Cultivation of Hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in the watershed [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Alexandra Gavilano
Kesht Angoza da abriza
technologies_1306 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
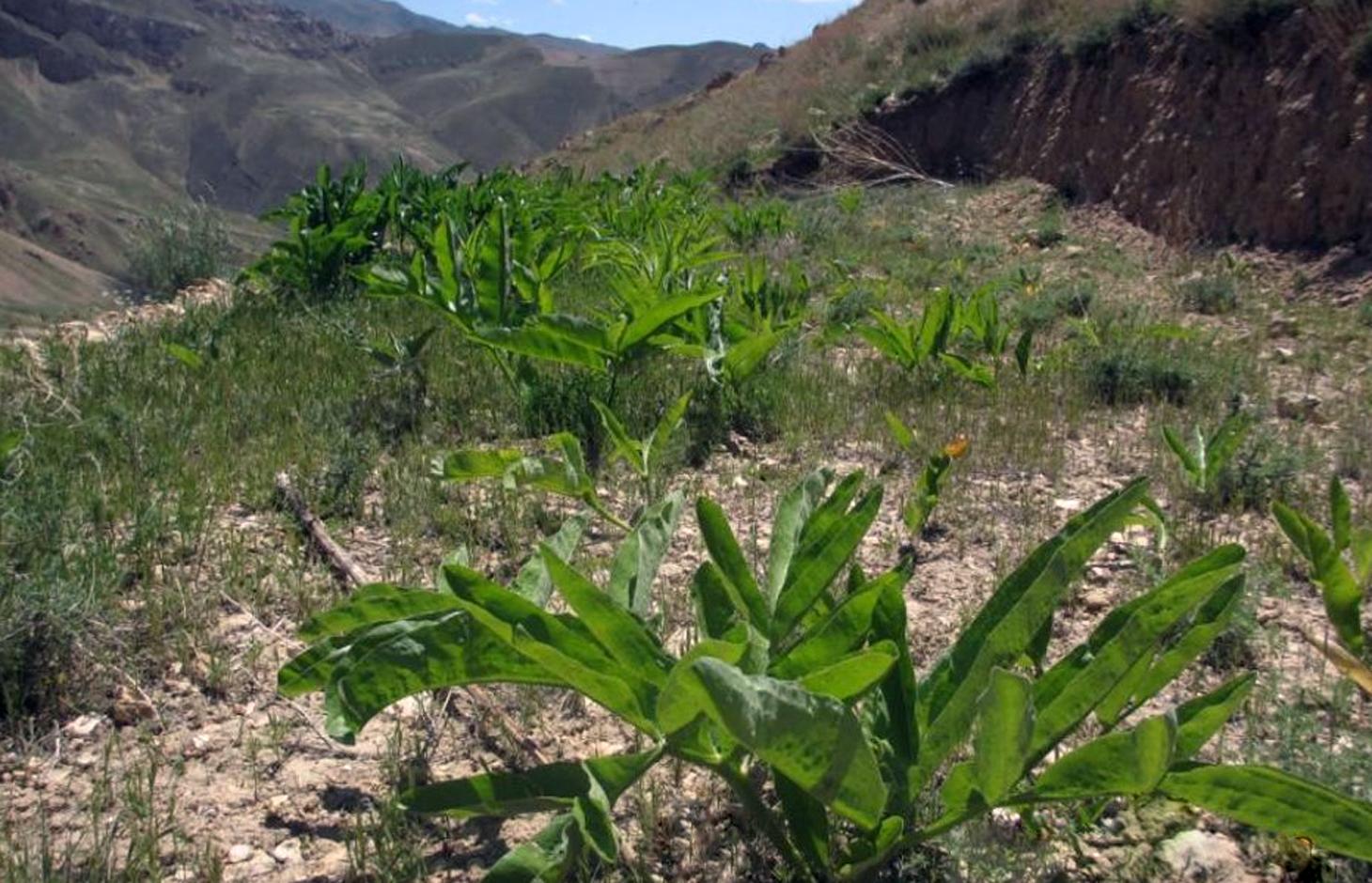
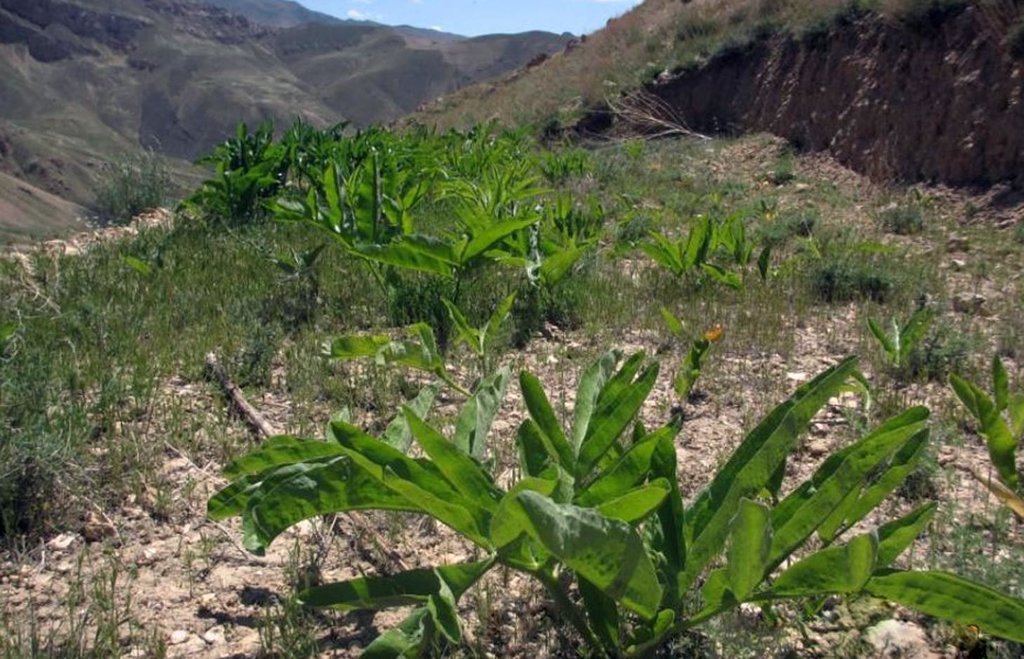
Ferula assa-foetida is an important medicinal plant, a valued cash crop and a native plant of Afghanistan’s range-lands.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Cultivation of hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in watersheds is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project which is implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). Ferula assa-foetida, or hing, is a medicinal plant that grows well in shallow sandy and alkaline soils in semi-arid climates and at high altitudes and is a native plant of Afghanistan’s upper catchment areas. Due to the enduring conflict and the consequent breakdown of community-managed grazing in upper catchment areas, most range-lands in Afghanistan are been seriously degraded. Uncontrolled grazing of animals and growing cereal crops on range-lands are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in upper catchments. One of the negative consequences are flash floods occurring several times a year, damaging agricultural lands, irrigation canals, houses and other infrastructure while often also causing fatalities.
In order to decrease the risk of flash floods, improve pastures and extend cash crop cultivation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation has implemented community-based watershed activities such as structural and agronomic measures to control water runoff.
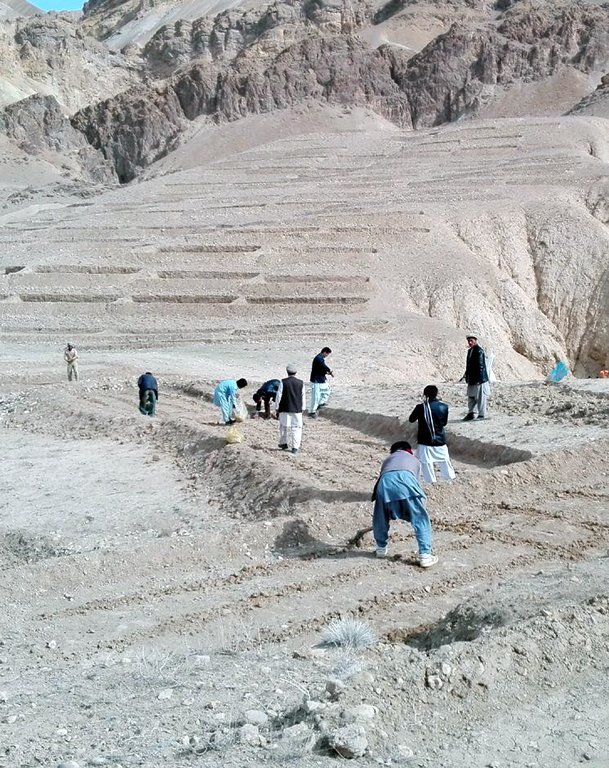
Hing has been identified as a suitable agronomic measure in watershed management in Saighan district. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and the target communities selected hing as a valuable cash crop and a suitable plant for watershed rehabilitation. Today, hing is cultivated on 1,400,000 m2 (140 ha) in nine watersheds and with the participation of 1500 families. The growing period of hing depends on the local climate but tends to be 5-10 years and culminates in the pants’ flowering. During the first five years hing has grey colored leaves. Later a stem appears and grows more than a meter high. The stem is large and yellow and at the end of the main and subordinate stems are yellow flowers. The width of the hing root varies between 7-15 cm and usually goes as deep as 30-40 cm into the soil. Hing plantations have been established with the involvement of the local communities and are managed by the responsible watershed committee. The harvest of hing is organized by the watershed committee and all households have the right to participate and sell hing for income generation. To maintain watershed activities, such as hing cultivation, a safe box has been created for each community-managed watershed. The watershed committee manages the safe box and collects funds for maintenance, community development and emergency projects, according to the watershed management plan which has been developed by the local communities with support of HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach to 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230 mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple (wheat) and fodder crops. Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity from May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Bamyan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Saighan
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
1,4
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
- Re-introduction
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was introduced since 2012
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- plantas medicinais, aromáticas, agrotóxicas - perenes

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of management in upper catchment area over the last decades resulted in a severe loss of vegetation and in the loss of biodiversity. Uncontrolled grazing of animals during the spring season prevented seed production of domestic plants. Hot temperature in summer burnt the remaining parts of domestic plants. Each year, the soil is washed away by heavy rainfalls creating gulleys which further reduced the vegetation cover.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The users of watershed areas cut shrubs for fuel and graze their animals. The lack of alternatives left them to overuse resources in upper catchment areas during war and conflict.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: March to July
Livestock density: 10-25 LU /km2
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Pastagem
- Extensive grazing
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- cultivation of medical plants
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The upper catchment area have broken to agricultural lands), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Domestic shrubs have been cut and have been used for fuel energy), overgrazing (Without management people grazed their animals in spring season and prevented from the plant seed production.), war and conflicts (3 decades internal wars in Afghanistan)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Continiuosly 3 drought years also had a rule for burning plants in upper catchment areas), poverty / wealth (During internal wars, people were not able to go in other provinces and only they had access to agriculture land and livestock for their livelihood)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
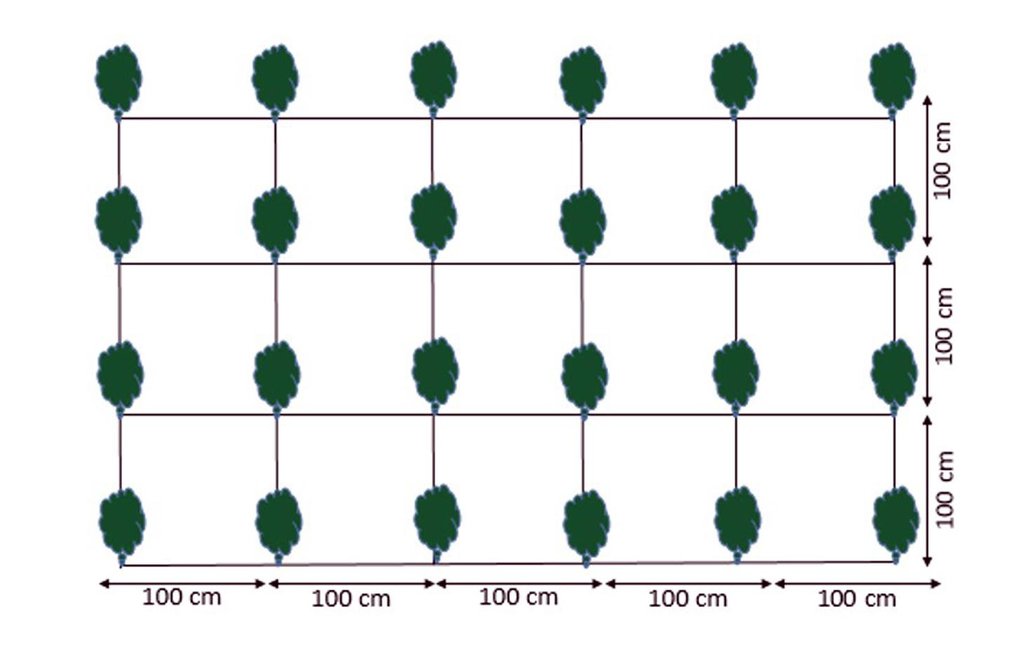
Cultivation plan of Ferula assa-foetida:
Plant to plant distance 100 cm.
Line to line distance 100 cm.
Seed depth 1-1.5 cm with;
3-6 seeds in one spot.
Location: Saighan watersheds. Bamyan
Date: 18/04/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, Increase vegetation cover through cash crop
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida
Quantity/ density: 4 plant/m2
Remarks: plant to plant and line to line 100 cm
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other domestic plants
Quantity/ density: 1 m2
Remarks: Growing domestic plants between Ferula assa-foetida plants
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other plants cover the naked area
Autor:
Shabir Shahem, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, Afghanistan
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Afghani
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
67,69
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.17
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 12,92 | 12,92 | 25,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 115,0 | 115,0 | 25,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 127,92 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1,89 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hiring guard for protection of watershed from uncontrolled grazing |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
In 2015, the government of Tajikistan did not limit the export of seeds to Afghanistan.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Good quality seeds are available in Tajikistan. If the government of Tajikistan limits exporting seeds to Afghanistan, seed costs may increase.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The importance of off-farm income is marginal. However, hing cultivation in the watershed presents a viable opportunity to generate income off-farm for the involved communities. Hing can contribute up to >50% of off-farm income.
The watershed belongs to the communities and all households have the same rights.
The income is saved in a communal safe box and is spent for community development and emergency issues.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Watershed committee manage the income of Ferula assa-foetida productions through safe box investment
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Improve the economic opportunities of the community to generate income
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation coverage
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10
Quantidade posterior à GST:
30
Comentários/especificar:
When the plants grow more, cover area and infilterate runoff
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation coverage
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Vegetation coverage
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
Reduction of flash flood protect lower part resources
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
Should be cultivated away from flood stream area.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The estabIishment costs are high because hing yields only after five years. However, the investments and maintenance costs are quickly returned once hing can be harvested.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
750 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
In this calculation, the total number of families in 13 villages are considered.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The establishment costs are too high.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Increase in production of the valuable plants in the upland areas. |
| Protection of the lower lands from the risk of flash floods. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Introduction and increase in valuable cash crop cultivation in unproductive lands. |
| New income opportunity and increase in income of the community members. |
| Reducing flash flood through increasing vegetation coverage |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The watershed area is common land. | Need active watershed committee members to manage well (good governance). |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| People lack alternatives and have therefore no stake to protect the upland areas. | Negotiation with herders to reduce the number of their livestock because of introduction of as new alternative source of income. |
| Tangible benefits are only visible after five years. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
17/04/2016
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos