Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Табдил додани чарохгох ба бог
technologies_1520 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation: 20 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
- Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation: 20 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation: 22 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation: 15 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - QuirguizistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
16/03/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Planting fruit tree orchards to increase the stability of the steep loess soil slopes.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
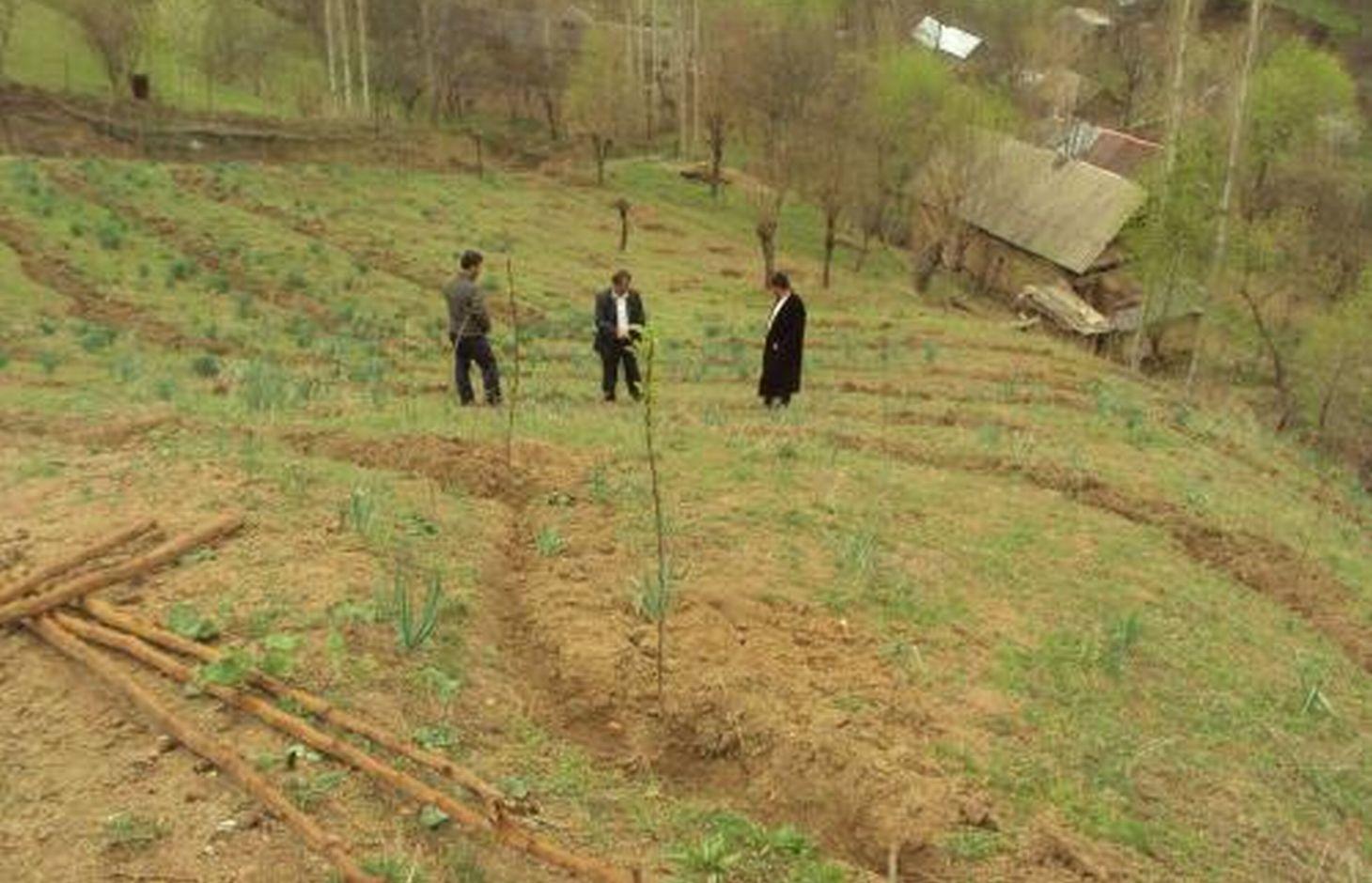
This technology involved the planting of several varieties of native fruit trees to help stabilise steep loess mountain slopes. Seven species of fruit trees were planted in seven different locations, in two watersheds within the district of Nurobod in Tajikistan. The locations were chosen as a result of a natural disaster workshop that identified the areas most susceptible to landslides.
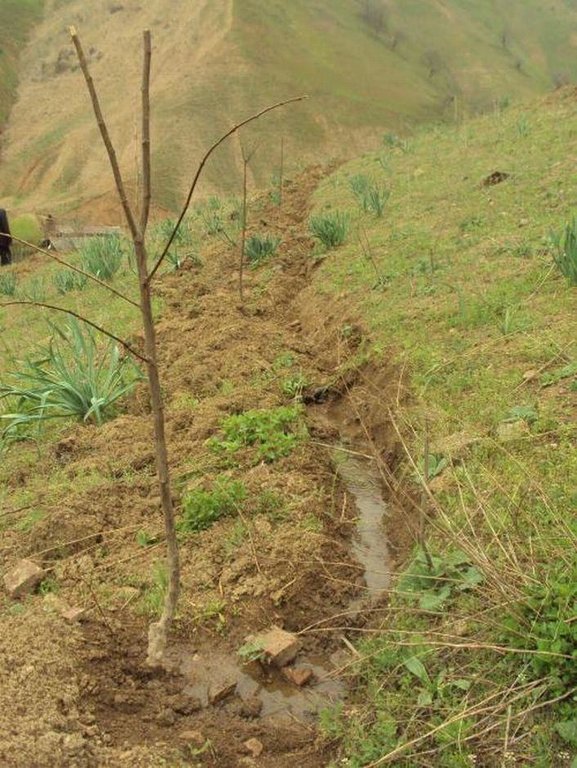
In consultation with the Institute of Horticulture a fruit tree planting scheme was devised and using project money the identified area was enclosed with a wire perimeter fence. The fruit trees were planted along irrigation contours running at shallow angles parallel to the slope.
Purpose of the Technology: The best locations for planting the fruit trees were decided on via a participatory community workshop on natural disaster risk management.
During the workshop the community identified areas around the village that were considered high risk. A fruit tree planting scheme was implemented in these areas to help stabilise the slopes, reduce surface water run off and top soil erosion, and reduce the risk of landslides. As the trees grew they were intercropped with wheat and espercet.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Several 'at risk' areas were identifed within these workshops, therefore the project team had to assess the areas for suitability. Two of the main criteria used included the access to water and if there was sufficient depth of top soil to sustain a fruit orchard.
Once the area was decided upon, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed with the particular land user. It was made clear to the community that the land was chosen based upon the decisions from the workshop and not because of any form of favouritism towards the land user. The MoU stated that the land user was responsible for the planting and maintenance of the orchards.
The Horticultural Institute devised a planting a scheme based upon the loaction and soil type. The implementation activities occurred in early spring. A continuos wire fence was erected around the area, and the fruit trees were planted at five metre intervals along a dug contour irrigation ditch. One kilo of organic fertiliser was applied to each tree and later in the season they were sprayed with pesticides.
Natural / human environment: Nurobod district is a mountainous area, with large tributaries flowing into the Vasht river. There are mass erosion processes at work, causing gullies and washing away the top soil. The previous civil war, compounded by harsh winters resulted in extensive clearance of the surrounding vegetation for fuel. These areas have became further degraded by over grazing on the remaining grass lands.
The local population suffers from high levels of labour migration of young men to Russia and resulting in a drain of knowledge and able bodied workers. This leaves the remaining families particulary vulnerable in this specific climate.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Nurobod
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The project was implemented in 2010.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Fazenda pecuária
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
cows, sheep and goats
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The steep loess slopes are devoid of vegetation, therefore the land is prone to washing away of top soil, gulley formation, and potential landslides.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land has become unuseable, it was used as pasture land but every year it seems to be getting worse.
Ranching: cows, sheep and goats
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 200Longest growing period from month to month: March - October
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1 m2.
The SLM technology was implemented in 7 different locations covering 5 villages within the Mujiharf and Hakimi jamoats of Nurobod District. The two main watersheds are shown in the googleEarth file. The plot sizes varied between 0.5 - 1 H.a.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Any shrubs and bushes previously on the land were removed.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Shrubs and bushes were removed as fodder and for fuel purposes.), war and conflicts (Natural resources became increasingly valuable during the civil war of the 1990's.)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Once the bushes were removed the area was used for grazing.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall events have contributed to the degradation of the land.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
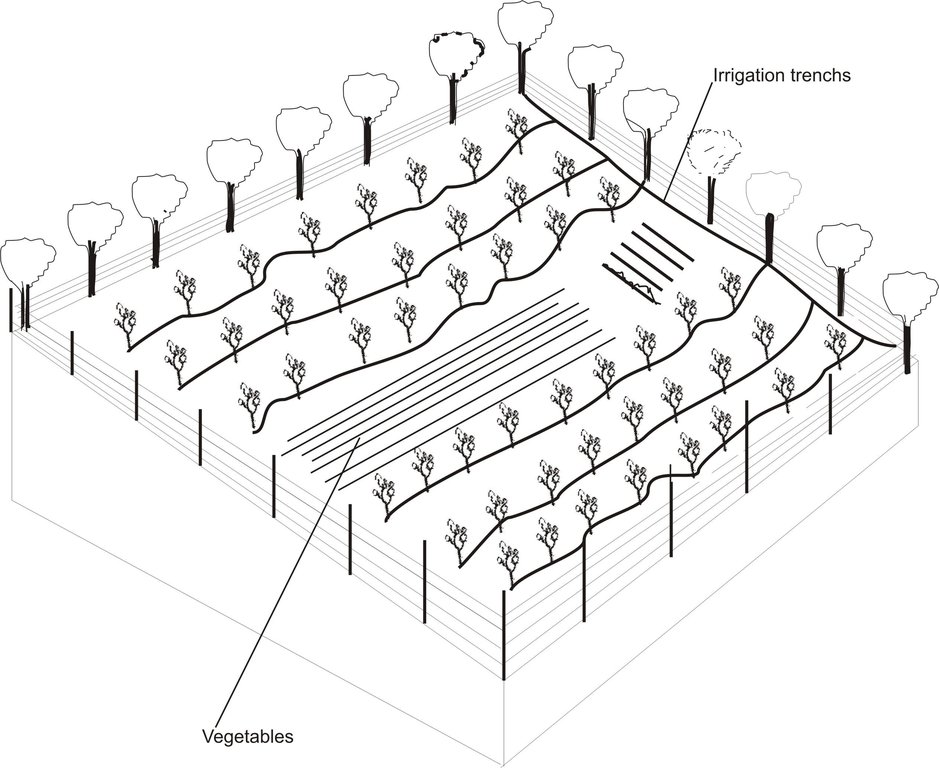
The drawing shows a perimeter fence enclosing terraces of fruit trees. The trees are irrigated through a contour trench running at a shallow angle perpendicular to the slope. The land users have taken the opportunity to optimise the cultivated land by planting perennial and wheat crops between the rows of trees.
Location: Mujiharf. Nurobod, tajikisatn
Date: 22nd June 2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The technology is relatively straight forward and easy to implement.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The land user is responsible for the continued maintenance of the fruit trees.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Cherry, Apple, Quince, Pear, Plum, Peach, Walnut
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2.00%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
somoni
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
25.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Erection of Fence | Vegetativo | Spring - end of march |
| 2. | Planting of fruit trees. | Vegetativo | March / April |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Building fence | Persons/day | 28,0 | 25,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting fruit trees | Persons/day | 40,0 | 25,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | Pieces | 6,0 | 20,0 | 120,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlimgs | pieces | 400,0 | 8,0 | 3200,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | tons | 1,0 | 225,0 | 225,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | 1,0 | |||||
| Material de construção | Metal fence and posts | meter | 400,0 | 12,0 | 4800,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 10045,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Horticulture Institue
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
Costs are per h.a.
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | pruning and tree care | Vegetativo | Annually |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Prunning and tree care | Persons/day | 15,0 | 16,6666667 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 250,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: spades, picks
The costs were calculated at 2010 prices for 400 trees planted over 1 h.a.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The main issue was the procurement of the fruit trees from a reliable credible source. Since the start of the project, land users purchased trees from local tree nurseries but the trees were of poor quality and some already had signs of disease. The scarity of natural resources, and the lack of controlled grazing means that wire fencing had to be used, This could only be purchased outside of the district and thus incurred high transport costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: For the seven plots.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): Silt
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The men were involved with the initial planting of the trees. However the women complete most of the ongoing care and maintenance of the fruit trees,
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most households in this district recieve remittances from abroad.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Low grade pasture land
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
most households in the region have 0.5h.a
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
All land in Tajikistan is owned by the state, user rights are defined here by the local government.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
400 trees planted
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
new products to sell
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
seven varieties of fruits
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
new source of sustainable income
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
New skills in fruit tree cultivation
Comentários/especificar:
The implementation of the technology is supported with training.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
increased fruit production
Estado de saúde
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Community knowledge of fruit tree cultivation
Comentários/especificar:
training provided
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Training on fruit tree cultivation was provided for the community in conjunction with the implementation of the planting of the trees, to help improve the fruit yields in the community and the health of the trees.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
trees absorb the water
Solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
regeneration of the biomass cycle
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
introduced new species to the area.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
main goal of the SLM technology
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| increase in pests | não bem |
Comentários:
The technology initially used 7 species of trees. However after a while it became apparent that the peach trees were more sensitive to heavy rainfall which occured especially in the spring, and therefore when the orchards were expanded peach trees were not planted again. Land owners have also planted espercet and wheat between the trees to help further stabilise the slopes.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Comentários:
It can take 3-12 years before the fruits can be harvested, depending upon the variety. The trees will require more care and attention in the first few years to ensure their long term survival.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
7 households in an area of 10 ha
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
7 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All seven families implemented the technology.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nothing has been physically monitored but there was lively discussion in the communuty about expanding the planting areas.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| It has made efficient use of the land that was previously used for grazing of livestock. |
| I have planted espercet in within the fence line, to improve my fodder production. |
|
I learnt how to care for the trees in the training provided. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further ongoing professional support for the land user would be beneficial. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It helped stabilise the soil and reduce the risk of mudslides. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other identified areas could be planted with trees. |
|
It helped to reduce the rates of surface water top soil erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The area of land could be extended. |
|
The fencing helped protect the technology from grazing livestock. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The fruit trees within the fence can be intercropped with perennial grasses or other crops. |
| It provides long term food and potential income for the land user. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| There are tree diseases in the district, which may spread to the fruit trees and many locals cannot afford the pesticides required to help prevent these. | Pesticides could be provided by larger farms or cooperatives could be set up. |
| The livestock broke through the fence and ate some of the saplings. | In some instances double fencing may be requried. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The areas identified to be stabilised do not always have access to water and therefore the technology is limited. | Piped irrigation and drip irrigation techniques could be applied. |
| The land owner does not have any returns on the intial investment for a minimum of three years. Also they will have to pay tax on the land after three years. Some trees will not produce fruits for up to 12yrs. | Loans or subsidies could be provided to the land user over this initial period of time. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos