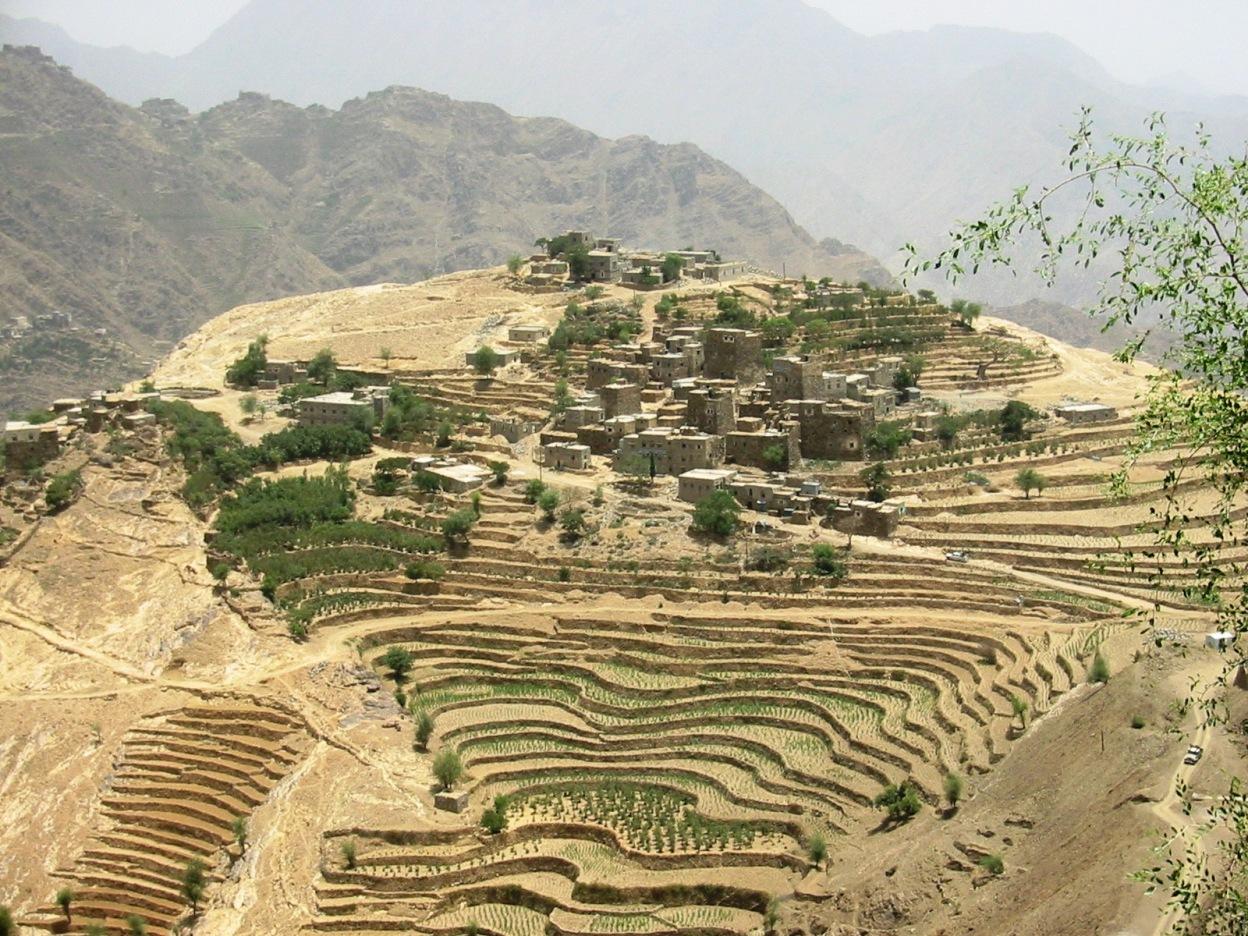
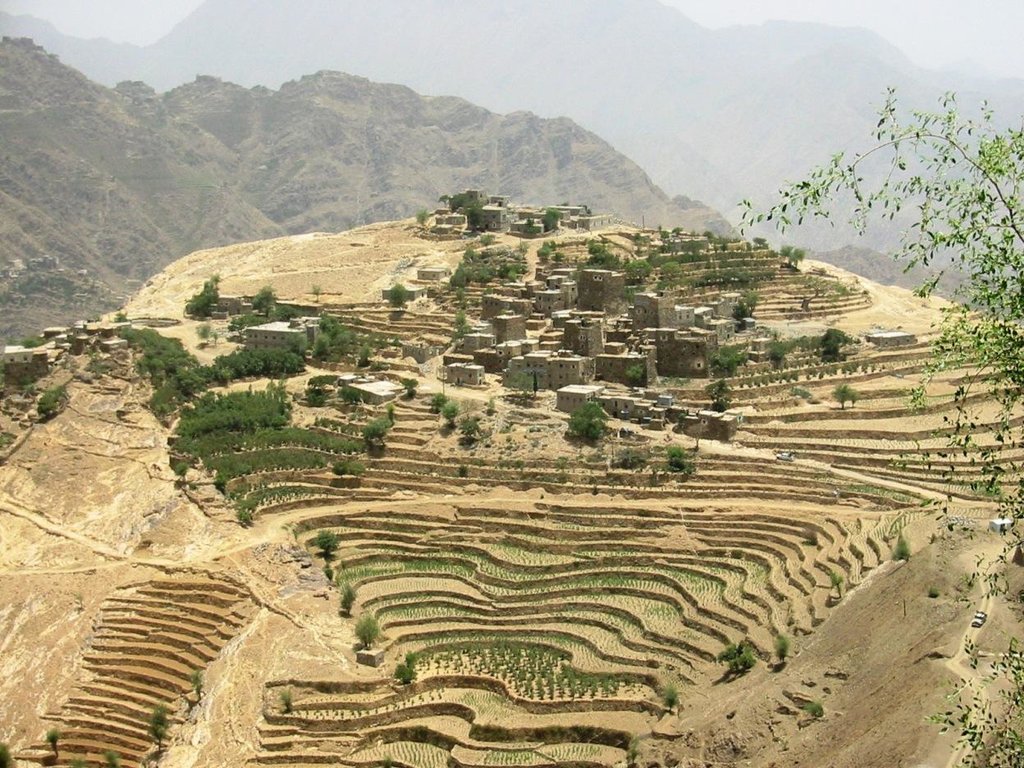
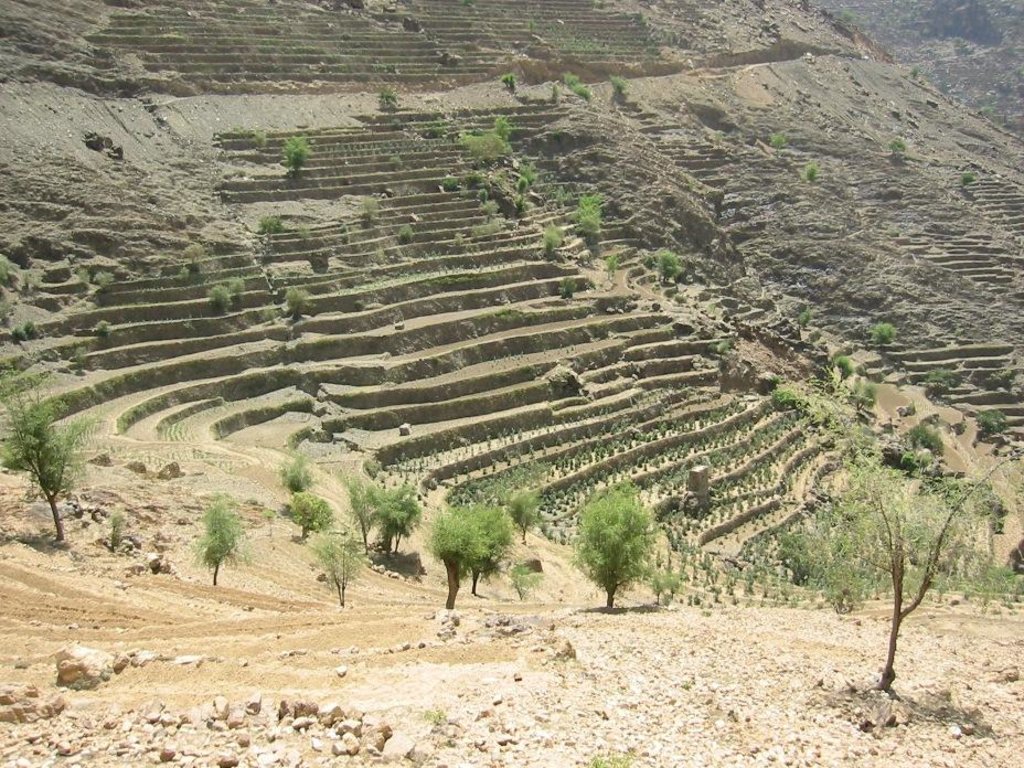
Flat Contour Terraces [Iêmen]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ahmed algalal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
المدرجات الكنتورية
technologies_1174 - Iêmen
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Sallam Ahmed
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority
Iêmen
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - Iêmen1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
07/02/2013
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST
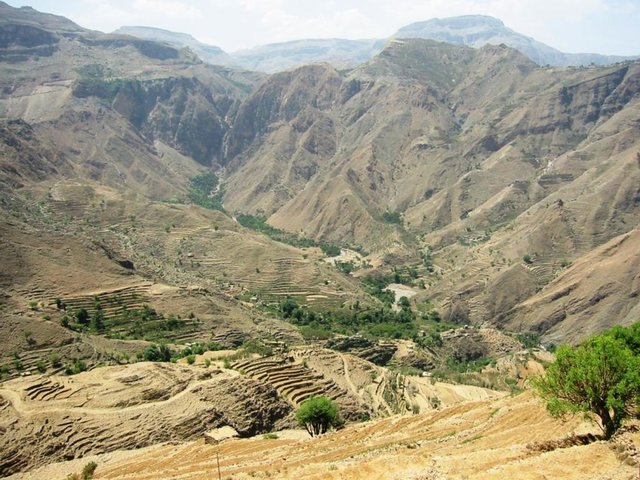

leveled mountain terraces [Iêmen]
organized collective action at a high pace for building agricultural terraces to improve livelihoods in resource-scarce regions in the ground
- Compilador/a: ahmed algalal
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Old flat terraces were built in accordance with the contour lines and surrounded by stones to create a suitable environment for the growth of crops, slope stabilization and reduce the risk of runoff and increasing water harvesting.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Yemeni farmer challenged the nature cruel and adopted to cope with the needs and requirements, including the construction of agricultural terraces utilizing all the resources available in the region, where he worked first on the extraction of soil located on the slopes of the mountains and booked by building a wall of stones around where were collected and brought stones from different places. Walls were built in very geometric creativity very well designed so that they work to minimize the risk of soil erosion and increase the use of water runoff without damages to the established terraces so through the construction of terraces along contour lines and making outlets in each terrace to drain excess water.
The process of building terraces using stones according to the contours, which works to prevent soil erosion and erosion, as well as help to increase soil moisture as a result harvest runoff, which leads to meet the needs of crop water and thereby increase production.
The main objective of building terraces is to increase production. The soil depth at the beginning of the establishment of the stands to be very shallow and increasing soil depth as a result of increasing deposits the soil.This process is booked by increasing the height of the wall that range between 1-3 meters, and a width runway between 1-6 meters As for the length of the runway It is 5 - 80 meters according to the contour line, which runs on reserve deposits and protect the soil from erosion.. Finally terraces are planted with annual crops mainly cereals crops, as well as perennial trees such as coffee, diamond, Qat and other perennial trees.
The terraces of the projects long-term where you need a long time to build due to the use of hands in the construction process as a result you cannot use the mechanisms, for maintenance operations in view of the building stands on the regions of steep and where the rate of runoff high result of heavy rains in a short time in addition to Regression factor that leads to increase the speed of the flow of water, which operate on a cliff erosion terraces in the event of lack of maintenance, which makes the process of ongoing maintenance is an urgent need to ensure the preservation and sustainability of the stands.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Iêmen
Região/Estado/Província:
Hajah Governorate
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kahlan Afar
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
too old since approximately 2000 BC
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Coffee and Qat
major food crop: Corn, wheat, barley, lentils and beans
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe slopes that works to increase the speed of runoff, which leads to soil loss
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 240
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5.4 km2.
The study area is located in the south west of Fort Kahlan Afar and stretches along the projected water severe slope, and include seven villages spreading from the highest peak of the mountain until the bottom of the valley respectively: Bait guardian, Al Qimmeh, Bait Al Farawi, Al-ubal, Fara'ah, Bani Bram , Wadi (Valley) EabrHajr.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour tillage
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (severe rainfall in a short time), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (severe slopes)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts (As a result of the fluctuation of rainfall), poverty / wealth (Poverty)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
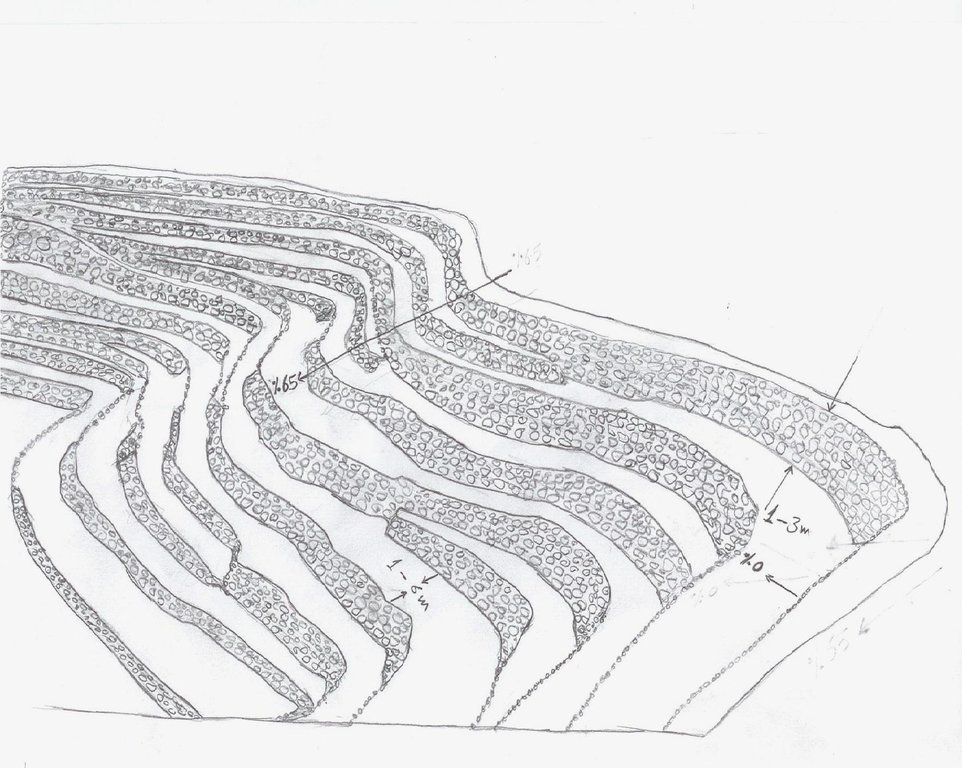
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
terraces built along contour lines
Location: Hajah Governorate. Kahlan Afer
Date: 10-2-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (does not have only a little experience)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Has enough experience)
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction surface runoff
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, water spreading
Contour tillage
Material/ species: agricultural tools, animal traction
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1 - 3
Spacing between structures (m): 1 - 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5 - 80
Construction material (earth): Collecting soil and reserve deposits to increase the soil depth
Construction material (stone): Stones available in the region
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 65%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
7.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Extraction of soil | Estrutural | Before the rainy season |
| 2. | Collecting stones | Estrutural | Before the rainy season |
| 3. | Build a wall to establish a terrace | Estrutural | Before the rainy season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Extraction of soil | ha | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Collecting stones | ha | 1,0 | 1162,8 | 1162,8 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Build a wall to establish a terrace | ha | 1,0 | 558,0 | 558,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 46,5 | 46,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 186,0 | 186,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 4453,3 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | plowing along contour lines | Agronômico | Before planting |
| 2. | Repairing damaged walls | Estrutural | annually after the rain |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Plowing along contour lines | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Repairing damaged walls | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 18,6 | 18,6 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 248,6 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel, local plow and a leveler, Shovel, Big hammer
calculated costs an average length of 60 meters along the wall stone and rising 2.5 meters. other operations were calculated per hectare considering that the land users who will carry the implemented works. with respect to maintenance has been calculated taking into account the fact that the stands terraces are considered investments long term and not subject to erosion annually, but in the event of a severe rain storm.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Collecting and transporting stones
Severe slopes
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: 30-80%
Altitudinal zone: 1600- 2700 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): Silty Clay loam
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: physically women to carry hard work, so the man who does the work on the farm and women are household.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
65% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
The average land tenure of between 0.5 - 2 hectares
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
- Waqf
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Waqf
Comentários:
There are three types of land ownership owned, hired and Waqf by 74%, 19%, 7%, respectively.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
As a result of the infiltration process
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Oportunidades culturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Comentários/especificar:
reduction of sediments
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
994 households covering 100 percent of stated area
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
994 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: because the technology is adopted in the whole Yemen, but there is difficulty with regard to the sustainability of technical maintenance due to lack of financial resources and poverty which leads to migration and lack of interest in the land
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Creating a suitable environment for the growth of various crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue the process of maintenance to maintain walls and outlets |
|
Water harvesting to increase soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance of water outlet constantly ensure that no water erosion by allowing excess water to drain out through the outlets. |
|
reduce runoff and Prevention of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? ongoing maintenance of outlets. |
|
discharge excess water in a systematic manner How can they be sustained / enhanced? ongoing maintenance of water exits |
|
reduce the length and angle of the slope How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining the terraces |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Low productivity in the first years of the Created stands terraces due to poor soil fertility and lack of depth | apply fertilizer and chemical and organic fertilizers |
| In the event of very heavy rain may be susceptible to erosion terraces | ongoing maintenance of the waterways and channels to ensure that no diversion of water to areas prone to erosion and maintenance of the walls of the terraces and drain excess water. |
| Due to the construction of terraces on the hillsides with steep slopes, which makes it difficult to use farm machinery and agricultural work is done by hand, which requires many labor somewhat | the search for new technologies that fit this purpose |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Mountain terraces study in the Kahlan Afar region (Mashreqi, et, al 2003)- 44. General Census of Population, Housing and Establishment (Census, 2004).- 45. Guide of agricultural climate in Yemen (Al Khorasani, 2005).
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA Central Bureau of Statistics.Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

leveled mountain terraces [Iêmen]
organized collective action at a high pace for building agricultural terraces to improve livelihoods in resource-scarce regions in the ground
- Compilador/a: ahmed algalal
Módulos
Não há módulos