Drip irrigation [Turquia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Faruk Ocakoglu
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Damla Sulama (Turkish)
technologies_1014 - Turquia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture (University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture) - Turquia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Minimum Water Use [Turquia]
Instead of flow irrigation that requires high water consumption and causes excessive evaporation, water can be transported in pipes till crop's body and can be given slowly under controlled conditions. The approach is brought to farmers by state institutions as well as banks, and education for the scientific background, installation …
- Compilador/a: Mehmet Zengin
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Drip irrigation is a method designed for minimum use of water and labour for the optimum irrigation of plants in arid and semi-arid regions.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
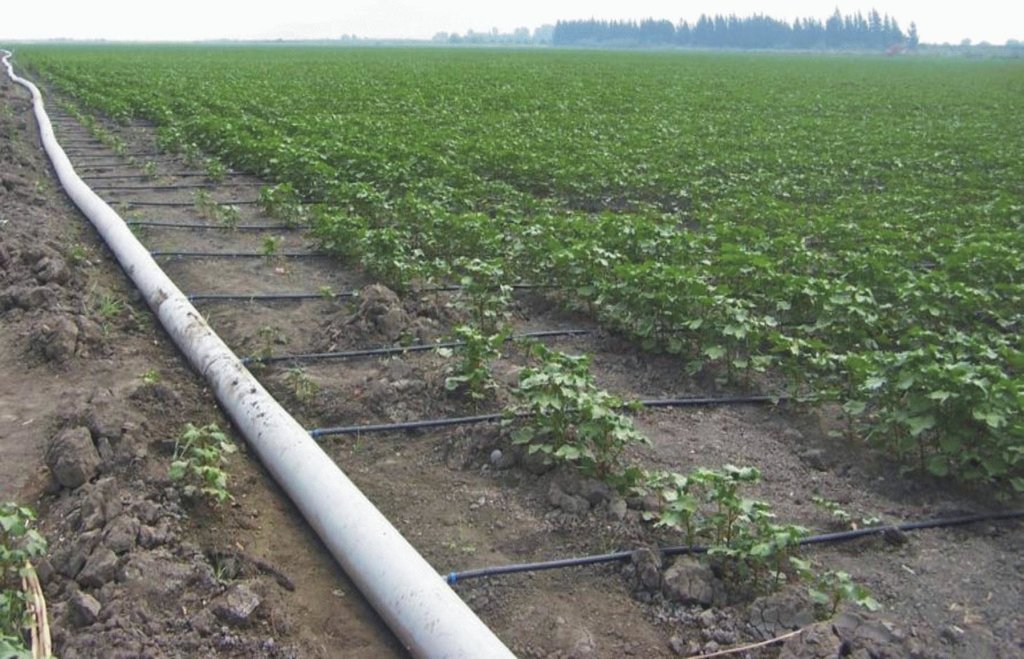
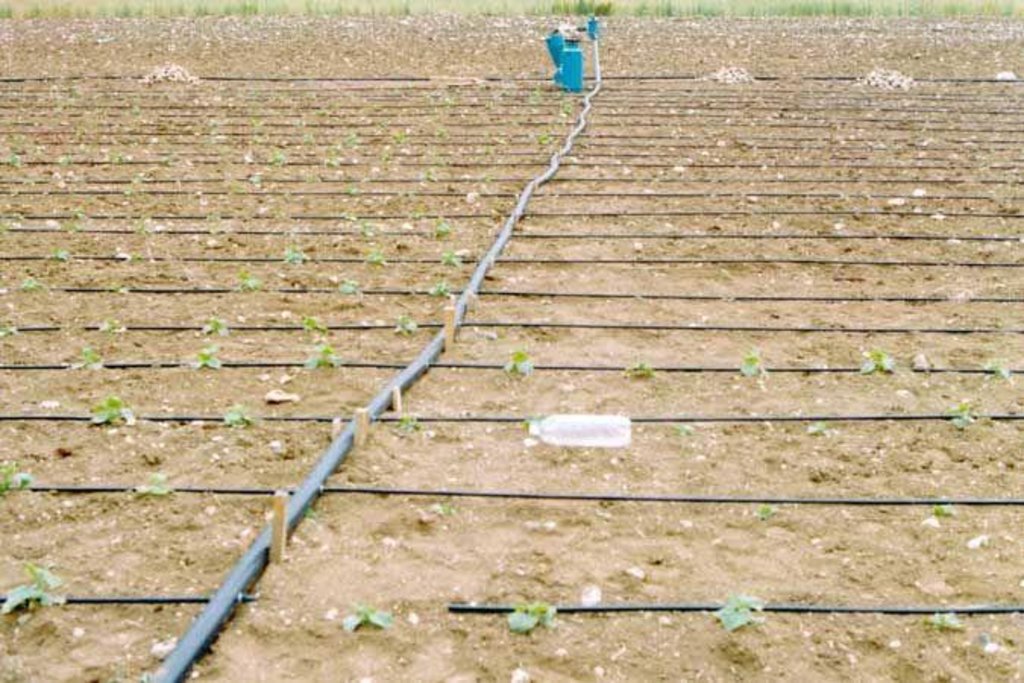
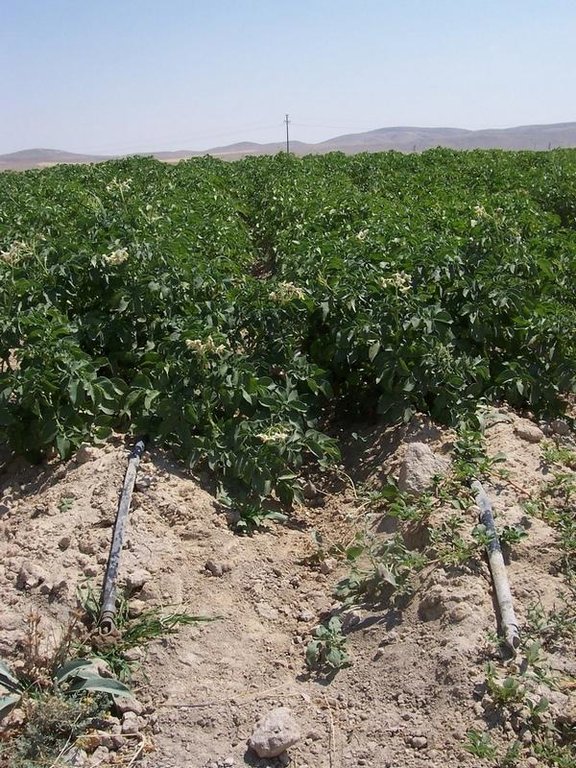
In drought–affected regions, fruit trees, vineyards, vegetables and other field crops such as maize, sugarbeet, potatoes, onion, etc. are watered by drip-irrigation using pipes with dripfeed points. This saves water and maximum benefit is achieved with a minimum of water. In this system, plant roots receive water at the right time and in sufficient quantities. Labour expenses with the system are low, but the first investment expenses are high. At current prices, it costs about 2000 US$ per ha, which varies with the density of the network required for the specific crop.
Purpose of the Technology: Depending on the size of the field to be watered, a main network of PVC pipes able to cope with the pressure necessary to convey water to secondary/lateral pipe systems is established. These pipes are mostly 2.5cm in diameter and have dripfeed points at their ends. The system is suitable for water conservation, because it enables watering to be focused where required, i.e. close to the root zone of the crops, but without wasting water. However, increased use in rainfed areas will increase the overall water demand. From the viewpoint of surface sealing of the soil, it has advantages since it causes wetting only in limited areas. Problems such as salinization and leaching of nutrients are also reduced by limiting the watering. At the same time, the method considerably increases farm income as excessive watering is avoided.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The basic land use types targeted with the technology are perennial tree crops (i.e. orchard and stony fruit crops) and annual crops with individual plant stems such as potato, maize and sunflower. Maize is used as fodder. It is particularly useful in arid and semi-arid regions where evapotranspiration is high, surface waters are scarce and groundwater is threatened due to high exploitation. It grows under all topographic conditions.
Natural / human environment: From the viewpoint of human environment, the technology is profitable for farmers who have a pressurized pumping system connected to a groundwater source. The basic costs are for the planning of the irrigation system, the hard PVC pipes and its set-up in the field. These services are provided by specialized companies, while the maintenance of the system can be done by the farmers themselves. The volume of the crops produced in this system is high and intended for commercial use.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Turquia
Região/Estado/Província:
Konya
Especificação adicional de localização:
Karapınar
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 km2.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - milho
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- culturas forrageiras - trevo
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- culturas de raízes/tubérculos- beterraba sacarina
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Apr
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problem in the Konya closed basin is the rapidly dropping groundwater levels. For this reason electricity expenses for watering is intolerably increasing for the farmers and groundwater resources are irreversibly rapidly decreasing. Moreover, other types of watering (sprinkler and flowing) in the Karapınar area cause secondary degradation problems such as salinization and sealing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): This system is good for increasing crop yield and quality, and to save groundwater, but we do not know in detail how to use the system and how to fertilise with this system.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Comentários:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A5: Gestão de sementes, variedades melhoradas

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: irrigation network
Type of agronomic measures: early planting
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Ha: aridification, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hp: decline of surface water quality, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Plants requiring much water are grown instead of cereals, causing the water to finish.), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), population pressure (Population increasing and yield capacity is decreasing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of technical information is hindering a success farming.), governance / institutional (There is not a forcing rule/law for drip irrigation, but there is subsidizing.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
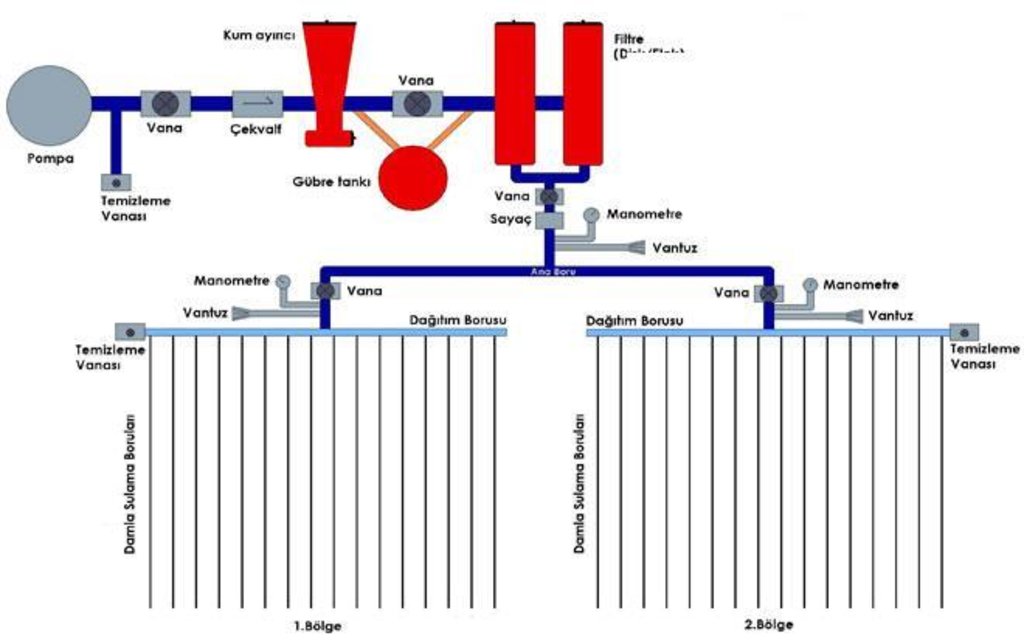
A sufficiently powerful pump provides pressurized water into the system. Before entering the distribution pipes, the water is cleared of silt particles in the filters and fertilizers are added if needed
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Selection of suitable pipe types and dimeters, and drippers are importants.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Mostly related with arranging pressure levels and fertilization equipments)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Early planting
Material/ species: plastic pipe with dripper.
Quantity/ density: 1- 2 /plan
Major change in timing of activities: In drip irrigation, water is given to plant root zone frequently, but low-low.
Autor:
http://www.ziraialet.com/haber
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
turkish lira
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
2,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
25.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of drip irrigation system | |
| 2. | Farmers training | Spring |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 90,0 |
| Outros | Drip irrigation system | ha | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 90,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2100,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1050,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
Life span of drip irrigation system: 10 years
Number of parties (sharing): 2
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Change of drippers | spring |
| 2. | Change of sediment filters | spring |
| 3. | Overall cleaning of the system | random |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Drip irrigation system | ha | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 300,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 150,0 | |||||
Comentários:
In the calculation, it is assumed that the crop is a legume with 50 cm regular row intervals and the distance between individual plants is of the order of 30 cm.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The main network of hard PVC pipes, pressure indicators, main distributor, and labour force are the main costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Seven months are drought in a year.
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertiliy is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Level of mechanization: Every kind of machine is used
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Wealth of farmers increased because of minimum water use and maximum plant production. Underground water loss stress finished in their mind.
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Certainly the technology supplies richness, easiness and low water consumption. It supports high quality and quantity of production due to the fact that plants grow without no water or excessive water stress.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Cheias de jusante
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| very low temperature | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Short- & long-term benefits are very positive. But the technique is new. Not enough knowledge of this system, especially in fertigation (watering + fertilizing). First investment costs high and peolpe do not believe drip water will feed the plants.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
580
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
290 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: In recent times, the area affected reached 20%, because the Turkish Government gives credit with no interest to farmers in dry regions.
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
290 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Initially, only rich farmers used this system because it is expensive.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government has responded positively to this situation by giving no-interest credit for 5 years.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Ease of watering with this system How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training and subsidies. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Minimum water use, easy using, low energy demand (fuel, electric, labour, etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Subsidizing. |
|
Sufficent watering enables an increased crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? education regarding the watering frequency would be useful. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Drip irrigation system has a short life (1-5 years). | UV-tolerant plastic must be manufactured and used. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Users do not know how to use this new system exactly. In particular, farmers do not know “fertigation” methods for their different plants such as maize, sugar beet, potato, and orchards. | More education and demonstration of fertigation methods by state institutions. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kara, M., 2005. Sulama ve Sulama Tesisleri. S.Ü. Ziraat Fak. Tarımsal Yapılar ve Sulama Böl., Konya, Turkiye.Şahin, M. ve Kara, M., 2006. Konya İklim Koşullarında Farklı Sulama Uygulamalarının Çim Gelişimine Etkisi ve Su Kısıtına Yönelik Sulama Alternatifleri. S.Ü. Ziraat Fak. Derg., 20(39), 118-128, Konya.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Minimum Water Use [Turquia]
Instead of flow irrigation that requires high water consumption and causes excessive evaporation, water can be transported in pipes till crop's body and can be given slowly under controlled conditions. The approach is brought to farmers by state institutions as well as banks, and education for the scientific background, installation …
- Compilador/a: Mehmet Zengin
Módulos
Não há módulos