Protection of water resources [Haiti]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Antoine Kocher
- Editor: Eveline Studer
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger, Eveline Studer
technologies_583 - Haiti
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Focal person EPA HELVETAS
Helvetas
Haiti
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [Haiti]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- Compilador/a: Antoine Kocher
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
The protection of water resources is essential for the supply of drinking water in the rural zones of Haiti, by enabling to preserve the water quality and facilitate the recharge of the resource. Organizing the actors related to the water resource and to the economic, environmental and communal challenges is crucial. This implies, apart from management, the implementation of various technical measures.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The majority of water resources in Haiti is subject to bacterial contamination, which endangers the health of the consumers. The infrastructure for the abstraction and conveyance of water is periodically put to the test by the large variation of discharge, like floods, but also by low flows. The protection of water resources aims to strengthen local actors to better manage water resources. The objective is to take care of the protection of water resources at local level according to rules which are established and accepted by the actors with regard to legal, sociocultural and biophysical aspects.
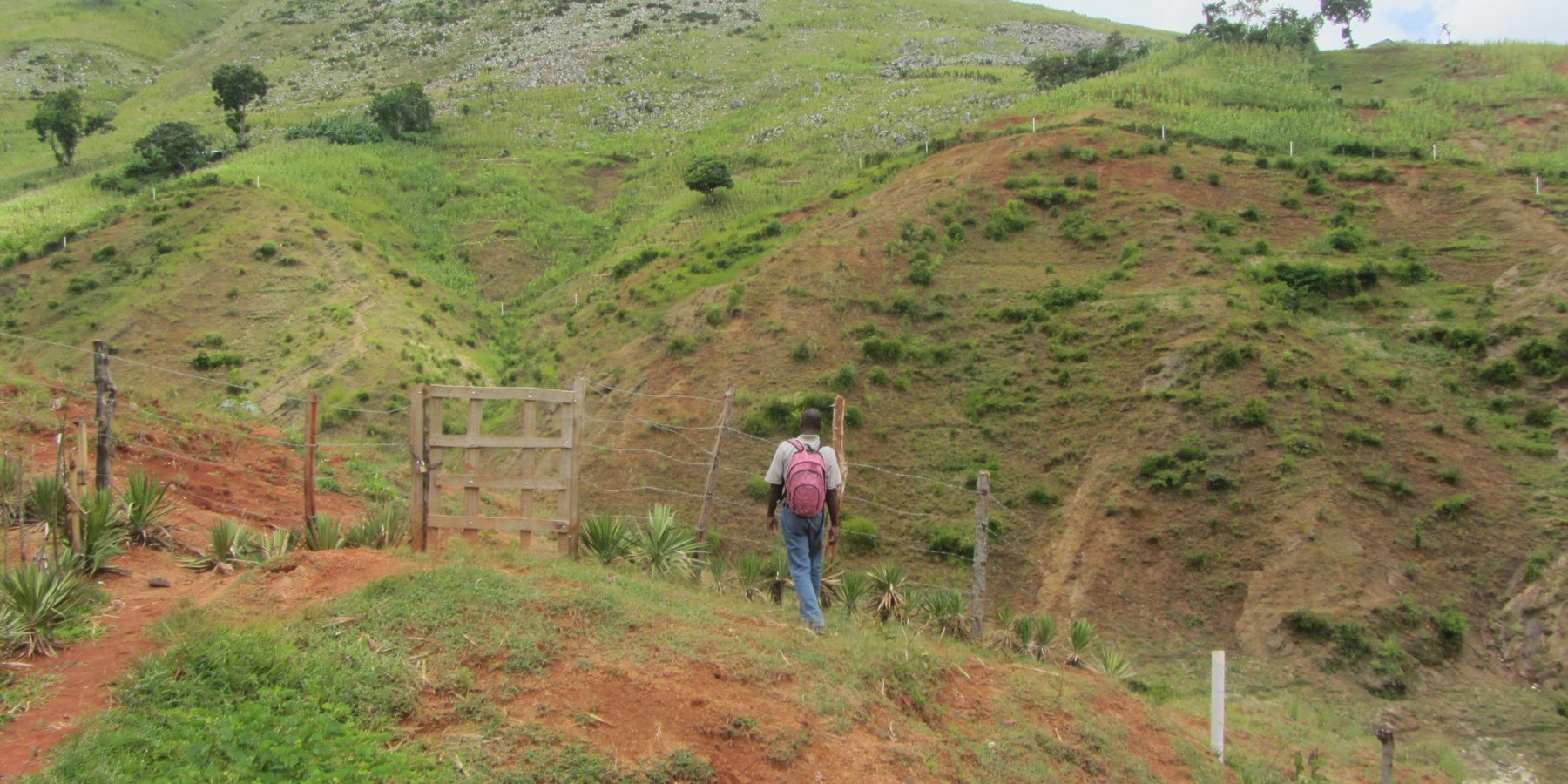
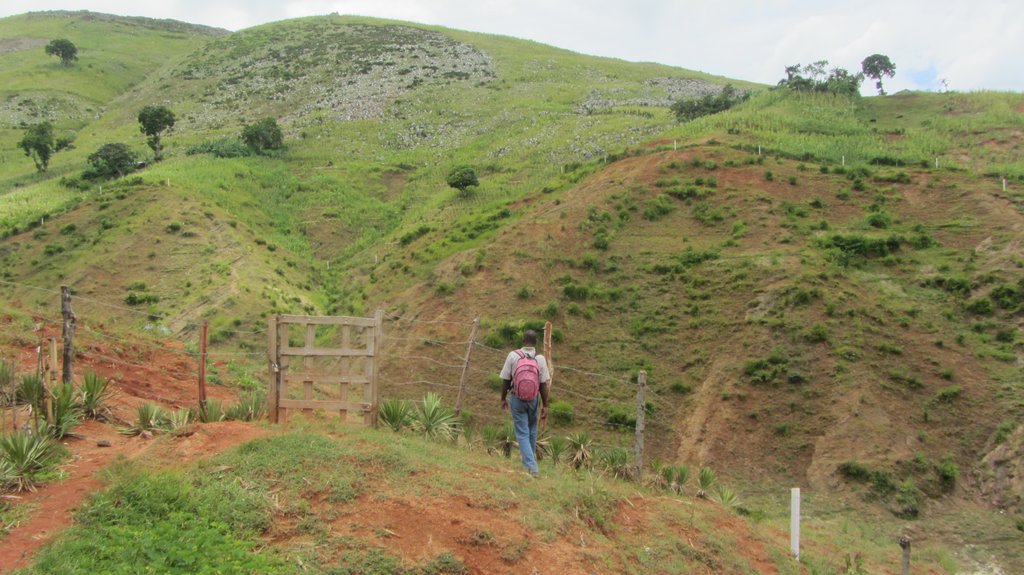
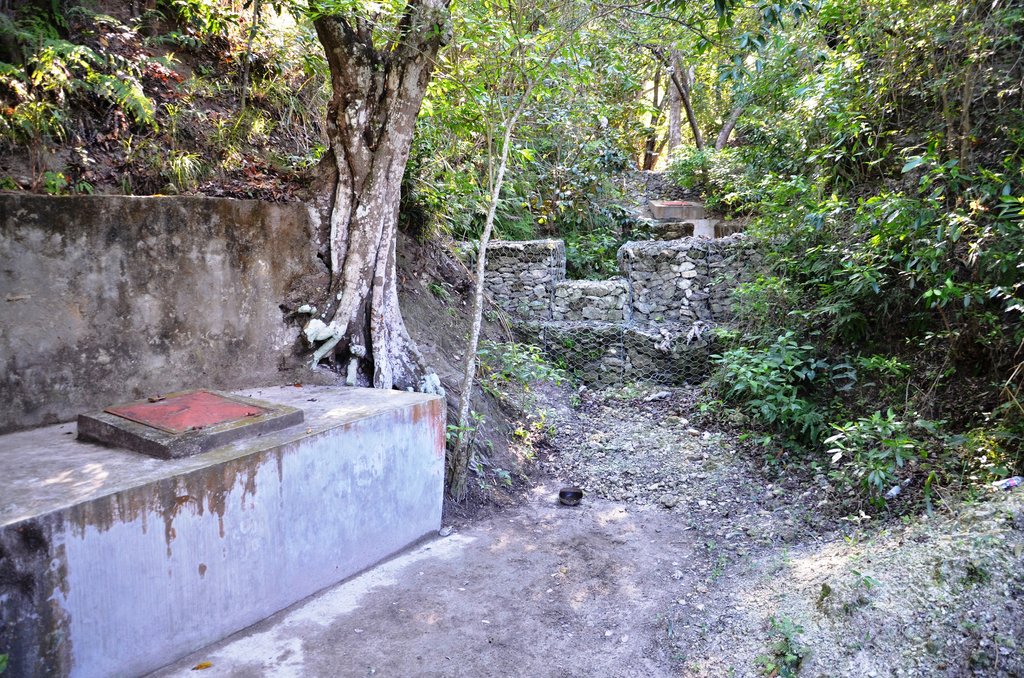
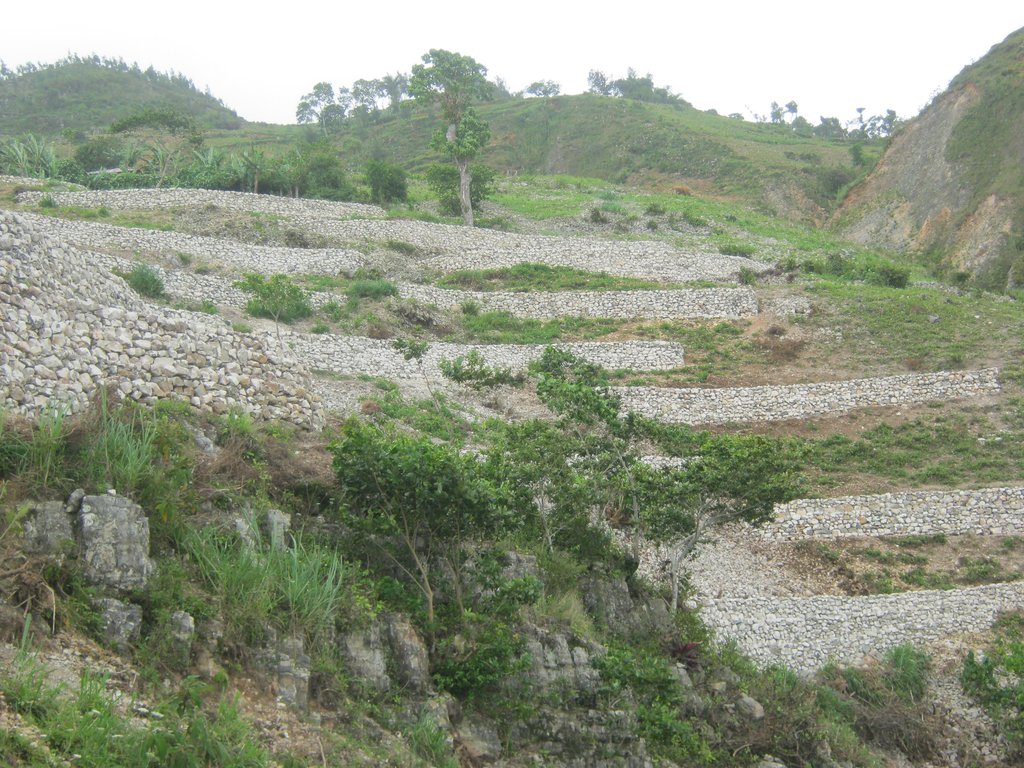
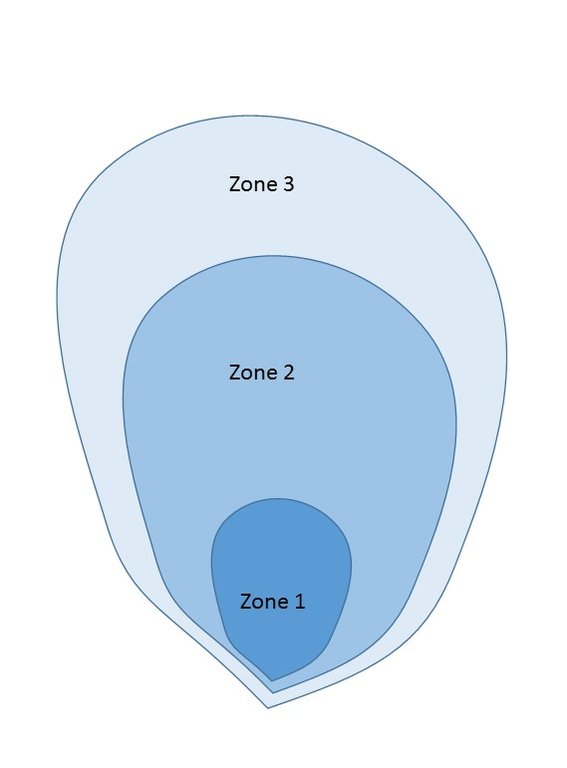
The protection of water resources also implies that technical measures are implemented to conserve and protect catchments, in order to ensure the quality and quantity of the required water and the recharge of groundwater bodies. The technical measures are defined for different zones. Three categories of zones are established with specific restrictions and recommendations, and formalized in a municipal decree which is published by the town councils. A first zone of 1000 m2 directly upstream of the water resource is brought into the domain of the state, fenced, reforested and totally protected from human activities.
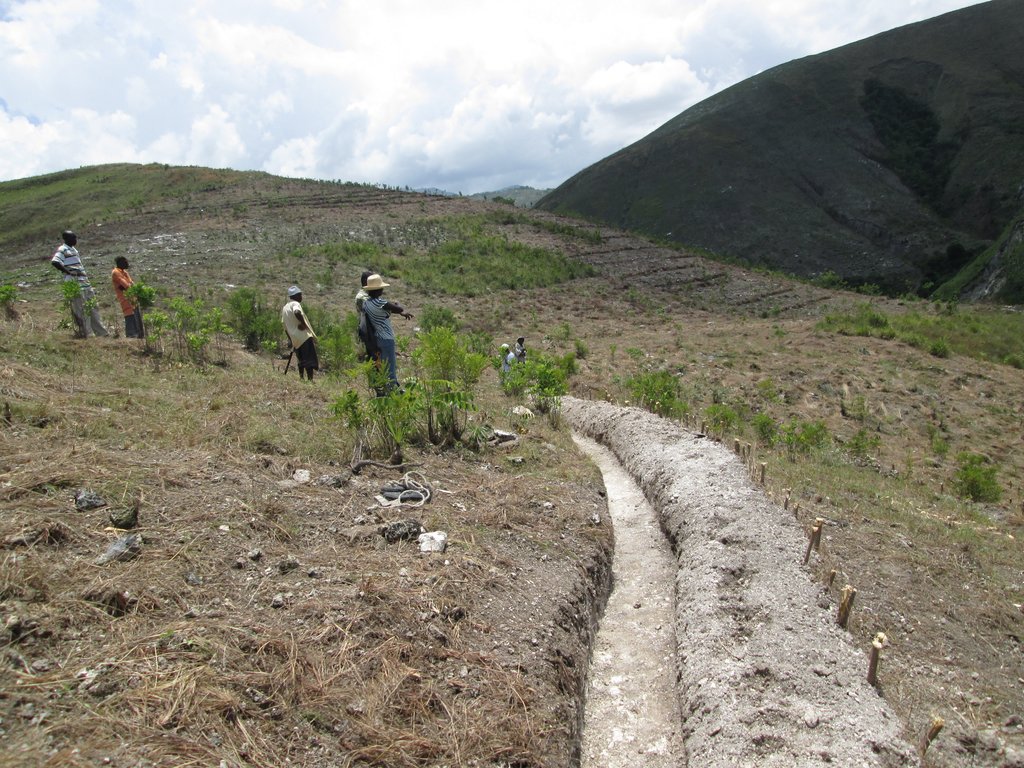
In a second zone of a minimum of 5 ha upstream of the resource, restrictions to the use of the terrain apply, notably with regard to defecation, free-range livestock farming and other harmful human activities, in order to protect the soil and the water quality. The terrain is managed so as to guarantee a good conservation of the soils by reforestation (agroforestry) with different varieties of fruit trees and timber. A third zone can be established if supported by the community, with restrictions on slash-and-burn and free-range grazing, as well as means to preserve the soils and to manage the vegetation cover. This latter zone can cover the whole catchment, and is meant to promote groundwater recharge. The restoration of the catchment through the zoning and the implementation of physical structures includes different techniques such as vegetative barriers and stone walls.
The restrictions on the use of zone 2 are not necessarily in contrast with the interests of the producers. It turns out that the rainfed crops are too much exposed to climatic hazards, and that forestry is a more reliable alternative. Therefore they perceive the development and reforestation of their land as an exploitation of their heritage, and as a profitable investment in the long term, when they will be able to manage the exploitation of the trees and their fruit production. In the first two years, a total maximum grant of 400 USD per ha is paid to the producers in different terms, depending on the success of the conservation activities. These experiences have inspired the setting of national standards on the protection of drinking water resources.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Haiti
Região/Estado/Província:
Artibonite, Central West
Especificação adicional de localização:
Municipalities of Petit-Goâve, Verrettes, Savanette and Lachapelle
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
The conservation measures are locally applied on the hillslopes, but the restrictions on the use of the protected zones apply uniformly.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Support and incentives through various projects from HELVETAS, in particular projects focused on water services, risk management and support to local governance.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Silvipecuária

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Fazenda pecuária
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
- cattle

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
Florestas (semi)naturais/ bosques: Especificar o tipo de manejo:
- Derrubada seletiva
Plantação de árvores, florestamento: Especificar a origem e composição das espécies:
- Variedades mistas
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Lenha
Comentários:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Two agricultural seasons with different crop species
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Some zones were cultivated with annual crop varieties, and were subsequently transformed into protected zones, where selective felling is only authorized if natural regeneration is guaranteed, and if the vegetation cover provides an effective soil protection.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão do lençol freático
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
- S2: Barragens, bancos
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bf: efeitos prejudiciais de incêndios

Degradação da água
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Three protection zones:
Zone 1: 1000 m2, public property, prohibition of any activity;
Zone 2: 50.000 m2, private property destined for agroforestry and protected by soil protection measures. Prohibition on housing, livestock farming, chemical fertilisation, latrines, waste disposal, slash-and-burn, etc.
Zone 3: all areas in the catchment upstream of zone 2, depending on agreements with the land owners and farmers, oriented on agroforestry and protected by sustainable land management measures.
Autor:
Helvetas Haiti
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
from 0,1 to 5 ha (reference unit 1 ha) - protection of one spring
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5
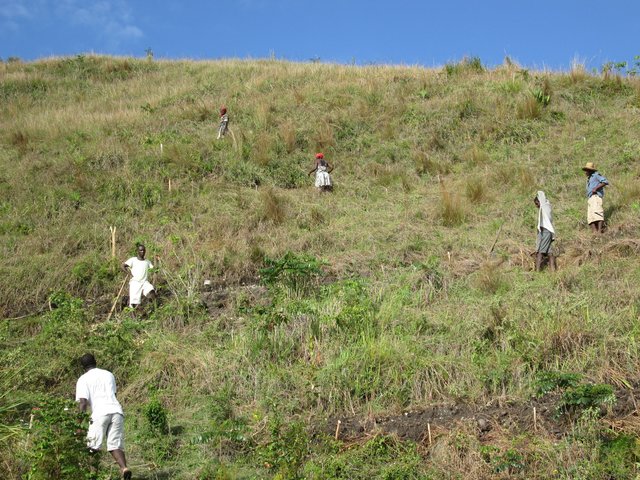
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Discussion on legal provisions with the different actors | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 2. | Elaboration of a municipal decree | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 3. | Acquisition of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 4. | Fencing of zone 1 | To be finalised in the dry period |
| 5. | Development of the land plots in zones 1 and 2 | During the dry period (availability of farmers and stability of the slopes) |
| 6. | Treatment of gullies | During the dry period (availability of farmers and absence of surface runoff) |
| 7. | Training of farmers on conservation practices | Before the rainy season |
| 8. | Afforestation | At the start of the rainy season |
| 9. | Maintenance of physical structures | On the long term |
| 10. | Monitoring and inspection | On the long term |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Afforestation, gully correction, land management, fencing | person days | 300,0 | 6,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | shovel, hammer, etc. | None | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings (lump sum for grass and bushes for slope stabilization) | average per site | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 4,0 |
| Material de construção | Cement, iron, PVC, piles | average per site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Outros | Acquisition of zone 1 (1000 m2) | lump sum | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Outros | Rehabilitation and legalization (zone 1) | site | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2680,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 2680,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The supporting project
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of physical structures (dry stone walls, etc.) | after the rainy seasons (two times per year) |
| 2. | Control and monitoring of the zoning regulation (the municipal decree) | Long-term monitoring |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance of physical structures (1 person-day) | person day | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 25,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 25,0 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The maintenance operations depend on the meteorological conditions (in particular heavy rainfall) and on the type and quantity of structural measures. The topography and geomorphology influence the stability of the structures and hence the maintenance. The maintenance costs are carried by the farmers, or in certain cases by the committee for the provision of drinking water. The control on the restrictions of use of the protected zones is carried out by the local authorities together with the committee for the provision of drinking water. Hence, the costs are distributed over the community funds and financial resources from the water services.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1500,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Very variable between the regions of the country (from 500 to 3000 mm and above)
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Intensive rainfalls lead to temporary excess of water, contributing to superficial erosion.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Access to drinking water and irrigation water is arranged by different rules. In general any individual has access to drinking water, but the rights to use water for irrigation are restricted. The capturing of sources for water supply to downstream areas most often causes difficult negotiations between the communities upstream and downstream in the catchment.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Quantidade anterior à GST:
No facility for water extraction
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Water extracted from source
Comentários/especificar:
Extraction and conveyance of water
Qualidade da água potável
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Contamination by human activities
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Decreasing contamination according to the monitoring of behavior
Comentários/especificar:
Defecation in the open air is practiced by half of the households in the rural areas. The restrictions on access of the protected zones must be accompanied by raising awareness on the hygiene and by improving the availability of sanitation services.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Impactos socioculturais
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to fecal contamination etc.
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Comentários/especificar:
The zoning and bio-engineering measures improve the water quality, which diminishes problems related to water rights, considering that water is a limited resource, and is often disputed.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of infiltration, reduction of runoff and surface erosion, which conserves the soil fertility.
Lençol freático/aquífero
Quantidade anterior à GST:
High surface runoff
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Improved recharge
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of infiltration and hence recharge of the groundwater table
Solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction of erosion by surface runoff
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Comentários/especificar:
Better infiltration and controlled deviation of surface runoff, which diminishes the risk of landslides.
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of soil moisture and recharge of the groundwater table, which diminishes the impact of droughts.
Impactos de ciclones, temporais
Comentários/especificar:
The measures diminish the effects of storms and heavy rainfall events by a reduction of surface erosion and a more controlled drainage of water in the gullies, which are stabilized by walls and vegetative barriers.
Risco de incêndio
Quantidade anterior à GST:
practice of slash-and-burn
Quantidade posterior à GST:
elimination of slash-and-burn practice
Comentários/especificar:
Certain bio-engineering measures such as dry stone walls or vegetative barriers can limit the propagation of fires.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Surface runoff and discharge upstream reduce the risk of flooding downstream.
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
The conservation of soils and woodland in the protected zones reduces and delays the surface runoff, and therefore flood events are less intense. Yet, the area covered by protection measures is still insufficient to manage flood risks.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | aumento | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Ciclone extratropical | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | moderadamente |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação súbita | bem |
| Deslizamento de terra | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The measures should be promoted as an investment with an initial cost but a positive return in the medium and long term.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Protection of 34 water resources; 27 ha in zone 1 have been fenced and afforested, 281 ha in zone 2 have been afforested and protected. More than 500 farmers were trained to implement and replicate the various protection measures.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
The number of replications is low due to the widespread poverty in the region.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The farmers are supported to implement a cost-effective forestry system to replace a very vulnerable rainfed agricultural production system. But it is the population in the downstream part of the catchment who benefits from the protection of the sources, since the quality and quantity of the water is improving. Therefore an equilibrium must be found between the two populations, in order to make both benefit. The water services can be profitable, and hence encourage participation in the efforts of protection upstream in the catchment, by supporting the producers and/or by financing jobs for the protection of land and water. |
| The protection of water resources increases the value of the common heritage and therefore calls for a community-based management. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| On the basis of the vulnerability of the population and the environment in the rural environment of Haiti, the protection of water resources should be established to guarantee a secure and profitable use of water. The participatory methods implemented allow to create a supportive environment, suitable for a community-based effort for local rural development. These mechanisms inspire a culture of citizenship in a local democratic context under development. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The management of state land in zone 1 poses a challenge because this land has to be integrated into the property of the state. The purchase or compensation of these lots can require a long negotiation between the local authorities and the owners. | It is important that the local actors resolve these matters among themselves, and that there is no interference from a project, in order to not distort the negotiation. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The sustainability of the measures and the cost of maintenance are largely dependent on the quality of the measures. | Ensure a good technical instruction and follow-up on-site by trained staff. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Monitoring of all sites by the actors, during the entire project.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Participatory process of capitalization.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Existing document on the capitalization of protecting water resources.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
20/09/2016
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (long version)
URL:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_source_vlongue.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Boire l’eau et penser à la source (short version)
URL:
https://assets.helvetas.org/downloads/capex_hsi_protection_des_sources_vcourte.pdf
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Concertation locale pour la protection des ressources [Haiti]
La concertation pour la gestion des ressources naturelles implique les communautés, les autorités et l'ensemble des acteurs dans la prise de décision collective pour protéger les ressources en eau notamment, et institutionnaliser leur gestion.
- Compilador/a: Antoine Kocher
Módulos
Não há módulos