers are managing themselves How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain production and produce such as vegetables and fishes deserve uninterrupted marketing linkage essential. |
|
Changes in land management by the farmer to grow multiple crops indeed scale up their economy than before. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain the farming system good variety and quality seeds supply will enhance the scenario. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Water management of the areas became critical, specially sweet water | Good water management system is to be introduced through local and regional planning. |
| Conflicts of land uses are prominent. | Social awareness and concept of land zoning seems to be essentials at all levels. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Due to construction or rearrangement of field bunds (Dykes) almost all drainages ways blocked. Consequently the whole area became water logged. This situation will definitely aggravate soil quality, environment and ultimate ecosystem | Community approach to manage the landscape will be effective. In this regard local administration and community leaders can play a vital role. |
| Soils of Gher boundaries (Dykes) are subject to erosion when exposed to rain water. | Good cover crops and management are necessary to protect soils from erosion. At same time farmers may be trained on this issue. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos