Village irrigation schemes developed using the PMN/IPRODI approach [Mali]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Dieter Nill
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Périmètres irrigués villageois type PMN/IPRODI (French)
technologies_1630 - Mali
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Ali Yehia Ag Mohamed
yehia@afribonemali.net
PMN/IPRODI
Mali
Especialista em GST:
Kliewe Matthias
kli@ces.de
PMN/IPRODI
Mali
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Alemanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/07/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Participatory approach to small-scale irrigation [Mali]
The participatory approach to small-scale irrigation ensures skills and expertise are transferred to scheme beneficiaries and other stakeholders.
- Compilador/a: Dieter Nill
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Village irrigation schemes (VISs) help to control the water supply and significantly increase yields.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Village irrigation schemes (VISs) are a concept and a development typology created in the 1970s and 80s. Using a relatively simple development concept, it was possible to create production units that were built and managed by local people in areas seriously affected by drought and a sharp decline in inundation events in the 1970s and 80s. Instead of being dependent on food aid, local people operating a VIS were able to guarantee sufficient rice production to cover their village’s food needs. With one pumping facility and one canal network installed, it is possible to control the water supply for an area of at least 20 hectares, thus creating the required conditions for intensive rice growing.
Prior to the installation of the scheme, the sites are not suitable for rice growing. Yields significantly increase as a result of the work carried out. An average harvest of six tonnes per hectare increases incomes. With an average price of 125 CFA francs per kilo of paddy, the rate of sales reaches 750,000 CFA francs per hectare. The surplus per hectare is estimated at 300,000 CFA francs.
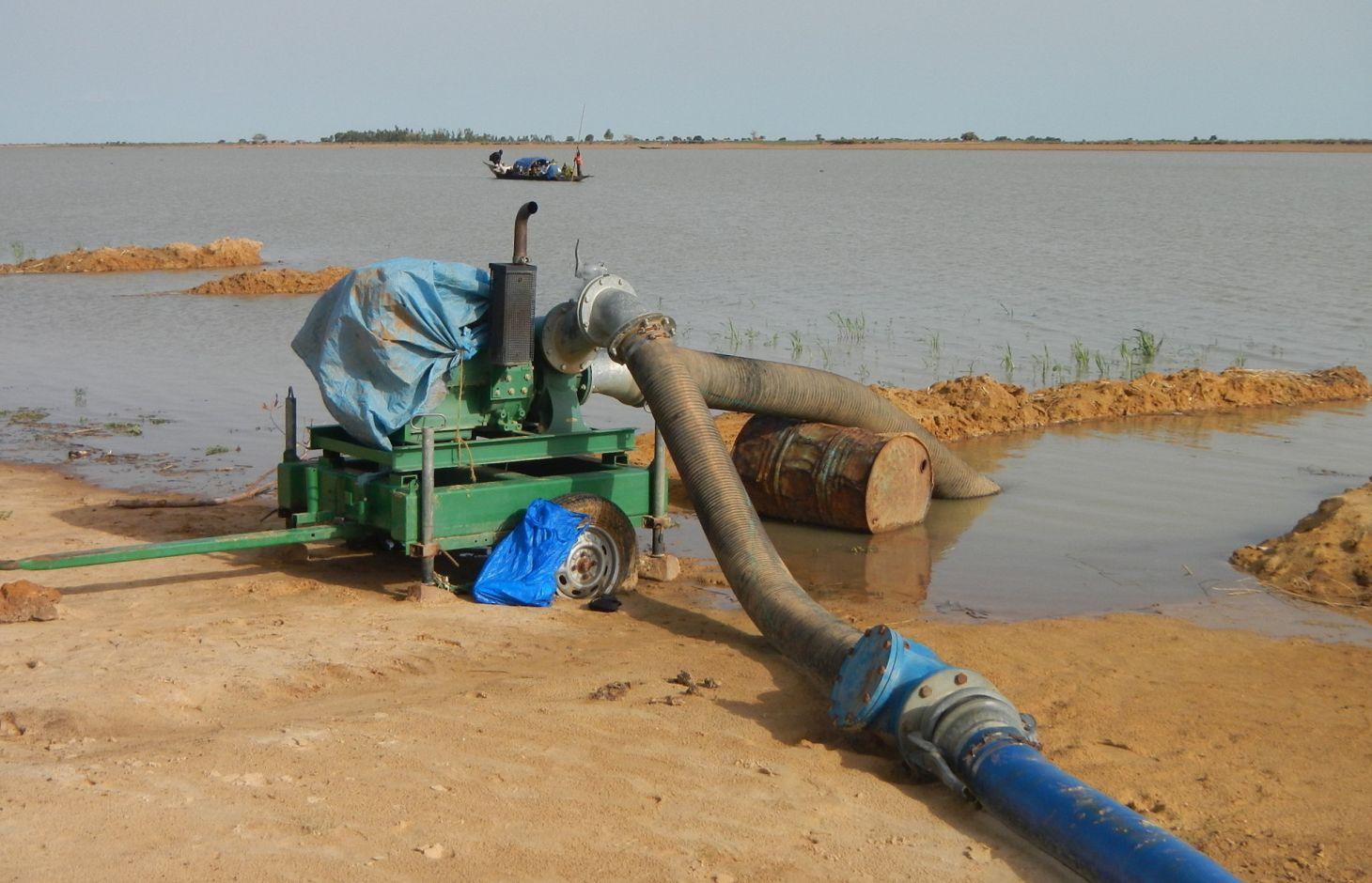
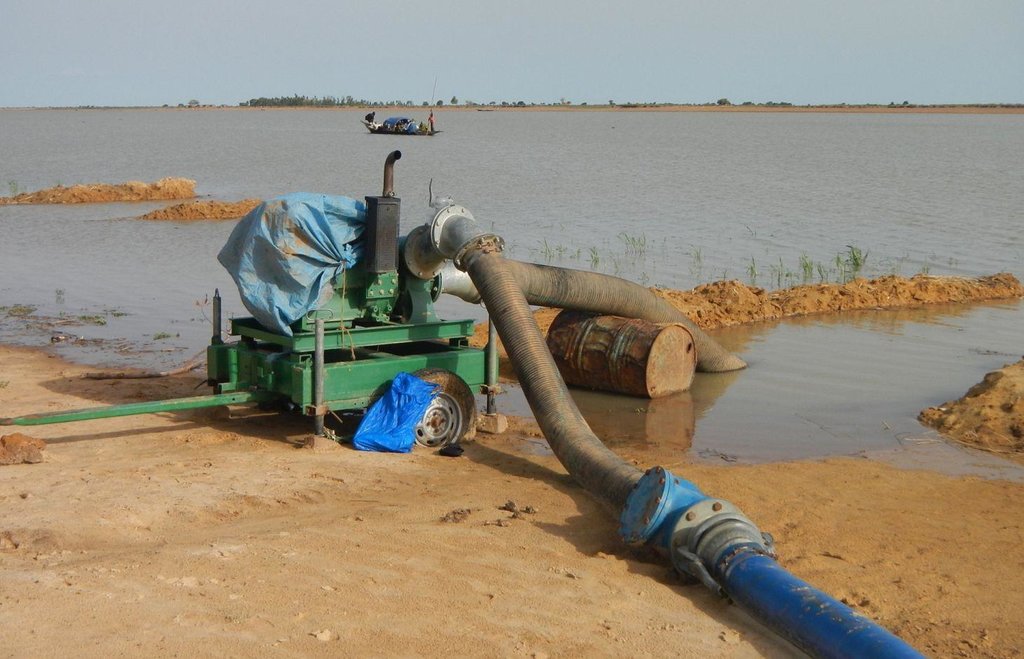
A VIS comprises a pumping station, small-scale facilities infrastructure, and irrigation and drainage networks. The pumping station consists of a pump unit fitted with a diesel motor with two or three 28 to 38 horse-power cylinders and a centrifugal pump with a capacity of 350 to 480 cubic metres per hour. The pump is positioned right alongside the water source (river, lake) and is mounted on a mobile chassis so it can be repositioned as and when required
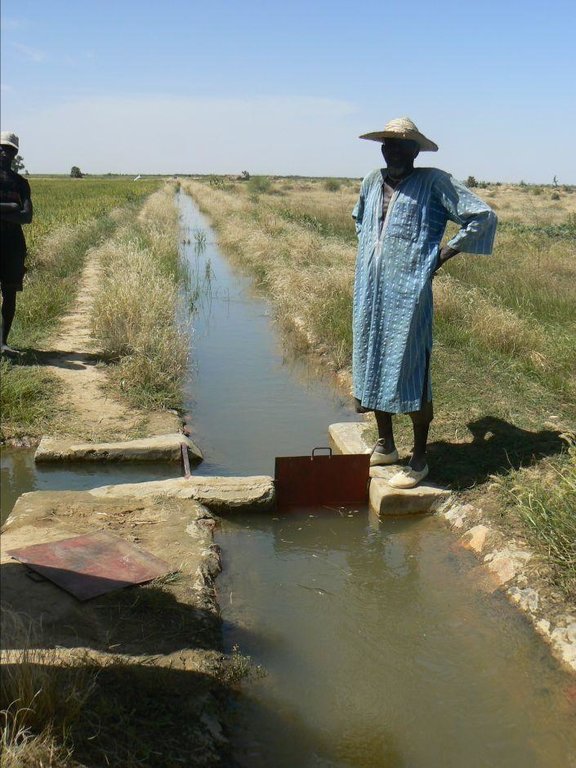
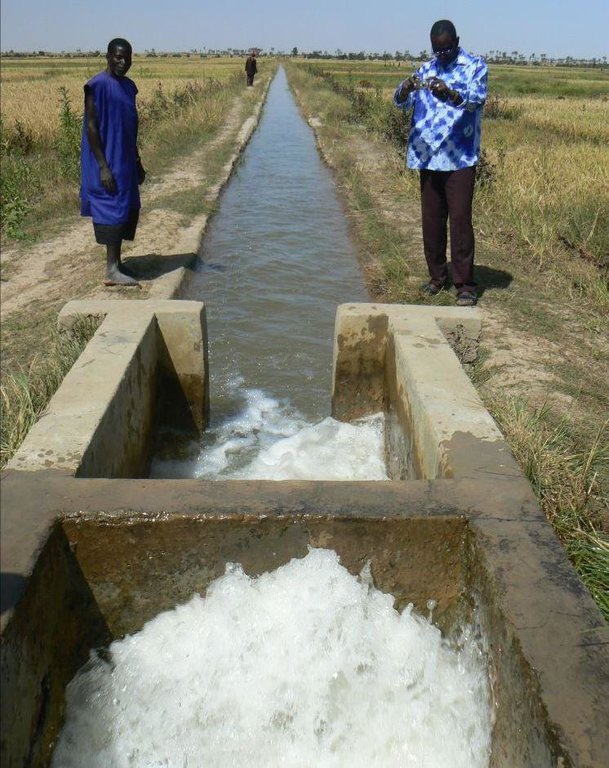
and depending on the situation of the water source, which can vary considerably during the winter growing season. At the end of the growing season, the pump unit can be stored in a secure, weather-proof location (out of the sun, rain, etc.). Water is then pumped through a flexible hose of reinforced polyethylene (the lengths generally being multiples of 50 metres, but no longer than 150 metres) up into the delivery basin where the energy carried in the turbulent pumped water is dissipated to prevent erosion damage and where the flow is calmed from turbulent to laminar. From the delivery basin onwards, the system makes use of gravity to feed its open canal network. The majority of the network is comprised of earthen structures, with only a section of the main canal being lined (usually a length of between 150 to 300 metres leading from the delivery basin outflow). The secondary and/or tertiary canals are supplied with water through a division box that apportions supply using a system of (‘all or nothing’) gates. Plots are watered from the tertiary canal by turning on the PVC hose.
Initially, villagers are able to express their need for a VIS through a village diagnostic exercise. This installation request is then taken up by the communes’ PDESC. A formal request is then referred to the mayor and drawn up by the community. The support structure (PMN/IPRODI) reviews the request and carries out a preliminary feasibility study. Decisions are then taken in a planning workshop on which schemes to prioritise. Following this, private planning consultants are commissioned to conduct feasibility studies. In parallel, technical and financial analyses are carried out by the programme’s planners, who also validate the studies. A meeting is held to inform and raise the awareness of the beneficiary communities about the development approach. The community is then requested to contribute their labour as part of the HLIW measures. The financial contribution required for the pump unit is up to 30% of its cost.
Farming a VIS (intensive rice growing) is fundamentally different to other, more traditional production systems to which farmers are accustomed (extensive rice growing in floodplains and millet growing in non-flooded areas). VISs require the purchase of inputs and the sale of at least part of the produce. Farming a VIS requires the development and good functioning of a value chain with many more links upstream and downstream of production and beyond the confines of the village than would be found in a traditional system. Although the VIS was initially conceived as a drought response mechanism in the 1970 and 80s, VIS farming encourages farmers to become more integrated in the rural and regional economy.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Mali
Região/Estado/Província:
Mali
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mopti, Timbuktu
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Since 1997, by PMN/IPRODI
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Preserva ecossistema
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agropecuária
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Prior to the installation of the scheme, the sites are not suitable for rice growing.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Desvio e drenagem de água
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.4 m2.
Five communes in the Mopti region and 38 communes in the Timbuktu region.
Installation of 489 VISs in at least 43 communes. Farmable land: 16,832 hectares. Approximate number of beneficiaries: 335,200 People.
The area of schemes developed by PMN/IPRODI ranges from 30 to 40 hectares. Initially, the programme installed 30-hectare schemes supplied with two-cylinder pump units. Since 2004, it has only developed 40-hectare schemes supplied with three-cylinder pump units. All the schemes are divided up into 0.25-hectare plots, making a total of 160 plots. The maximum distance from the sprinkler to the drain on the other side is 100 metres.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Specification of other management measures: irrigation schemes
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
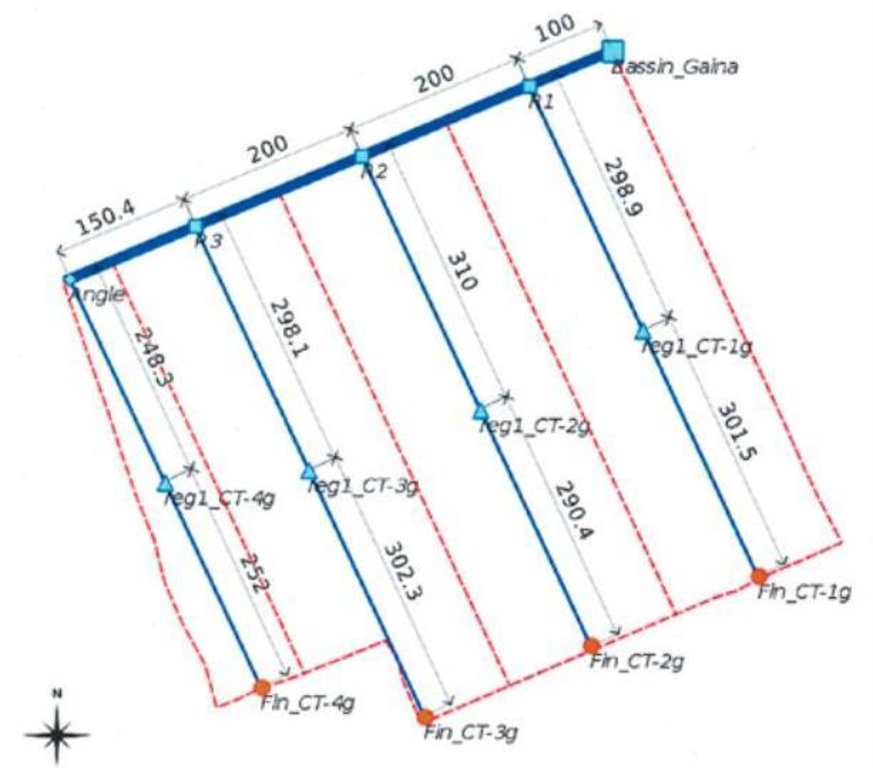
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Layout plan of the irrigation network (in blue) and the drainage network (in red)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
CFA Franc
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
517,0
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | formal request for irrigation scheme | Gestão | |
| 2. | support structure (PMN/IPRODI) reviews the request and carries out a preliminary feasibility study | Gestão | |
| 3. | Decisions are then taken in a planning workshop on which schemes to prioritise | Gestão | |
| 4. | private planning consultants are commissioned to conduct feasibility studies | Gestão | |
| 5. | In parallel, technical and financial analyses are carried out by the programme’s planners | Gestão | |
| 6. | meeting is held to inform and raise the awareness of the beneficiary communities about the development approach | Gestão | |
| 7. | community is then requested to contribute their labour | Gestão |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outros | total construction | ha | 1,0 | 2497,0 | 2497,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2497,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Regularly maintaining the facilities and networks | Gestão | |
| 2. | Agricultural advisory support and monitoring of crops by the technical services | Gestão |
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The development costs are estimated at 1.3 million CFA francs per hectare (2,497 Dollar).
On the technical side, numerous scheme configurations have been observed. The most common involves a limited number of small-scale distribution control structures and a network of open, earthen canals. This type of scheme requires an investment in the order of between 1 and 1.5 million CFA francs per hectare. It also fosters the large-scale participation of villagers in all the building works, particularly excavation work and the installation of plots. At the other end of the spectrum are the VISs that have lined canals throughout their entire irrigation network. These require much more substantial investment (up to 7 or 8 million CFA francs per hectare) and building works (including plot installation) are generally carried out by contractors. As yet, no study has indicated that the yields and technical lifespan of such high-cost ‘sophisticated’ schemes are greater than those of ‘basic’ schemes.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are very poor.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Comentários:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Instituições comunitárias
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Instead of being dependent on food aid, local people operating a VIS are able to guarantee sufficient rice production to cover their village’s food needs.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
The community is requested to contribute their labour as part of the HLIW measures. The financial contribution required for the pump unit is up to 30% of its cost
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
On the back of over 15 years’ work and major investments, the programme has been able to develop 489 VISs across an intervention area that covers six circles (second-tier government structures). While most of the VISs grow in-season rice (July to December), 10% grow rice off season and 20%, located mainly in the Diré area, grow wheat (October to March). A small percentage of VISs (around 2%) grow two crops a year. The reasons for this low percentage are the risks involved and clashes in the growing calendar. Many of the pump units are, however, used several times over (on different sites for different crops).
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Option for scheme extensions to be undertaken by the beneficiaries themselves |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Yields significantly increase |
| Building more sustainable and less costly schemes through the careful configuration of irrigation canals |
| Low investment costs |
| Existence of 15-year-old schemes that are still productive and in good condition |
| Possibility for beneficiaries to replace spent pump units using their own savings |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| scheme areas may become a source of conflict |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
IPRODI (2009): Approche du PMN pour le développement de l’irrigation de proximité, region de Tombouctou [North Mali Programme’s approach to developing small-scale irrigation in the Timbuktu region].
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory approach to small-scale irrigation [Mali]
The participatory approach to small-scale irrigation ensures skills and expertise are transferred to scheme beneficiaries and other stakeholders.
- Compilador/a: Dieter Nill
Módulos
Não há módulos