Disability inclusive, flood resilient cluster village [Bangladesh]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Subir Saha
- Editores: Subir Saha, Manuel Rothe
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
"Protibandhita Bandhob Bonna Sohisnu Gucca Gram"
technologies_2005 - Bangladesh
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Christoffel Blindenmission (CBM) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Not problematic with regard land degradation. It provides efficient and sustainable use of available land resources.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilador/a: Subir Saha
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
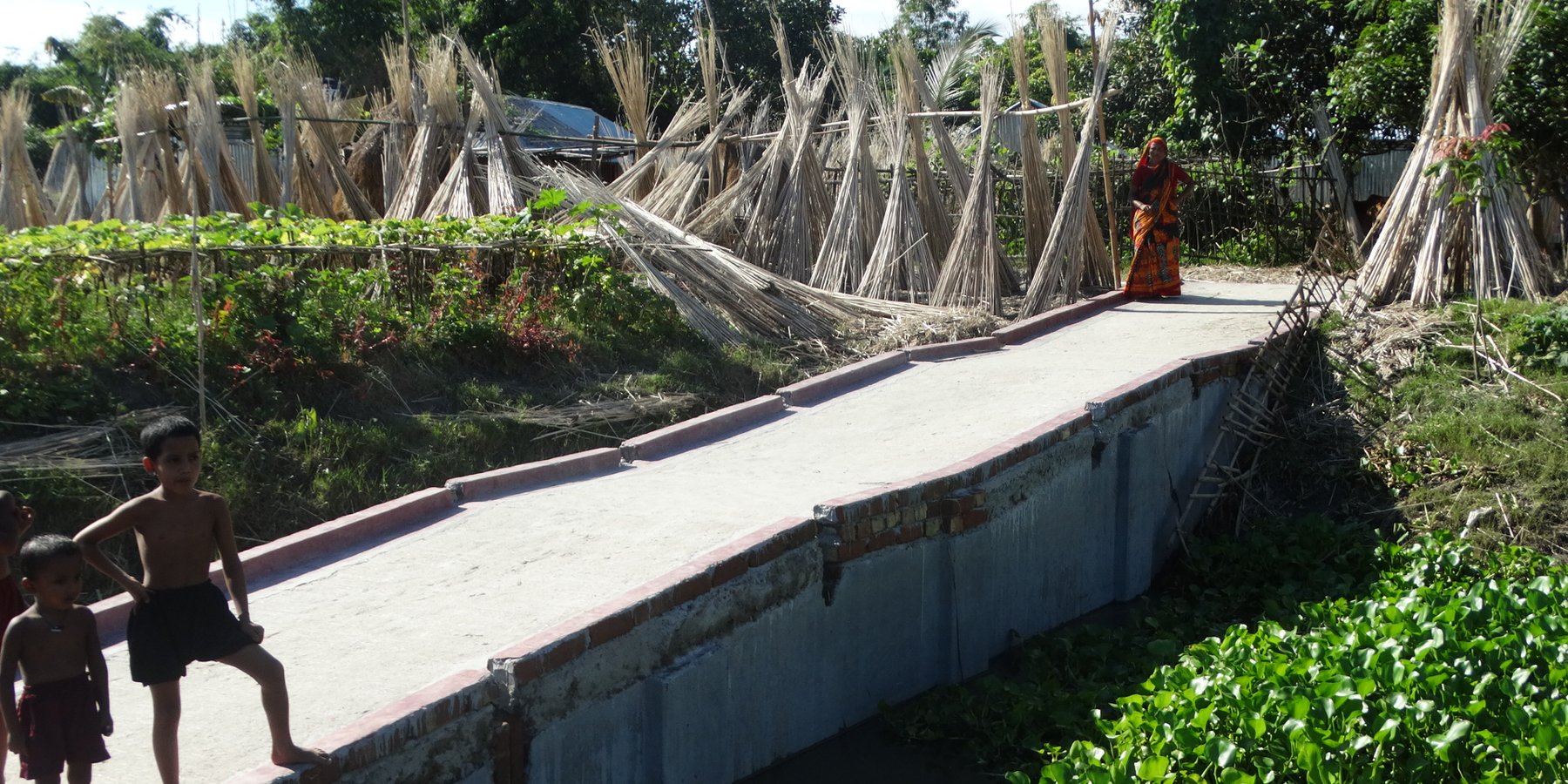
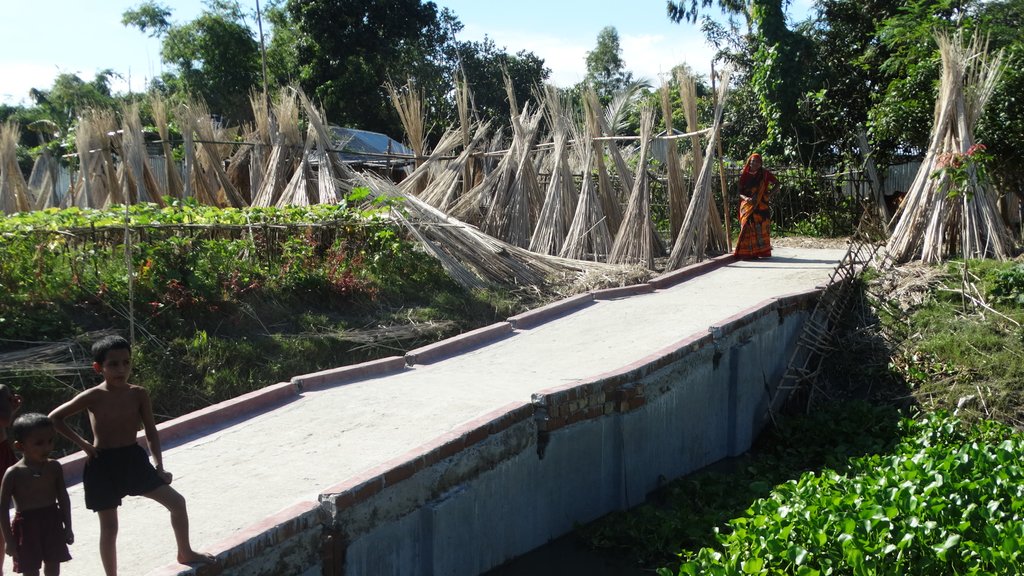
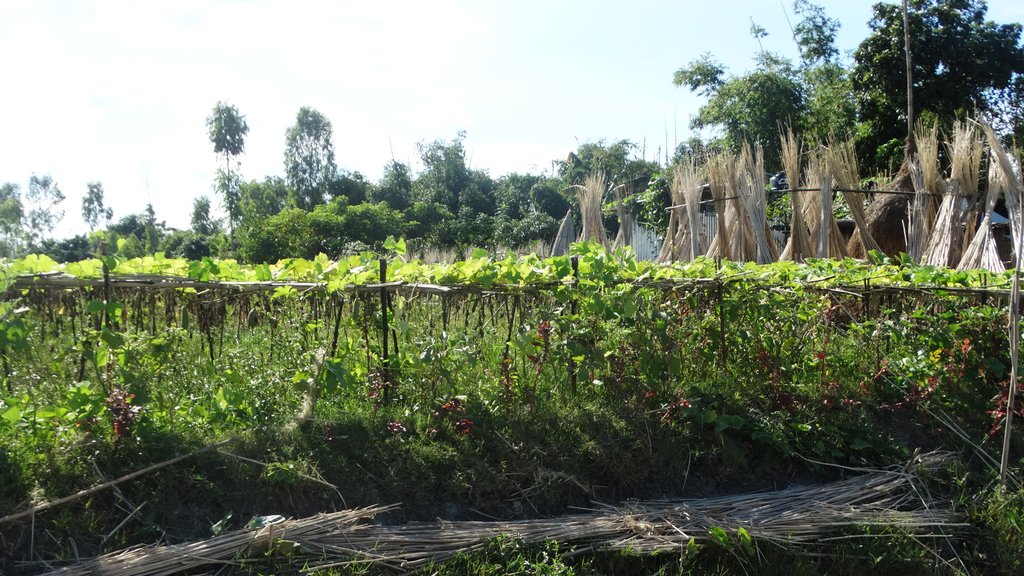
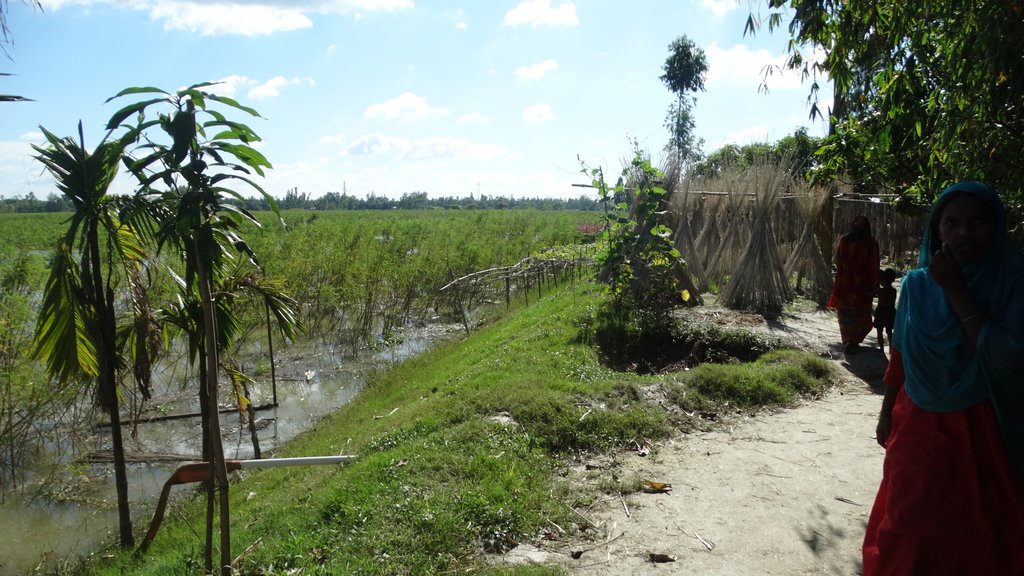
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village provides safe housing, food security and income generation for multiple families, including persons with disabilities, in a highly flood prone area of Gaibandha District in northern Bangladesh. The land was raised above flood level and is protected by deep rooted fruit trees to prevent soil erosion and provide income for the land users.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
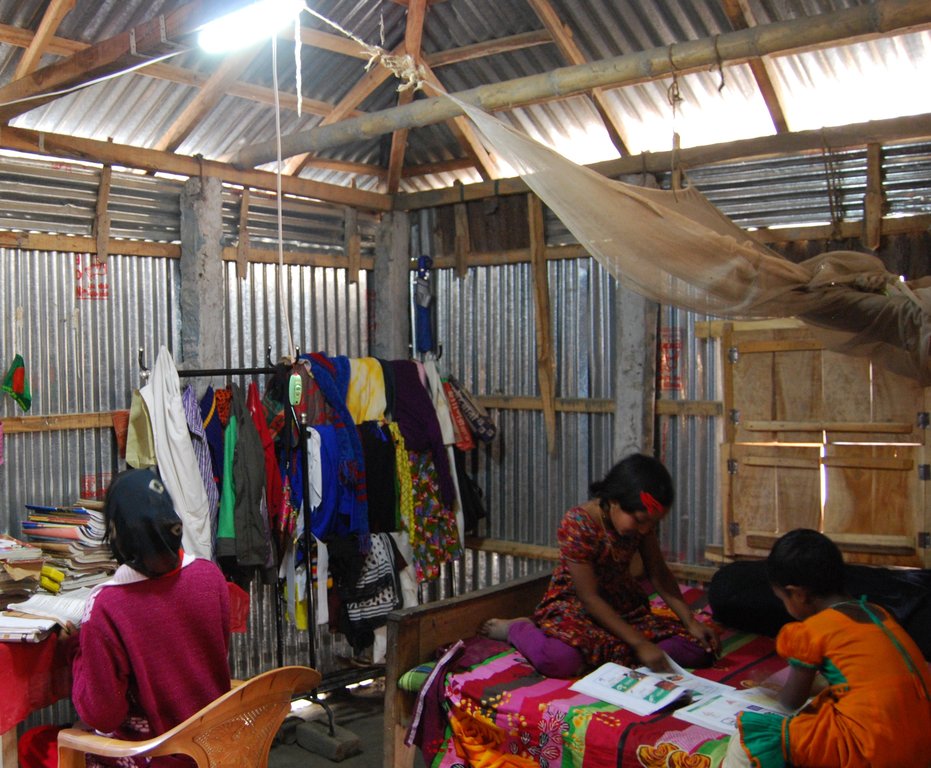
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village was introduced in a rural area with a high risk of recurring monsoon floods. The purpose of the technology is to provide safe housing, safe shelter for livestock, food security and income generation for ten families, including persons with disabilities.
The main components of the technology are:
1) The raising of a piece of land by seven feet (213cm), to three feet (91cm) above expected highest flood levels. Solid soil was banked up to encircle a 30'000 square feet (roughly 50x57m) piece of land and then the space within was filled up with sand collected from a nearby river bank. A one-foot layer of solid soil was added to cover the entire area.
2) The protection of the raised land from soil erosion during floods by planting a combination of deep-rooted fruit- and medicine trees around the border of the raised land. The trees include a number of different types of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees and one type of medicine tree, Azadirachta Indica, locally known as "Neem". In addition, the slope of the border area was covered by grass turf to protect the soil from being washed out by rain. Two types of deep-rooted and flood resistant grasses were used. A drainage system was installed to facilitate water runoff.
3) The planting of a 150 square feet (14m2) commonly used homestead vegetable garden at the center of the cluster village. The cultivated vegetables include red spinach, jute leaf, basella leaf, spinach, radish, cabbage, okra, bottle-guts, cucumber and beans, allowing for a summer and a winter harvest. Together with the fruit trees, the vegetable garden provides food security during prolonged flooding. They also provide improved nutrition and income generating opportunities through selling of a part of the harvest in the market.
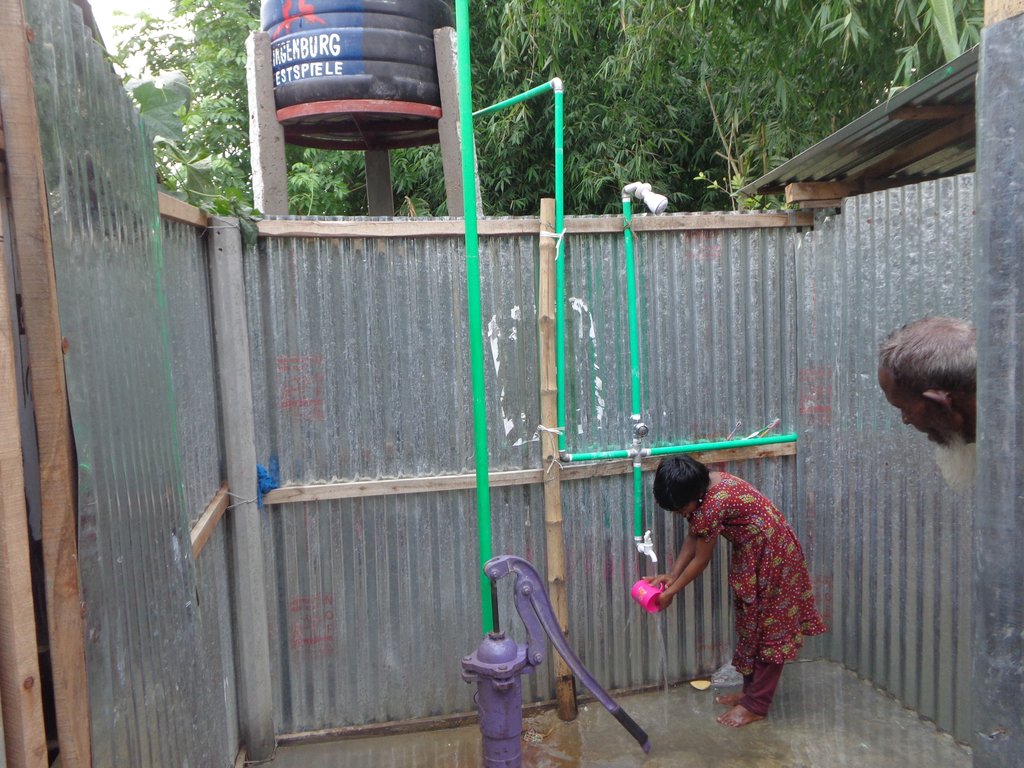
4) Making the village accessible for persons with disabilities through different accessibility measures, including the construction of a ramp, connecting the cluster village entrance with the road, and of accessible common Water-, Sanitation- and Hygiene (WASH) facilities, including a latrine, deep bore hole water source and water storage tank.
5) Installation of a solar panel to ensure uninterrupted, flood-resilient power supply. The level of power supply is sufficient to ensure coverage of electricity needs during flood season, when regular supply is around 15% below annual average.
The Cluster village was constructed as part of a disaster risk reduction project by CDD (Center for Disability in Development) from Bangladesh, with the support of CBM (Christoffel Blindenmission), an international development organization and funded by a donor from Germany. The main cost for inputs were provided to the land users by the project, including rent of construction machinery, paid labor, soil and construction material for the ramp and WASH facilities. The land users contributed labor and seedlings for the planning of the border trees and the homestead vegetable garden.
The main benefits of the technology from the perspective of land users are the protection it provides for houses and livestock, which would otherwise be in danger of loss during floods. The availability of food, water and electricity allows land users to remain in their homes during floods and avoid evacuation and the risk associated with it, including for example protection risks or the risk of theft. The flood protected vegetable gardens and fruit trees provide a year-round, sustainable source of food and income, providing food security and improved nutrition. The Neem tree provides medical and hygiene uses of the branches and leaves.
The cluster village is used as a safe space for the land users and other members of the community and their livestock during floods. Land users who are persons with disabilities or elderly benefit from the accessible infrastructure. With multiple families sharing land, the cluster villages provides optimal utilization of land resources. An additional benefit mentioned by land users is that the joint use by multiple families led to a more progressive social culture.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bangladesh
Região/Estado/Província:
Gaibandha District
Especificação adicional de localização:
Horipur Union, Sundargonj Sub district,
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
Kani Charitabari, Horipur Union, Sundargonj sub district, Gaibandha District.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2016
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was introduced as part of a disaster risk reduction project, implemented the Center for Disability in Development (CDD) with the support of Christoffel Blindemission (CBM) and with participation and leadership of the local community. The project was financially supported a group of donors from Germany.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Assentamentos, infraestrutura
- Assentamentos, edificações
Comentários:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2 (Summer and winter)
Livestock density : Livestock are available in every household.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Hortas familiares
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
- S8: Saneamento/estruturas de águas residuais
- S9: Abrigo para plantas e animais
- S10: medidas de economia de energia

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M6: Gestão de resíduos (reciclagem, reuso ou redução)
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wr: erosão das margens
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
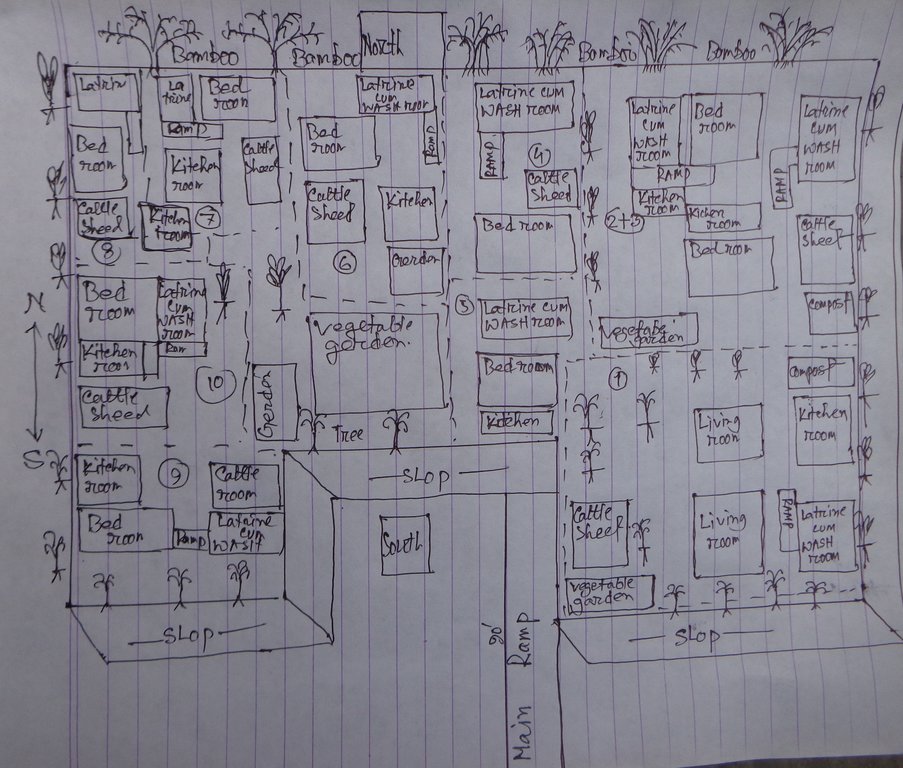
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The drawing shows the layout of the disability inclusive, flood resilient Cluster village. The components of the technology are:
Raised land/plinth: 1) Purchase of land of a total area of 18'000 square feet (ca. 40x40m). Land ownership transferred to joint ownership of 10 families. 2) Collect 15'000 cubic feet (425m3) of solid soil from different pieces of land in the community. The soil was donated by members of the community, who were either related to the land users of the cluster village or donated in support of the construction of a safe space which can be used by the community during floods. 3) Banking up of 3 feet (91cm) of solid soil along the borders of the land. 4) Filling of area with 140'000 cubic feet (3965m3) of sand, extracted from a nearby riverbank with a rented sand extraction machine, raising the land to 6 feet (183cm). 5) Covering the entire area with one additional foot of solid soil, rasing the land to 7 feet (213cm), which means 3 feet (91cm) above the maximum expected flood levels.
Soil protected through deep-rooted trees: 1) Planting of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees, surrounding the entire border of the raised land. The trees include deep rooted fruit trees like mango, black berry, jack-fruit, guava, coconut and areca nut, light-rooted fruit trees like banana and Papaya, a deep-rooted medicine tree, locally called "Neem" and the light-rooted Dhol Kalmi tree (pink morning glory). The number of deep-rooted threes was 100, with a spacing of around 5 feet in between each. They were planted to cover the entire perimeter of the raised land. In between the deep-rooted trees, 60 light-rooted trees were planted. In front of the deep-rooted trees, 60 bamboo bushes were planted to provide additional protection from wind and rain. 2) Turfing of the entire slope surrounding the cluster village with two flood resistant grasses: Durva (Cynodon dactylon) and Catkin grass. 3) Installation of a central drainage system with 15 plastic pipes ensuring water runoff from the wastewater pond.
Road access through ramp: The connecting ramp of the cluster village is 90 feet length, 6 feet width. There are five landing point of this ramp with smooth slopping. The construction material includes class one brick, brick stone, cement, sand, polythene and red oxide color for color contrast, which is appropriate for low vision and visually impaired persons. There is a 5 inch border on both sides of the ramp for safe movement of a wheel chair user.
Accessible household water and sanitation facilities: Latrine and wash-room are constructed for every house in the cluster village, following universal design standards. Latrines are connected to the wash room and the main house through ramps. There is a railing on both sides of the latrine and the entrance is wider for access of a wheel chair users. Water system for the latrine and wash room is provided from a water tank on three pillars behind the latrine, which is also connected to the main house for provision of drinking water. The tank is filled by hand pump ('magic pump') which functions with minimal hand pressure. The WASH facilities are accessible and usable by everyone including persons with disabilities, pregnant women or aged persons.
Home vegetable gardens: Every household has an individual homestead vegetable gardens where land users cultivate seasonal vegetables year-round. Gardens vary in size between averaging about 1.5 decimal (60m2) in size and are surrounded by bamboo fencing. The land owners are using organic fertilizer/compost for the vegetable production of their choice. By using cow's manure and wastage they are producing the compost in the behind of their houses in a ditch.
Solar system: A mini solar system is installed on the roof for each house by using a small panel with a 12-volt battery . Each system has the capacity of providing power for light for 8 hours. An introduction to system maintenance was given to the land users by the provider of the solar system.
Autor:
Shahidul Islam
Data:
09/11/2016
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Cluster village
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
18'000 square feet piece of land
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Bangladeshi Taka
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
80,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
300
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selecting the place for cluster village construction | During rainy season in 2015 |
| 2. | Establish collaboration with 10 families who will become land users | December 2015 |
| 3. | Land Raising & Ramp construction | December 2015 to March 2016 |
| 4. | Reconstruction the existing houses of the land users on the raised land | April 2016, before onset of rainy season 2016 |
| 5. | Planting of deep- and light-rooted fruits trees, bamboo bushes and grass turfing along the boundery | February 2016 to March 2016 |
| 6. | Install accessible water & sanitation system | April-June 2016 |
| 7. | Establish home garden in front of each house | June-July 2016 |
| 8. | Install mini solar system for each house | Aug-sep 2016 |
| 9. | Prepare livestock shed for each house | October 2016 |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land raising, tree planting and turfing on slope | person days | 290,0 | 300,0 | 87000,0 | 10,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Ramp construction | person days | 115,0 | 350,0 | 40250,0 | 10,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | House reconstruction and WASH facilities | person days | 200,0 | 400,0 | 80000,0 | 10,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Solar system installation | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipamento | WASH equipment (latrine, magic pump, water tank, pipes, switch, pillars and other) | pieces | 10,0 | 46658,0 | 466580,0 | |
| Equipamento | Solar system | pieces | 10,0 | 6300,0 | 63000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Deep rooted trees | pieces | 100,0 | 40,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seed for vegetable | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Sapling purchase | pieces | 100,0 | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Light rooted tree | pieces | 60,0 | 30,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Organic fertilizer (compost) | KG | 600,0 | 10,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Rent for shallow machine for sand extraction | Daily rent | 10,0 | 28800,0 | 288000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Grass turfing | square feet | 15000,0 | 10,0 | 150000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Allowance for house reconstruction material | House | 10,0 | 2000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Ramp construction | Piece | 1,0 | 125750,0 | 125750,0 | |
| Outros | Project management (monitoring and support) | persons-days | 180,0 | 2400,0 | 432000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1777380,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 22217,25 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The project, human resource supported by CBM, CDD and a funded by private donor.
Comentários:
Labor for tree plantation, home stead gardening & house reconstruction was contributed by the land users.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turfing: Repair leakages, replace grass etc. | before onset of rains |
| 2. | Tree maintenance: Cutting branches, manure of roots etc. | Rainy season |
| 3. | Vegetable gardening | Summer & Winter season |
| 4. | Housing repairs | After harvesting season/ once in a year |
| 5. | Water and Sanitation system servicing and repairs | After harvesting season/once in a year |
| 6. | Solar system maintenance | Winter season/once in ayear |
| 7. | Village group meeting for decision making and conflict resolution | Once in a month |
| 8. | Organic composting/fertilizer production | Continuous |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | House repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Ramp repairs | person days | 10,0 | 300,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Plingth raising and plantation | person days | 30,0 | 300,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Solar system servicing by technical experts | piece | 10,0 | 500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seed for vegetable gardening | KG | 5,0 | 1000,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Soil for slope maintenance | square feet | 5000,0 | 10,0 | 50000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Sand for slope maintenance | KG | 5000,0 | 2,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 85000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 1062,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Land users are agreed to contribute 100% maintenance cost
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Market fluctuation and scarcity of goods in the flood season.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Heavy rainfalls are one of the causes for flooding
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Frequentemente
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Age of land users includes children, youth, middle-aged as well as elderly.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Land users jointly own the land of the cluster village. They do not own any additional agricultural land and work as daily laborers and sharecropers.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Grupo
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Land users own the land of the cluster village jointly, including a proportional share of land- and water use rights.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Fruit and vegetable production increased after introduction of the cluster village. Because of decreased loss of home and property during floods, labor is freed for crop production which increased overall crop production in the wider area.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Fruit and vegetable quality is improved because of availability of Irrigation.
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
Livestock mortality rate is reduced because of safe space in Cluster village.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Homestead vegetable garden and fruit tree plantation above flood level has a significantly reduced risk of production failure.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
The flood-protected homestead vegetable garden allows for higher product diversity.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Increased availabilty of flood protected land for vegetable gardening.
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Energy supply was not available before installation of solar panel.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
Qualidade da água potável
Comentários/especificar:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Irrigation available to land users after installation of deep tube well.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Demand for irrigation water increased because of vegetable garden.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of farm income through selling of fruit and vegetables.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Additional income source through selling of fruit and vegetables.
Disparidades econômicas
Comentários/especificar:
Decreased income disparities between the land users of the cluster village due to fruit and vegetable production available to all land users, Decrease income disparities between land users of the cluster village and other members of the communty because of the reduction of loss from flood damage.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Somewhat increased workload for maintenance of technology but decreased because of avoidance of damaged from floods.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Increased food security through flood prodected homestead garden and tree plantation.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Higher attendance of health workers because the cluster village offer suitable group meeting rooms and accomodation. Cluster village was constructed in vicinity of community clinic. Better hygiene through WASH facilities.
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
The cluster village is a suitable meeting point for the entire community, for social gatherings or festivals.
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
Cluster village offers common space for children and other land users for Joint recreational activities.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Much improved situation for persons with disabiltiies who are part of the land users. All persons with disabiltiies in the wider community use the cluster village as a safe space during floods. Improved situation for all land users who are from marginalized parts of society (daily laborers and share croppers).
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Soil erosion during floods decreased because of deep- and light-rooted border tree plantation.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
Raised land as safe space above flood level.
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Drought impact in summer season decreased because of Irrigation.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
available shelter and safe space
Comentários/especificar:
Cluster village provides additional safe space/shelter for the wider community.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | muito bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Around 10-15% of households which equals roughly 70 households.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
The technology is replicated by households who receive assistance from local government for families at risk of flood damage.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mercados dinâmicos
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Peoples of cluster villages are selling vegetables and fruits in the local market and some of them are carrying the fruits in the distance market. They are becoming more interested to plant more fruit trees in the cluster village. If it is continue in future it would be a fruits and vegetable market in the cluster village. At the same time they started selling cows milk in the local market and its demand is increasing day to day.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Ownership of the land user's are there. Its a community driven initiative & disability inclusive in all respect. They are happy to give shelter to the other villagers during flood season. There is an opportunity to create an example of a model village in this area. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Its an innovative program. Peoples participation and their contribution is the main asset. Universal accessibility of the cluster village communicating benefit to other villagers during rainy as well as flood season. This pilot program can be replicated to other riverine areas in Bangladesh. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The intensity of floods is difficult to predict. With average flood levels rising, land users still have to live with the risk of flood levels going beyond the level of their rised land. | More research on changing weather/climatic patterns and scientific measurement of expected flood levels. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Government and Non government organizations extension services are not available in this area. Livelihood of the cluster village peoples depending on seasonal agriculture. | Income raising multiple activity need to be introduces. A small scale disability inclusive comprehensive project could be implemented here. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
7
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
10
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
1
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
4
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
09/11/2016
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [Bangladesh]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- Compilador/a: Subir Saha
Módulos
Não há módulos