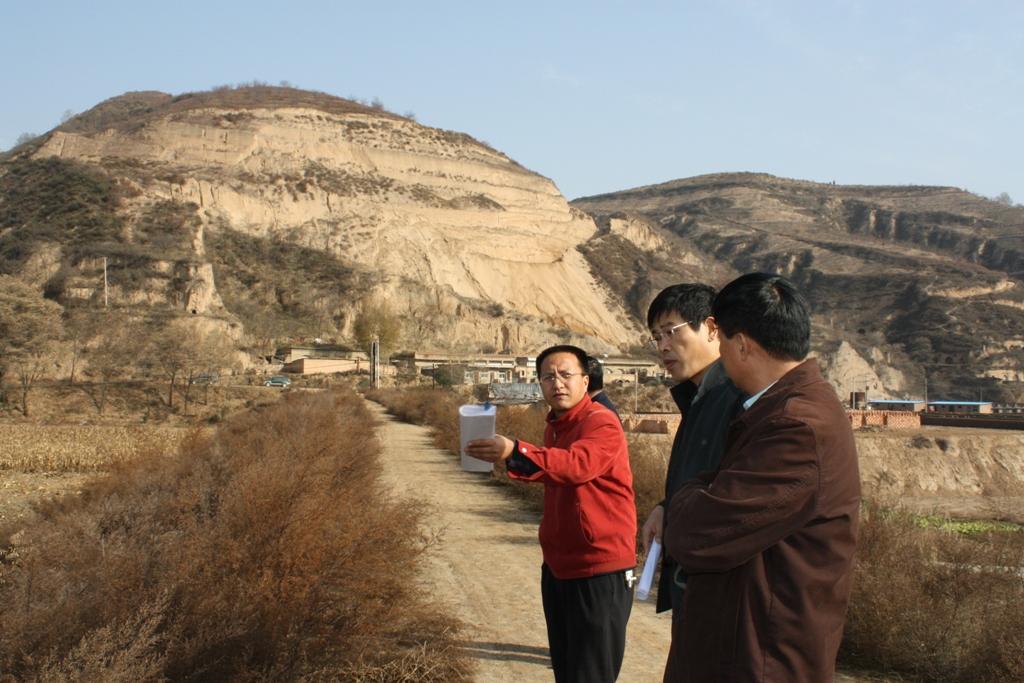
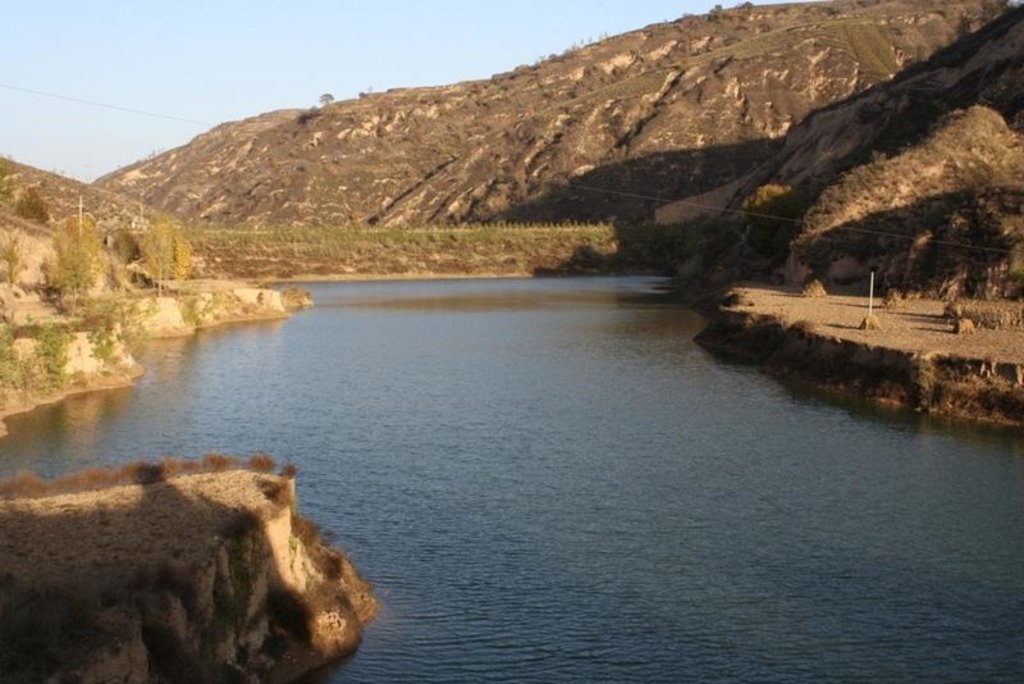
Check dam for land [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Fei WANG
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
淤地坝,谷坊
technologies_1455 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Mu Xingming
xmmu@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista em GST:
Wen Zhongmin
zmwen@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Chen Yun-ming
ymchen@ms.iswc.ac.cn
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - China1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
20/12/2008
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST
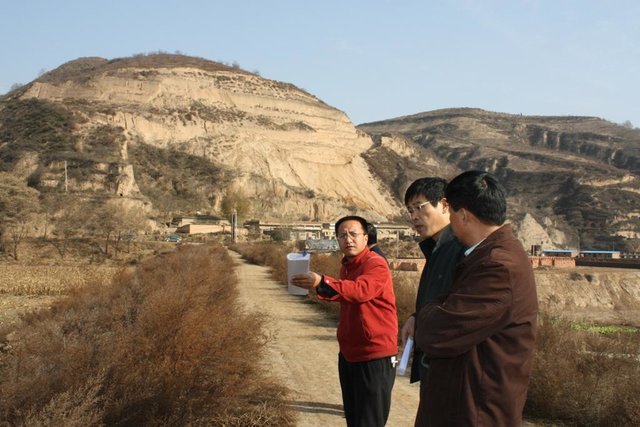

Project of check-dam for land [China]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilador/a: Fei WANG
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are imporved.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The check dam is a small dam designed to reduce flow velocity, control soil erosion, and allow to settle on the bed of the valley. The whole system includes main body of dam, spillway, overflow and supporting measures. The check dam for land is a small dam mainly for land after it is filled up by the sediment from upstream area, from several years to 20 years in common, it could be flat land in the valley, not mainly for water collection (different from reservior).
Purpose of the Technology: Check dams in the Loess Plateau are very common. There are many advantages. The check dam could not only reduce the erosion of the gullies, furthermore it retain the sediment in the flow and this decreases the sediment of the Yellow River. The check dam is good quality land for the soils because of the sedimentation of organic matter and other nutrients from topsoil . In this region soils are deep and very fertile because most soil is from the top soil upstream. The soil moisture of check dam is also much better than in any other places in the watershed because the flood should go away from its surface and the water inflitration is great in raining seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment needs enough money because it has to be safe enough, and the maintenance cost is not so high. The catchment with great soil erosion is better when we considered the formation time of land.
Natural / human environment: The controlling area of check dam for land varies greatly from 30 square km or more. Since the "Grain for Green" Project of China in 1999, the soil erosion on the slope decreased. The time from reservoir to land need more time because there is less and less sediment from upstream and the sedimentation changed slowly.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Shaanxi Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Yanhe River Basin
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Only one check-dam for land is listed here.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is an old methodology in the Loess Plateau. Since 2003, the check dam had been determined as "Highlight Project " of the Ministry of Water Resources in order to expand in the whole area of the Yellow River Basin.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Silvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
major cash crop: beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
major food crop: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crop: vegetable

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Lagos, represas
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Normally, the bed of valley is V-shaped and is covered by grass and trees. For the seasonal torrent or flash, it is very difficult to plant crops. The gully also cuts down by runoff and extends because of erosion's gravity .
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It can not be used as agricultural purpose, especially to get more food.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 19.4 m2.
The total area with different measures is almost 2000 km2 . Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is situated in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is broken seriously. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776 million tons, and the sediment flow modulus accounting for 8,100 t•km-2•yr-1. The coarse sediment (sediment particle diameter not less than 0.05 mm) flow modulus is 2,430 t•km-2•yr-1 on the Ganguyi Hydrology Station.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It is the reason of erosion that influence the valley.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
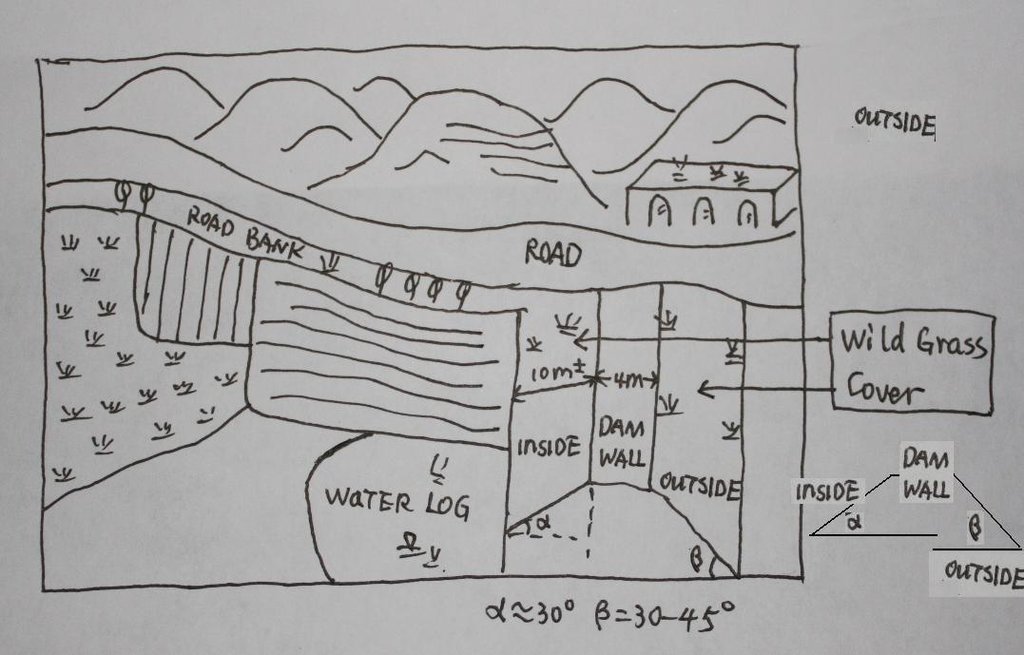
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The check dam land.
Location: Mazhuang Watershed. Baota County, Yan'an City, Shaanxi China
Date: 2008-10-20
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The design and construction need professional knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (it is easy to use, like alluvial land or wide terrace.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Spillway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 10
Spacing between structures (m): 100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-100
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300-1000
Construction material (earth): The earth-bank dam is built in Yanhe River Basin.
Construction material (stone): to build the spillways
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2-5%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 180000m3
Catchment area: 58.3km2m2
Slope of dam wall inside: 30%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 60%
Dimensions of spillways: 3m
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
-2,17
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
8.80
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field survey and location selection | Estrutural | Before design |
| 2. | Design | Estrutural | before construction |
| 3. | Build the dam wall | Estrutural | |
| 4. | Check and accept | Estrutural | After the construction |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Building the wall/ field survey and planning | Person/day | 180,0 | 8,8 | 1584,0 | 90,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Building the wall/ field survey | Machine/hrs | 75,0 | 43,8 | 3285,0 | |
| Material de construção | Stone | m^3 | 40,0 | 26,35 | 1054,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 5923,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | check the dam wall | Estrutural | annually |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | check annualy the dam wall | Person/day | 15,0 | 8,8 | 132,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 132,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: crawler type bulldozer, giant jet, tractor, traditional tools, ruler,
The grass on both sides of check wall is natural grass.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The wide of dam wall affects the cost greatly, the wider, more expensive.The labour cost and the distance of rock quarry are also important.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours
It is based on the classification sysytem only based on the rainfall.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: All check dam and check dam liand here is in such altitudinal zonation.
Slopes on average: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: The depth of Loess varies from nearly 30 m to more than 100 m in Yanhe River Basin. The depth of soil is less than this but it could be nearly 10 meters in commom.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle which are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM
Topsoil organic matter: <0.5%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration in Loess is very fast, but it prones to sealing when flashing
Soil water storage capacity low: Evaporation and drainage are easy
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water also poor/ none and: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal rivers
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region
Water quality (untreated): Good quality for there are few pollution sources
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
It is very stable in this region
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(The Check dam for land are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national sub).
Level of mechanization also manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: Tillage with machine in large area check-dam land.
Market orientation of production system mixed: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
According to 0.054 ha per capita
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
Like other rural areas in China
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
600
Quantidade posterior à GST:
6000
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4500kg/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2500kg/ha
Comentários/especificar:
In extreme year with great rainfall, low yield of check dam land
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
950
Quantidade posterior à GST:
59
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições nacionais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
200 kg
Quantidade posterior à GST:
350 kg
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Quantidade anterior à GST:
8 m
Quantidade posterior à GST:
4-6m
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
12-16%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16-22%
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60t/ha/yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5t/ha/yr
Outros impactos ecológicos
long time period to form land
Comentários/especificar:
Sediment from slope decelerate the process of building arable land. In other words the economic function can not appear soon.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2events/yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
nearly no
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
The better condition of soil and water of check dam land improves the capacity of land tp cope with the changing climate.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
In the first stage, there is no economic output but the check dam is going to fill up with sediments. Afterwards the check dam forms land and with it benefit which would keep up a long time.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 10-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
675 households in an area of 19.4 km^2 (11 percent of the area)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
675 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All the lands (cropland on the slope or check dam land and forest et al, ) are shared evenly by people. Of course, the work like to build check dam should be finished by all the families.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No single farmer or family can finish this work because the land right and great investment.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more local farmers want to get more check dam land for its long-term benefits.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The yield of check dam land is much higher than that on the slope land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the local people to do more work without payment because they would get more benefits from this land as such. |
|
The yield is stable because the soil moisture is good even in dry year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use the land efficient and mainten it. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It could reduce the soil erosion originated from the gully. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The local people know this benefit that make them try to find chance to build check dam. |
|
The dam can retain the flow and sediment and reduces the sediment delivery of the downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the people or government of the lower reaches to combat soil erosion through the building of check dams. |
|
The check dam land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
|
Land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the awareness of local people to use this technology. |
|
The ceck dam can be used as rural road. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It is too expensive to build the check dam. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams.The local people can work together without payment. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The land in a check dam with less and less soil erosion on the slope, needs longer time to form | It is difficult to overcome this because the control of erosion on slope has higher priority. We can find how to use the water or the temporary wetland. |
| The input of check dam is quite high. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams. The local people can work together without payment. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Project of check-dam for land [China]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- Compilador/a: Fei WANG
Módulos
Não há módulos