Vegetated earth-banked terraces [Espanha]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Joris De Vente
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Terrazas de tierra vegetadas (Spanish)
technologies_1516 - Espanha
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
López Carratala Jorge
+34.950.281045
carratala@cebas.csic.es
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Estación Experimental de Zonas Áridas (EEZA-CSIC)
General Segura 1, 04001; Almeria; Spain
Espanha
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - Espanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
05/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Regional rural development programme [Espanha]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Compilador/a: Joris De Vente
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
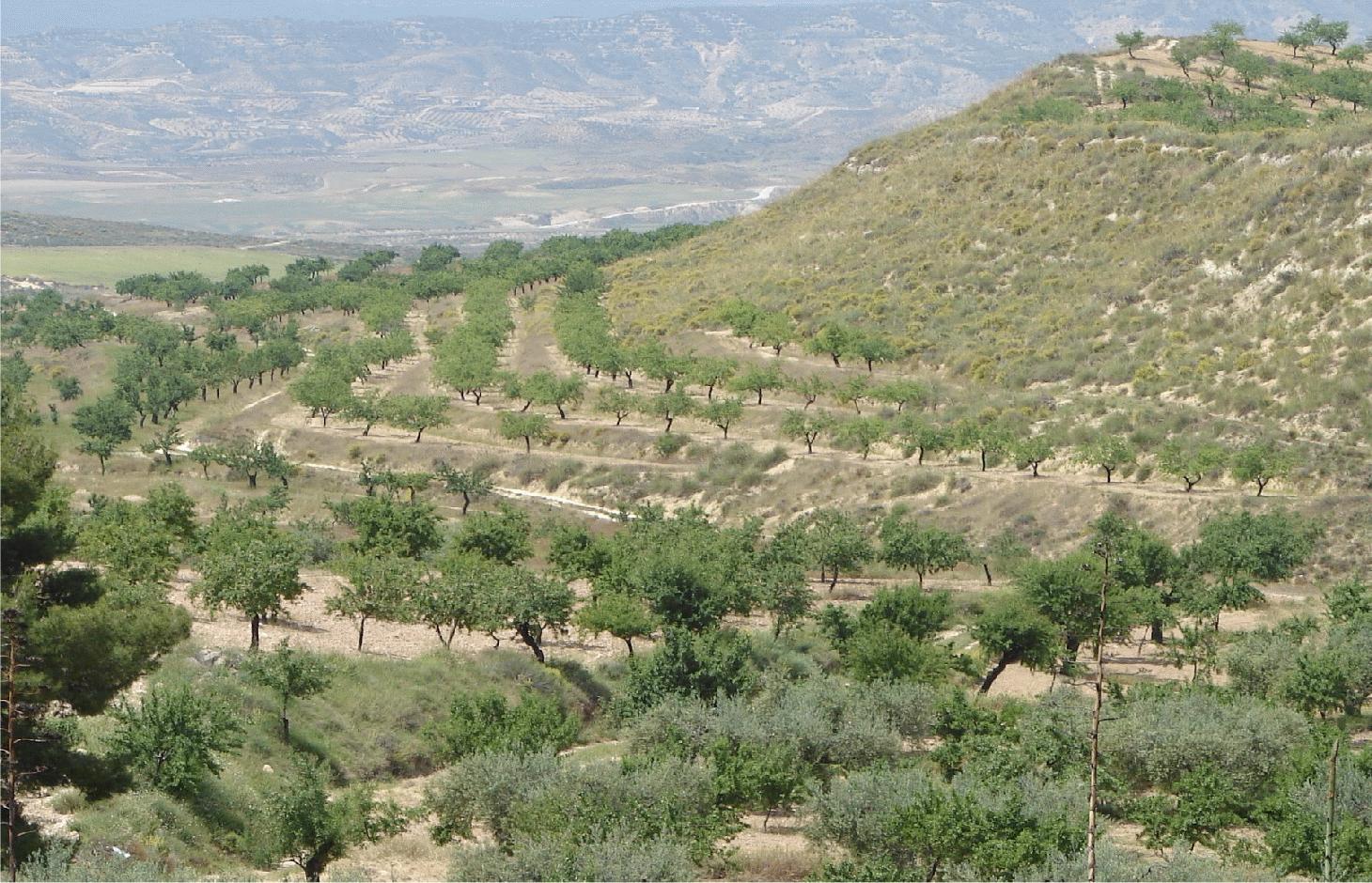
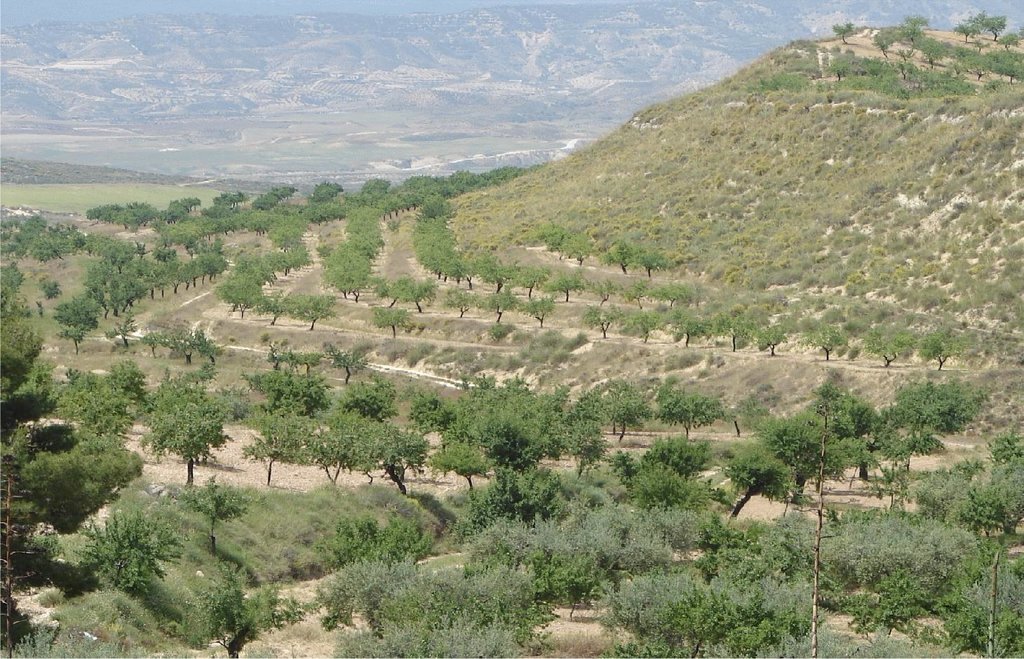
Earth-banked terraces in cereal and almond cropland covered with drought-resistant shrubs.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
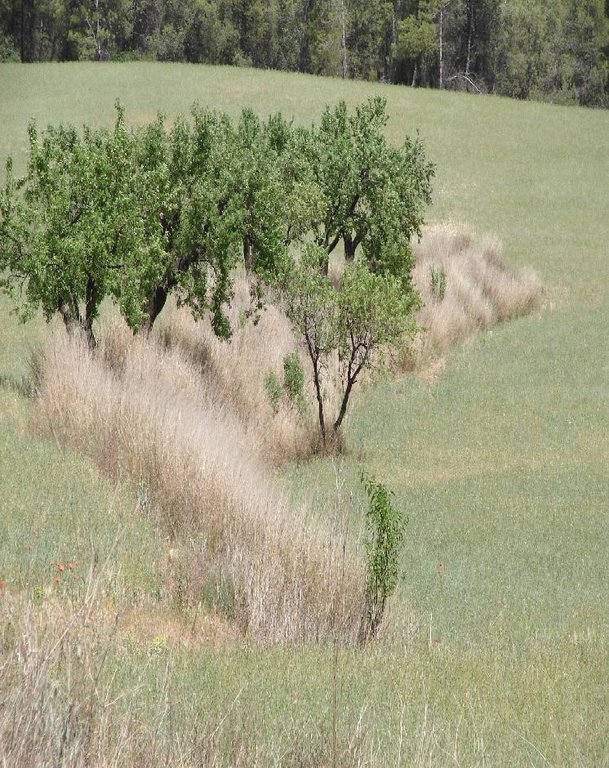
Earth-banked terraces are constructed by carefully removing a superficial soil layer (~10-20 cm) from one part of a field, concentrating it on the lower end of that field in order to reduce slope gradient and length. Another terrace is created directly downslope to form a cascade of terraces. Terrace risers have to be of restricted height (~50-150 cm) to prevent steep and unstable terraces. Stones from the fields can be used to reinforce the terrace ridge. After terrace construction, fields should be gently sloping (<3%) in the direction of the main slope. The distance between terraces must be enough to allow tractor movement during normal cultivation activities and it depends also on the slope gradient. The steeper the slope, the shorter is the distance between terraces. Terraces reduce the formation of gullies and retain water from upslope. The terraces are made with locally available machinery (tractor, small bulldozer). The terrace ridges are optimal locations to plant olives, almonds or fruit trees. Moreover, to be most effective, the terrace ridges are vegetated with shrubs adapted to semi-arid conditions and with a good surface cover (>~30%) throughout the year (e.g. Stipa tenacisima, Rosmarinus officinalis, Thymus vulgaris, Ulex parviflorus, Rhamnus lycioides, Pistacia lentiscus). Natural regeneration of vegetation is allowed without limitation on the terrace ridges, so no herbicide application or burning are carried out to remove weeds. Where possible, regeneration should be stimulated by planting the same adapted species in at least 25% of the terrace ridge. Optionally, in the other 75% of the terrace ridge, cereals or other leguminous species can be sown, but should not be harvested or used for grazing.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology reduces flooding, damage to infrastructure and siltation of water reservoirs, while maintaining (or slightly increasing) crop productivity. This is achieved by reducing runoff, soil erosion and hydraulic connectivity through a decreased slope gradient and an increased vegetation cover. The terrace ridge functions as a sink for runoff within fields and reduces runoff velocity. The vegetation leads to increased soil organic matter content below plants, producing an improved soil structure and a higher infiltration capacity. The use of stones from the fields to reinforce the terraces is optional, but facilitates crop production in the fields and makes the ridges more resistant to higher runoff velocities. The technology requires an initial investment in the construction of the terraces. Terraces can best be located on thalwegs and on areas where gully formation is often observed. Maintenance consists of filling up possible bank gullies developed in the terraces after important rainfall events and, if needed, substitute decayed shrubs with new ones.
Natural / human environment: The technology is generally applied on soils of shallow to medium depth (20 – 60 cm), and slopes are gentle to moderate (5-15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, peaking in summer commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanized and market-oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately-owned.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Espanha
Região/Estado/Província:
Murcia
Especificação adicional de localização:
Guadalentin catchment
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Most of the earthen terraces are already much older than 50 years. Recently, the regional administration is promoting clearly defined vegetated strips with minimum dimensions in order to apply for subsidies.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agrofloresta
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and loss of soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: November to June
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
The exact area is not known, but the technology is widely applied throughout the province of Murcia and the district of the upper Guadalentin.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Almond and cereal fields often have a relatively low surface cover by vegetation during long periods of the year, leaving the soil unprotected against raindrop impact and rill or gully formation), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Reduced infiltration capacity causing runoff and soil erosion), other human induced causes (specify) (Cropping of relatively steep slopes sensitive to erosion because of slope gradient), governance / institutional (spatial planning of land use results in formation of too large fields without field boundaries)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (High intensity erosive rainfall is common), droughts (Dry periods and dry years require higher water availability)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
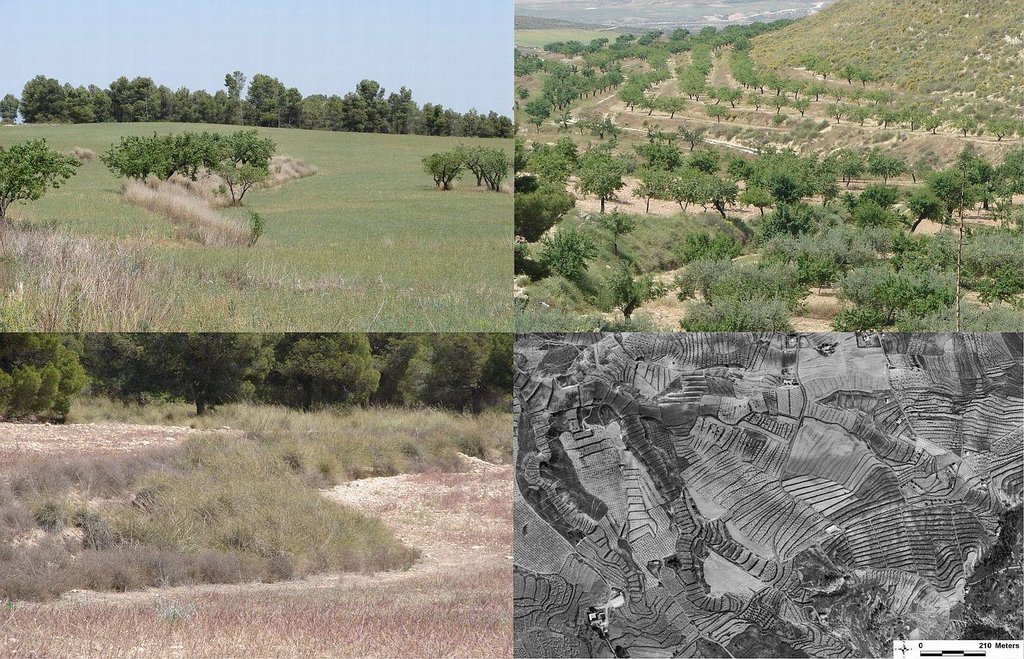
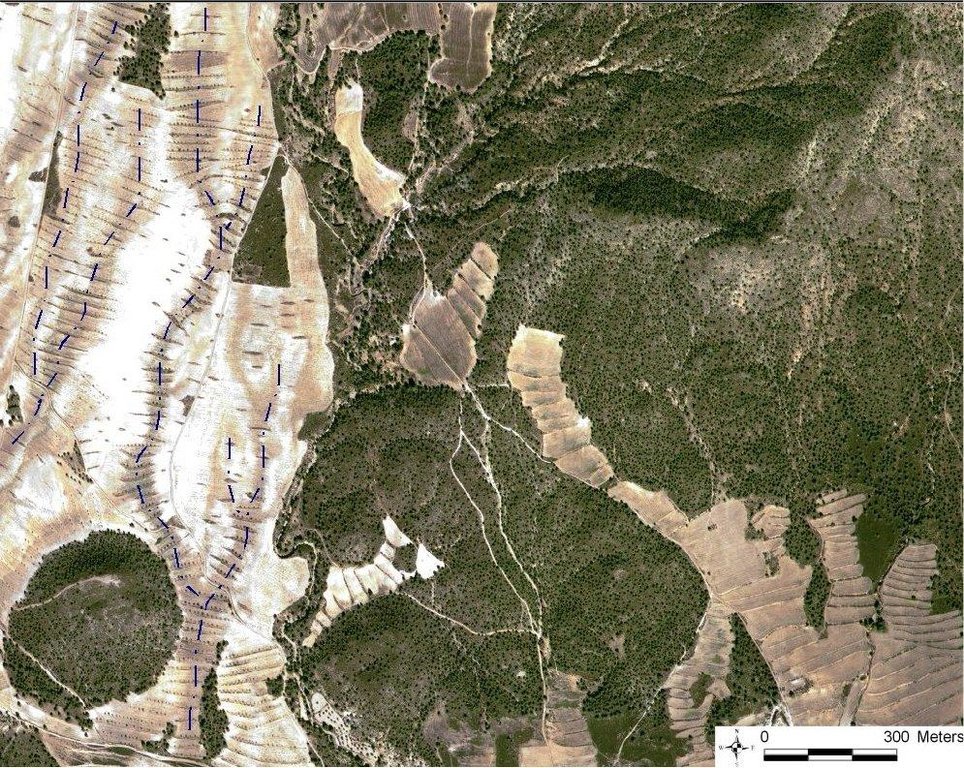
Quickbird satellite image showing the concentration of terraces along natural drainage lines (thalwegs) where runoff concentrates. Drainage lines are indicated with dotted lines.
Location: Torrealvillla. Murcia
Date: Satellite image 2003
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Design of the terraces and selection of the location requires some technical knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Practical implementation of the terraces does not require a high level of knowledge)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 42
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-7
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: alligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): >30% cover
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: natural regeneration of shrubs with possible additional plantation of almond trees and/or woody shru
Grass species: Natural regeneration assisted by seeding of legiminous species and cereals
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-200
Construction material (stone): Only when many stones are present in the fields
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: <3%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
EURO
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
0,63
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
79.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantation of shrubs and cereals or Leguminous species (optional) | Vegetativo | Autumn - winter |
| 2. | Construction of terraces | Estrutural | autumn or winter |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 270,0 | 270,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 428,0 | 428,0 | 12,0 |
| Material vegetal | shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1,0 | 218,0 | 218,0 | 10,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 916,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replace died shrubs (optional) | Vegetativo | autumn-winter |
| 2. | Filling up bank gullies in terraces | Estrutural | twice a year or after heavy rainstorms |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 28,0 | 28,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | 10,0 |
| Material vegetal | Shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 10,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 74,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: For initial construction a large tractor or small bulldozer is required. For maintanance a normal tractor can be used.
The costs were indicated assuming a distance between terraces of 50 meter, meaning two terraces of 100 meter long per hectare. Prices are for spring 2008. Subsidies are foreseen for the installation of the vegetated terraces and for maintenance during at least 4 years if all requirements are fullfilled that are described in the regional development programme.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Price of fuel and labour are the most important determinants of the costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
300,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Dry period in summer during 3-4 months (June – August/September)
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Hill slopes-footslopes (mostly on concave slope segments)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: >50m (There is a lowering of groundwater table due to overexploitation for irrigation purposes)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (excess: sporadically there are flash floods during extreme rainfall events)
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only (irrigation) (groundwater)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who don’t. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory, or office.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
All cropland is privately owned. Some shrubland or forest is state property. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the Segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Depending on local conditions yield may be the same or increase slightly
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Field paths become shorter, so more tractor movement is required (not more kilometres!)
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Implementation of terraces is considered relatively expensive
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Depends on crop yield.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Less damage to fields due to less gully formation
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Less damage to neighbours fields by gullies and flooding
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
There is less damage to fields and to infrastructure due to gully formation and flooding.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
On the long term higher infiltration capacity of the soil
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation on the terraces increases vegetation cover
Perda de solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Terraces provide corridors connecting fields and provide shelter
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Comentários:
The crop type is sensitive to changes in water availability under the semi arid conditions
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Comentários:
Implementation of the terraces is relatively expensive. Additionally planting of shrubs is also relatively expensive and requires a subsidy. Once installed, maintenance is not expensive and pays off because of less damage to fields and infrastructure.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Terraces are traditionally widespread in the region. Most of them were installed without external support. Nowadays there are subsidies for construction and maintenance of vegetated strips and terraces.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is acceptance, but it is not growing. In some parts terraces are removed to make larger fields, and some new ones are also constructed. Recently installed subsidies may change this
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The terraces prevent gully formation and damage to the fields and to their neighbours How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance is needed and should be promoted. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
This technology is very effective at reducing surface runoff and erosion by reducing slope gradients and connectivity. In addition, it has a water harvesting effect. So it reduces on-site and off-site erosion problems and potentially increases water retention in the fields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology can be enhanced by providing more info and publicity so that existing terraces are maintained. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It is considered relatively expensive to implement and particularly the optional planting of woody species is considered complicated in dry years | Subsidies for terrace construction and planting of woody species as well as cooperation between farmers to reduce costs of maintenance when subsidies stop. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology does not significantly improve farm income and has a significant implementation cost. | Provide information on all the advantages that include many costs for society (including floods, reservoir siltation etc.). The subsidy for implementation already solves the problem of implementation costs. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Garcia-Fayos, P. and Gasque, M., 2002. Consequences of a severe drought on spatial patterns of woody plants in a two-phase mosaic steppe of Stipa tenacissima L. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(2): 199-208.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
internet
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Hooke, J.M., 2006. Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region. Geomorphology, 79(3-4): 311-335.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
internet
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kirkby, M.J., Bracken, L.J. and Shannon, J., 2005. The influence of rainfall distribution and morphological factors on runoff delivery from dryland catchments in SE Spain. CATENA, 62(2-3): 136-156.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
internet
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo I. 508pp
URL:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Regional rural development programme [Espanha]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Compilador/a: Joris De Vente
Módulos
Não há módulos