Marshy land transformed into productive land [Bangladesh]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Rahatul Islam
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Ursula Gaemperli, Donia Mühlematter
technologies_1769 - Bangladesh
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Marshy land is transformed into a ridge and ditch area, where the ridges are wide enough for the nursery of diverse plants and seedlings and where after 6-8 years the yearly management practices the land got strong enough for various agricultural practices (i.e. guava, hog plum, plums and timber wood plantation).
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
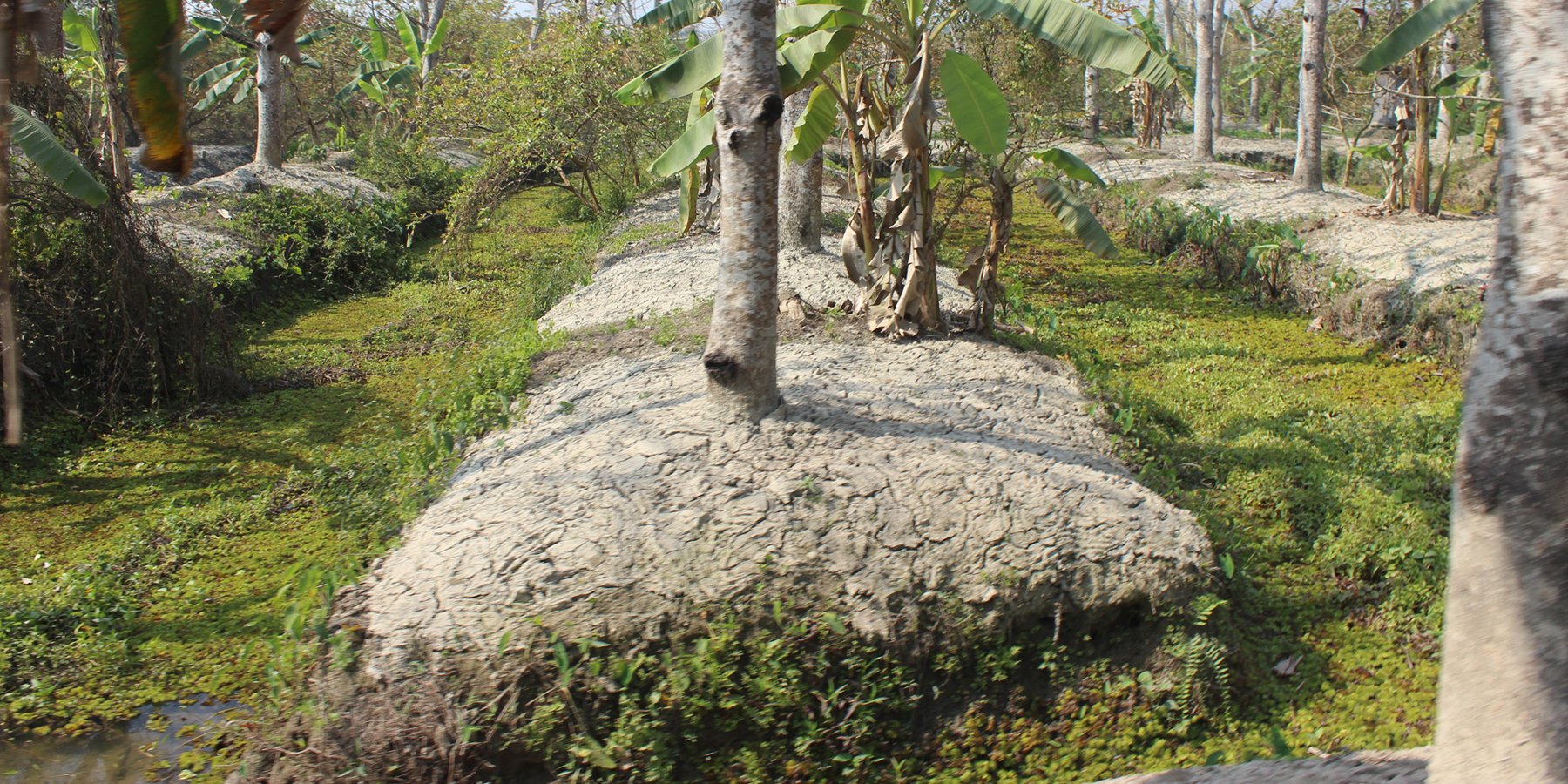
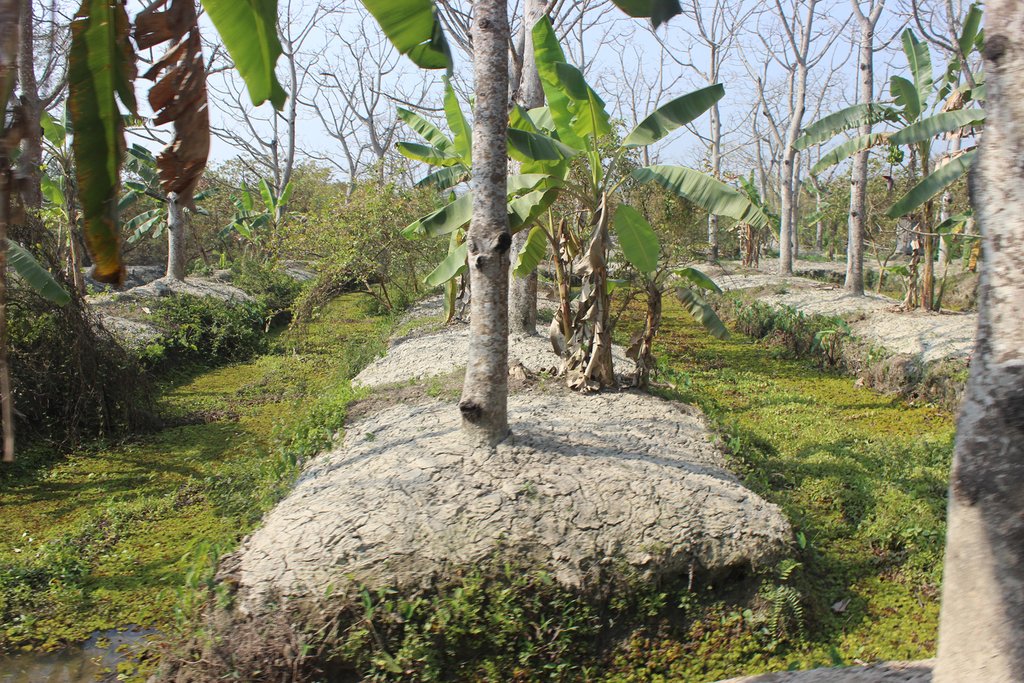
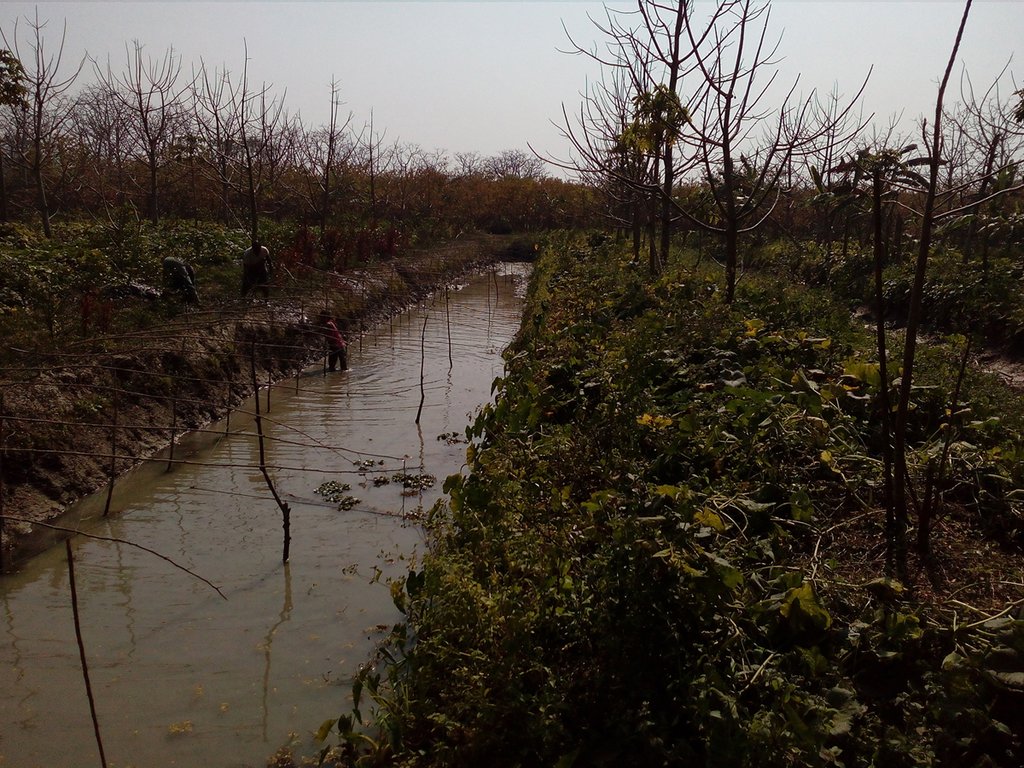
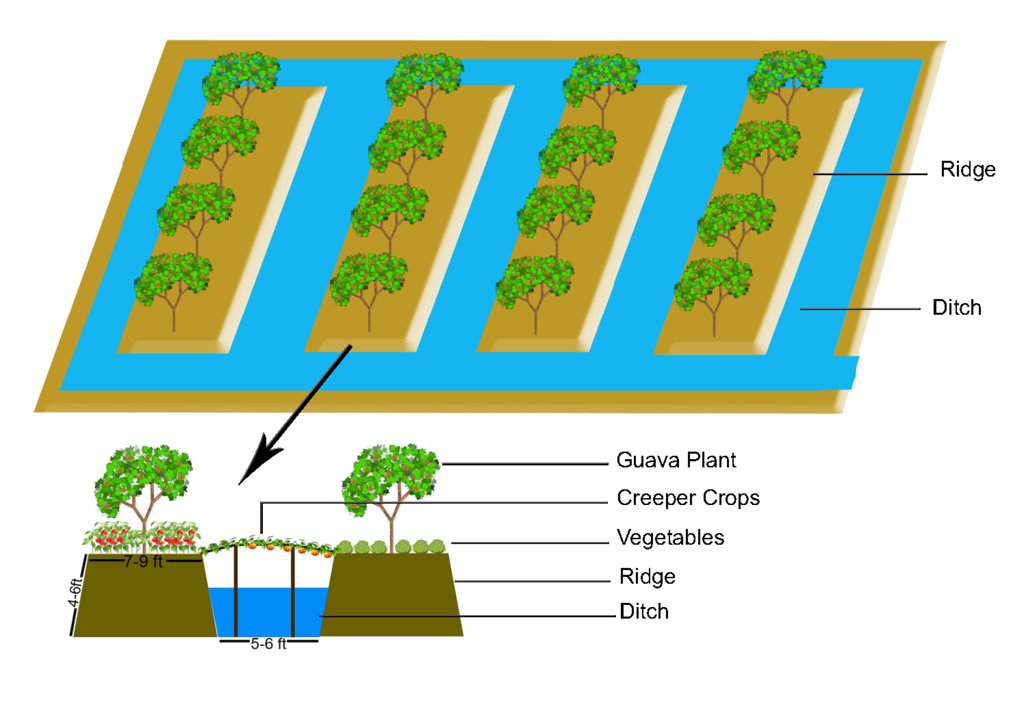
The technology of marshy land convert into ridge and ditch was taken by a community of southern of Bangladesh in order to make that area productive. Long year ago a continuous marshy land covered most of the area of southern Bangladesh like Pirjpur, Jhalokath. This area was flooded more than 9 month and remain perennial wet, that were totally unproductive. So, that technology not only increases agricultural production or economical benefits but also creates a green belt by developing agro-forest. The technology consists of ridge and ditch area. Ridges are elevated beds - land which is 4-6 feet high from surface and 7-9 feet wide. Length of each bed is variable according to size of the land. And ditches are canals - areas that are 5-6 feet wide and deeper than the normal surface area.
At initial stage elevated areas are not strong enough to start cultivating trees like guava, hug plum or other fruit plants. So they use it for nursery of diversified plants, fruit trees such as Banana and Papaya, vegetables, preparation of seedling sapling or as seedbed (rice). Management practices are running every year to develop the ridges and make them strong. Land users are putting soil/muck from the ditches on the ridges to make them higher and to give better protection from flooding water, to increase the fertility, to conserve moisture and reserve organic matter. Though eroded soil and other plant residues are accumulated in the ditches so ultimately they return over the ridge surface. Land become suitable after 4-5 year for planting various trees like guava hog plum, plums, lemons, Areca nuts and various timber producing tress like Teak (Tectona grandis), Mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni). Approximately 7 – 8 year after fruit trees are become appropriate and the physical and biological conditions of the sites have improved. Then land user start to cultivate various vegetables and other agricultural practices. Furthermore, sometime users set up a platform for creeper crops on the canal which works as support for Pumpkins and gourds. Trees and vegetables are irrigated from ditch/canal where water is reserve over the year, even in dry season if necessary. As a result of growing biomass, land degradation from the site has reduced and the fertility of the soil has increased. When fruit trees have reached its harvesting stage, the land users collect fruits for sale with expected income of about 1000USD. Vegetable also provide more than 500USD benefit from each site every year. Approximately 25 years after Mahogany, Teak, and other timber producing trees are getting mature and reach their harvesting stage. Land user cut the trees for selling with expected income of about 10000 USD from each site and size of approximately one hectare.
The technology is working well and is easily manageable by the land users. Nowadays not only farmers but also a large portion of population are interacting with that technology and their lifestyle have changed. Many people are also working to manufacture initial nursery products like seedling bag, earthen pot, creeping materials like bamboo, string, yarn, net, seedling and other material for preparing plant nursery, fruit garden, mixed agro-forest etc. Other people work to transport product from the area to the consumers and some people work to manufacture vehicles like boats, local vans etc. Also locale communities developed the largest floating market of Bangladesh.
The farmers are applying the technology without any extra financial support. According to the land users, they estimate about 200 – 300 family which have applied the technology. Approximately 350 person-day/ha were employed for construction and 50 person – day/ha sufficient for yearly maintenance work. 1600 USD was spending on the construction and most of the cost covered by owner. Farmers have faced some drawback such as undeveloped communication infrastructure and insufficiently developed market places. On the other hand, if they get support from government and related authority, this technology even become more beneficial for them.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bangladesh
Região/Estado/Província:
Atghar Kuriana Union, Swarupkati, Pirojpur
Especificação adicional de localização:
Barisal
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
sites are increasing day by day and enter into deep swampy land.
The technology expanding with time.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- legumes - outros
- rice
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
- mamão
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
perennial
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim

Floresta/bosques
Tipo de árvore:
- Tectona grandis
- Swietenia mahagoni
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Frutas e nozes
Comentários:
Main crops are guava and hog plum. vegetables are harvested within five to six month. Bananas and papaya stay for several years. woody trees are harvest after they get mature.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Gestão/proteção de zonas úmidas
- convert marshy land into productive ridge and ditch
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pw: estagnação hídrica

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Land was lower and flooded more than 9 month and remain perennial wet. So the technology helps to overcome waterlogged condition and remain surface water over the year even in dry season at ditch area.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Method of marshy land transform into productive land bases on ridges and ditches. ridges are 7-9 feet wide and 4-6 feet high. Height is variable because yearly management practices increase the height of the ridges. Ditches are connected with each other from the edge/end of the each ridge. This types of connection support water movement and the moving of the boats for crop management and crop harvesting.
Autor:
Selim Hossain
Data:
03/02/2017
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1 hectare
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5 USD
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Develop ridge and ditch | 7-15 days |
| 2. | vegetative cover with vegetables, seedling, sapling | 2-3 months |
| 3. | fruit trees, timber producing trees | 3-25 years |
Comentários:
Mainly the structural measure are important. But other measures are also important to make the technology stable. At initial stage without vegetative measure, soil will not become stable enough to take further steps of plantation.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | skilled labor | person-days | 300,0 | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seedling (fruit trees) | piece | 500,0 | 0,1 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seedling (timber producing trees) | piece | 300,0 | 0,1 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | seedling bag | 1000,0 | 0,01 | 10,0 | 100,0 | |
| Outros | earthen pot | 1000,0 | 0,01 | 10,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1600,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1600,0 | |||||
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
3,0
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | management practice to make ridges and ditches uniform and productive | 3-7days |
| 2. | seasonal vegetable | 2-3 month |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | skilled labor | person-days | 50,0 | 5,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seedling vegetable ( e.g gourd) | pieces | 250,0 | 0,05 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | bamboo | pieces | 50,0 | 1,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | string, ropes | piece | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 317,5 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 317,5 | |||||
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Basket, spade and other equipment which are needs to develop the site is not carried by land user, these are collecting by laborers. transportation cost also carried by local traders. farmers are represent their product in local market (floating guava market) and then local traders are buy it and transport it to city or capital
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Length of rainy season 5 month that causes water level becoming close to the bed.
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
flooding normally occur in rainy season but it is not destructive for the technology
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
This green belt workes as shelter for birds.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Size depends on user capability. Sometime users like to make smaller sites which are easy to maintain. Larger sites reduce waste of land and give extra space to cultivation.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
bare land become productive
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
organic materials are mainly used
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
vegetable and fruit resides can use as animal food
Qualidade da forragem
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
timber trees not only fill local demand but also supply in many area of Bangladesh
Qualidade da floresta/do bosque
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Crop failure by flooding is protected
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Here produce timber, fruit, vegetable, seedling sapling etc
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
production area remarkably increase
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Very easy and local farmers manage it easily.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Water is available even in dry season
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
ditch contain enough water in available condition for plant
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Peoples not only depend on agriculture.
Disparidades econômicas
Comentários/especificar:
It reduces the economic disparities as it opens new working places.
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Net yearly production of food increases.
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
People get proper nutrient from fruits and vegetable, which are totally chemical free
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Oportunidades culturais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
not only men but also women are work on site. normally land users family members are always help them every way
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Total amount of water is reduced.
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Good quality water found in all seasons.
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Drainage condition of cultivated ridge area is very good
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetative cover reduces the total evaporation .
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Yearly management practice helps to increase the soil moisture.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Annual and perennial crops cover the area.
Perda de solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Plant residue.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Release reserved carbon from muck.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
A bare land convert into vegetative cover
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Variety among plants and crops is seem.
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
The trees serve as nesting habitat
Espécies benéficas
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
ridges are free from flood
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
water reserved in ditch in dry season
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
large vegetation consume huge amount of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases
Velocidade do vento
Microclima
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
To develop such kinds of structure requires a huge amount of investment which is not covered in a short time. But in the future it becomes highly beneficial. Yearly maintenance practices not only increase soil fertility, moisture and nutrient availability but land become higher from flooding water as well.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 51-90%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The Technology increase the amount of productive land. |
| Peoples economic condition have changed to the better. This technology creates working place for many people. |
| The Technology increase availability of fresh products. e.g vegetable, fruits. |
| The development of largest floating market of Bangladesh is seen as very positive. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The Technology increase the greenhouse gas consumption. |
| Seedling and sapling are distributed in whole country and increase the vegetation cover. |
| It fulfills the demand of timber and it reduces the deforestation of natural forests. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The communication and transport infrastructure is not very well developped. | Reconstruction of the road. |
| Floating market are temporary and disapear after morning. | Make stable market places. |
| Farmer have no precise knowledge about crop, seeds and hybrid varieties. | Government and non-government organizations services is required. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Water ecosystem is hampered | More research should be taken |
| Huge amount of reserved carbon get released. | Planting enough tree to consume that |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
24/01/2017
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos