Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Daler Domullojonov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Пуркунии селрохахо
technologies_1450 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures: 20 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures: 22 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures: 19 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Barotov Bahrom
Welthungerhilfe
Tajiquistão
Especialista em GST:
Ashurov Bakhtiyor
Welthungerhilfe
Tajiquistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - Tajiquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Reclamation and infilling of eroded gullies using barriers of willow branches and live mulberry cuttings to trap loess soil from surface water runoff.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
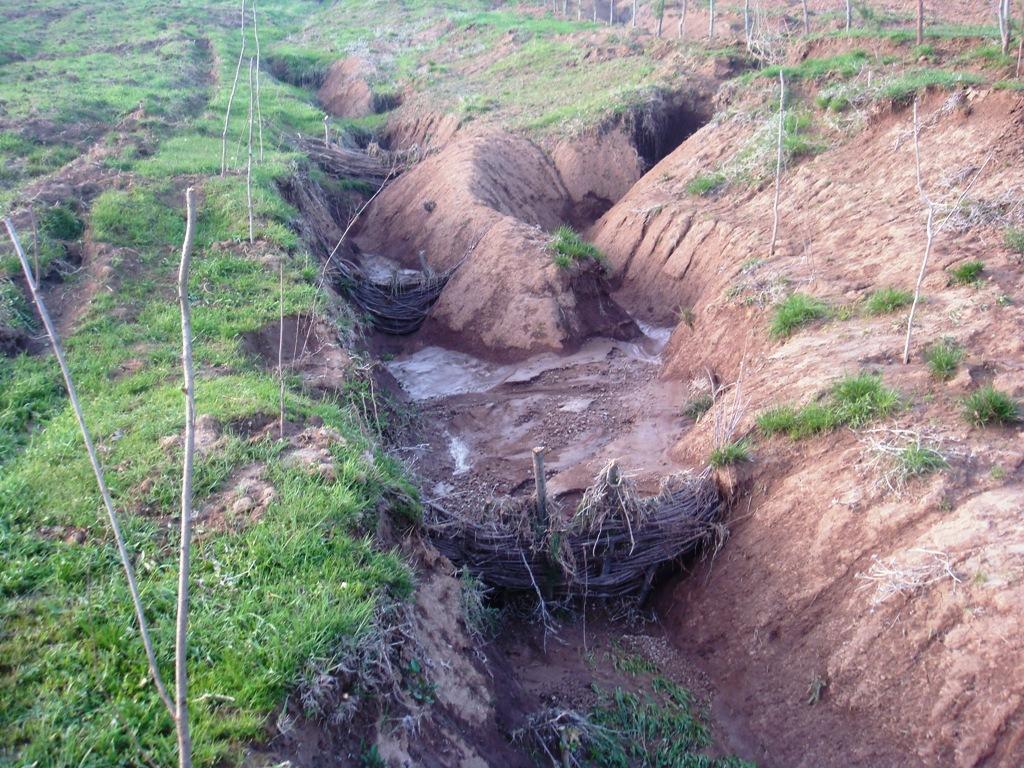
Due to many different factors and mechanisms, soil erosion is at an advanced stage in many of the hilly and mountainous parts of Tajikistan. After disrupting the soil cover in steep areas, starting the process of soil detachment and transportation water runoff gets concentrated into specific areas. As a result, rills develop on the steep areas, and eventually enlarge into gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, low cost barriers are constructed from flexible living branches of a sprouting variety of tree, such as willow. These branches are placed along the gulley at intervals of 3-10 metres, so that they slow down the flow of surface water and trap the sediment, thus eventually filling in the gulley over a period of several years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The barriers are designed to slowly help infill eroded gullies by trapping the sediment from muddy surface water runoff. This helps prevent further erosion, increases the amount of land available for pasture, and reduces the risk of mud flows or floods further down the slope.
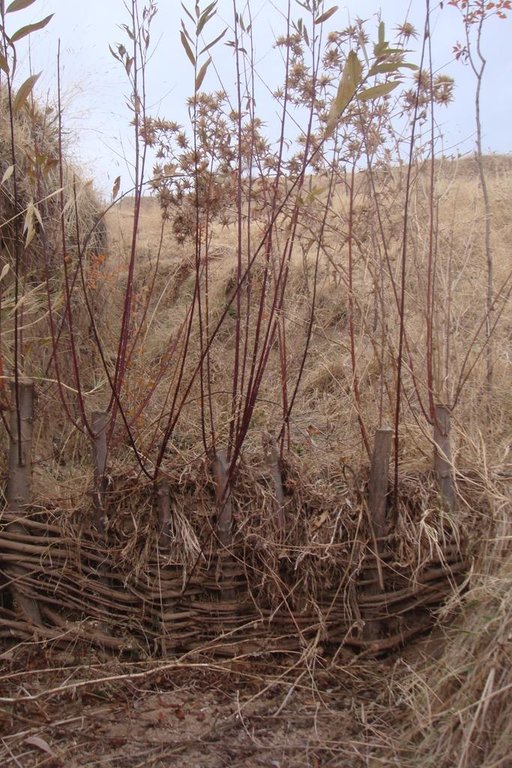
In gullies no wider than 1-2m, live cuttings from local tree varieties with a diameter of 3-5cm and 1 metre in length can be used to establish horizontal woven barriers across the gulley. The barriers are placed at 3-5m intervals along the gulley, starting at the base.
These barriers are constructed from cuttings that are woven in narrow sections with 5-6cm intervals between them. Enforcement and strengthening of these plugs can be achieved through the use of long branches of locally available mulberry. The height of the plug should not exceed 0.5m. The construction activities start in the spring and within several weeks some of the cuttings begin to sprout and grow. To avoid erosion at the sides of the structure, the cut offs are embedded into the sides of the gulley.
Natural / human environment: Gulley plugging is used in pasture land that suffers from overgrazing, deforestation and trampling, which has resulted in the degradation of the soil. Subsequently, the soil has become more vulnerable to the impact of heavy rain in the spring and autumn months, and is prone to erosion from surface water runoff.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tajikistan / Khatlon
Especificação adicional de localização:
Khovaling / Dorobi
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.017 km2.
Approximately an 800 m long eroded gully was reclaimed.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was developed and promoted using the framework of EC TACIS funded Welthungerhilfe project in Khatlon
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- frutas silvestres

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
- gado - lácteo
- ovelhas
Comentários:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing on pasture lands, that leads to reduced vegetation cover and deforestation, contributes greatly to the causes of top soil erosion and gulley formation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies are formed after intensive rainfall events. There is nothing in place to stop this erosion.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cows, goats. sheep
Grazingland comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of grazing system comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- frutas silvestres

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Number of growing seasons per year:
1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: March - June
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Trees were cut from a steep slope on the side of the hillside.), overgrazing (Freely grazed area, carrying capacity less than animal numbers grazing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More intensive rainfall.), land tenure (Lack of control of livestock grazing activities.), poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Gullies appeared after civil war.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
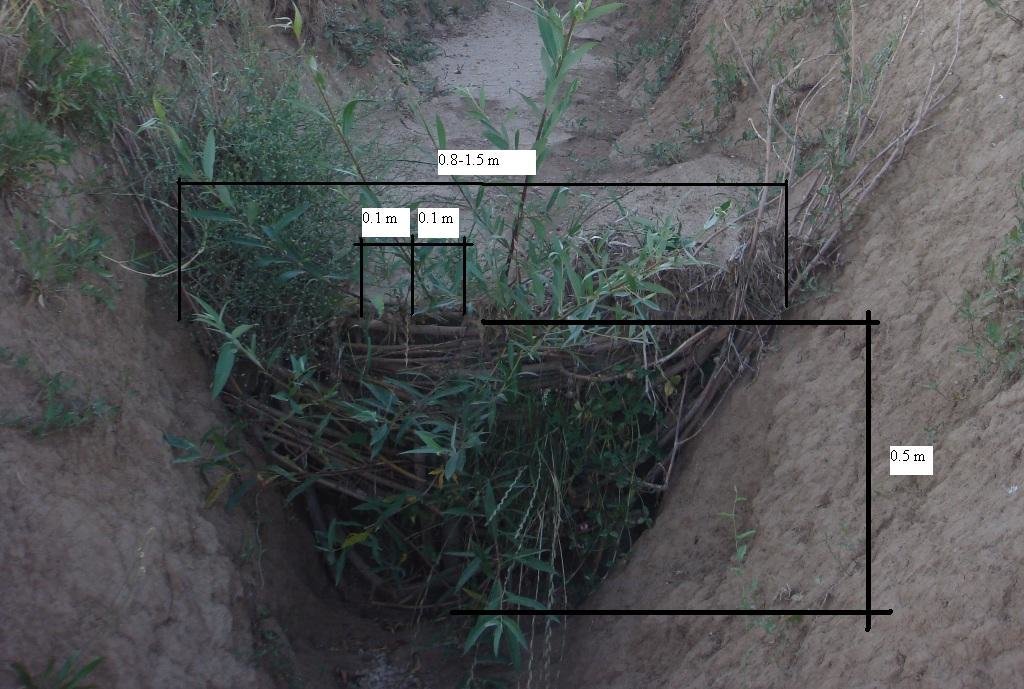
For the plugging of the gully, a low cost and simple barrier was made from locally available fast sprouting species of trees; in this case live willow cuttings were used. In the gully a narrow section was selected, and cuttings (3-5 cm diameter, 1 m length) were placed in a line with 10 cm intervals in between. One third of the cuttings were planted in the gulley, and the rest were used to create a 'wave' wall of flexible branches, which was planted with local mulberry trees (1-1.5 cm diameter). The weaved branches have to be pushed down from the top to make the barrier suitably dense. The ends of the mulberry branches have to be stuck securely to the soil inside the gulley.
Location: Dorobi village. Khovaling / Khatlon / Tajikistan
Date: 2nd July, 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: mulberry
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Construction material (wood): Willow and mulberry branches
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem street, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tajik Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.50 $
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting mulberry in willow wave structure | spring |
| 2. | establishment of barriers in gully bed | once in the beginning |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting mulberry | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Establishment of barriers in gully | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 90,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 20,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce structure with additional seedlings when needed | annually |
| 2. | establishment of additional barriers after filling existing barriers with sediments | once per year in beginning of rainy season |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Reinforce structure | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Establishment of additional barriers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 90,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 20,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The unit cost is for a gulley plug, 1.5 metre wide and around 1m in height.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The materials used to construct the gulley plug are locally available, and are therefore free of charge to the land user. The labour (or time in labour) is the most substantial cost, and this is directly proportional to the number of gulley plugs required to infill the entire eroded gulley. If there is a big sediment load in the surface water runoff it will back fill behind the gulley plugs rapidly and additional barriers will need to be established.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Precipitation is concentrated during the autumn and spring, averaging 1100-1200mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1257 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Average slope 12.6%, max slope 17.2%
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture = loess soil
Soil fertility is low due to over use and lack of fallow time.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: In the area around the gulley the land is compacted.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
20% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
The trees can be harvested once the gulley is full of sediment.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1.5
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1.6
Comentários/especificar:
Gully filling can help create new areas of arable land.
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Sediments are trapped
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
As a living barrier it needs to grow, and therefore it is sensitive to drought conditions.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
10 households in an area of 1.7 ha
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
No training and additional skills are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Broad promotion to other communities with similar climatic conditions and similar issues. |
| It is low cost option. |
| Easy to establish, with a low workload. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Gulley plugs are relatively easy to construct and have a low initial outlay. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be further supported by the strong involvement of local authorities, through the organisation of cross visits, and disseminating ideas between farmers. |
| It is flexible as various varieties of local sprouting trees can be used to build the gulley plug. |
| It can prevent further erosion and expansion of the gulley. It can also increase the amount of land available for pasture activities. |
| Environmentally friendly |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The gulley plug is weak in the beginning as the mulberry trees become more established. It is more susceptible to the impact of heavy rainfall events and concentrated run off down the gulley. | High levels of maintenance in the first initial few seasons. |
| The gulley plug becomes less effective as the gullies become wider and deeper. | Fencing around the gulley. |
| The gulley plug has to be protected from livestock who will eat the vegetation. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Welthungerhilfe projects in Khatlon region, Temurmalik district
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos