Soil productivity improvement and BXW control in epidemically affected banana zone [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: ALLAN BUBELWA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1204 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Pesha
Kyerwa District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - แทนซาเนียชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kyerwa District Council - แทนซาเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Restoring banana production through temporal crop substitution and the use of SLM and recommended husbandry practices in controlling the deadly BXW disease.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
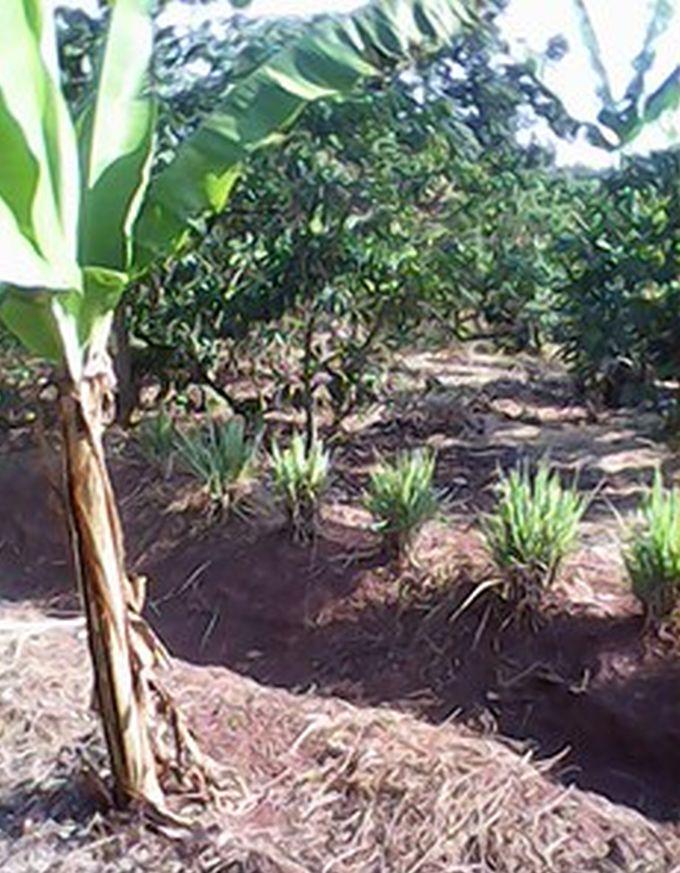
This conservation measure is used in BXW epidemically affected areas. Land users in affected areas are trained on the principle behind the diseases and means and ways to overcome it. Banana plants in seriously affected farms are uprooted and destroyed and non disease host crops usually maize and common beans are grown for starvation and destruction of BXW pathogen. The land is not used for banana production for a period of 6 months and instead substitute crops ensures food and income security to land users. Leguminous cover crops (beans) and crop residual management skills applied on the farm revitalize the soil health in terms of biomass, moisture and nutrient recycling. After 6 months, banana production is resumed where production is based on recommended husbandry practices combined with SLM conservation measures. The use of certified banana cultivars, optimal plant geometry and disease control cultural practices are some of the basic recommendation. Certified banana cultivars are planted at a space of 3m x 3m. The size of a hole used to plant banana is 0.9x0.9 m wide and 0.6 deep. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. 2 -3 tins of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The holes are left for microbial decay to take place and banana planting is done after 1 or 2 months. The tied Fanya chini water retention ditches are water harvesting and conserving structures constructed by digging trenches along the contour where dug soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. A-FRAME method is used to mark a contour line and on the other hand ARM OUTSTRETCHED LEVEL method determines how far apart the Fanya chini retention ditch should be. Unlike other retention ditches, the dug ditches are not continuous but instead are tied at regular interval with small cross–ties of 0.4-0.6m length. Ties intercept the ditch at right angle to form a series of narrow rectangular segments of infiltration ditches each of 5 meters long, 0.6m wide and 0.6m deep arranged in series within a contour line. Ties helps to prevent irregular flow of runoff and to ensure an evenly distribution of captured water. Fanya chini embankments are stabilized by planting crops on them the common crops are pigeon pea (space used between plant is stand is 1m x 1m), lemon grass (30cm x 30cm) or pineapples (60cm x 60cm). Mulching is done using grasses. The dominant grass species used is Hyperrenia rufa where a mulching depth of 15 cm is used.
Purpose of the Technology: PURPOSE: Improved food and fodder productivity, soil moisture and water holding capacity, nutrient recycling, and organic matter content, biomass cycle, crop tolerance to drought, income and food security, poverty reduction and health. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water, combating soil erosion by water runoff and biological degradation due the deadly BXW disease.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT: procurement and mobilization of working tools, uprooting and destruction of infected plants in affected fields, land tilling and harrowing, planting of alternative crops or creation of a productive disease free buffer zone, temporal harvesting of maize and beans, land preparation/ demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting, digging holes, manure application before planting, banana planting, demarcation of contour line for construction of Fanyachini contours with ties, digging and construction of Fanya chini contours with ties, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini bunds (using lemon grass, pineapples or pigeon pea), random planting of castor oil plants for future anchoring support of plants with heavy bunches and mulching application. MAINTENANCE: hand weeding to control noxious weeds combined with other pest and disease control (control of nematodes and weevils), de-suckering to leave the mother plant and two baby plants, de-trashing or trimming of unproductive leaves, regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector , recurrent manure application, removal of sediments and maintenance of Fanyachini bunds, harvest of bananas, maize, pineapples and pigeon pea. INPUTS USED: largely includes labour (strenuously varying from light, medium and heavy), tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock and A-frame), seedlings; improved or certified banana varieties, pineapples suckers, lemon grass and castor oil, seeds (beans, maize and pigeon pea), farm yard manure and mulching materials (preferably Hyperennial spps).
Natural / human environment: NATURAL ENV: The land use type is cropland with annual, perennial and some fruit tree crops. The technology involves a combination of agronomic, vegetative, structural and management conservation measures. Management measure involves all activities related to temporal shift to alternative crops for making the farm disease hot free and for staving and destroying the disease pathogen. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 days of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. A soil texture class is sandy loam with medium depth categories. HUMAN ENV: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market or commercial oriented). The average costs of inputs required is 3015.68 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kagera Region Tanzania
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kyerwa District Council
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area includes the totality of all farms of FFS members who applied the technology after being trained.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
This is one of the technologies tested and demonstrated under the support of the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project. Analysis and documentation of this technology is based on perspectives and experiences of field SLM specialist and FFS group members.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root crops, pigeon pea, lemon grass
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- pineapple
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- coffee, open grown
- coffee, shade grown
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land problems without land conservation are BXW disease, poor soil fertility, and moisture stress and soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): BXW disease.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Banana is the major food crop but in the recent years the crop was substituted by maize and beans due the out break of BXW.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืชแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงเกษตรอินทรีย์ด้วย)
- crop substitution
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A7: Others

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
- V5: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M7: อื่นๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Use of leguminous plants
Specification of other structural measures: Water retension ditches with fanya chini bunds and ties.
Specification of other management measures: Temporal substitution of a dominant crop by non disease host crops for pathogen distruction
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation on slopy land and nutrient mining without replenishment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor practices that encourage spread of BXW.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (No use of cross slope barriers.), change in temperature (Unproductive loos of green water due direct hit of of the soil by sunshine), change of seasonal rainfall (Due to climatic change and variability), poverty / wealth (Incapacity to invest in capital heavy conservation measures), labour availability (Rural to Urban migration of the enegetic youths), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (High input expenses.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Ignorance of SLM and shortage of field extension workers.), governance / institutional (Low capacity of rural based environmental/land committees)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Due unpredictable climatic change and variability), population pressure (Continuous land fragmentation)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Most of the concepts and principles were taught to field/agricultural advisers at the college.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (New innovations and change of mind set is crucial e.g. the use of A-frame, the principle behind BXW and cultural methods of controlling the disease.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyperania grass
Quantity/ density: 15 m3 /ha
Remarks: Across the slope
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure
Quantity/ density: 40ton/ha
Remarks: 3 tin applied to each banana plant.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: pegion peas
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pineapples
Grass species: lemmon grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 12
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70
Construction material (earth): Soil
Other type of management: Temporal substitution of the a diseased plant with other non-host plants for staving and complete wipe out of the disease causing pathogen. (BXW affected bananas substituted with maize and beans)
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.353
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | |
| 2. | Initial manure application (before banana planting) | |
| 3. | Initial banana seedlings (certified varieties) | |
| 4. | Initial mulching application | |
| 5. | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants in affected fields. | Before onstart of rain |
| 6. | Land tilling and harrowing. | Before onstart of rain |
| 7. | Planting of alternative crops (maize and beans) for starving and killing the pathogen. | After the first rains (usually September) |
| 8. | Demarcation of contour line using A-frame for construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 9. | Digging and construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 10. | Planting of lemon grass , pineapples and pigeon peas on bunds. | After constrution of fanya chini retension ditches with ties |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 5.0 | 2.353 | 11.77 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Demarcation of contour line | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.26857 | 15.88 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Digging and construction of Fanya | persons/day | 10.0 | 2.353 | 23.53 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants | persons/day | 11.0 | 2.353 | 25.88 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | ha | 1.0 | 76.47 | 76.47 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Lemon grass and pidgeon seeds | kgs | 5.0 | 2.94 | 14.7 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Pineapple seedlings | pieces | 513.0 | 0.0588304 | 30.18 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Initial banana seedlings | pieces | 660.0 | 0.441181818 | 291.18 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Maize and bean seeds | kgs | 81.0 | 0.947654 | 76.76 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Initial mulching application | bundles | 900.0 | 0.1764666 | 158.82 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Initial manure application | tons | 28.0 | 10.084 | 282.35 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Land tilling and harrowing | persons/day | 11.0 | 2.353 | 25.88 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Planting of alternative crops | persons/day | 9.0 | 2.353 | 21.18 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1054.58 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1054.58 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting and hole digging for planting bananas | Before onstart of rain |
| 2. | Manure application before planting Banana | Before onstart of rain |
| 3. | Banana planting | one to two months after manure application |
| 4. | Recurrent mulching application | once per season |
| 5. | Hand weeding to control noxious weeds, De-suckering, De-trashing and trimming | April and December |
| 6. | Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector | Routinely as need be |
| 7. | Recurrent manure application | September/October |
| 8. | Banana harvesting | Routinely after mature |
| 9. | Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas. | April |
| 10. | harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | |
| 11. | Removal of sediments and reshaping/maintenance of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | May |
| 12. | Weeding and thinning | (twice) first and second |
| 13. | Harvesting of maize and beans. | January/February |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting | persons/day | 35.0 | 2.353 | 82.36 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Manure application before planting Banana | persons/day | 33.0 | 2.353 | 77.65 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Banana planting | persons/day | 13.0 | 2.353 | 30.59 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Recurrent mulching applicatio | persons/day | 6.0 | 2.205 | 13.23 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Mulching material | bundles | 900.0 | 0.176464 | 158.82 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | tons | 16.0 | 13.235 | 211.76 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Labour: Maintenance of Fanya chini | persons/day | 3.0 | 2.353 | 7.06 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Labour: Weeding an thinning | persons/day | 12.0 | 2.05916 | 24.71 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Labour: Harvesting of maize and beans | persons/day | 12.0 | 2.05915 | 24.71 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Hand weeding to control noxious weeds | persons/day | 15.0 | 2.353 | 35.3 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence | persons/day | 15.0 | 2.353 | 35.3 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Recurrent manure application | persons/day | 22.0 | 2.353 | 51.77 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Banana harvesting | persons/day | 16.5 | 2.353 | 38.82 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.353 | 16.47 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7.0 | 2.353 | 16.47 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 825.02 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 825.02 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattocks and forked wooden poles., Hand hoe, forked hole and machetes, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, spade, mattock and A-frame, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattock.
The above cost were calculated per unit of one land user's land (1.5 acres) where the technology was applied and estimate also done per hectare.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Manure is the most determinant factor
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature is 21°C
Average length of growing period is 210 days.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture (topsoil): The average soil texture is sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Low use and application of mulching and cover crops
Soil fertility is low due to continue washout of the soil surface with rainfall runoff
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium because slope effect minimize the time required for water to infiltrate into the soil.
Soil water storage capacity is low because of low amount of humus and underused of mulching
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Only a few perennials and annual crops and minimal fauna diversity due to the washout of organic matter by rainfall runoff
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the land users who are using the technology are running petty business and groceries (selling local brew).
Level of mechanization: Dominated by the use of small tools/implements.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
5 fingers
หลังจาก SLM:
12 fingers
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased banana yield due to use of SLM and good husbandry practices
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Risk due to low moisture
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Caused by the use of mulching and manure
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Income accrued from increased production and diversification to pineapples and lemon grass
ภาระงาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Attributable to added tasks from use of SLM
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved nutrition from e.g. introduction of pineapples
สถาบันของชุมชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of FFS have induced togetherness and group working spirit
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SLM knowledge and skills gained through FFS trainings
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Indiscriminate participation of all genders, age and ethnicity
livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Initially the technology has resulted to increased production, diversification to production of other income generating crops and dietary enrichment crops. The overall result is farmers capacity to meet education and health expenses
attraction to theiving
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Good looking banana bunches attract thieving
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of mulching and water retension ditches
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Following use of mulching and manure
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved soil coved caused by the use of grass mulching
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Controll of soil erosion attributable to use of mulching and construction of water retension ditches.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of luguminous plants, application of manure and mulching
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of manure
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Biomass result from use of mulching and improved managment of crop residuals
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased richness of soil fauna caused by the use of manure
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0%
หลังจาก SLM:
95%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Control of BXW
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased tolerance to drought and BXW infestation
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Managment of crop residues and manure
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
low
หลังจาก SLM:
high
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Of the neighbouring Kashasha wetland
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
high
หลังจาก SLM:
low
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Retention ditches supported with ties to prevent flow of water and to encourage evenly distribution of water. The fanya chini bunds are stabilized by planting vegetation on them (pineapples, pigeon peas and lemon grass).
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The high investment costs cause slight realization of rewards but in the long run very positive benefits are realized by land users.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
42 households covering 77 percent of the stated area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
42 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Supplied with banana suckers, farm yard manure and grass mulch.
42 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: land users who received suckers from neighbors but procured grass mulch and manure.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: most of the land users are impressed with the results attributable to the technology in terms of control of BXW, increased banana production, control of soil erosion and promising increase in income.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology useful to the community and is easy to learn. |
| Encouraging results in terms of improved productivity and general performance of banana and other crops like coffee within the technology area attributable to use of technology. |
| The technology has made significant achievement in terms of decrease of BXW infestation. |
| Soil health has improved as the result of use of mulching materials, manure, leguminous plants and application water harvesting cross slope barriers. |
| There is positive change of mind set towards the use of SLM |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Good and attractive crops that consumers are willing to purchase at a high price have resulted to emergence of thieving. | Spread the technology and supply improved banana suckers to other farmers so that more farmers are engaged in banana production. Strengthen community police. |
| The technology initially is labour and capital intensive | Encourage group working spirit. |
| Unplanned Changes of service providers which may fall in the hands of untrustworthy service providers. | Pluralism in service delivery should be planned with doubly consciousness to take care of untrustworthy service providers. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
25/07/2014
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล