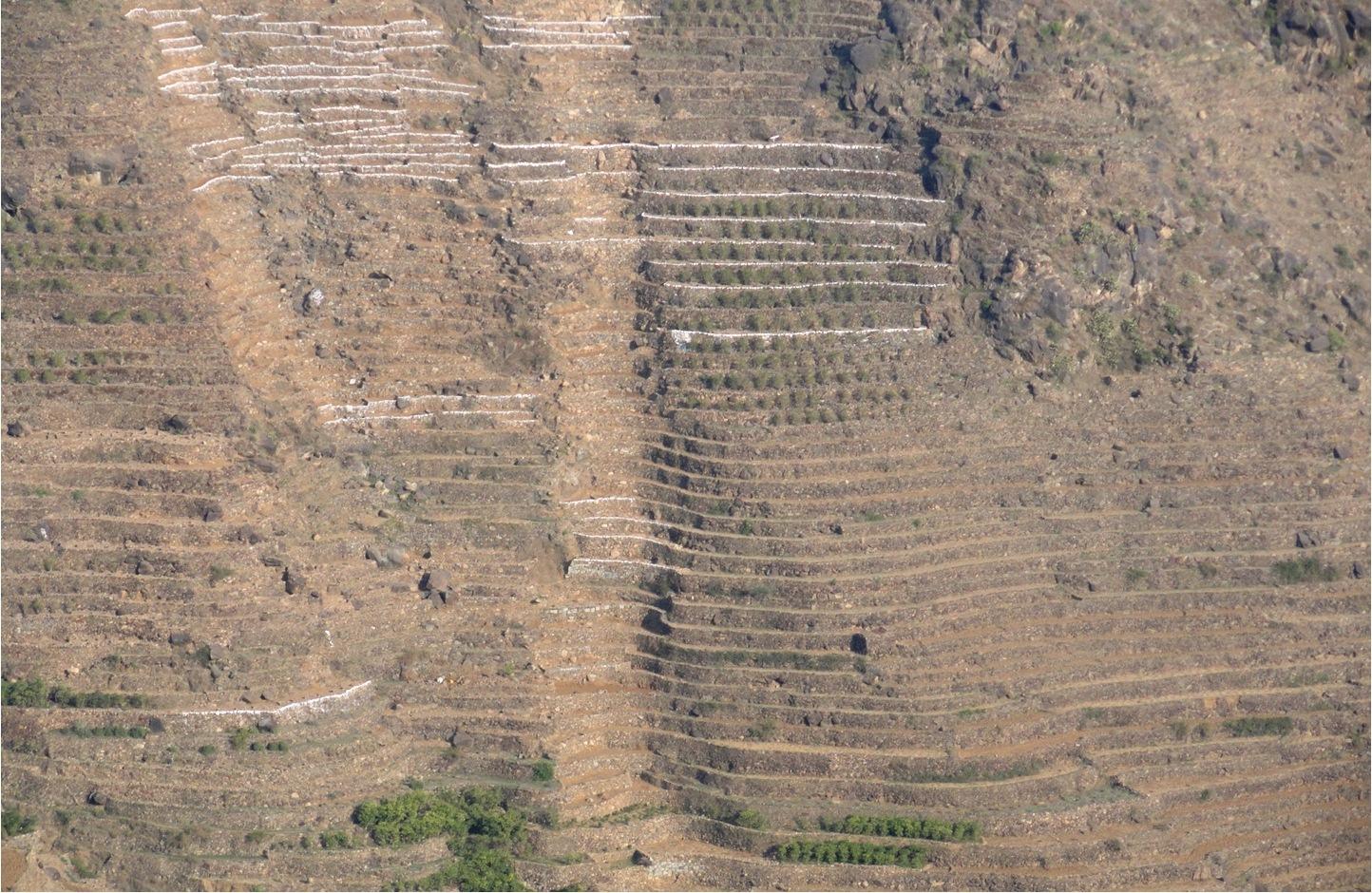
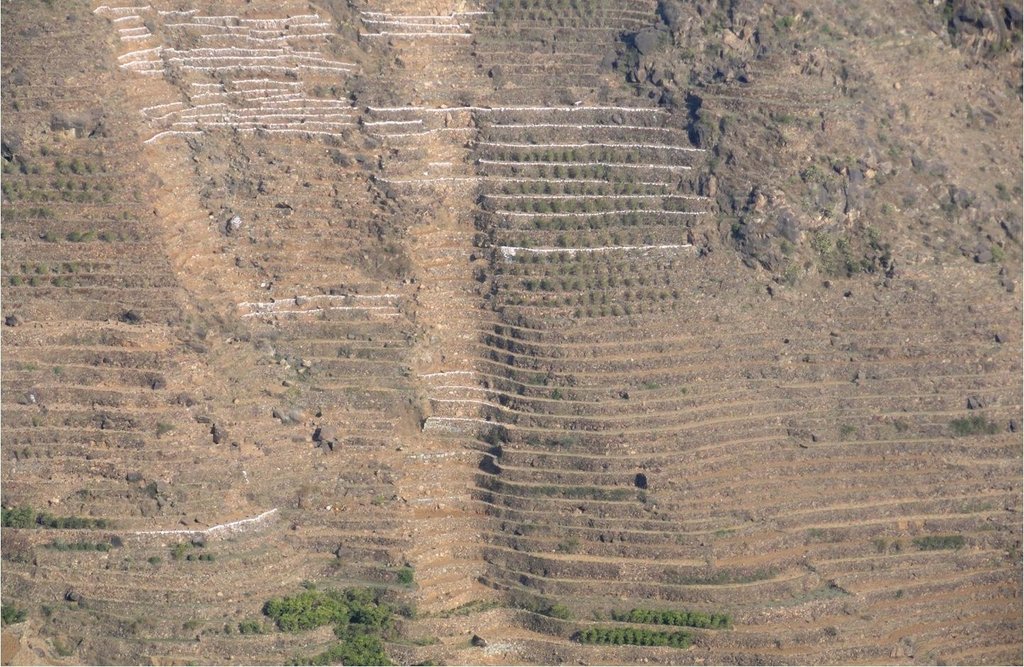
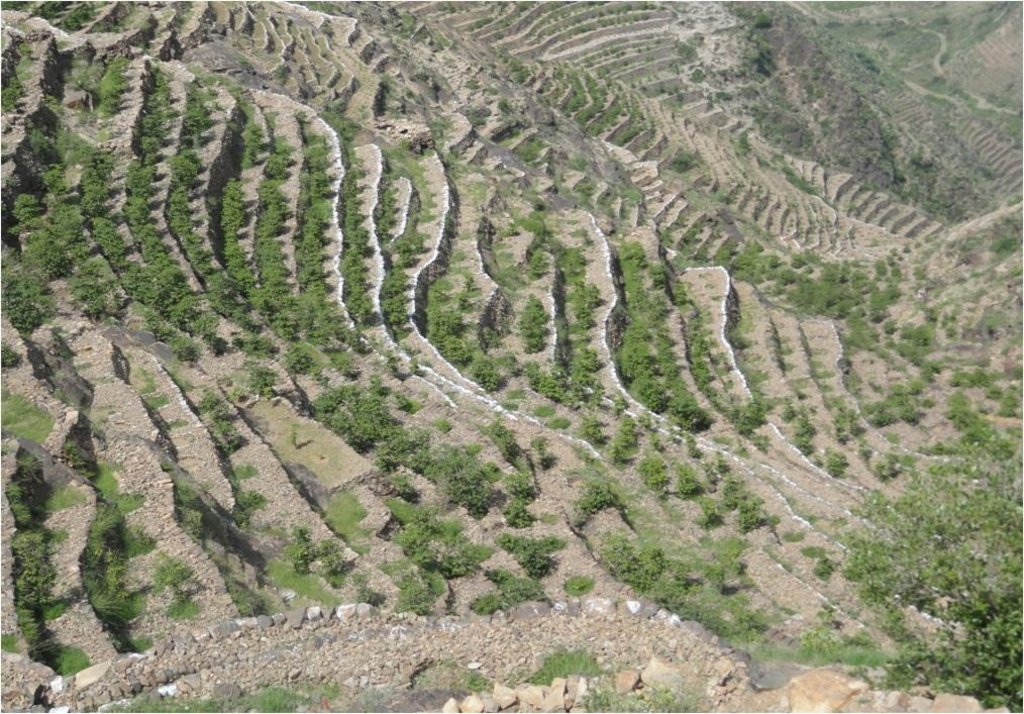
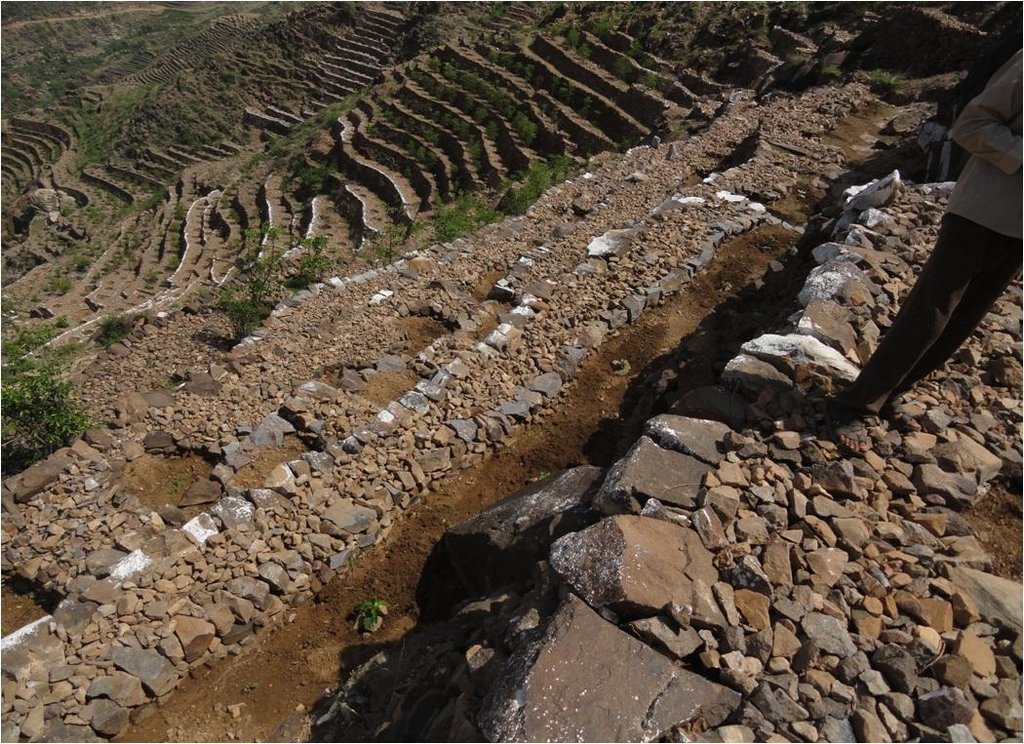
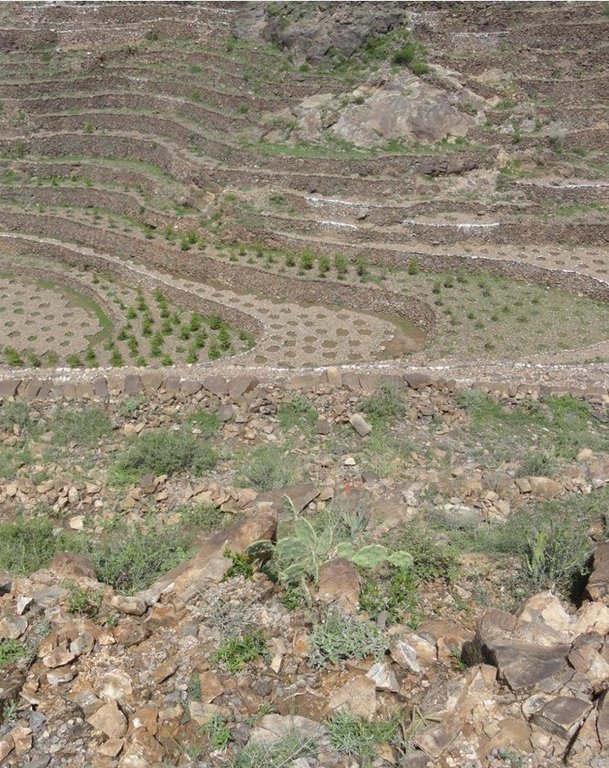
Bench terraces covered with small stones [Iêmen]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ahmed algalal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
المدرجات المغطاه بالأحجار
technologies_1560 - Iêmen
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - Iêmen1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
20/02/2013
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Building terraces in steep areas for the purpose of reducing the slope, water harvesting and soil moisture conservation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Cutting and collecting stones for the construction of terraces on steep slopes of the mountains, structural measure to reduce the length and angle of the slope and the speed of runoff. This makes it easier to harvest water and reserving deposits. A wall terraces is built of stones where the height of a wall should be increased height of 1.8 - 3 m, a width of 1.5 - 4.3 m and the length from 8 - 14 m to keep the accumulated deposits. The cutting stones are brought from distant places for the purpose of building the walls. These terraces are similar to mountain terraces but the top soil surface can be covered with stones to protect it from heavy rain storms and prevent sheet erosion that results from raindrops hitting the bare top soil surface. The stone layer, also prevents evaporation and maintains soil moisture. The stones are arranged in a layer of about 0.25 – 0.7 m thickness over the entire surface of the soil except where to put the coffee trees with an average diameter of 1 m. It is difficult to use equipment in the process of building the terraces due to severe slopes. Therefore it is a labor intensive process of manually building terraces. Due to the slow process of construction it requires a lot of time. However, building terraces on steep slopes can lead to increased erosion in the absence of well maintaining outlets that allow draining the excess water from one terrace to another, avoiding breaking of terraces' walls. In any case, terraces need regular maintenance to ensure the sustainability of this technology. The landscape of the region is mountainous, bench terraces which are used for crop production exist in slopes exceeding 60%. The texture of the soil is silty loam and the depth of the terraces is moderate to deep. Due to small holdings and steepness of the terraces, the local implements are used for land preparation. The climate in the region is arid to semi-arid and annual precipitation ranges between 200 and 450 mm. The major crop in this area is coffee, which is cultivated because of its high economic value on the market.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Iêmen
Região/Estado/Província:
Sanaa governorate
Especificação adicional de localização:
Bani Ismail- Manakha District
Comentários:
Bani Ismail's Uzlah is situated in west part of the capital Sana'a
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is very ancient technology but was rehabilitated in 2011 by the users of the land by getting a fund from the Social Fund for Development
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Main cash crop: Coffee
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water erosion in the form of Gullies, large stones loss (landslides) due to the sever steepness in addition to low soil moisture.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: post-flooding
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Coleta de água
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.75 m2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Severe rainstorm), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Severe slopes and fall of large rock masses), land tenure (Fragmentation of holdings), Immigration and search for other income sources
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (For domestic use due to lack of gas as a fuel source), poverty / wealth (Poverty), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
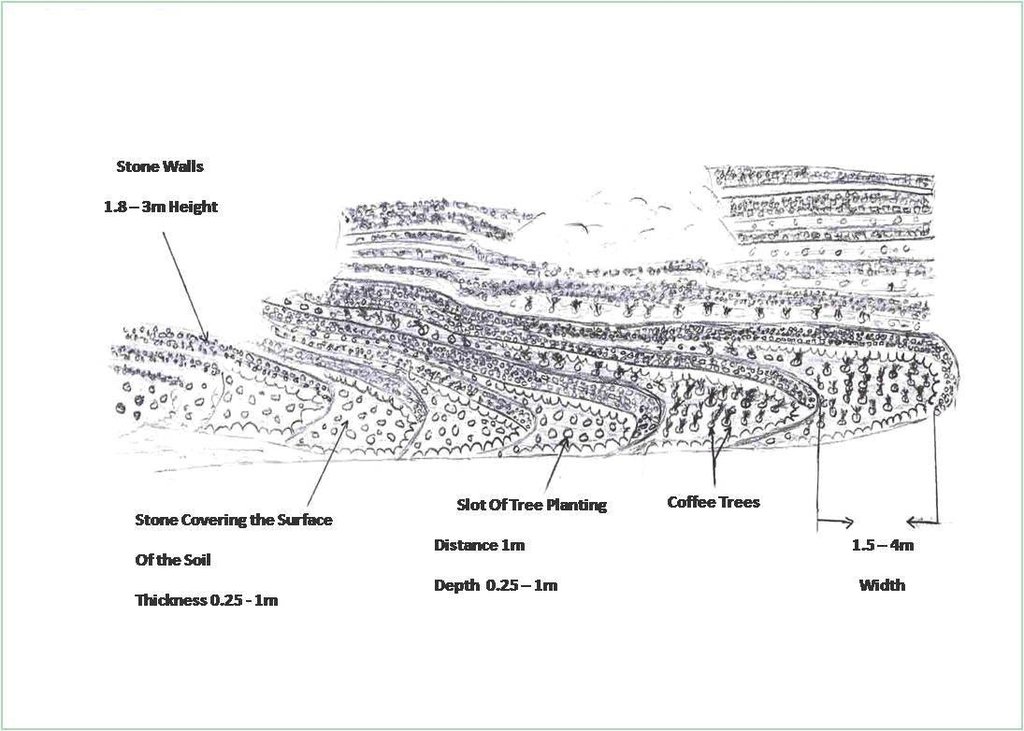
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Flat agricultural terraces covered with stones on the soil surface
Location: Bani Ismail. Sana'a governorate - Manakha district
Date: 5/3/2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Construction process needs skill and experience)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Has experience)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, Reduce speed of runoff
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.8 -3
Spacing between structures (m): 1.5 – 4.3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.8 -3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5– 4.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 8 - 14
Structural measure: The Coverage with stones
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5– 4.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 8 - 14
Construction material (earth): Remove residuals of water erosion and refill the soil-eroded with soil
Construction material (stone): Construction of walls from the existing stones in the region
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 66.7%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
6.30
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Remove the spate deposits and filing the gullies with soil, then the top soil surface has to be leveled | Estrutural | Before the rain season |
| 2. | Collecting and transporting stones | Estrutural | Before the rain season |
| 3. | Building the walls of the terraces | Estrutural | Before the rain season |
| 4. | Cover the top soil surface of the earth with stones | Estrutural | Before the rain season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Building terraces | ha | 1,0 | 42430,0 | 42430,0 | 11,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 42530,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair walls that were destroyed | Estrutural | annually after the rain season |
| 2. | Inverse the soil covered with stones | Estrutural |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Repair walls that were destroyed | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Inverse the soil covered with stones | ha | 1,0 | 186,0 | 186,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 236,0 | |||||
Comentários:
It is important to note that the implemented works to achieved is about 6 hectare, the project which support money against work, contributed with 231720.54$ to cover most of works such as collecting and transfer stones, and constructing the wall of terraces at 16639.16 m, and covering soil surface with stones for an area estimated of 53560.08 m2. While the land users performed cleaning waste of constructions, filling the target area with soil and leveling it. The total cost of constructing per hectare for building walls terraces at 3273.2 m long and 1.8-3 m height and covering soil surface with stones for an area of 8926.68 m2, and 0.25-0.7 m thick, this cost including other works which already have discussion before.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
1- Collecting and transporting stones and arable soil manually as a result of the bad road accessibility.
2- Severe steep slopes
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1400 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: 150 cm
Soil texture: Flood deposits
Topsoil organic matter: Soil covered with stones except where the tree plantation
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men have more experience and more power for work than the women.
Women carried out the weeding in the field in addition to food preparation at home.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
90% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Growth of weeds competing for water
Comentários/especificar:
Due to coverage of the top surface of soil with stones
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
As a result of not repair the damage occurring in some of the terraces and that lead to the damage of other terraces.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
soil fertility
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
120 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
120 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is one of the old folk traditions, but due to the deterioration of the living conditions of families and high maintenance costs the terraces left abandoned and when support is available by the government to help farmers rehabilitate and terraces rundown Reclamation. As for the adoption of the technique is essentially the traditional techniques of farmers and they have knowledge of their importance, but in the event of major damage farmers are unable to repair where it needs to expensive costs. Consequently, farmers have to leave and search for another source of income through internal migration. Such as these damages do not happen like this only in the event of a heavy rainstorms and it is very rare, which leads to washed and destroyed many of the terraces. Consequently, the farmer cannot repair the damage by himself. As previously stated it was targeting a group of land users who do not applied to the project to ask for help.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
This ancient technology is original and appropriate to the local situation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Raise awareness among land users of the importance of maintaining the technology. |
|
The sustainable cropping of the soil terraces on steep slopes prevent soil loss and degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue maintenance and appropriate land management |
|
Increase soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Periodic maintenance |
|
Reducing runoff and increasing water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Periodic maintenance |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue to add organic matter to increase soil fertility and conservation |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The high cost of rehabilitation and maintenance of the terraces by an individual user | Strengthening cooperation and assistance in the rehabilitation and maintenance collectively by land users |
| High runoff may lead to the erosion of terraces | Planting the upper part of higher slopes with trees or water breakers (controls) for water runoff to reduce the flow velocity, as well as periodic maintenance of watercourses and water outlets in the terraces |
| Cover the surface of the soil with stones may lead to soil compaction | To avoid compaction due to covering soil with stones reduce the thickness of this layer |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Technical study for construction and reclamation for terraces in some villages, Bani Ismail's uzlah, Manakhah district.2- Mid-monthly reports for implanting terraces construction in Bani Ismail's uzlah, Manakhah district.3- General Census of Population, Housing and Establishment (Census, 2004).4- Guide of agricultural climate in Yemen (Al Khorasani, 2005).
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Social Fund for Development, Sana'a 976714496722- Social Fund for Development, Sana'a 97671449672 3-Central Bureau of Statistics4-Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos