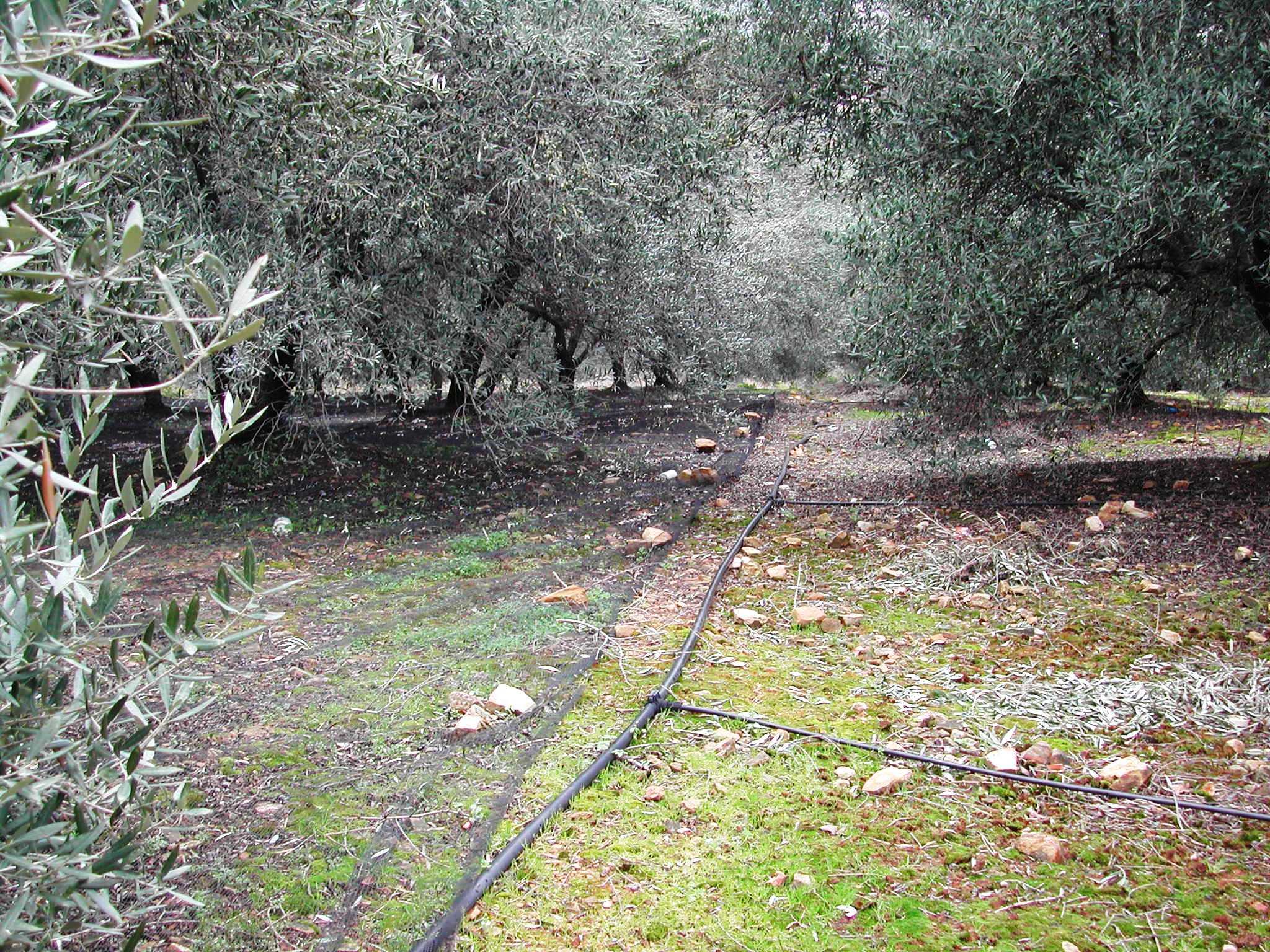
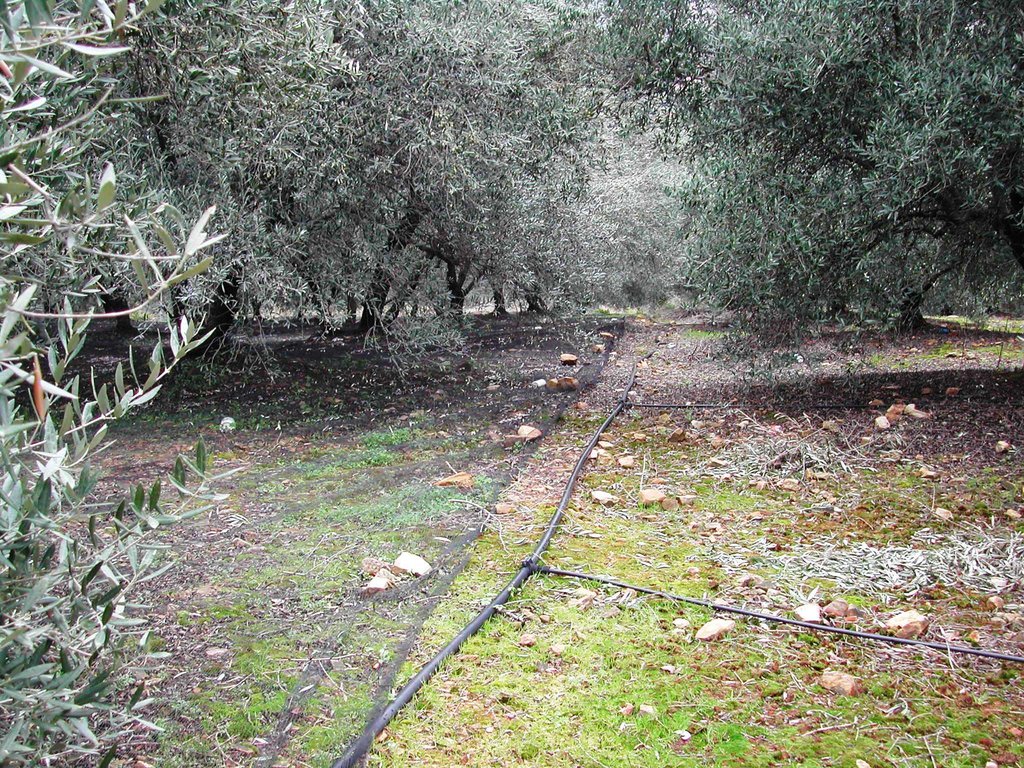
Application of water by drip irrigation [Grécia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Costas Kosmas
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Αρδευση με σταγονες
technologies_1456 - Grécia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Bardoulaki-Spanoudaki G
Organization for the Development of Western Crete OADYK Agia, Chania
Grécia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - GréciaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Organization for the Development of Western Crete (OADYK) - Grécia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Sustainable use of water [Grécia]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilador/a: Costas Kosmas
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation is a method which minimizes the use of water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Irrigation is very important for increasing crop yields in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid climates. The area of irrigated land has increased more than twice in the last decades in the study areas. In recent years, the considerable reduction of winter and autumn rainfall has caused a serious lack of water resources. The production of the various crops is substantially reduced if water is not provided during the summer period.
The high demands for water consumption or other economic activities have increased the price of water, forcing up the cost of agricultural production. In addition, in many cases, low quality (with high electrical conductivity) water is used for irrigation. The need for intensification of agriculture to meet the high cost of production, the use of poor quality of water, the lack of drainage systems are in many cases responsible for soil degradation resulting from water logging, salinization, alkalinization, and soil erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: Drip or trickle irrigation achieves the highest irrigation efficiency since about 90% of the applied water is available to the plants. This SWC technology is especially suitable for watering trees or other large plants keeping strips among trees dry. Application of water by drip irrigation can be considered more as more efficient method using low quality of irrigation water. Irrigation water of high salt content can be applied in higher quantities in spots leaching salts to deeper soil layers. Drip irrigation can be applied in any type of soil from coarse- and fine-textured and without any limitation to slope gradient requiring little labour during installation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzle.
Natural / human environment: In recent years the increasing awareness of farmers on issues relating to the sustainability of the environment and conservation of water by promoting SWC technologies has led to widespread of use of drip irrigation in the area of Crete and in many other parts of the Country. The categorization of the specific SWC technology according to the WOCAT questionnaire is defined as: CtWtA3.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Grécia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kidonia
Especificação adicional de localização:
Chania Crete
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 480 km2.
Map
×2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- azeitona
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 150Second longest growing period from month to month: March to June
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): availability of irrigation water, loss of water in the network, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): availability of irrigation water, conflicts between districts and economic sectors of tourism and agriculure
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (lack of water), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (salinization)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzles.
Location: Kasteli. Chania
Date: March 2007
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (system installation requirements)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
In blocks
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Perennial crops species: olives
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 15.00%
Structural measure: irrigation system
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Construction material (other): plastic, plastic tubes 12-32 mm in diameter
Other type of management: Water distribution among farmers, water is provided under the control of local authorities
Autor:
C. Kosmas
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting the olive trees | 2 days/ha |
| 2. | transporting plastic tubes | once during installation |
| 3. | Whole system of tubes, filters and system of fertilizers application | once during installation |
| 4. | Main network of irrigation system | once per year |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | >Installation | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1650,0 | 1650,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 2000,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
Life span of the irrigation network: 20 years
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cleaning filters and replacing destroyied tubes | 3 hours every year/ha |
| 2. | Checking outlets and conectors | once per year |
| 3. | Control of network for loss of irrigation water | once per year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 60,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 60,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools, System of applying fertilizers through the irrigation water, filters for keeping various solid materials
per hectare of land affected
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
the reguired materials (tubes, filters, etc)
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
With six months of dry period
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is very high-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high-very high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: 5-50 m, > 50 m
Water quality (untreated): good drinking water, for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women in rural areas are involved in other type of work
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich (cost for buying materials).
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: working in tourist business
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1500 kg/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2000 kg/ha
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Cultivation of the land is hindered by the irrigation network
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4500 euro/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5800 euro/ha
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Significant environmental benefit from the rational use of irrigation water
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Salinidade
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
Waste
Comentários/especificar:
environmental pollution due to presence of plastics not easily recycled
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Comentários:
Control of flooding by adjusting river bed
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
3850
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
65% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1650 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Increase crop production in some cases up to 50% How can they be sustained / enhanced? providing more water |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Technologies on conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete are mainly related to land management. Olive groves are widely expanded in the island due to the importance of olive oil as one of the essential material for daily human food needs. Furthermore, olive groves can survive under adverse climatic and soil conditions supporting a significant farmer’s income under relatively low labour. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and transfer knowledge by the local institutes and specialists. In addition, irrigation of the land by the drip system is considered as a very promising technique for conserving water resources in the area. Land terracing is a human intervention in sloping semi-natural landscapes, which have suffered losses, to some degree, in their sustainability and resilience. How can they be sustained / enhanced? by providing additional water resources in the area (build a water reservoir) |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High cost for buying materials, better education | subsidizing materials, technology transfer |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| increased cost for the first installation | subsidizing the system |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Sustainable use of water [Grécia]
Sustainable use of water
- Compilador/a: Costas Kosmas
Módulos
Não há módulos