Traditional irrigated rice terraces [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Ramanand Bhattarai
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Tari khet (Nepali)
technologies_1099 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - NepalNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/11/2003
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Level bench terraces with risers protected by fodder grasses, used for the irrigated production of rice, potatoes and wheat
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
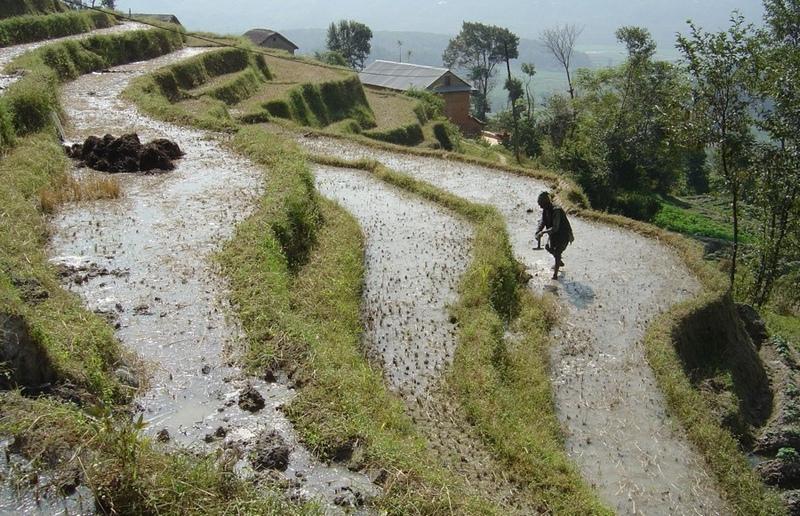
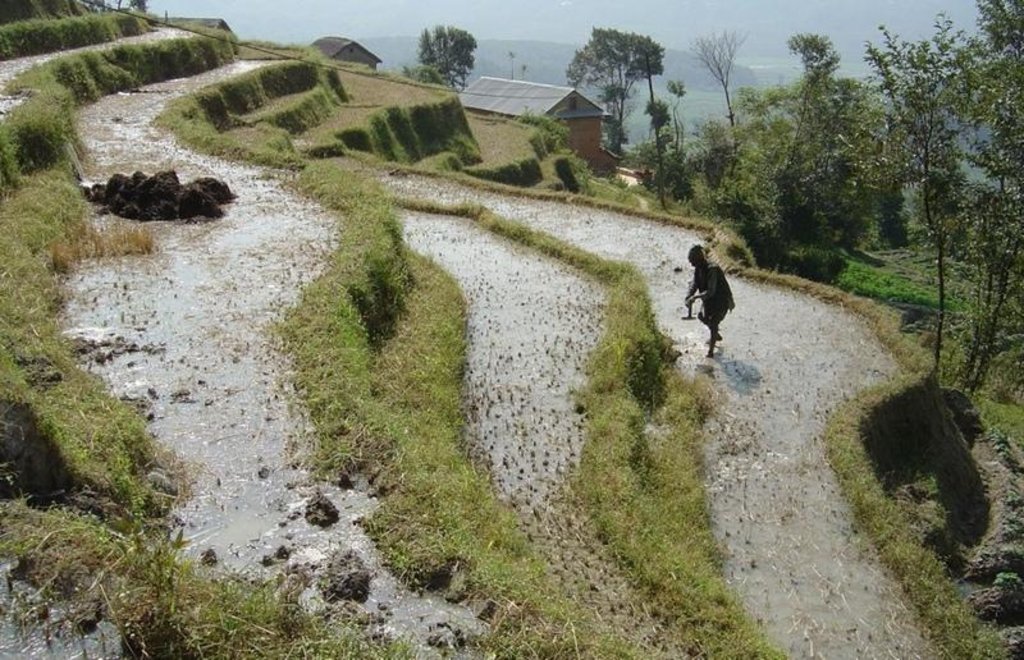
The level bench terrace is a traditional technology that makes irrigated crop production possible on steep, erosion prone slopes. The majority of such terraces in Nepal were constructed by hand many generations ago, but some new land - mostly already under rainfed cultivation on forward sloping terraces - is still being converted into irrigated terraces. The initial costs for the construction of the terraces are extremely high – and annual maintenance costs are considerable also. The climate is humid subtropical, slopes are steep (30%-60%) and soils generally have a sandy loam texture. Terraces are cropped by farmers who mostly have less than 0.5 ha of land each.
Two to three annual crops are grown per year starting with paddy rice during the monsoon, followed by potatoes and/or wheat.
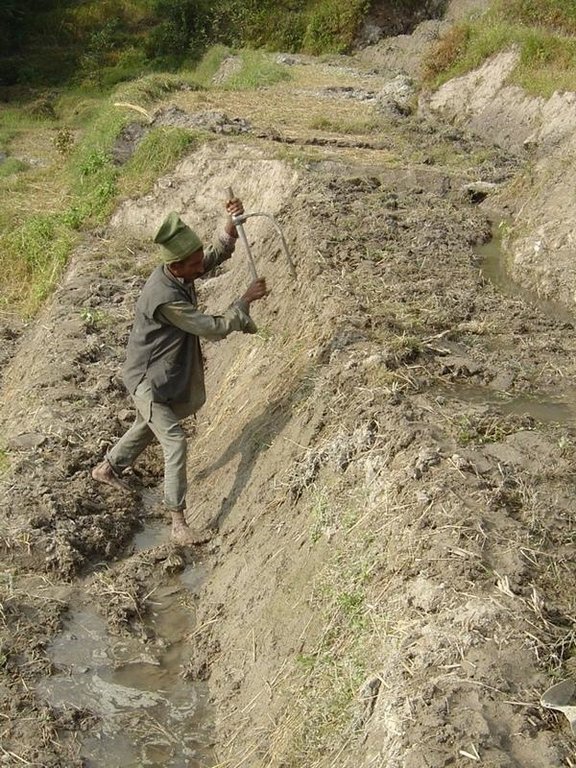
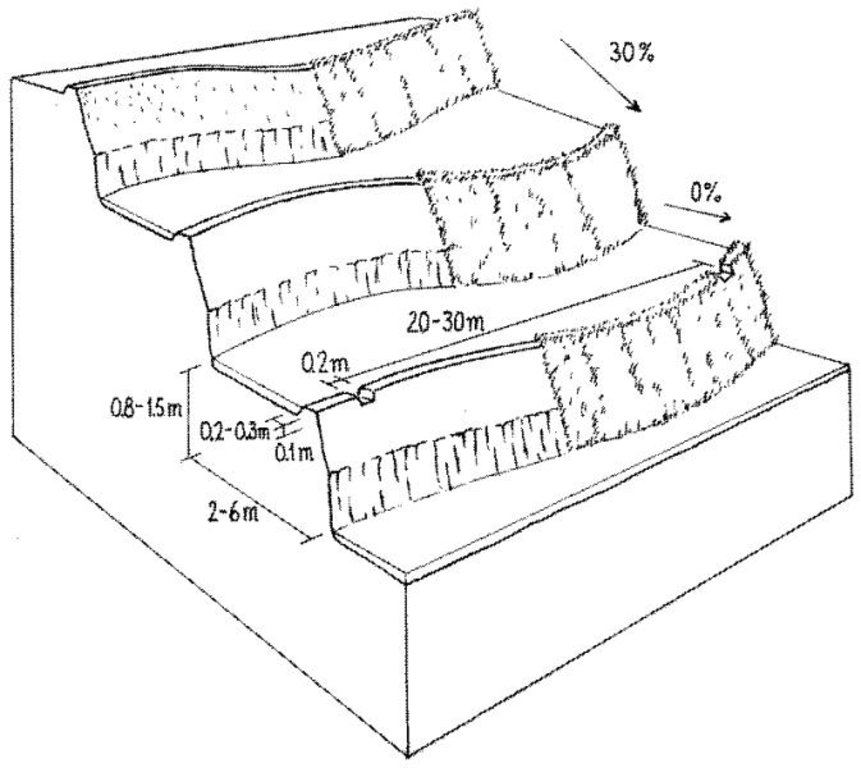
While terrace beds are usually 2–6 m in width, to save labour they are made as wide as they can be without increasing the danger of slips/land slides. Surveying was traditionally done by eye, but now a water-tube level may be used. Risers are 0.8-1.5 m high with a small lip (20-25 cm). The slope of the riser varies from 80 to 160%, depending on the initial gradient of the hill. Stones are incorporated in the risers if available, and grass species such as bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and napier (Pennisetum purpureum) may be planted for stabilisation and as cattle fodder. The risers are compacted (with hoes) to improve ponding conditions for the paddy rice. Twice per year the risers are scraped with a special tool: (1) at the time of land preparation for paddy rice the lower part of riser is sliced, but the upper part is left protected with grasses against the monsoon rains; (2) at the time of wheat planting the whole riser (including the lip) is scraped and spread as green manure on the terrace.
Terraces are flooded with water for paddy rice cultivation: a smaller amount of water is diverted into the fields for other crops. Excess water is drained to the lower terrace by openings in the lip, which are filled with rice straw in order to filter out sediments. The depth of water for rice - when flooded completely - is normally between 10 and 15 cm. Fertility is maintained by addition of farmyard manure, spreading the scraped soil from the riser, and also through sediment carried in the irrigation water. Nowadays, mineral fertilizers are also applied.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Região/Estado/Província:
Kathmandu
Especificação adicional de localização:
Manmata subwatershed
Map
×3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Potatoes
major food crop: Rice and wheat
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - steep slopes, not suitable for agriculture in their original state (better for forestry, agroforestry, horticulture, and fruit
trees)
- small and scattered plots of land
- land users find chemical fertilizers and water expensive
- there is water scarcity from September to May and too much rain in the monsoon period (June to August) with the danger of erosion and collapse of the terraces
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 sq km2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Layout of irrigated terraces. Openings in the lips drain excess water, grass cover stabilises lips and risers (right). After harvesting of rice, the grass is scraped off the lower part of the risers (left) and spread on the terrace beds
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, control of dispersed and concentrated runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green/farmyard manure
Vegetative measure: fodder grass at risers
Terrace
Material: earth
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting grasses including bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon). | Vegetativo | during monsoon |
| 2. | Construct bunds (risers) with soil from upper and lower sides | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 3. | Level terrace beds (soil moved from upper to lower part of terraces). | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 4. | Make lips on edges of terraces | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 5. | Compact risers | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 6. | Construct irrigation canal | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 7. | Make openings in lips for drainage of excess water | Estrutural | before monsoon |
| 8. | Test-irrigate terrace for accurate levelling | Estrutural | during monsoon |
| 9. | Plant grasses including Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) | Estrutural | during monsoon |
| 10. | After 2–3 years: some narrow terraces may be merged to form single, wider terraces | Estrutural | during monsoon |
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flood the paddy fields .. | Agronômico | (June/July) / Repeated 3–4 times during |
| 2. | Slice/scrape grass and soil on lower part of risers and spread on terraces | Agronômico | (when flooded, June/July) / |
| 3. | Plant rice and apply mineral fertilizer | Agronômico | (June/July). / |
| 4. | Harvest rice | Agronômico | (October) / |
| 5. | Apply manure (cattle manure), after rice harvest | Agronômico | (October). / |
| 6. | Slice/scrape grass and soil from whole of risers and spread on terraces; repairsmall collapses/slumps in risers | Agronômico | (October/November) / |
| 7. | Pprepare land | Agronômico | (November) / |
| 8. | Apply mineral fertilizer | Agronômico | (November/December). / |
| 9. | Irrigate | Agronômico | Nov. / repeated several times during cultivation |
| 10. | Harvest of potato/wheat | Agronômico | (January-March). / |
| 11. | Planting of rice | Vegetativo | June,July / |
| 12. | planting of potatoes, wheat | Vegetativo | November / |
| 13. | Repair of small collapses/slumps in risers. | Estrutural | (Oct./Nov.)/ |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 185,0 | 185,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 840,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade, baskets, (doko), special tool for scraping
Current establishment costs are very difficult to determine since the majority of the traditional terraces were
established a long time ago. Costs depend closely on the present state of the land (forward sloping terraces or uncultivated) and the need for irrigation canals. Farmers say that construction now could cost up to US$ 10,000 per ha if carried out by hand at full labour cost. The cost given for maintening the terraces (approx. US$ 840 per ha) includes all associated annual crop production costs. In this case study, 100% of the construction costs were borne by land users.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because of the geology and soil texture (loam)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Off-farm income specification: hired labour (on other farmers’ fields) or as porters
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (rice/wheat) and commercial (potatoes)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Land use rights: leased (90% of farmers), individual (10%)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
the technology is a part of a complex farming system
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Disparidades econômicas
Comentários/especificar:
not everyone has access to land for irrigation
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Livestock fodder
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
when the agreed and scheduled water extraction amounts are exceeded
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
poor maintenance of topmost terraces may cause landslides
Outros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
Biodiversity
Number of crabs in irrigation water make holes in the terrace risers
Comentários/especificar:
which in turn can cause pipe erosion and riser collapse
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Groundwater recharge
Soil moisture and nutrients downstream
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Income and production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the terraces (including all maintenance activities) |
| Easier to cultivate flat terraces/less labour required (after establishment of terraces) |
|
Work sharing: traditional terraces are part of a long tradition of work sharing within the community with no external labourneeded How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established traditions and norms |
|
Technology is easy to understand/apply. Increased opportunities for irrigation facilities: farmers without level terraces are not allowed (by the irrigation committee at village level) or do not claim irrigation water |
|
The irrigation element of this technology fosters social bonds within the community How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established norms and traditions. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Decreased grass production (grazing area reduced) | Promote planting of high value grass species on risers (such as bermuda grass). |
| The farmers believe that the terraces are too narrow (for efficient use of tractors); they would like to have wider terraces |
Investigate possibilities of constructing wider paddy rice terraces on steep slopes, which, according to present experience, is not possible. |
| High labour costs for establishment. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
There is considerable literature on the construction and maintenance of irrigated terraces in general, but no references thatspecifically describe the traditional paddy rice terraces in Nepal
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos