Soil productivity improvement and BXW control in epidemically affected banana zone [República Unida da Tanzânia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Ursula Gaemperli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1204 - República Unida da Tanzânia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Pesha
Kyerwa District Council
República Unida da Tanzânia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - República Unida da TanzâniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - República Unida da TanzâniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Kyerwa District Council - República Unida da Tanzânia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Restoring banana production through temporal crop substitution and the use of SLM and recommended husbandry practices in controlling the deadly BXW disease.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
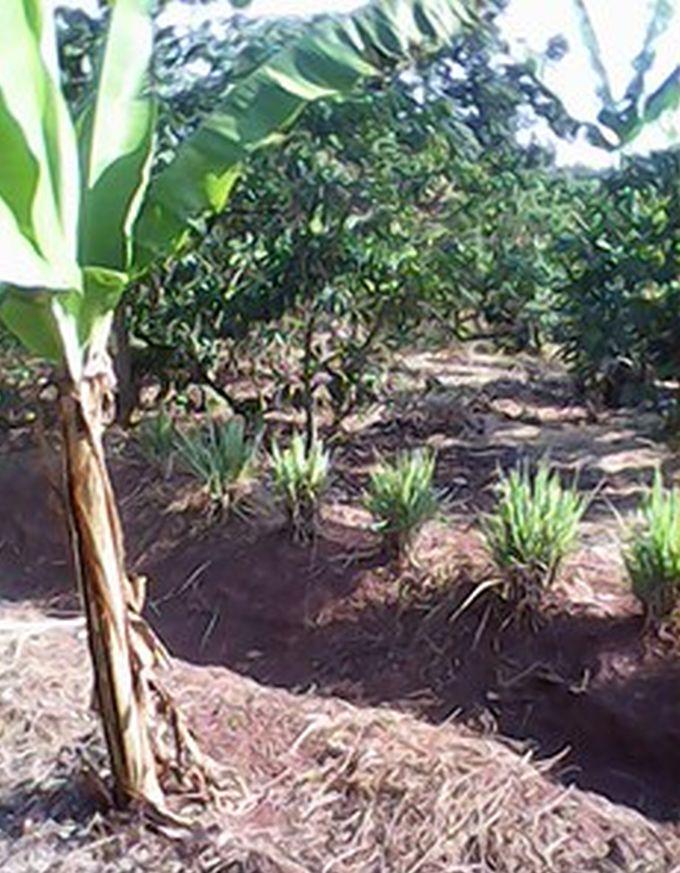
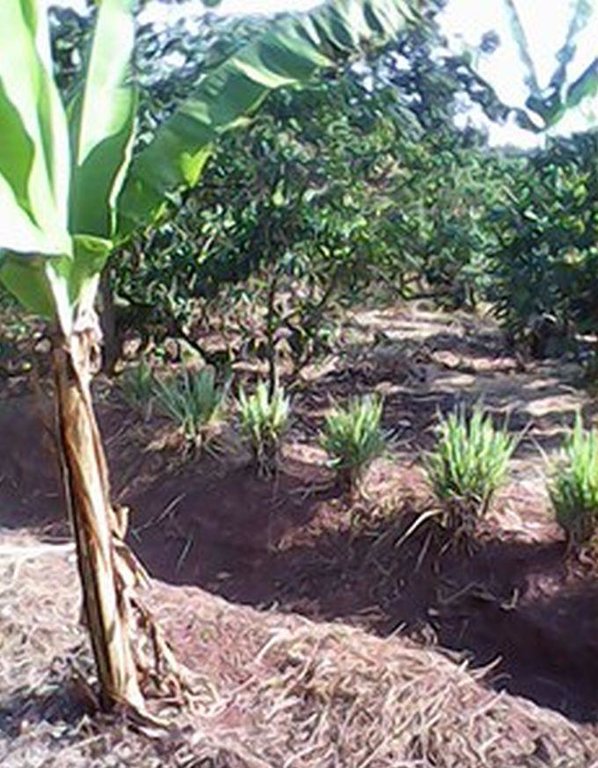
This conservation measure is used in BXW epidemically affected areas. Land users in affected areas are trained on the principle behind the diseases and means and ways to overcome it. Banana plants in seriously affected farms are uprooted and destroyed and non disease host crops usually maize and common beans are grown for starvation and destruction of BXW pathogen. The land is not used for banana production for a period of 6 months and instead substitute crops ensures food and income security to land users. Leguminous cover crops (beans) and crop residual management skills applied on the farm revitalize the soil health in terms of biomass, moisture and nutrient recycling. After 6 months, banana production is resumed where production is based on recommended husbandry practices combined with SLM conservation measures. The use of certified banana cultivars, optimal plant geometry and disease control cultural practices are some of the basic recommendation. Certified banana cultivars are planted at a space of 3m x 3m. The size of a hole used to plant banana is 0.9x0.9 m wide and 0.6 deep. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. 2 -3 tins of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The holes are left for microbial decay to take place and banana planting is done after 1 or 2 months. The tied Fanya chini water retention ditches are water harvesting and conserving structures constructed by digging trenches along the contour where dug soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. A-FRAME method is used to mark a contour line and on the other hand ARM OUTSTRETCHED LEVEL method determines how far apart the Fanya chini retention ditch should be. Unlike other retention ditches, the dug ditches are not continuous but instead are tied at regular interval with small cross–ties of 0.4-0.6m length. Ties intercept the ditch at right angle to form a series of narrow rectangular segments of infiltration ditches each of 5 meters long, 0.6m wide and 0.6m deep arranged in series within a contour line. Ties helps to prevent irregular flow of runoff and to ensure an evenly distribution of captured water. Fanya chini embankments are stabilized by planting crops on them the common crops are pigeon pea (space used between plant is stand is 1m x 1m), lemon grass (30cm x 30cm) or pineapples (60cm x 60cm). Mulching is done using grasses. The dominant grass species used is Hyperrenia rufa where a mulching depth of 15 cm is used.
Purpose of the Technology: PURPOSE: Improved food and fodder productivity, soil moisture and water holding capacity, nutrient recycling, and organic matter content, biomass cycle, crop tolerance to drought, income and food security, poverty reduction and health. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water, combating soil erosion by water runoff and biological degradation due the deadly BXW disease.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT: procurement and mobilization of working tools, uprooting and destruction of infected plants in affected fields, land tilling and harrowing, planting of alternative crops or creation of a productive disease free buffer zone, temporal harvesting of maize and beans, land preparation/ demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting, digging holes, manure application before planting, banana planting, demarcation of contour line for construction of Fanyachini contours with ties, digging and construction of Fanya chini contours with ties, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini bunds (using lemon grass, pineapples or pigeon pea), random planting of castor oil plants for future anchoring support of plants with heavy bunches and mulching application. MAINTENANCE: hand weeding to control noxious weeds combined with other pest and disease control (control of nematodes and weevils), de-suckering to leave the mother plant and two baby plants, de-trashing or trimming of unproductive leaves, regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector , recurrent manure application, removal of sediments and maintenance of Fanyachini bunds, harvest of bananas, maize, pineapples and pigeon pea. INPUTS USED: largely includes labour (strenuously varying from light, medium and heavy), tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock and A-frame), seedlings; improved or certified banana varieties, pineapples suckers, lemon grass and castor oil, seeds (beans, maize and pigeon pea), farm yard manure and mulching materials (preferably Hyperennial spps).
Natural / human environment: NATURAL ENV: The land use type is cropland with annual, perennial and some fruit tree crops. The technology involves a combination of agronomic, vegetative, structural and management conservation measures. Management measure involves all activities related to temporal shift to alternative crops for making the farm disease hot free and for staving and destroying the disease pathogen. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 days of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. A soil texture class is sandy loam with medium depth categories. HUMAN ENV: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market or commercial oriented). The average costs of inputs required is 3015.68 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
República Unida da Tanzânia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kagera Region Tanzania
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kyerwa District Council
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
The area includes the totality of all farms of FFS members who applied the technology after being trained.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
This is one of the technologies tested and demonstrated under the support of the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project. Analysis and documentation of this technology is based on perspectives and experiences of field SLM specialist and FFS group members.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- root crops, pigeon pea, lemon grass
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
- abacaxi
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- café, cultivado ao ar livre
- café, sombra cultivada
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land problems without land conservation are BXW disease, poor soil fertility, and moisture stress and soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): BXW disease.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Banana is the major food crop but in the recent years the crop was substituted by maize and beans due the out break of BXW.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
- crop substitution
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A7: Outros

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
- V5: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Use of leguminous plants
Specification of other structural measures: Water retension ditches with fanya chini bunds and ties.
Specification of other management measures: Temporal substitution of a dominant crop by non disease host crops for pathogen distruction
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation on slopy land and nutrient mining without replenishment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor practices that encourage spread of BXW.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (No use of cross slope barriers.), change in temperature (Unproductive loos of green water due direct hit of of the soil by sunshine), change of seasonal rainfall (Due to climatic change and variability), poverty / wealth (Incapacity to invest in capital heavy conservation measures), labour availability (Rural to Urban migration of the enegetic youths), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (High input expenses.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Ignorance of SLM and shortage of field extension workers.), governance / institutional (Low capacity of rural based environmental/land committees)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Due unpredictable climatic change and variability), population pressure (Continuous land fragmentation)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Most of the concepts and principles were taught to field/agricultural advisers at the college.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (New innovations and change of mind set is crucial e.g. the use of A-frame, the principle behind BXW and cultural methods of controlling the disease.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyperania grass
Quantity/ density: 15 m3 /ha
Remarks: Across the slope
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure
Quantity/ density: 40ton/ha
Remarks: 3 tin applied to each banana plant.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: pegion peas
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pineapples
Grass species: lemmon grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 12
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70
Construction material (earth): Soil
Other type of management: Temporal substitution of the a diseased plant with other non-host plants for staving and complete wipe out of the disease causing pathogen. (BXW affected bananas substituted with maize and beans)
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.353
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | |
| 2. | Initial manure application (before banana planting) | |
| 3. | Initial banana seedlings (certified varieties) | |
| 4. | Initial mulching application | |
| 5. | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants in affected fields. | Before onstart of rain |
| 6. | Land tilling and harrowing. | Before onstart of rain |
| 7. | Planting of alternative crops (maize and beans) for starving and killing the pathogen. | After the first rains (usually September) |
| 8. | Demarcation of contour line using A-frame for construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 9. | Digging and construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 10. | Planting of lemon grass , pineapples and pigeon peas on bunds. | After constrution of fanya chini retension ditches with ties |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 5,0 | 2,353 | 11,77 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Demarcation of contour line | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,26857 | 15,88 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Digging and construction of Fanya | persons/day | 10,0 | 2,353 | 23,53 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | ha | 1,0 | 76,47 | 76,47 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Lemon grass and pidgeon seeds | kgs | 5,0 | 2,94 | 14,7 | |
| Material vegetal | Pineapple seedlings | pieces | 513,0 | 0,0588304 | 30,18 | |
| Material vegetal | Initial banana seedlings | pieces | 660,0 | 0,441181818 | 291,18 | |
| Material vegetal | Maize and bean seeds | kgs | 81,0 | 0,947654 | 76,76 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Initial mulching application | bundles | 900,0 | 0,1764666 | 158,82 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Initial manure application | tons | 28,0 | 10,084 | 282,35 | |
| Outros | Labour: Land tilling and harrowing | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Planting of alternative crops | persons/day | 9,0 | 2,353 | 21,18 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1054,58 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1054,58 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting and hole digging for planting bananas | Before onstart of rain |
| 2. | Manure application before planting Banana | Before onstart of rain |
| 3. | Banana planting | one to two months after manure application |
| 4. | Recurrent mulching application | once per season |
| 5. | Hand weeding to control noxious weeds, De-suckering, De-trashing and trimming | April and December |
| 6. | Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector | Routinely as need be |
| 7. | Recurrent manure application | September/October |
| 8. | Banana harvesting | Routinely after mature |
| 9. | Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas. | April |
| 10. | harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | |
| 11. | Removal of sediments and reshaping/maintenance of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | May |
| 12. | Weeding and thinning | (twice) first and second |
| 13. | Harvesting of maize and beans. | January/February |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting | persons/day | 35,0 | 2,353 | 82,36 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Manure application before planting Banana | persons/day | 33,0 | 2,353 | 77,65 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Banana planting | persons/day | 13,0 | 2,353 | 30,59 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Recurrent mulching applicatio | persons/day | 6,0 | 2,205 | 13,23 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Mulching material | bundles | 900,0 | 0,176464 | 158,82 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | tons | 16,0 | 13,235 | 211,76 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Labour: Maintenance of Fanya chini | persons/day | 3,0 | 2,353 | 7,06 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Labour: Weeding an thinning | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05916 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Labour: Harvesting of maize and beans | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05915 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Hand weeding to control noxious weeds | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Recurrent manure application | persons/day | 22,0 | 2,353 | 51,77 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Banana harvesting | persons/day | 16,5 | 2,353 | 38,82 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 825,02 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 825,02 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattocks and forked wooden poles., Hand hoe, forked hole and machetes, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, spade, mattock and A-frame, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattock.
The above cost were calculated per unit of one land user's land (1.5 acres) where the technology was applied and estimate also done per hectare.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Manure is the most determinant factor
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature is 21°C
Average length of growing period is 210 days.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): The average soil texture is sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Low use and application of mulching and cover crops
Soil fertility is low due to continue washout of the soil surface with rainfall runoff
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium because slope effect minimize the time required for water to infiltrate into the soil.
Soil water storage capacity is low because of low amount of humus and underused of mulching
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Only a few perennials and annual crops and minimal fauna diversity due to the washout of organic matter by rainfall runoff
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the land users who are using the technology are running petty business and groceries (selling local brew).
Level of mechanization: Dominated by the use of small tools/implements.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5 fingers
Quantidade posterior à GST:
12 fingers
Comentários/especificar:
Increased banana yield due to use of SLM and good husbandry practices
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Risk due to low moisture
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Caused by the use of mulching and manure
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Income accrued from increased production and diversification to pineapples and lemon grass
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Attributable to added tasks from use of SLM
Impactos socioculturais
Estado de saúde
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Improved nutrition from e.g. introduction of pineapples
Instituições comunitárias
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Use of FFS have induced togetherness and group working spirit
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
SLM knowledge and skills gained through FFS trainings
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Indiscriminate participation of all genders, age and ethnicity
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Initially the technology has resulted to increased production, diversification to production of other income generating crops and dietary enrichment crops. The overall result is farmers capacity to meet education and health expenses
attraction to theiving
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Good looking banana bunches attract thieving
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Use of mulching and water retension ditches
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Following use of mulching and manure
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
90%
Comentários/especificar:
Improved soil coved caused by the use of grass mulching
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Controll of soil erosion attributable to use of mulching and construction of water retension ditches.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Use of luguminous plants, application of manure and mulching
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Use of manure
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
90%
Comentários/especificar:
Biomass result from use of mulching and improved managment of crop residuals
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Increased richness of soil fauna caused by the use of manure
Controle de praga/doença
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
95%
Comentários/especificar:
Control of BXW
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Increased tolerance to drought and BXW infestation
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Managment of crop residues and manure
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Of the neighbouring Kashasha wetland
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
Retention ditches supported with ties to prevent flow of water and to encourage evenly distribution of water. The fanya chini bunds are stabilized by planting vegetation on them (pineapples, pigeon peas and lemon grass).
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The high investment costs cause slight realization of rewards but in the long run very positive benefits are realized by land users.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
42 households covering 77 percent of the stated area
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
42 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Supplied with banana suckers, farm yard manure and grass mulch.
42 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: land users who received suckers from neighbors but procured grass mulch and manure.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: most of the land users are impressed with the results attributable to the technology in terms of control of BXW, increased banana production, control of soil erosion and promising increase in income.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The technology useful to the community and is easy to learn. |
| Encouraging results in terms of improved productivity and general performance of banana and other crops like coffee within the technology area attributable to use of technology. |
| The technology has made significant achievement in terms of decrease of BXW infestation. |
| Soil health has improved as the result of use of mulching materials, manure, leguminous plants and application water harvesting cross slope barriers. |
| There is positive change of mind set towards the use of SLM |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Good and attractive crops that consumers are willing to purchase at a high price have resulted to emergence of thieving. | Spread the technology and supply improved banana suckers to other farmers so that more farmers are engaged in banana production. Strengthen community police. |
| The technology initially is labour and capital intensive | Encourage group working spirit. |
| Unplanned Changes of service providers which may fall in the hands of untrustworthy service providers. | Pluralism in service delivery should be planned with doubly consciousness to take care of untrustworthy service providers. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
25/07/2014
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos