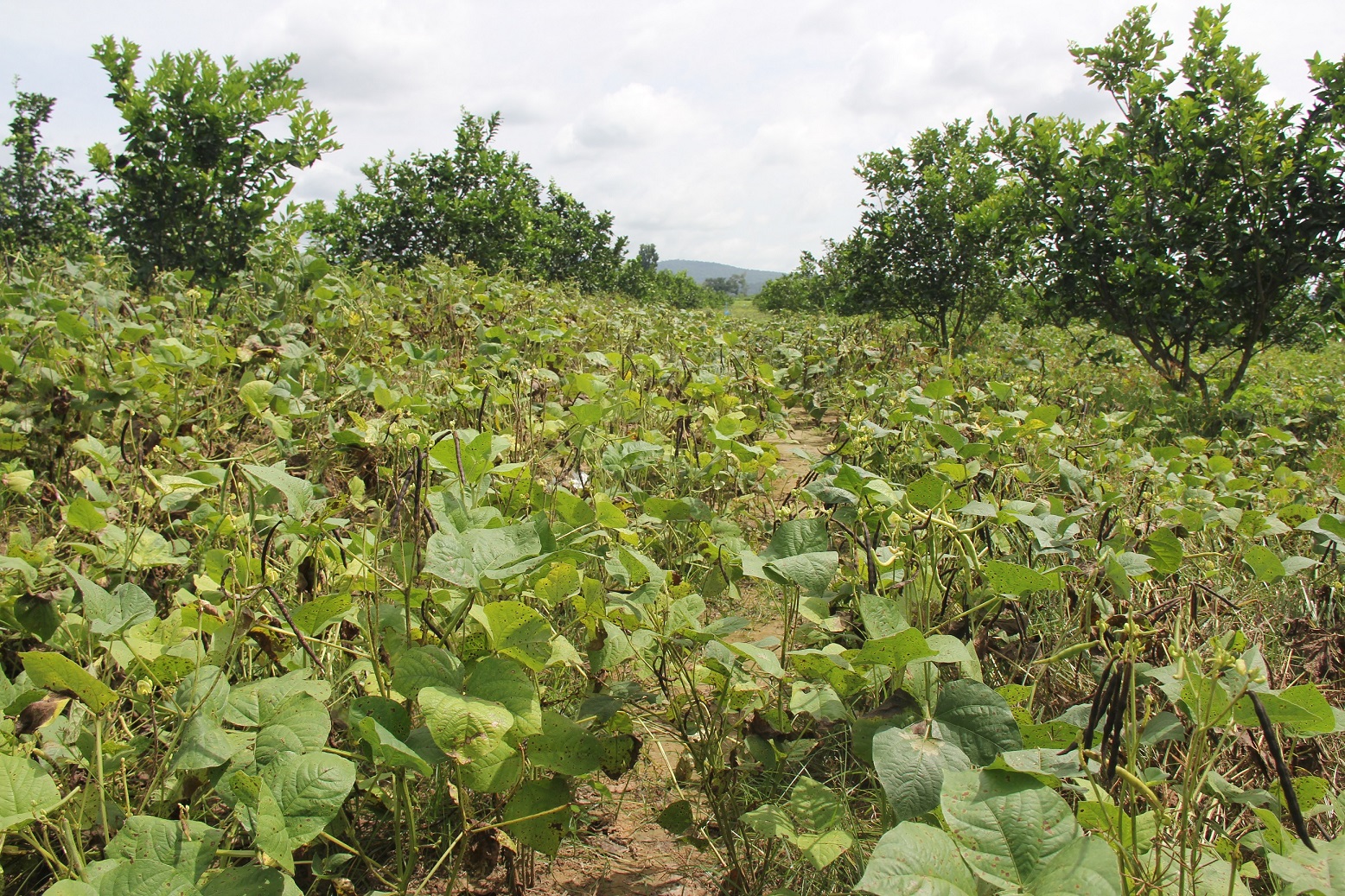
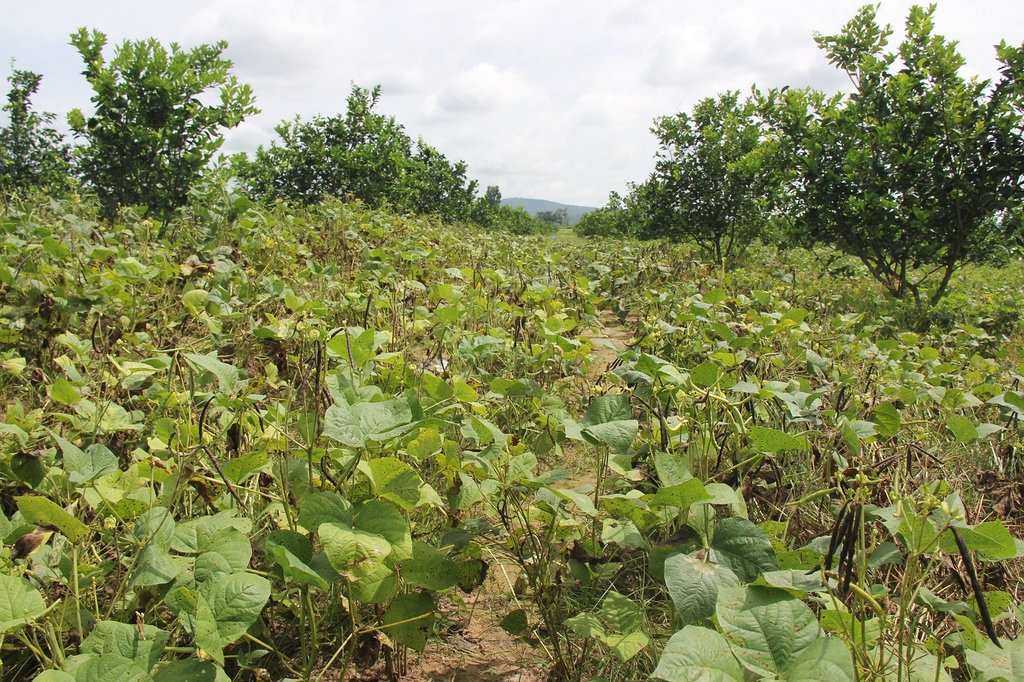
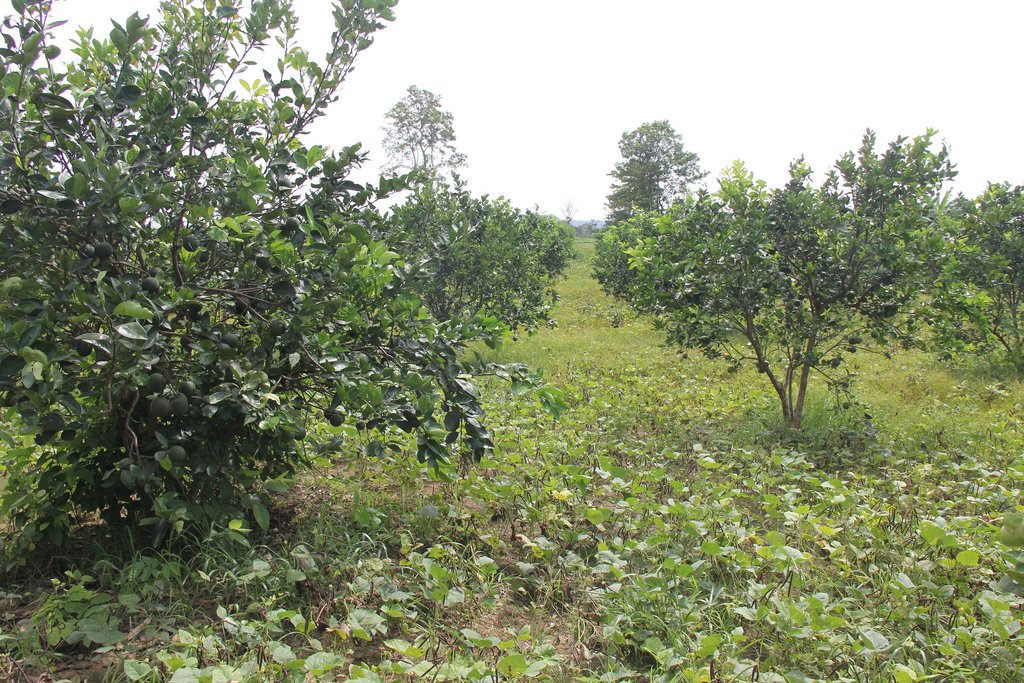
Intercropping of orange trees with mungbean in mountainous areas [Camboja]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Navin Chea
- Editores: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Revisores: Nimul CHUN, SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Intercropping
technologies_3146 - Camboja
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Chea Sarith
Land User
Camboja
Acting Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh:
Doung Phanny
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh.
Camboja
Chief Office of Agricultural Extension at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat:
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Bakan:
Agronomic Official at District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng:
Seng Kompheak
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng
Camboja
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Camboja1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Intercropping of mungbean between orange trees improves soil fertility and generates income before the orange trees bear fruit.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Agroforestry is a farming practice that can involve growing of a mixture of woody perennials like trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc. with crops and/or animals, on the same land-management units. Agroforestry systems play an important role in ecological and economical interactions between the different land use components (Lundgren and Raintree, 1982). It represents an interface between agriculture and forestry, and encompasses mixed land-use practices. Agroforestry systems are composed of three attributes:
1. Productivity (improved tree products, yields of associated crops, reduction of cropping system inputs, and increased labor use efficiency);
2. Sustainability (beneficial effects of woody perennials);
3. Adoptability (MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP, 2016).
In Cambodia, mungbean grows throughout the whole year almost, depending on the moisture factor. Mungbean is short maturity crop which can be grown both in sloping upland and in lowland areas. In upland areas farmers usually plant their second crop in August and harvest it in October. Mungbean is a crop that can be grown on many soil types, but grows best on alluvial, sandy, and volcanic soils which well drained containing high levels of nutrients (incl. N, P, K, Ca, Mg) and organic matter (MAFF, 2005). Mungbean crop duration depends on the variety, with short-term, medium-term and long-term being harvested between 60-65 days, 65-75 days, and 75-80 days, respectively.
Mungbean residues can make an active contribution to improvement of soil quality through nitrogen fixation and subsequent incorporation of this nitrogen into the soil after root and nodule degeneration by Rhizobium bacteria. The incorporation of the organic root material also improves the soil structure (MAFF, 2005, Chadha, 2010, IRRI-CIMMYT Alliance, 2009). The taproot of the mungbean can penetrate the soil to a depth of 50-60 centimeters. Sometimes, some land users grow mungbean as a green manure crop specifically to improve soil quality (Tauch Ung, 2010).
Mr. Chea Sarith is one example of land user who practices intercropping of orange trees with mungbean since 2013. The main purpose is to improve soil fertility, to prevent soil erosion, and to generate income before the orange trees provide fruit. In addition, it eases the weed control. After the harvest the farmer leaves the plant residues on the soil to provide organic matter. With the objective not to harm the roots of the orange trees, he avoids tilling the soil. In general, mungbean grows twice a season depending on the rainfall distribution and soil moisture.
The average yield of direct seeded mungbean as an intercrop between orange trees is about 1,200 kg/ha (harvested 3 times per crop). If mungbean is grown as a single crop the yield is usually ranges from 1,300 to 1,400 kg/ha. The market price for mungbean grain is usually about 4,500 to 5,000 Riel/kg.
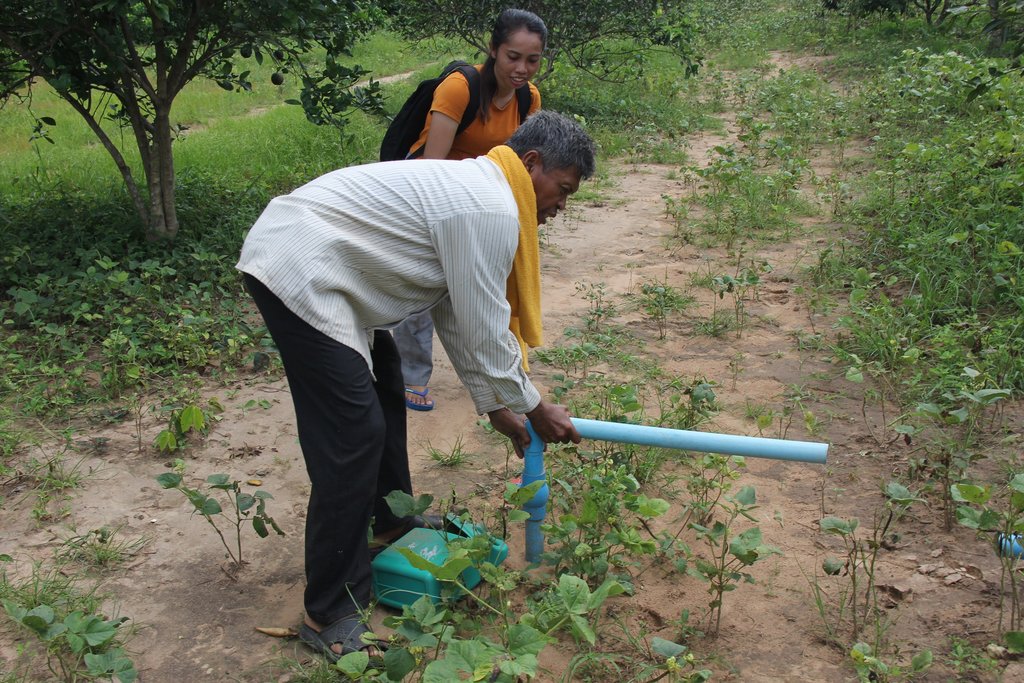
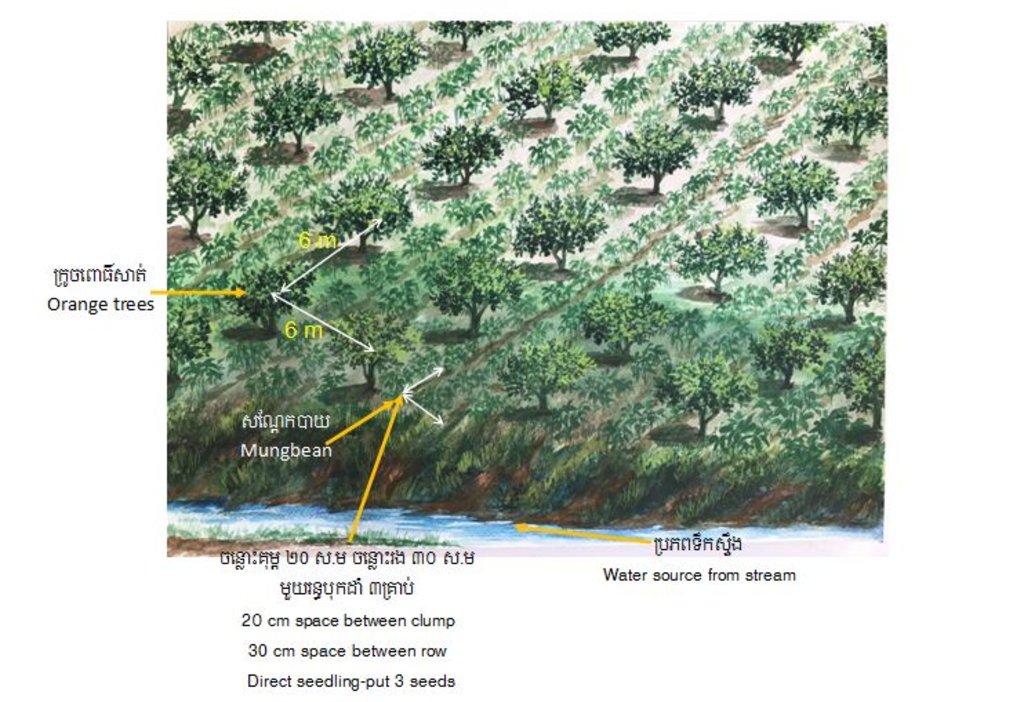
Before planting orange trees the soil requires two turns of ploughing. After first ploughing the soil should dry during 1-2 months, before it can be ploughed again by a wheel harrow. Orange trees then are planted in rows into pits of 1 m x 1 m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between the trees, as well as between the rows is usually 6 meters. Before planting, the orange tree seedlings (bought from outside) are usually kept at the farm site for 15 to 20 days, which to allow them to adapt to the conditions of the growing environment. The farmer installed a water pipe in the underground to irrigate the fruit orchard. The nearby stream serves as water source. After the tree plantation, mungbean is sown by direct seeding on the remaining bare soil. This is done by putting 3 to 4 seeds into the seed holes (3 to 4 cm sowing depth at a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm. After harvest the residues of the mungbean plants are squashed by machine and left to rot on the soil surface until is the next mungbean cycle starts by direct seeding.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Camboja
Região/Estado/Província:
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Especificação adicional de localização:
Phnum Kravanh of Cambodia.
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2013
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Through farmers experience, investigation on cropping and natural fertilizer application.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- cítrico
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Orange trees belong to the long lifespan crop which provide fruit at the age of 4 years. The lifespan of getting fruits is approximately 20 years. Then in general, the farmer cuts the trees down and grow it again. However, it depends on the yield it provides. Mungbean can be harvested within two months and half and can be harvested 3 times per crop cycle.
Comentários:
Orange and mungbean.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Floresta/bosques
Comentários:
Degraded forest, soil from termite mound.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
There is a stream near the farm for supply the water for orange trees.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo

Medidas estruturais
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The former degraded forest soil was rehabilitated by the rotten residues of the mungbean, the deep penetration of its taproots, and by the nitrogen fixation through the symbiotic association of nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nodular roots of the mungbean. Thus, the soil structure and the soil fertility were improved little by little.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The area of implementing this technology is 4 hectares with 1096 orange trees. The pit of planting orange trees is 1m x 1m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between trees and between rows is usually 6 meters to get enough sunlight. The mungbean is planted by direct seedling by inserting 3 to 4 seeds per hole (the hole is 3-4 cm in depth). The spacing between the holes is 20 cm and the row spacing is 30 cm. The farmer of this farm also installed an irrigation system by setting up a pipe under the ground.
Autor:
Mr. Khoun Sophal
Data:
05/07/2017
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
4 hectares
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
KHR (Riel)
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4000,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
20000
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear degraded forest | January |
| 2. | Clear the termite mound to flatten the area | Dry season |
| 3. | Drying the soil by sunlight | Dry season |
| 4. | Buy orange trees and adapt them to the condition of the area | Dry season |
| 5. | Planting orange trees | August |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Clear the degraded forest soil | Person-day | 80,0 | 2000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Collect the residue of forest and then burn | Person-day | 60,0 | 20000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Clear 40 termite mounds in 4 hectares | Person-day | 48,0 | 20000,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Hire labor to carry the soil of termite mound to put in the hole of orange tree for planting | Person-day | 180,0 | 20000,0 | 3600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Grass cutting marchine | piece | 2,0 | 1200000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Two wheel tractor | piece | 1,0 | 12000000,0 | 12000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Orange seedlings | seedling | 1026,0 | 6000,0 | 6156000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Pumping machine | piece | 1,0 | 1200000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Irrigation system such as big tube, small tube etc | set | 1,0 | 8000000,0 | 8000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Planting orange trees | Person-day | 51,0 | 20000,0 | 1020000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Pesticide sprayer machine | piece | 3,0 | 600000,0 | 1800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Spraying pesticide hand pump sprayer | piece | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 38776000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 9694,0 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering during dry season in the first year of planting orange trees | Two times per day during dry season |
| 2. | Spraying pesticides when there is present of insects on orange trees | Spray once time per season |
| 3. | Pruning some branches of orange trees | When the orange trees 2 years (One year cut some branches once time) |
| 4. | Apply organic fertilizer for the orange trees | When the orange trees are 4 years |
| 5. | Spray against weeds | Spray once time per half month. |
| 6. | Spray pesticides on mungbean plants | When mungbean flowering |
| 7. | Direct seeding of mungbean | August |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Watering the orange trees | Person-day | 11,0 | 20000,0 | 220000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Person-day | 100,0 | 20000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Hire labor to spray pesticides | Person-day | 8,0 | 20000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Hire labor to harvest mungbean when mature | Person-day | 120,0 | 20000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Mungbean seed (1 hectare need 25 kg of mungbean) seeds) | hectare | 4,0 | 312500,0 | 1250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Pesticides for orange trees | bottle | 4,0 | 40000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Chemicals for improving of stem of mungbean | package | 60,0 | 1500,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Pesticide to kill worms on mungbean | bottle | 2,0 | 40000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Direct seeding of mungbean | Person-day | 56,0 | 20000,0 | 1120000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 7480000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 1870,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The maintenance costs then depend on the age of orange trees. The cost calculation of maintenance of orange trees is for year period, but the the recurrent costs for mungbean cultivation is calculated only for one crop cycle (two months and half).
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The establishment of an orange tree orachard requires a lot of money.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1225,70
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
In 2015 the annual rainfall is 1225.7 mm, in 2014 is 1128.1 and in 2013 is 1316 mm.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Ministry of water resources and meteorology, 2015
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
On Phnum Kravanh mountain area.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
PH=6
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
The total crop land is 15 hectares.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
There is free access of water stream nearby. He never has water usage conflict.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The soil fertility was improved, so that the crop production increased steadily. In addition, the farmer now doesn't grow only orange trees, but he also grows mungbean.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
The residues of mungbean contain many nutrients, which is suitable for getting good crop quality.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
As the farmer plants more than one crop on the plot now, it reduces the production failure. This means that farmer get income from mungbeans before the orange trees provide fruits. The better weed control also reduces insects, which could be harmful to the crop.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
There are mungbean and orange trees, now.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced chemical fertilizers on orange trees and mungbean, because after harvesting mungbean residues are kept on the soil which is very good green manure for soil.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
The farm income increases considerably due the intercropping system, as both mungbean and orange trees provide yield. In addition, mungbeans provide yield two times per year. Last but not least , mungbean play a key role as green manure which reduces the input of chemical fertilizers and therefore cost.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
The mungbean and orange tree cultivation does not consume much of labor force because he doesn't have to spend a lot of time for weeding (as instead of weed mungbeans cover the soil now). On the other hand, the farmer mentioned that the orange plantation is time consuming at the beginning, when the orange trees has to be planted. As well the mungbean need more time at the moment when the plot has to be prepared for first direct seedling. But the technology as a whole entails not a lot of maintenance workload as he uses machinery such as pesticide sprayer machine and mungbean squash machine to facilitate the labor.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
The diversification of the crops (oranges and mungbean) has considerably raised the income and therefore strongly prevent food insecurity situations.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
The reduction of chemical fertilizer and pesticides provides safer products that improves the health situation. In addition, mungbean and orange fruit deliver many nutrition benefits to human health.
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
He has joined the orange trees community to sell the orange fruits. Many researches are convinced of his success and the tastiness of his oranges; as for example researchers from the District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh, Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat etc.”
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
By doing the farmer learned that degraded soil can be rehabilitated by the mean of mungbean residues acting as green manure. And from the moment the soil is rehabilitated he can see that this green manure prevents soil degradation at high degree.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Mungbean and orange trees keep the soil moisture, prevent the evaporation to the atmosphere.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Orange trees and mainly the mungbean intercrop cover the soil almost entirely all year around.
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The residue of mungbean reduce soil compact by improving the soil structure through providing organic matter to the soil. The increased amount of soil organisms make the sol less compact.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
The residues of mungbean left on the soil after harvesting are transformed to organic matter by the process of decay and therefore contribute essentially to increased soil organic matter.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Orange trees and mungbeans are the vegetation cover to avoid bare land, so the sunlight will not come directly to the the soil.
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
There is more than one crop (orange trees and mungbean).
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
Now, the soil is somewhat richer in termites, ants, earthworms, crickets ect.
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Orange trees and mungbean cultivation promote soil organisms in the habitat.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | aumento | moderadamente |
| Temperatura sazonal | estação seca | aumento | bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | aumento | moderadamente |
Comentários:
Change in rainfall. If there is too much rain, the soil will be saturated and the root will be spoiled what reduces the yield of mungbean.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
When the orange trees grow bigger, it will provide very high income.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Get income from the mungbean before orange trees provide fruit as a potential source of income. |
| The residues from the mungbean plants help to improve soil fertility. |
| The potential market of orange tree fruits is good, with traders buying directly from producers at the farm. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Residues of mungbean improve soil fertility, reduce soil degradation and help rehabilitate the degraded land. |
| In the initial 3 to 4 years of growth of orange trees it is important to grow short term crops like mungbean to provide an income source. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Orange trees require a lot of water. | Grow near a water source such as a stream or river, or dig ponds to hold water. Land users need to consider a potential water source. |
| When the soils become saturated due to excessive rain, the mungbean plant roots can degenerate and result in low grain yields and low grain price (due to poor grain quality). | There is little that farmers can do to improve the performance of the mung bean crop in conditions of soil moisture saturation. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| As the orange trees grow bigger there is reduced opportunity for intercropping with mungbean. | Grow intercrops that do not require much sunlight, such as ginger or galanga |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
One place
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
one person.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
4 persons
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
04/07/2017
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Chadha, M. L. (2010). Short Duration Mungbean : A New Success in South Asia.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
N/A
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP. (2016). Forest Restoration and Rehabilitation “ Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia .”
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Ministry of Environment(MoE). Free of charge.
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
MAFF. (2005). Mung bean.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.maff.gov.kh/agri-tech/56-ដំណាំឧស្សាហកម្ម/ការដាំដុះសណ្តែក/1519-ដំណាំសណ្តែកបាយ.html
Título/ descrição:
Tauch Ung. (2010). Overiew of mung bean.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwhP4tVirBPsOTM3OWFiMzktZTdmNi00NjMyLTg1NjktMzFhYzhmMzUyMjVl/view?hl=en
Título/ descrição:
IRRI‐CIMMYT Alliance. (2009).The importance of legumes in cereal cropping systems.
URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/pdfs/the_importance_of_legumes_in_cereal_cropping_systems.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos