Multiplier fertilization of banana using small ruminants in Kibanja farming system [República Unida da Tanzânia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
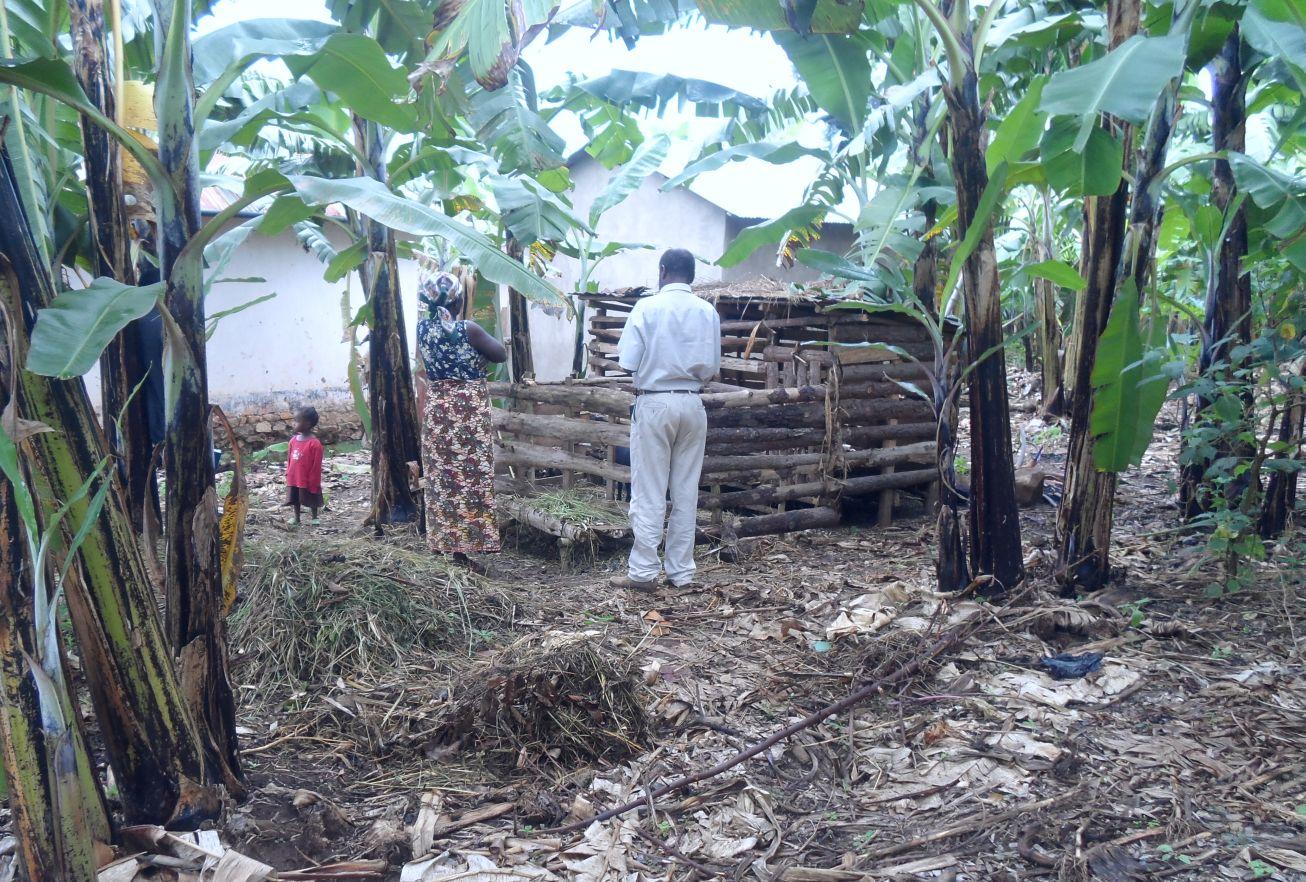
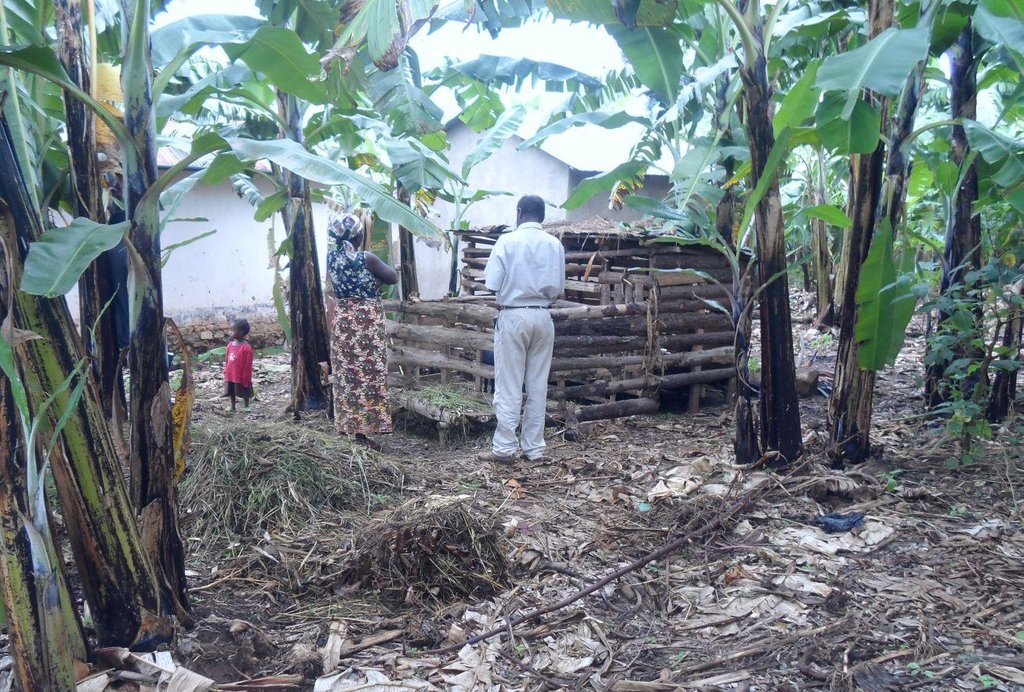
Matumizi ya mifugo katika shamba la kibanja.
technologies_1207 - República Unida da Tanzânia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Pancras Egidius
Missenyi District
República Unida da Tanzânia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - República Unida da TanzâniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - República Unida da Tanzânia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Enhancement of sustainable land management by capitalizing on the rapid growth, short gestation nature and multiple benefits of small ruminants kept under zero grazing in a banana based farming system.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Multiplier banana fertilization is a system where rapid growing small ruminants (preferably dairy goats) of low gestation period are kept under zero grazing within a banana based (Kibanja) farming system and their excrement are used in complementing other fertilization of the banana fields. Dairy goats also improve diet of the rural poor and diversify their income. The animals were initially supported by SLM projects as quick win income generating motivation/incentives to farmer who spent their valuable time in SLM activities of long term benefit realization. In multiplier fertilization, a farmer starts only with a few numbers of animals (as kick start). Usually 2 female dairy goats and one improved male goat (buck) suffice. Goat dung collected from the shed is used to perform selective and on spot application of manure to banana plants. Because of their rapid growth and short gestation nature, goats multiplies and increase in number within few years and at the same time in multiplier terms farmers spread and apply manure to more banana plants. Farmers begin with a small animal shed of usually carrying capacity of 4 to 6 goats and can expand it as goat increases. Goats feed on products cut and carried outside or within the kibanja farm. Animals also feed on domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels), food supplements and water for their maximum performance. Goat dung is collected weekly from the shed and is piled in layers, covered with grass and kept shaded under banana canopies to allow microbial action and minimize nutrient loss through volatilization. Depending on the growth stage of banana, dry manure is applied on sport and selectively after every three months of microbial decay. The numbers of animal increases year after year at the same time farmer benefit from the use/sale of animal product (milk in the short term and meat in the long term) and in multiplier manner continue expanding manure application to other banana plants. Manure from goats contributes in improved banana productivity. Benefits accrued from goats also motivate and induce farmers’ patience in terms of their participation in SLM interventions of long term benefit realization.
Purpose of the Technology: Purposes: improved banana productivity, livelihood diversification, income of the rural poor and soil ecosystem through fertility and organic matter replenishment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities includes, kick start support of farmers with goats (two dairy goats and an improved buck), construction of the goat shed (100% borne by land user to inculcate self-initiative and ownership) and purchase of working tools (spade, rake, hand hoe).
Recurrent activities largely includes, fetching fodders and feeding the animals (cut and carry products outside or within the kibanja), weekly cleaning of the goat shed and manure collection, manure heaping and grass covering for microbial decay/reducing nutrient volatilization, spreading/cooling, monthly on spot and selective application of manure to banana plants, milking of the animals, disease control/deworming and providing supplements.
Natural / human environment: Multiplier banana manure application is used in kibanja farming system in sub humid tropical highland plateau/plains of 1000 -1500m a.s.l. with annual rainfall between 1000 – 1500mm, moderate soil depth and medium loam textural class.
Is used by small scale land users both men and women individual households. In Kibanja farm, land ownership is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial).
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
República Unida da Tanzânia
Região/Estado/Província:
Tanzania/Kagera
Especificação adicional de localização:
Missenyi Disrict/ Kiziba division/ Kitobo ward/ Kyazi village
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
The technology is implemented in Kibanja cropping land use type by individual farmers who received support of diary goats from the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (TAMP) as quick win and environmental sound motivation for farmers who spend their valuable time in implementation of SLM intervention of long term benefit realization.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Started in December 2012 as part of environmental sound income generating activities promoted and supported by the Trans-boundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project (KAGERA TAMP).
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- culturas de raízes/tubos - batata doce, inhame, taro/cocoyam, outros
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- café, cultivado ao ar livre
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Without land conservation there will be inadequate/poor soil fertility and organic matter content, low soil moisture holding capacity, poor health of banana and their increased vulnerability to pest and diseases especially the most devastating Banana Xanthomonas Wilt (BXW).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Banana Xanthomonas Wilt, weak banana plants and low production.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A7: Outros
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, green manure, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Low soil fertilization/manure application), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor banana husbandry practces), population pressure (High land requirement and continuous utilization without fallowing.), poverty / wealth (low investment capacity), education, access to knowledge and support services (Shortage of staff, inadequate extension services and provision of subsidies.), governance / institutional (Low bylaws/law enforcements (e.g. on BXW control))
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
and rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Involve simple retraining of technologies already taught to staff in school/agricultural collages.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Have some elements of new skills and knowledge. e.g. a farmers must be taught of the principle behind zero grazing and manure preparation (microbial decomposition/control of mineral volatilization))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana, castrol oil, yams
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Mulching
Material/ species: Banana thrashes and stems
Quantity/ density: 100m3/ha
Remarks: thinly pread seasonaly twice per year
Green manure
Material/ species: Various types of weeds
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: scattered
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: various
Remarks: random
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Goat dung, grass and domestc residues
Quantity/ density: 222 m3/ha
Remarks: Assuming got dung is applied once per hactere
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
1700,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.20
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase goats (dairy goats) | |
| 2. | Build animal shed | |
| 3. | Purchase tools |
Comentários:
Lifespan of the goats and tools: 5 years
Lifespan of the shed: 3 years
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Tools | piece | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Goat shed | piece§ | 1,0 | 29,0 | 29,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Goats | piece | 3,0 | 70,33333 | 211,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 254,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 0,15 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | Daily/annually |
| 2. | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | weekly/annually |
| 3. | Heaping manure and compost | weekly/annually |
| 4. | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | March, June, Sept and Decemb |
| 5. | Disease control/de-worming | weekly/annally |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Fetching fodder (cut and carry) and use of domestic residuals. | person/days | 120,0 | 1,175 | 141,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning shed and collecting manure | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Heaping manure and compost | person/days | 26,0 | 0,8848 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Tilling on sport and selective application around banana | person/days | 16,0 | 1,1875 | 19,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Biocides | litres | 12,0 | 3,91666 | 47,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Disease control/de-worming | person/days | 26,0 | 1,1925 | 31,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 284,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 0,17 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, rake, hand hoe, machete and bucket.
The costs were calculated per unit of kick start animal flock (three dairy goats) needed annually per individual farmer household.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
September to December 120 days, March to Maya 90 days = 210 days . Average length of growing period is 210
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average temperature is 20°C
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (about 60cm)
Soil texture: Medium (highly clay loam)
Soil fertility: Low (due to excessive nutrient uptake without replenishment)
Top soil organic matter: Low (low crop remains)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (no water logging)
Soil water storagce capacity: Very high (nature of soil is loamy)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Medium (water is available in nearby natural water spring. There is reduction of water flow during the dry season)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water as it comes from a natural spring
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Soil microorganisms e.g earthworms and ants.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
6% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
64% of the land users are average wealthy and own 64% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 6% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some have established small kiosk at the village center and most have additional income items of regular support, assistance and cash transference from children or family members who work or have big business in cities, town and in some cases in diaspora.
Market orientation: Mixed (Banana and goats/milk are produced for both sell and home consumption)
Level of mechanization: Manual work (land form and agroecological nature of the kibanja farm cause hand hoe to be the best means of cultivation)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
< 0.5 ha, Ranked 2, about 30% of household fall in this category
0.5-1 ha: Ranked 1, account for 60 % of the household
1-2 ha: Ranked 3, account for 10% 0f the household
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
Land is largely acquired by inheritance. Traditionally water is open accessed for public use through customary law.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
15-20kgs/banch
Quantidade posterior à GST:
35-40kgs/banch
Comentários/especificar:
manure application have contributed in increase of banana yield
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0 goat per household
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3 goats per household
Comentários/especificar:
goats introduced through projects.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
385 usd
Quantidade posterior à GST:
200 usd
Comentários/especificar:
manure received from goat overshadow the costs of fodder, concentrates and waters for goats
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3.5 usd
Quantidade posterior à GST:
6.5 usd
Comentários/especificar:
net income gain due to use of manure
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1 enterprise
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2 enterprises
Comentários/especificar:
additional income sources from goat keeping
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
237
Comentários/especificar:
Increased labour needed for goat keeping
Impactos socioculturais
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Farmer use additional income generated from banana production to pay for debts and other commitments like school fee and health expenses. Goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services. There is also nutritional improvement to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein).
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
improved water holding capacity
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low N
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high N
Comentários/especificar:
due to application of goat dung
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
due to goat manure
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Increased soil micro-organism/insect
Controle de praga/doença
Quantidade anterior à GST:
low
Quantidade posterior à GST:
high
Comentários/especificar:
Due to improved plant health.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
Storage of crop remains, hay making for animal to have enough food and produce more meat, milk as well as manure.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
goats give quick win benefits because have short gestation period, usually gives twin kidding twice per year. Their average lactation period is 250 days and a single goat can produce average of 750 litres of milk per year worthy about 441 American dollars.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
317 households and 23% of the area covered
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
4% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The project supported procurement of goats.
31% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: goat keeping is part of tradition and culture.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some neighboring farmers have started adoption.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The technology is simple and easy to learn and have a short establishment time due to the short gestation nature of the goats themselves (only two female goats and an improved buck, a goat shed and some concentrates suffice for initial investment). |
| In the long term has synergistic effect and complements other existing land fertilization, moisture conservation and erosion control methods e.g. the quality of compost is improved. |
| Improves livelihood (goats act as moving banks and contributes in farmer income assurance during the sensitive time e.g. sending children to school or wives to maternal/birth services) and nutrition to farmers (farmers attain a balanced diet from milk protein). |
| Increased banana production and continuous returns in multiplier terms. Goats also convert domestic residuals (e.g. banana peels) into useful products . |
| Maintenance activities can be covered by land users and this help in ensuring self-initiative and ownership |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High workload in looking for fodder | Introduce fodder within kibanja farm |
| Shortage of genetically improved dairy goats | Introduce genetically improved dairy goats. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Shortage in the number of field extension workers needed for effective extension service delivery | Government employ more extension worker |
| Limited reach ability of extension staff due to shortage of transport facilities. | Provision of reliable transport facilities to extension workers. |
| Agro-vert/input dealers services are not available in the rural premises. | Introduce agro-vert/input dealers in rural premises. |
| Goat provision and distribution to farmers done at a small pace | Expand goat provision and distribution to more farmers. |
| Rural urban migration of the youth searching for greener pasture leaving behind the less energetic elders. | Introduce attractive and decent income generating activities for youth in the rural areas. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
04/06/2014
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos