Non-inversion shallow cultivation [Bélgica]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Oppervlakkige niet-kerende bodembewerking
technologies_966 - Bélgica
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Gillijns Katleen
Catholic University of Leuven
Bélgica
Especialista em GST:
Govers Gerard
Catholic University of Leuven
Bélgica
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Catholic University of Leuven (KU Leuven) - Bélgica1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
08/11/2010
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [Bélgica]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
The technology consists of the use of cover crops and of a non-inversion seedbed preparation
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
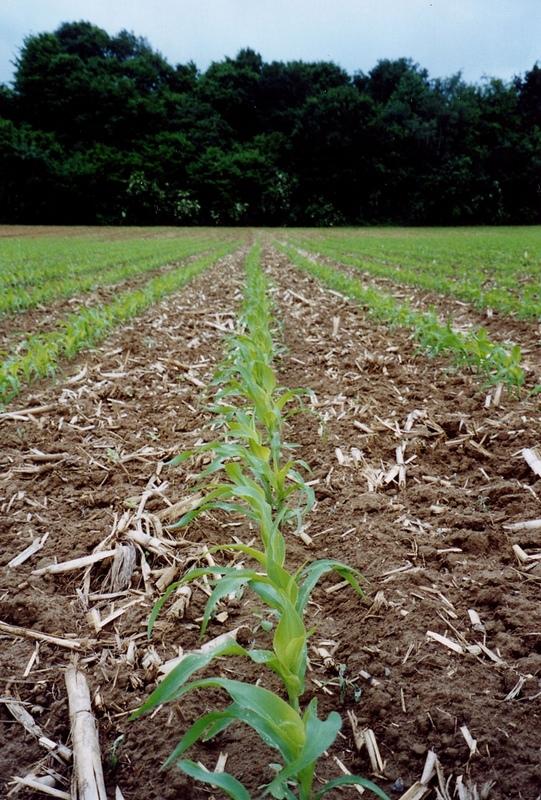
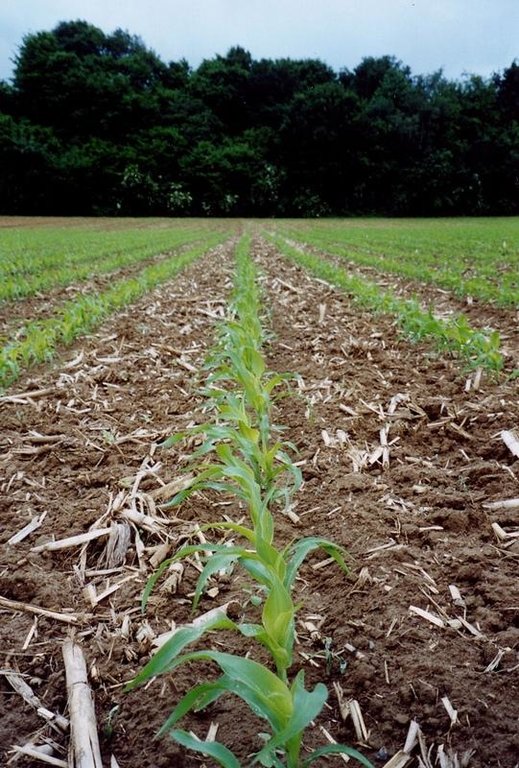
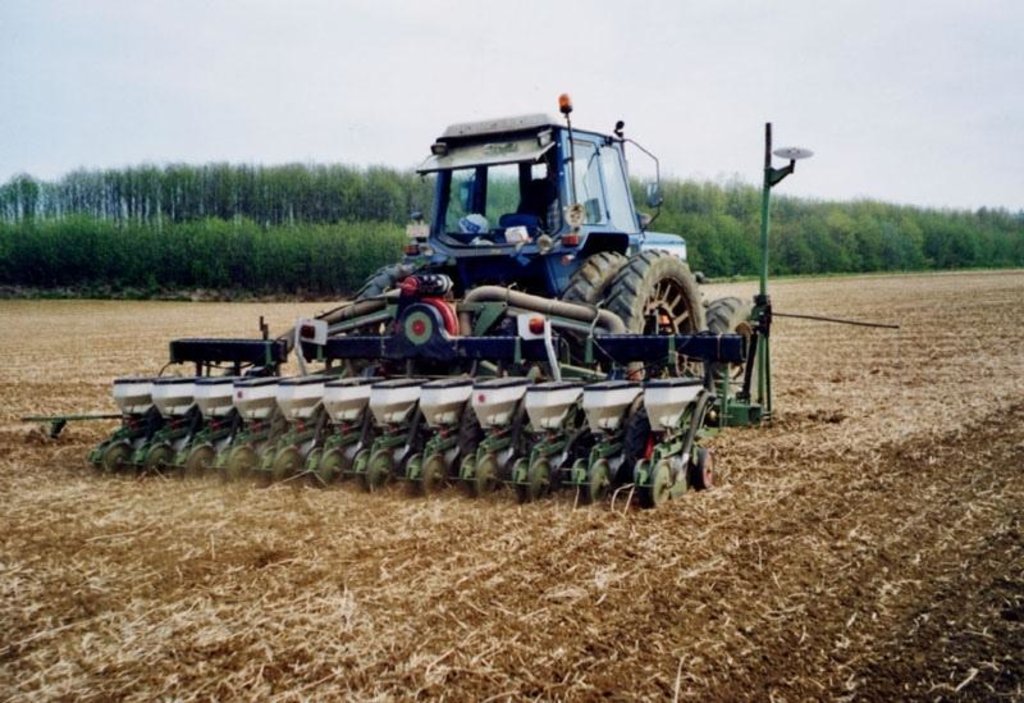
The technology consists of agronomic measures. The most important thing is that the farmers are not allowed to invert the soil by ploughing. Farmers may only cultivate their fields as minimum and as shallow as possible. Farmers also have to use a cover crop, if possible. In this way the soil is always covered with residues of a previous crop or with residues of the cover crop. The improvement of the ground cover protects the soil against different kinds of water erosion. In the long term period, the soil structure will improve (more organic matter in top soil) and more earthworm activity will be determined. The infiltration of water will increase.
Purpose of the Technology: Protecting the soil against erosion and increasing infiltration.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer may never plough.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on cropland with annual crops.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bélgica
Região/Estado/Província:
Flanders
Especificação adicional de localização:
Vlaams-Brabant
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
In the Walloon part of Belgium and in the surrounding countries (France, Germany), farmers are already applying this technology for a long time. In Flanders, the technology was introduced in the '1970 by a professor De Ploey of our Faculty. Farmers didn't see the benefits of the technology and decided not to implement the technology. Now time has changed: farmers know that they have to do something ageist the erosion problem.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major cash crop: Sugar beet
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Soil loss by water erosion. 2. soil erosion related environmental problems (muddy floods, retention pond sedimentation, declining water quality due to sediment and sediment - fixed contaminants)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Strong nitrogen regulations and EU rules are hindering the farmer.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat- potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat - sugar beet.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period from month to month: Mar-Oct; Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0046 km2.
It's a fiedl trial with 3 treatments: every treatment is 4620 m² (see map). The treatments are: non-inversion shallow cultivation, non-inversion deep cultivation and conventional ploughing. In the region of this field, other farmers are also experimenting with new technologies on their own fields.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
- A4: Tratamento do subsolo
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soil erosion), lack of knowledge
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes: hevay machinery)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter
Better crop cover
Material/ species: winter barley 2003
Quantity/ density: 200 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover (every year)
Remarks: by not ploughing
Agronomic measure: better crop cover2004
Material/ species: maize 2004
Quantity/ density: 178600
Remarks: seeds/ha
Agronomic measure: better crop cover 2004
Material/ species: winter wheat 2004
Quantity/ density: 165 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: better crop cover 2005
Material/ species: oats 2005
Quantity/ density: 110 kg/ha
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: slury injection 2004
Quantity/ density: 40000l/ha
Remarks: before sowing
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2004
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: 26%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 175 kg/ha
Remarks: 39%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 45 kg/ha
Remarks: 27%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Haspargit
Quantity/ density: 800 kg/ha
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen 2005
Quantity/ density: 120 kg/ha
Remarks: 38%
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: every year
Remarks: the field is cultivated as minimal as possible
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | sowing maize, inorganic nitrogen | Agronômico | apr 2004 / |
| 2. | sowing winter barley | Agronômico | oct 2003 / |
| 3. | injection of slurry, herbicide paraquat | Agronômico | mar 2004 / |
| 4. | spraying herbicides | Agronômico | may 2004 / |
| 5. | harvesting, sowing winter wheat | Agronômico | nov 2004 / |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Comparing to ordinary field operations, there are normally no additional costs if applying the new technique. The farmer will not plough anymore, this is an economic benefit. In some cases and for some crops the farmer will use another machine, for example: the farmer will need a direct drilling machine for sowing sugar beets in stead of a normal sowing machine. In Flanders, always agricultural contractors are sowing beets (not farmers). The agricultural contractor will ask the same price for normal sowing machine as for the direct drilling machine. Although farmers have no additional costs, they get subsidies (80€/ha.year for shallow cultivation, 200€/ha.year for no tillage) from the Flemish Government for practicing the new technique - subsidies are mainly given to encourage the farmers.
Additional info: inorganic nitrogen - mar 2005 spraying herbicides - apr 2005 inorganic nitrogen - apr 2005 spraying herbicides - apr 2005 spraying herbicides - may 2005 spraying herbicides - jun 2005 inorganic nitrogen - jun 2005 harvesting winter wheat - aug 2005 injection of farm yard manure - sep 2005 sowing oats - sep 2005 broadcasting Haspargit - sep 2005
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
780,10
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: 10 %
Landforms: The main topography is a plateau (100 m above sea level) in which rivers are incised. The technology is applied at fields situated on the slopes between the plateau and the valley
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: The loess deposits which vary in thickness between a few dm to several m cover Tertiary sands
Soil texture (topsoil): 60% loam, 30% sand and 10% clay
Topsoil organic matter: 1,2%
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is only working with his own farm.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Because of reduced working time and lower fuel consumption.
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
special equipement
Impactos socioculturais
Atenuação de conflitos
farmers opinion of a non-ploughed field
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
34
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16
Comentários/especificar:
Also 21 before and 16 after
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
More residues
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4.47
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1
Comentários/especificar:
Significant reduction in soil loss
Outros impactos ecológicos
biodiversity
Comentários/especificar:
more earthworms
use of herbicides
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Because of less runoff
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays about 49% of the farmers in the region are practising conservation tillage, whereas only 33% was doing it in 2001. At the beginning of the project 63% of the farmers intend to cultivate their fields in a conservative way into 3 years. (based on e
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| less soil erosion |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The technology clearly reduces the erosion risk while maintaining profitability. |
| The new technology also has other benefits on soil structure and biodiversity. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| high investment costs for buying new agricultural machinery | |
| more attention to crop damages caused by slugs and mice should be given | |
| Practicing the new technology requires a relative dry soil |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Practicing the new technology requires a greater skill of the farmers. | education, training |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
SOWAP - Project. 2003-2006.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www. Sowap.org
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [Bélgica]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
Módulos
Não há módulos