Contour bunds for crops and forest/rangeland [Níger]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Dieter Nill
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Banquettes agricoles et sylvo-pastorales (French)
technologies_1652 - Níger
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP) Niamey, Niger
Níger
Especialista em GST:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
Alemanha
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Alemanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/07/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Contour bunds, built with earth or stones, increase the amount of water available to crops and vegetation, thus contributing to the restoration of degraded land
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
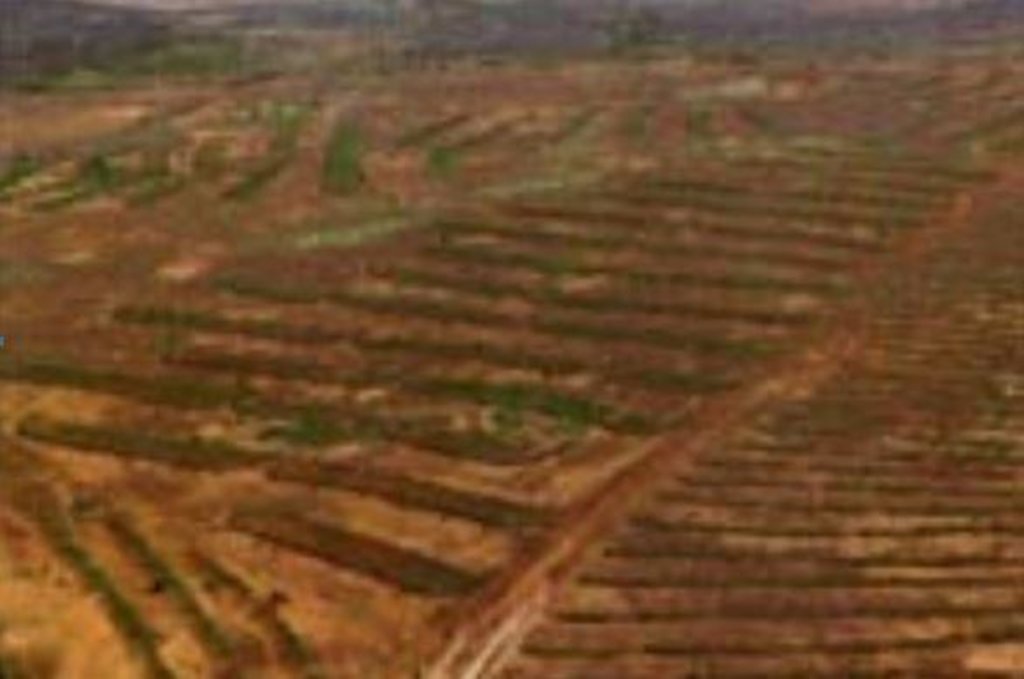
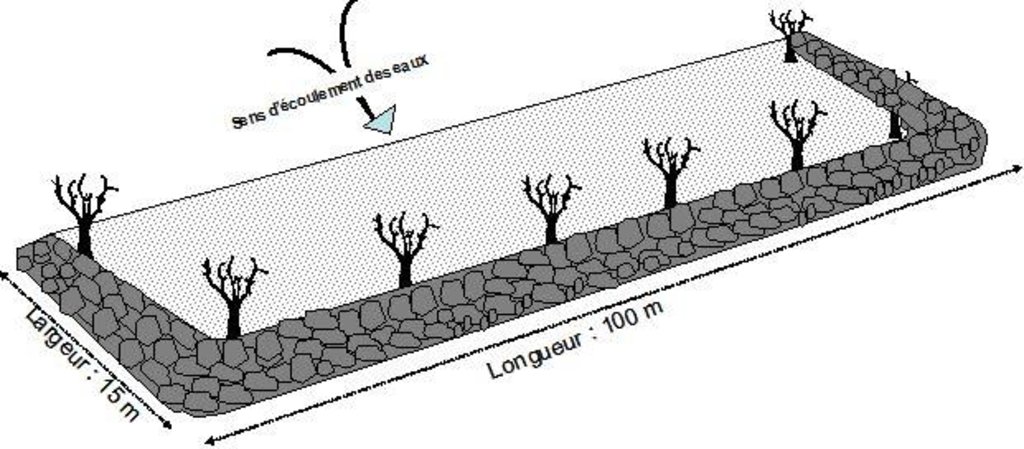
A contour bund is a rectangular structure consisting of bunds built with earth or stone or a combination of both, which can be permeable or impermeable. The bottom bund is up to 80 m long, and the wingwalls extend up to 15 m upslope. The contour bunds are built in staggered rows along the natural contour of the land with the open end facing uphill. Patches in the same row are spaced 6 m apart, and the rows are positioned about 25 m apart, depending of the gradient of the slope. Downslope of the structure, a water collection ditch 0.50 m wide and 0.30 m deep is dug. The earth excavated from the ditch is piled up and compacted to construct the main bund. When used for growing crops, a third of the total surface area inside the contour bunds is loosened by subsoiling. The remaining two thirds of the surface are left unworked and serve as a catchment area. This doubles or triples the volume of water available to crops. Trees are planted along the main bund to stabilise the structure.
Contour bunds for forest/rangeland work as contour bunds on cropland (described above), except that the sizing is slightly different. The main bund of patches used for this purpose is up to 100 m long and the rows are spaced up to 30 m apart.
In Niger, contour bunds for forest/rangeland are used to restore land in plateau areas which have been completely degraded and denuded by severe water and wind erosion. Contour bunds for growing crops are recommended for the restoration of pediments, particularly in areas where land use pressure is high. The technique is recommended for areas with a low gradient and rainfall of less than 600 mm.
The bunds capture and retain runoff for several days. Infiltration of the water into the soil increases, and there is a gradual build-up of sediment behind the bunds, creating favourable conditions for the establishment of vegetation. Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops. An advantage from the perspective of watershed development is that contour bunds constructed on plateaux areas protect areas downstream against heavy runoff.
Before constructing the contour bunds, it is essential to clarify the ownership status of the land where the measures are to be implemented and who the users will be, with a view to avoiding disputes later on.
When constructing the contour bunds, it is important to mark out the contour lines correctly and ensure that the earth is firmly compacted.
With some upkeep, stone or stone-lined contour bunds last at least 20 years. Earthen bunds do not last as long. Good vegetation cover established along the bunds increases their lifetime.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Níger
Região/Estado/Província:
Niger
Especificação adicional de localização:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahoua
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Floresta/bosques
Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais:
- Derrubada seletiva
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
- Outros produtos florestais
- Pastagem/Alimentação de folhas e brotos
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): crusting, surface runoff, water and wind erosion, unadapted land use methods, rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land, reduced or abandoned fallow periods, insecure access to land
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão natural e seminatural de floresta
- Agrofloresta
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed common land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
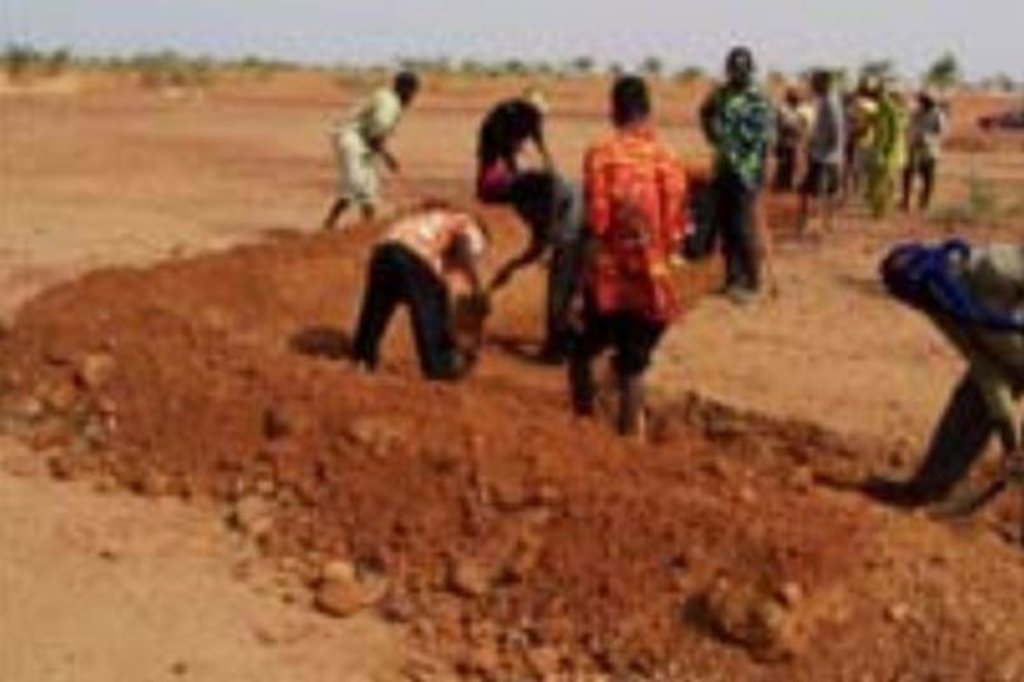
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The contour bunds are built in staggered rows along the natural contour of the land with the open end facing uphill. | Estrutural | |
| 2. | Downslope of the structure, a water collection ditch 0.50 m wide and 0.30 m deep is dug. | Estrutural | |
| 3. | The earth excavated from the ditch is piled up and compacted to construct the main bund | Estrutural | |
| 4. | When used for growing crops, a third of the total surface area inside the contour bunds is loosened by subsoiling | Estrutural | |
| 5. | Trees are planted along the main bund to stabilise the structure | Vegetativo |
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Damages caused by excessive rainfall need to be repaired quickly | Estrutural |
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour: 54 man-days per ha.
Equipment: pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level.
Other costs: hire of machine for subsoiling (1 day per ha).
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Atenuação de conflitos
Contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
Physical structures can be biologically stabilized through planting of grass, bushes or trees. Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 10-50%
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The techniques were implemented with food for work in the 1990s to 2000. At the end, the work provided by land users was not compensated. Only small equipment and transportation were provided for free.
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem. Potential for replication depends on the type of terrain, there being a nearby supply of the materials needed (stone). Subsoiling needs mechanical treatment by tractor.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
In a low-rainfall scenario, the construction of contour bunds helps to restore vegetation cover on vast areas of denuded land from the first year after they are established. Infiltration of the water into the soil increases, and there is a gradual build-up of sediment behind the bunds, creating favourable conditions for the establishment of vegetation. |
| Good vegetation cover established along the bunds con- tributes to lowering soil temperature and providing pro- tection from wind erosion along the entire length of the patch. |
| The construction of contour bunds upstream of river basins reduces the risk of gully erosion and siltation downstream. |
| In Niger, it is mainly women who have benefitted from efforts to rehabilitate land on the plateaux. With the support of development projects, women were able to secure five-year leases from land owners. |
| This technique transforms unproductive land into land that is economically valuable. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| There are also disadvantages associated with subsoiling in the contour bunds. Although subsoiling permits rapid, relatively deep infiltration, the water is situated below the level where the roots of young crops or grasses are growing, which means that the infiltrated water is not used optimally in the initial stages. Furthermore, the surface of the subsoiled land becomes hard again after several years of cultivation, because the soil structure is broken down owing to a concentration of fine particles of earth in the grooves of the subsoil, which can clog up the pores of the soil. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Patches with impermeable bunds are not appropriate when there are heavy rains, as the flow of water can destroy the bunds. | The extensive work required to construct the contour bunds means that the community must be strongly motivated and well organised. |
| Contour bunds for growing crops can be used to restore land that has become unproductive. This technique is not, however, very cost-effective, because of the scale of the work involved. | When constructing the contour bunds, it is important to mark out the contour lines correctly and ensure that the earth is firmly compacted. |
| The distribution of water in the contour bunds is often uneven, because the terrain is not level, which means that production varies considerably from one area to another | |
| When there is heavy rain, runoff accumulates at the lowest point of the collection ditch, which can sometimes cause rilling | |
| There is a risk of the patches becoming waterlogged, which can damage the crops |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos