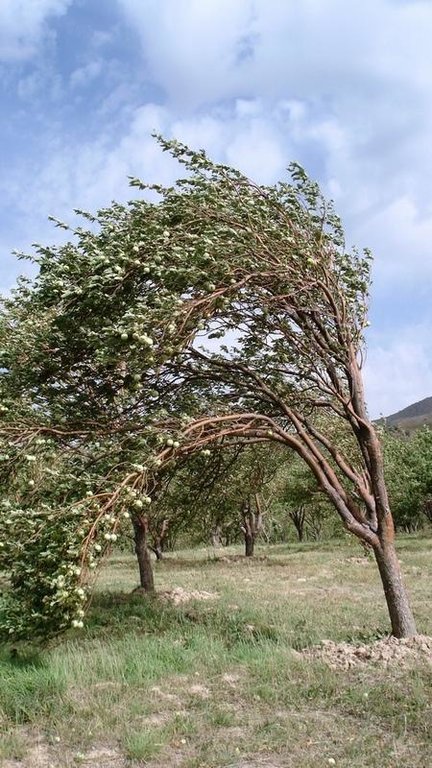
Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Christian Wirz
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Зина бох (tajik for terrace garden)
technologies_1406 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/08/2008
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tajiquistão]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilador/a: Christian Wirz
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Fruit- and nut-trees give the production system the characteristics of an orchard, whereas sour cherry trees rather provide for a jungle atmosphere. They spread very quickly once they are planted. Hayproduction substitutes other uses of the lowest vegetation layer, since grazing is forbidden. The whole territory is concipied as a research station.
Purpose of the Technology: In general trees act against erosion: By their stabilising function they prevent soil from being washed out. Especially nut-trees with their 20 to 25 m long roots preserve soil moisture and by that consolidate soil structure. Terraces contribute to this moisture-preserving and production-enhancing function. They are very important in order to make rather steep land exploitable by reducing slope. Haymaking does not damage soils, but is only allowed after the end of June so that grasses can reproduce before.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Both the establishment of terraces and the planting of trees on such a big surface are costly in terms of labour and money. Maintenance means taking care of trees, taking measures against diseases and conserving soil fertility. Fertilisers are very costly and therefore dung has been substituting them in the last years.
Natural / human environment: From the two research stations of the orchard institute - one in the upper hill-zone and one close to the village Karsang - only the second one is assessed. This area is surrounded by two rivers in the West and in the East, with its main exposition to the South. It is in direct competition for irrigation water, especially needed for the trees, with the village. The orchard is situated on a ridge that is in the haymaking area, but is accessible for animals from the village.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Region of Republican Subordination
Especificação adicional de localização:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
1961 the national orchard institute began with developing a research area in Karsang, which should be further enlarged from 1975 onward.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
Access for livestock forbidden.
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problems are arid conditions and the loss of fertility, mainly by processes of water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gully erosion by water and wind erosion together with droughts are the main problems. Gullly erosion may also be caused by
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Access for livestock forbidden.
Grazingland comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
Type of grazing system comments: People have goats, sheep and cows and 1-2 donkeys, if they can afford.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: post-flooding
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 270 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jul
Densidade animal (se relevante):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Of the 70 hectares nearly half of the surface can be considered as unproductive with protective functions against erosion (many sour cherry trees planted).
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
- Pi: selagem do solo

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (According to agronomist and elderly persons steady decrease of rainfall Causing aridification..), droughts (No considerable precipitation for one and a half years. Causing compaction, crusting and aridification.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (The lack of fertilisers and other inputs is a consequence of the breakdown of URSS.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Causing gully erosion and loss of topsoil by water.), war and conflicts (Many trees were chopped illegally during war to have energy (charcoal mines were occupied by armed men)), Unsuitable soils especially in the upper part (loe (Causing compaction, crusting and loss of topsoil by wind.), Steep topography with high sun inclination angle (Causing compaction.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
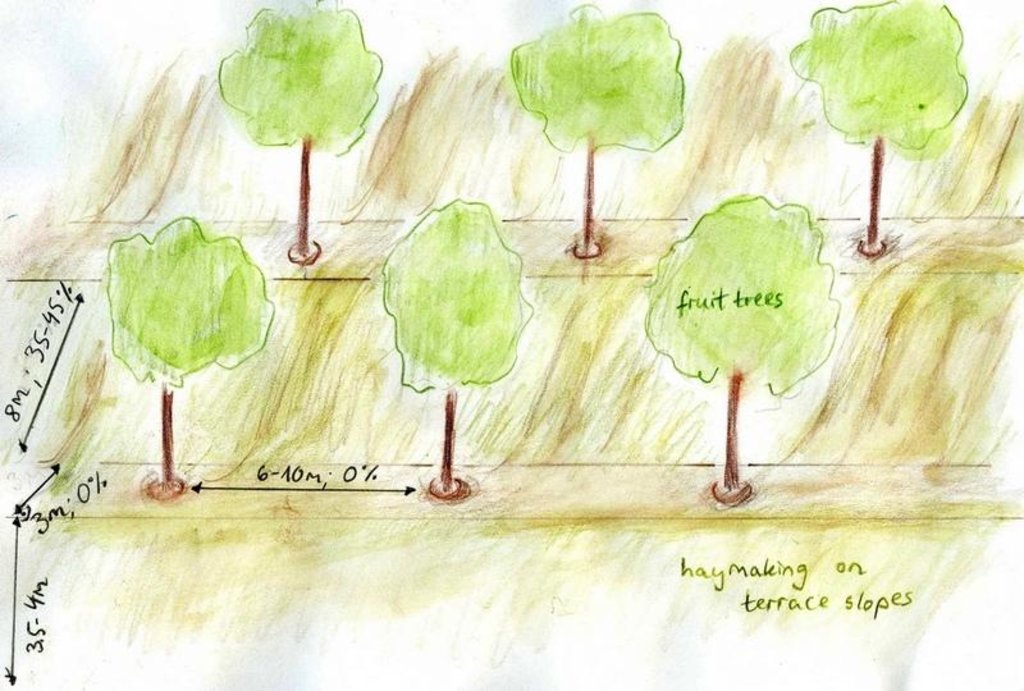
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Terraces with fruit trees.
Location: Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Cutting trees and maintaining tree nurseries)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Fieldwork such as haymaking)
Technical knowledge required for Research coordinator: high (Carrying out of workshops)
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, trees protect from snow
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Apple, apricot, almond, walnut, quince, pear, peach trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Sour cherries, mostly through vegetative growth
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Terrace: bench level (earth)
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 11
Construction material (earth): endogenous material used
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 33-45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Strictly regulated haymaking, only after the end of June.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
0.70
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of trees with provenance from Russia and Ukraine | Vegetativo | Tree plants |
| 2. | Tree-planting, grafting, giving dung | Vegetativo | 20 persons for 3 years |
| 3. | Terrace establishment | Estrutural | 2 tractor drivers for 1 year |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting | ha | 1,0 | 714,0 | 714,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Outros | Terrace establishment | ha | 1,0 | 614,0 | 614,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1428,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
research stations of the orchard institute
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Yearly replacement of fruit-trees (10-15% per year) | Vegetativo | 10 persons plus brigadier, always employed |
| 2. | Aerating soils around trees, each spring | Vegetativo | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 3. | Applying animal dung and / or fertilisers | Vegetativo | 10 workers, fix employment |
| 4. | Seasonal workers for harvesting | Vegetativo | 10 workers, additionally |
| 5. | Planning of activities | Vegetativo | 1 director |
| 6. | Haymaking | Gestão | 1 month |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance | ha | 1,0 | 93,0 | 93,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 121,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The data on the establishment of the orchard are an estimation of the director. The recurrent costs are based on the director's and other person's declarations and are rather a rough estimation than a precise list of the costs.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The costs today are strongly determinated by labour input, whereas during establishment and till the end of USSR costs for pesticides, fertilisers, new trees and equipment were very high.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
In the long-term average, 600-650 l, but in the years 2007 / 2008 only 200 l, since no rains in autumn.
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zonation: The orchard is located between 1300-1500 m.
Landforms ridges: A part of the area surrounds a ridge
Landforms hill slopes: Generally slopes are of moderate steepness.
Slopes on average gentle: The terraces themselves are quite flat.
Slopes on average hilly: A great share of the area are slopes, either natural ones or from terraces.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average shallow: In the higher part stony soils prevail.
Soil fertility low: When gypsum and loess soils.
Soil fertility medium: In the lower part soils with little humus.
Soil drainage / infiltration good: 3-4 m infiltration capacity.
Soil water storage capacity medium: Thanks to trees not low.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Insufficient: only permitting to irrigate 5 ha of totally 30 ha classified as "irrigated cropland"
Water quality (untreated): According to expert, water contains iodine, but is otherwise "light" and clean, without calcium carbonate
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Typical plants of the foothills can be found in the area.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (all smallholders owning additional income by the work for the institute).
Off-farm income specification: Nearly all people have family members (mostly sons) in Russia, who send remittances.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The employees produce hay on maximally 7 ha.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Whereas land use rights are restricted to those employed by the research institute, water use is negotiated between the research institute and the village authorities.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The reason is the decision not to plant wheat anymore, partly because of droughts and partly because of the trees having reached a critical height (shadow).
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Animals eating this fodder give more milk.
Produção de madeira
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
On the neighbour-ridge no irrigation water.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Trees require more water than simple pastures, especially in the establishment period.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Especially fruit production is important, to make jams, dried fruits etc. for winter.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
The milk is of better quality and leads to less sicknesses
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
The institue is in conflict with the village for irrigation water.
Open-access pasture-area
Comentários/especificar:
No strong effect, because it is a research territory.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Is especially a function of cover and infiltration capacity
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Plants are greener and less dusty thanks to moisture
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Plants are taller, wider and denser.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Thanks to strongly reduced erosion, organic matter is conserved
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Less crusting than without technology, but more than without droughts.
Salinidade
Comentários/especificar:
Due to lacking drainage system
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
More nutrients given, for example by the trees' leaves.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
More than 50 pasture species
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Risco de incêndio
Comentários/especificar:
Forest administration considers the proportion of trees to be one of the decisive factors of fire-risk.
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
High proportion of trees leads to longer snow cover and thus soil protection in spring
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
No damages by heavy rainfall in the orchard, whereas next to it there is damage. Especially winds cause damages by covering vegetation with dust and impeding them from making fotothynthesis. Plants can die therefore.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government wants more people to adopt the technology and their has effectively been an increase of such initiatives over the last years.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tajiquistão]
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
- Compilador/a: Christian Wirz
Módulos
Não há módulos