Postpone grassland renewal [Países Baixos]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Jason Stuka
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Uitstellen van graslandvernieuwing
technologies_1662 - Países Baixos
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
Países Baixos
Especialista em GST:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
Países Baixos
Especialista em GST:
Leever Henk
Hoeduurzaam
Países Baixos
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Hoe Duurzaam - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Ministerie van Economische Zaken - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Gemeente Berkelland - Países Baixos1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Regional process, social innovation [Países Baixos]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilador/a: Simone Verzandvoort
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
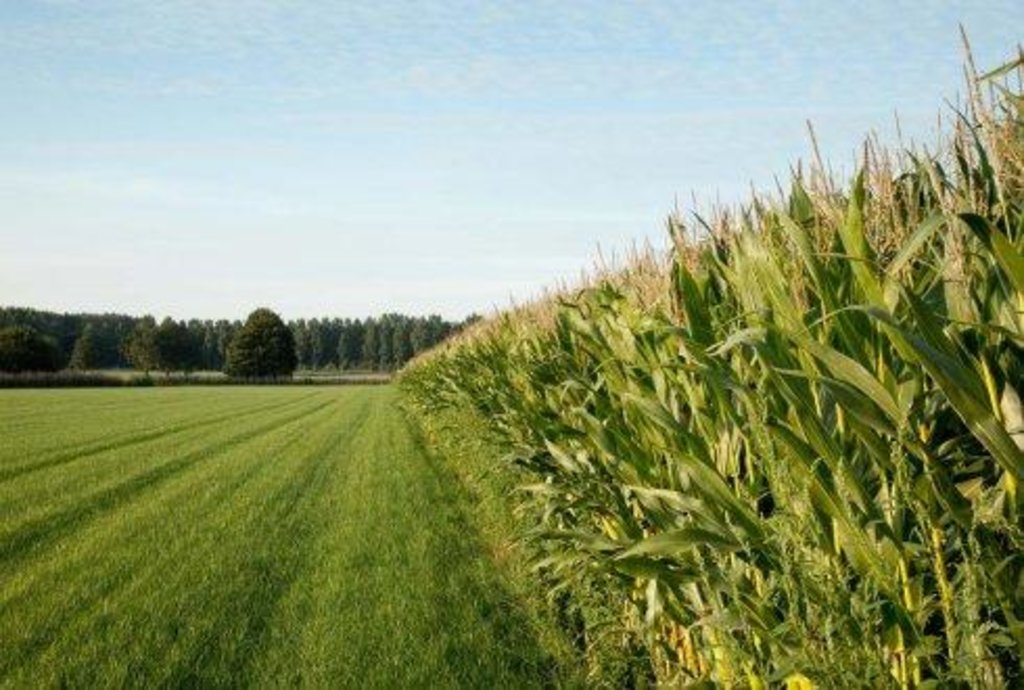
Postponing the timing of ploughing a grassland field by one or two years to reduce nutrient losses and organic matter decomposition.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
On the sandy soils in this part of The Netherlands permanent grassland seems the best measure to increase the organic matter content of the soil, to reduce the leaching of minerals and to reduce loss of soil moisture.
Customary maintenance of grassland fields is to plough and reseed or rotate the grass every 5 years. 5 years is the minimum length of time required by legislation. For growth and field rotation purposes, many farmers have preference to rotate fields in intervals less than 5 years. Under this technology, farmers instead wait 6 or 7 years before ploughing.
Purpose of the Technology: Ploughing grasslands increases the breakdown and decomposition of organic matter in soils. Farmers post-pone ploughing to increase soil organic matter content and reduce losses.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A well established permanent grassland requires good drainage, frequent liming (possibly from residual products from water purification), deep rooting grass, reseeding after 10-15 years, and fertilisation using sufficient organic manure.
Natural / human environment: Dairy farmers on sandy soils in the eastern part of The Netherlands. In the pilot Gezond Zand 44 farmers participated, owning 720 ha agricultural land, of which 344 in use as permanent grassland.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Países Baixos
Região/Estado/Província:
Gelderland
Especificação adicional de localização:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
In entire area there is 344 ha of grassland owned by 44 farmers. Only 2 of those farmers implemented the technology.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Fazenda pecuária
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
- Pastos melhorados
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decrease of soil organic matter content.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience decreasing organic matter content in soil.
Ranching: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: farmers also keep cattle in stable to prevent unequal grazing and dispersed manuring
Improved pasture: Yes
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 250 Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (ploughing intensive grassland renewal)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (rotation with more corn and less grassland)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
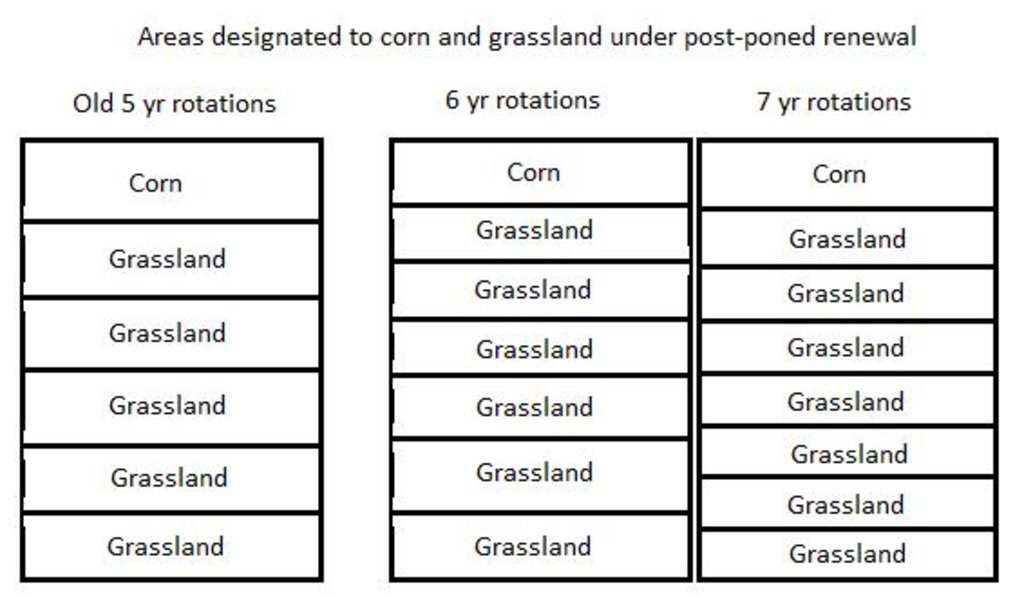
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Demonstrating area designated to corn and designated to grassland under old management of renewing grasslands every 5 years and comparing to the area under the new technology of renewal every 6 or 7 years.
Location: Wageningen. Gelderland
Date: March 20, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (knowledge is required on the maintenance of permanent grassland, the proportion of grassland in the total farm, the frequency of reseeding and rotations with arable crops, in particular for grassland)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge is required on the maintenance of permanent grassland, the proportion of grassland in the total farm, the frequency of reseeding and rotations with arable crops, in particular for grassland)
Main technical functions: Reduce decomposition of organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Plough grassland every 6 to 7 years instead of every 5 years.
Major change in timing of activities: Plough grassland every 6 to 7 years instead of every 5 years.
Autor:
Jason Stuka, Wageningen University
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Information on costs for the technology are not yet available, and therefore no information on costs was entered into section 2.6.
Costs involved with postponing grassland renewal include the costs of yield foregone from rotations with arable crops that have not taken place, and costs of manuring of the grassland.
Costs avoided include all costs of management operations and inputs associted with rotations of grassland and arable crops that would have taken place in the life cycle of the permanent grassland (6-7 till 15 years).
Benefits include 1320 kg of additional DM/ha, or € 145,-/ha additional revenues.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The life cycle of permanent grassland determines both the costs foregone due to missed yields from shorter term rotations with arable crops and costs avoided due to saved operations and inputs on shorter term rotations which have not taken place.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
182 days of precipitation annually
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Gentle (only incidentally)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Deep (A en B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area). Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm.) and very deep (deep topsoils rich in organic matter in Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture: Coarse/light ( Most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area). and very high (fimic Anthrosols originating from application of farmyard manure since medieval times.)
Topsoil organic matter is medium (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water. Sandy soils.) and medium (some shallow groundwater)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (dependent on soil organic matter content)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality or craft work. No B&B activities or educational services.
Market orientation is subsistence (grass is used to feed the cattle of dairy farmers, not sold)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Average grassland is 7.8 ha per household.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
All agriculture land is owned by farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. There are some regulations on land uses set by communities.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. More grass, less corn. Overall less yield.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Uncertain. More grass but less corn.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven.
Less rotation and management flexibility.
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Created farmer's foundation
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts.
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers collaborating with water company
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet. Little to no
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Not measured.
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Not measured.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente negativo
Comentários:
Less frequent rotation and fertility for corn production, but better for soil health.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measures and subsidy or payment for environmental service to compensate foregone revenues if rotations with arabale crops would be inserted. |
|
increases grassland quality and yield in the long term; estimated added value of postponing grassland renewal is € 145,-/ha How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measure, preferably maintain life cycles of 10-15 year for permanent grassland |
|
reduces leaching of nutrients, herbicides and pesticides to the groundwater How can they be sustained / enhanced? financial support from the drinking water company Vitens, who has interest in reduced influx of substances to the groundwater. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measures and subsidy or payment for environmental service to compensate foregone revenues if rotations with arabale crops would be inserted. |
| increases available soil moisture |
|
reduces leaching of nutrients, herbicides and pesticides to the groundwater How can they be sustained / enhanced? financial support from the drinking water company Vitens, who has interest in reduced influx of substances to the groundwater. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| long-term investment, requires time to return improved grassland yield |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| long term permanent grassland prevents rotations with arable crops; this may reduce farmer's income | reward the benefits of increased SOM through subsidy or payment for environmental services by the drinking water and dairy companies |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden Eibergen By Willem Rienks and Henk Leever 2014 Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The Netherlands Arjan Reijneveld 2013RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2 Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort 2014
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Free http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdfWageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden EibergenBy Willem Rienks and Henk Leever2014
URL:
http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdfWageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Regional process, social innovation [Países Baixos]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilador/a: Simone Verzandvoort
Módulos
Não há módulos