Carob tree protection from rats [Chipre]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Michalakis Christoforou
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Προστασία χαρουπόδενδρων απο προσβολές αρουραίων και ποντικών
technologies_1703 - Chipre
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Governement official:
Costas Michael
+357-26-804567
costasmichael@ymail.com
Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment, Cyprus
B18, Nicosia, Zypern
Chipre
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Cyprus University of Technology (Cyprus University of Technology) - Chipre1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/06/2014
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Carrob tree protection from rat attacks include protection of trees directly by using aluminium layers as rings on the neck of the carob trees in order to keep rats away from climbing on the threes and thus causing problens on fruits and new branches. Furthermore, poisonus rat baits are attached on the trees in case the aluminium layers can not be used.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
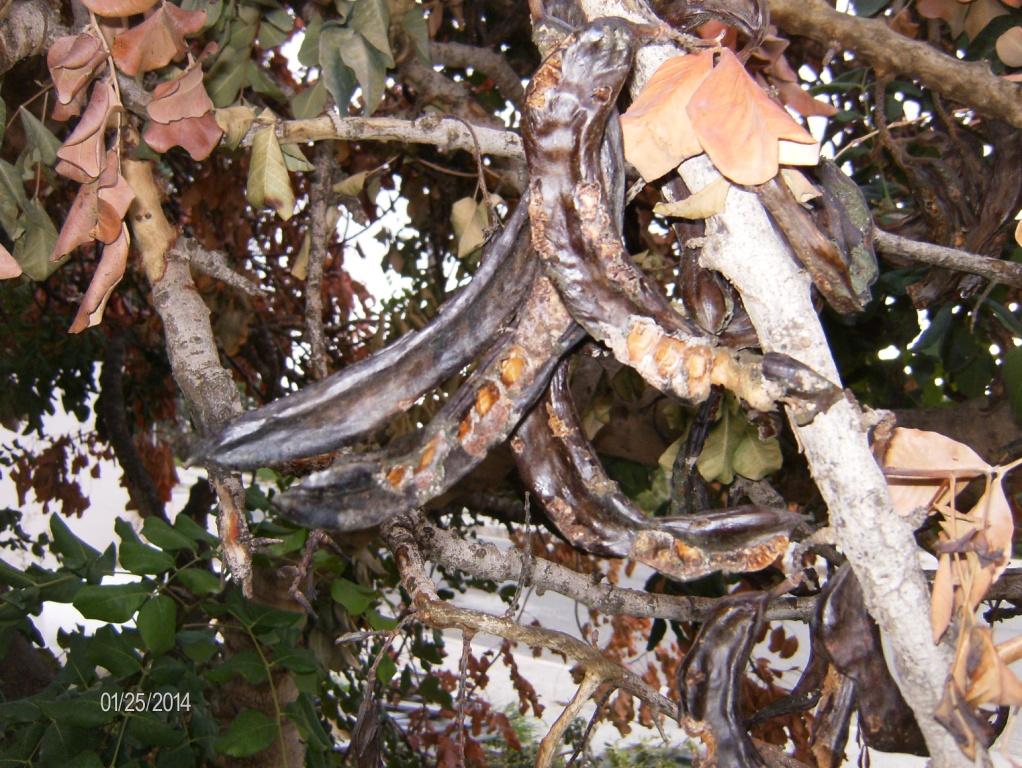
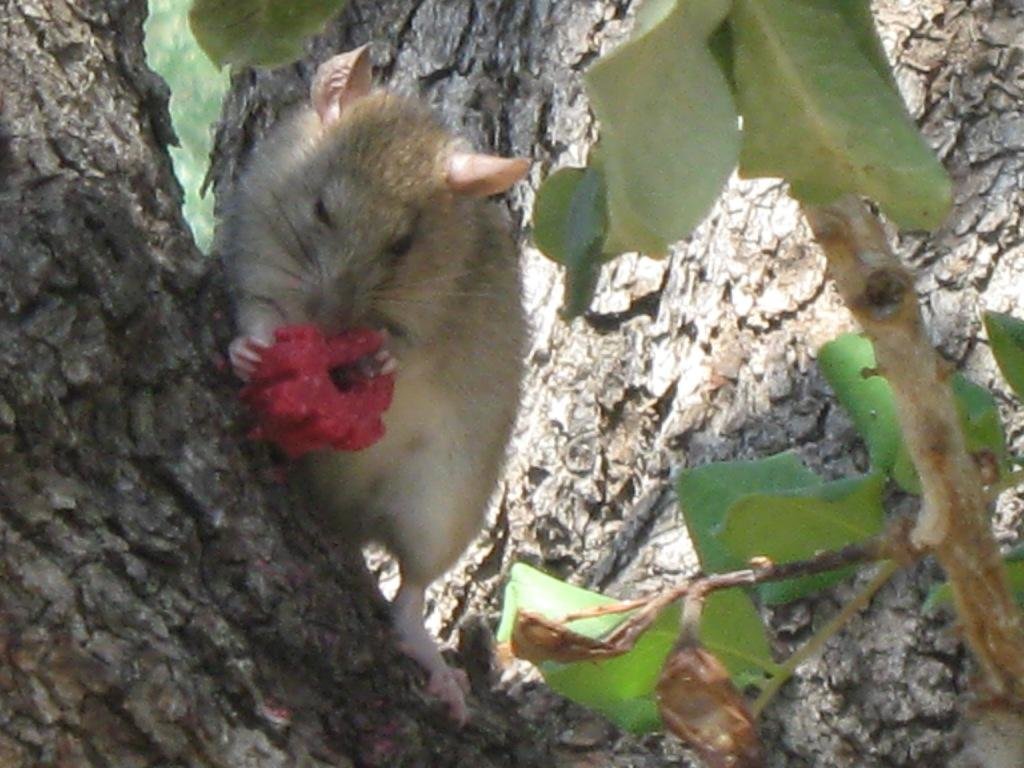
Carob trees are attacked every year by rats who nibble the trunk stem of the tree, remove the bark of the trunk and the branches sucking the juice and eat the mature fruits. Rats nibble the bark of the tree in order to reduce their teeth size which tends to enlarge year by year. This results in the death of the tree branch or even of the entire tree. The tree may also show symptoms of hemiplegia. Rats run on the tree through the trunk. Apart from the direct effect of rat attacks on carob trees, rats also cause other problems to humans and animals. Rats are vectors for serious pest and diseases
Purpose of the Technology: The rat population increases rapidly when there is enough food (such as carobs) available, and the population grows even faster in the absence of natural enemies. . Through interrupting the access from the ground to the tree trunk, or by pruning the branches which are connected to the ground, the rats are hindered from climbing the trees. Rats can also be controlled through the use of chemical baits. However, these baits should only be used by experts who know where and how to place them in order to avoid that other animals come in contact with the baits. Natural enemies such as cats, snakes and birds (e.g. Bam owl (Tyto alba)) should be breeded and established on the carob trees, and farmers, hunters and locals should be informed not to kill the natural enemies of rats.
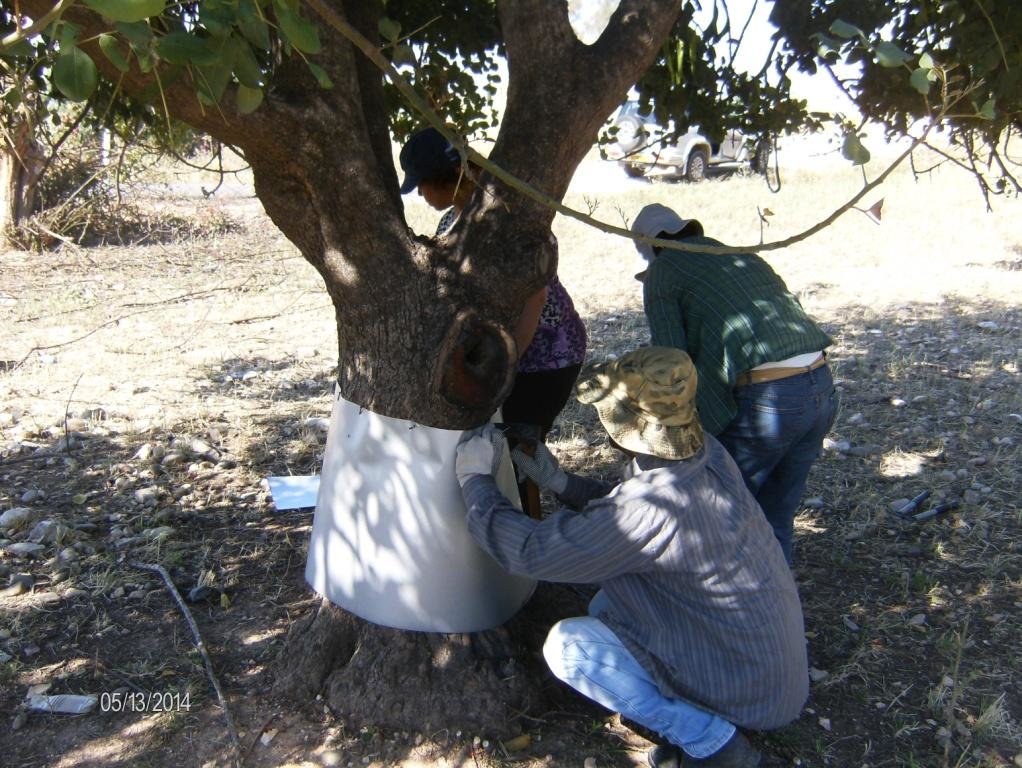
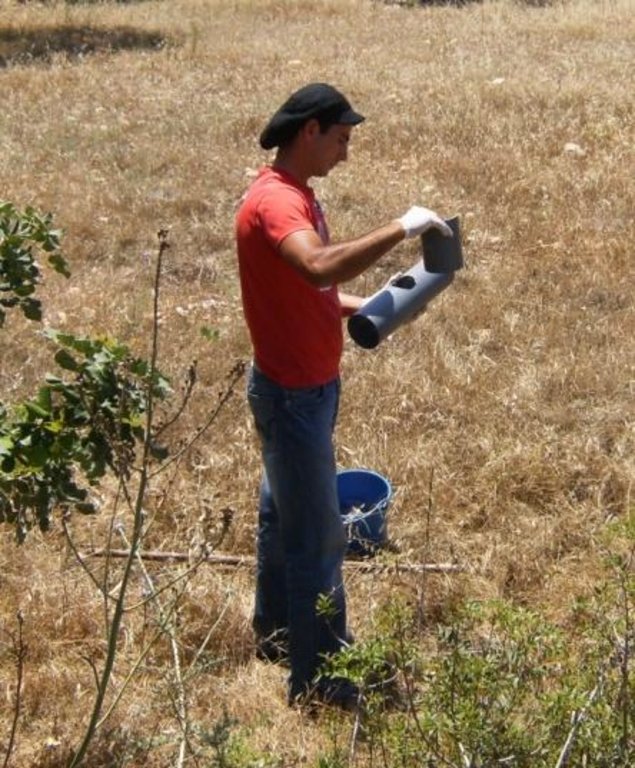
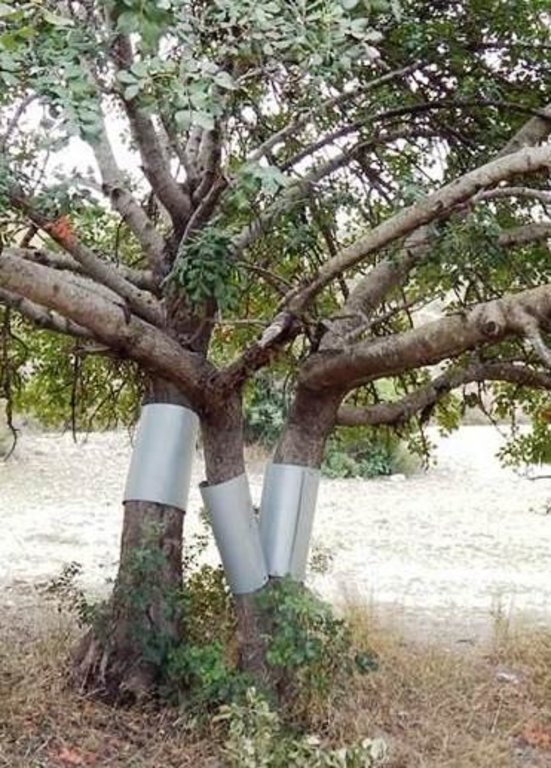
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The carob trees can be protected from rats by covering the tree neck and trunk from the ground up to 1 meter with a hard material such as aluminium with a slippery surface. This way the rats are not able to climb the trees since they will slither on the ring layer.
Natural / human environment: The carob tree protection will increase the production of carobs and therefore the income of the growers. Already established carob trees could provide a good income to growers with low production cost. The population of rats will decrease since the major source of food will not be provided anymore. Educating farmers, hunters and the local population about the benefits of natural enemies will allow that the environment regulates the rat population by itself.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Chipre
Região/Estado/Província:
Limassol
Especificação adicional de localização:
Pissouri
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The use of aluminium layer covering the trunk of carob trees was applied in an EU project called Agrolife which started in 2014, http://agrolife.eu/
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Majors cash crop: Carobs
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Rat attacks on carob trees cause severe problems for plants health and the fruit quality and production.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Carob growers: Rats are attacking the carob trees causing the death of the trees and damage of fruits.
Locals: The rat population increased during the last 30 years especially in areas where carobs are grown.
Agricultural officer: Rat population increased rapidly causing serious problems in carob production due to heavy rainfall in 2012 and to the hunting and killing of the natural enemies such as snakes and birds by the locals and the farmers.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: mid October to mid May
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
- Tree protection
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 m2.
Carob trees are grown in dry lands such as Pissouri and its sorrounding villages. In Cyprus a total of 4000 hectares with 300'000 carob trees are cultivated. The annual production of carobs is around 9000 to 12000 tons. Carob growers use minimum agricultural practices such as mechanical weed control and pest control (insects and rats)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A6: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: covering the tree trunk with aluminium layer
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Hunting and killing the natural enemies such as snakes and birds)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rat popuation increases rapidly after rainy year)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Aluminium layers are placed aroud the bark of carob trees as a ring. The aluminium is thin and light thus does not affect the growth of the tree. The hight of the aluminium is more than 50cm so that the rats can not climb or jumb on the bark of the tree
Location: Pafos. Pafos
Date: 10/3/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Agricultural advisors will inform the land users about the rat life cycle and their charactiristics in order to understand the use of the technology)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land users will implement the technology by installing the zinc or alluminium layers around the tree trunk)
Technical knowledge required for wildlife department: low (will release natural enemies such as the bird Tyto alba)
Main technical functions: reduction of rat population, protection of carob trees and fruits
Structural measure: tree trunck cover with aluminium layer
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (other): aluminium layers 1m X 1m X 0,01mm
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
euro
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
0,91
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
33.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | covering the tree trunk with an aluminium layer | Estrutural | winter, spring |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 265,0 | 265,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Aluminium layer | ha | 1,0 | 1116,0 | 1116,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Iron nails | ha | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1393,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of aluminium layers | Estrutural | once a year |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hammer, nails
The costs were calculated for 8 persons working 8 hours per day and per ha. The costs were calculated on the 28th of August 2015.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The costs are affected by the trunk diameter and the plant height
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Total annual rainfall in 2013=255mm
Total annual rainfall in 2014=363mm, and in 2015=300mm from Jan to May
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics. In Jan and Feb the temp can go below 5 C for few hours in one or two days.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l (most of carob trees areas)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (most trees are planted in plateaus. The technology is not affected by landform)
Slopes on average: Flat (most of the plantations), gentle (some fields) and moderate (few plantations, old age carob trees)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (plateaus, flat areas) and shallow (hills with aged carob trees)
Soil texture: mdeium (in plateaus and flat areas) and fine (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil fertility is medium in plateaus and flat areas and low mostly on the base of the hill
Topsoil organic matter is medium (in plateaus and flat areas) and low (mostly on the base of the hill)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low (due to lack of rainfall, when it rains the water is immediately absorbed by the soil)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table is 5-50m (if a field is near a river) and >50m if a field is far from rivers
Availability of surface water is poor/none (When it rains it does not last long enough in order to cause floods)
Water quality (untreated) is for agriculutral use only ( ground water analysis showed that in some cases the water is contaminated with boron)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Few species grow within the carob trees and those are mostly weeds. Once a year the growers remove the weeds from the fields. Fauna is also poor and consists of rodents, snakes, few birds and insects
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most of the land users are old men and women. Very few young men are involved in the carob tree production.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
80% of the land users are poor and own 50% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Since rat attack is the most damaging factor affecting the growth of carob trees and the quality of the product, the land users who apply the technology have more income with unsignificant yield losses caused by other factors.
Level of mechanization is manual labour (pruning, irrigation and harvesting) and mechanised (cultivating, weeds control, pesticide applications)
Market orientation is mixed (farmers either sell their products individually or sell them as a group)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
35 Kg/tree
Quantidade posterior à GST:
45-50Kg/tree
Comentários/especificar:
Trunk and branch protection lead to yield increase
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Although other factor like fire, frost, pests and diseases can cause production failure, rat attack is considered as the most damageable
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1,5 euro/tree
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1 euro/tree
Comentários/especificar:
During pruning, large dead branches should be removed
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50 trees/day
Quantidade posterior à GST:
65 trees/day
Comentários/especificar:
During pruning,
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Carob fruits are free from infectious diseases transferred by rats
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction of rat populations within the production area minimizes the risk of man diseases infection like typhos,
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The technology improved both livelihoods and human health. The growers income has increased more than 10-20% due to the reduction of the damage caused by rats every year. The reduction of the number of rats minimized the risk of human pathogens such as typhus which was very common in these areas.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of predators in the areas around the carob trees since rats can not climb on carob trees
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Risco de incêndio
Comentários/especificar:
Fields with carob trees being attacked by rats are more sensitive to fires since they are abandoned by their owners
Outros impactos ecológicos
Control of rat population
Quality of carob trees and fruits
Plant growth
Comentários/especificar:
On small trees the aluminium layer is pressing the trunk in a way the tree can not grow normally. In this case the aluminium layer must be replaced with a layer once every few years
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
rat population around the SLM technology is decreased therefore the damage caused by rats to the neighbours is also decreased
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Comentários/especificar:
Decrease in rat population rear farms also decrease the damage caused on the farm infrastructure (wires, wood, plastic equipment), by rats
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
The use of aluminium layers covering the trunk of carob trees is not affected by the climatic conditions. Climatic conditions such as heavy rain could affect the use of plastic tubes which include poisonous bait or the direct poisonous cubes placed on the tree branches.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Due to the damage caused on the carob trees by rats already, the trees will need some time (2-3 years) to create new branches able to produce fruits. Furthermore no new damages occur on trees.
During the first 3-5 years the aluminium layer can remain on the trees. After this period the aluminium should be replaced with a larger one due to the enlargement of the tree trunk.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
10
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to the lack of effective and cheap ways for controlling rat attack on carob trees the land users are adopting the technology, and so far they get positive results.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Few other land user are interested in adopting the technology. Many other land users are not adopting the technology because they inherited the land and they are not actually working on the land in order to make profit.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| easy to install |
| the technology can be used over a long time |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
the technology can be used over a long time How can they be sustained / enhanced? use of non-oxidizing material |
|
the aluminium layer can be bent easily How can they be sustained / enhanced? both vertical edges should be hold each other by the use of a spur |
| low cost |
| easy installation |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer can be a target for thieves who steal metal |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| the aluminium layer should be replaced in time because the trees are growing in size | install larger aluminium layers and lold it with spring |
| The aluminium (metal) can overheat during summer time | Spray the layer with white paint |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos