Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd production [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Richard Allen
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Karela kheti ma thopa sinchai ko satha ma pasu mutra ko prayog (Nepali)
technologies_1751 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Nepal
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - NepalNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador/a: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador/a: Richard Allen
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
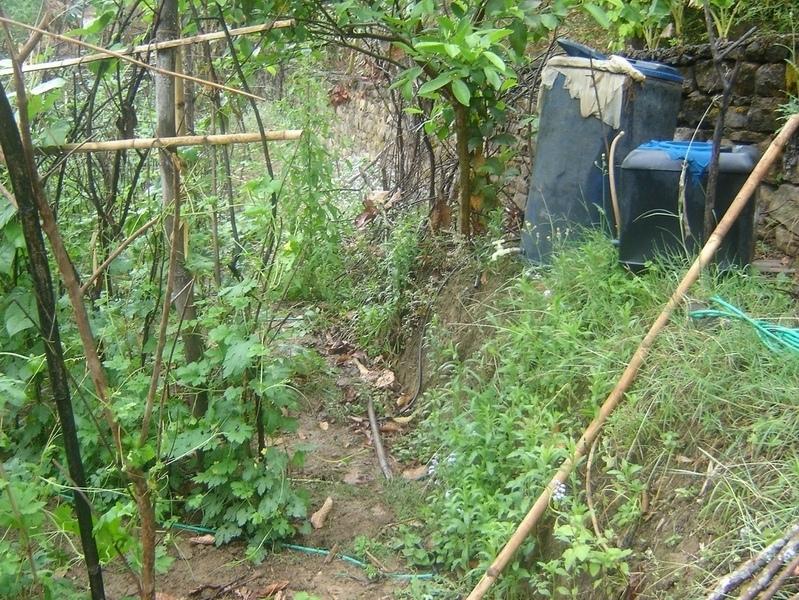
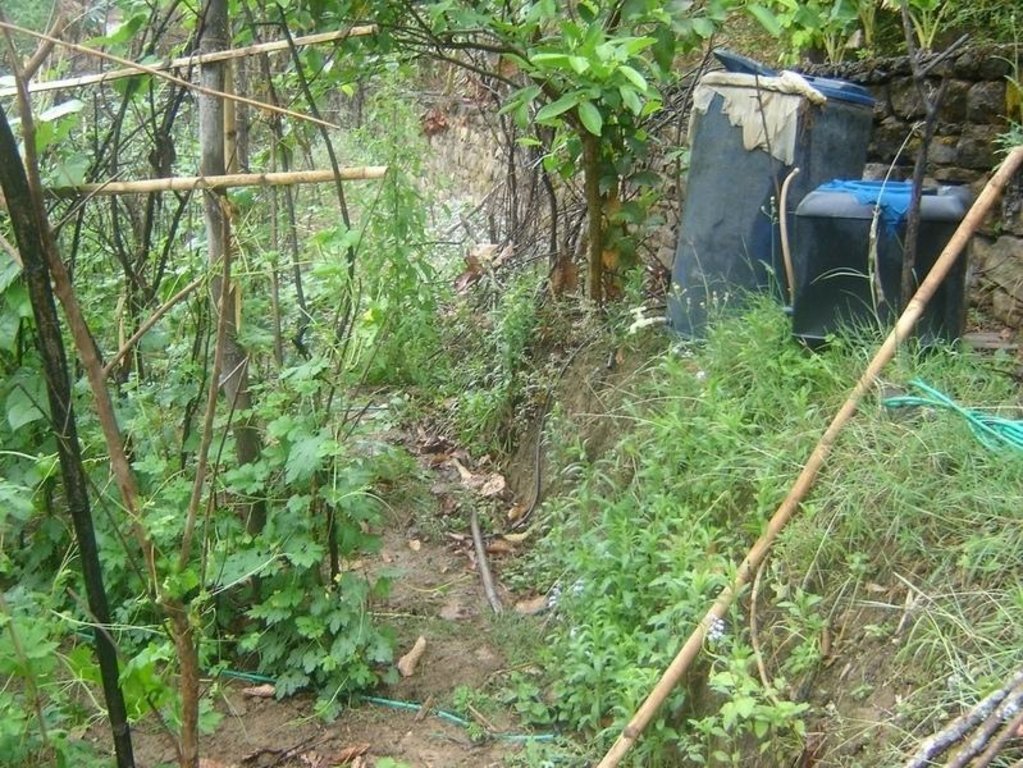
Descrição:
Bitter gourd vegetables fetch a high price in the off-season and respond well if grown with drip irrigation. This crop is planted in December/January and harvested from May through to July/August. The growing period mainly falls in the driest period of the year and therefore requires irrigation.
In addition to water, the plants need fertiliser to ensure healthy growth and good production. Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants and high crop productivity can only be achieved if sufficient nitrogen is available. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in most areas of Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure; but in many places this is being supplemented or entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser, mainly urea. However, fertiliser prices have increased substantially in recent years and this type of fertiliser is often not available in sufficient quantities in areas away from the roadheads. At the same time cultivation practices are intensifying with greater cropping intensities and more nutrient demanding crops as local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are introduced. This can easily lead to nutrient mining and soil fertility decline unless there is an equivalent increase in inorganic or mineral fertilisation.
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser; it is nitrogen rich. The urine is collected in improved cattle sheds (fact sheet on urine collection QT NEP1). For constant fertiliser application and to reduce the water requirement, the collected urine can be added to the irrigation water in the drip irrigation tanks (fertigation). Farmers who have tried this say it has increased the yield of bitter gourd and other cash crops, in some cases by as much as 100%. Other crops that can be grown using drip irrigation with a water-urine mixture are cauliflower, cucumber, and other types of gourd.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Midhills districts of Nepal
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Map
×3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- legumes - melão, abóbora ou aboborinha
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater. Also, irrigation water is in short supply during 6 to 8 months of the year. Fertigation allows about 20 to 30% of the irrigation water to be replaced by urine.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
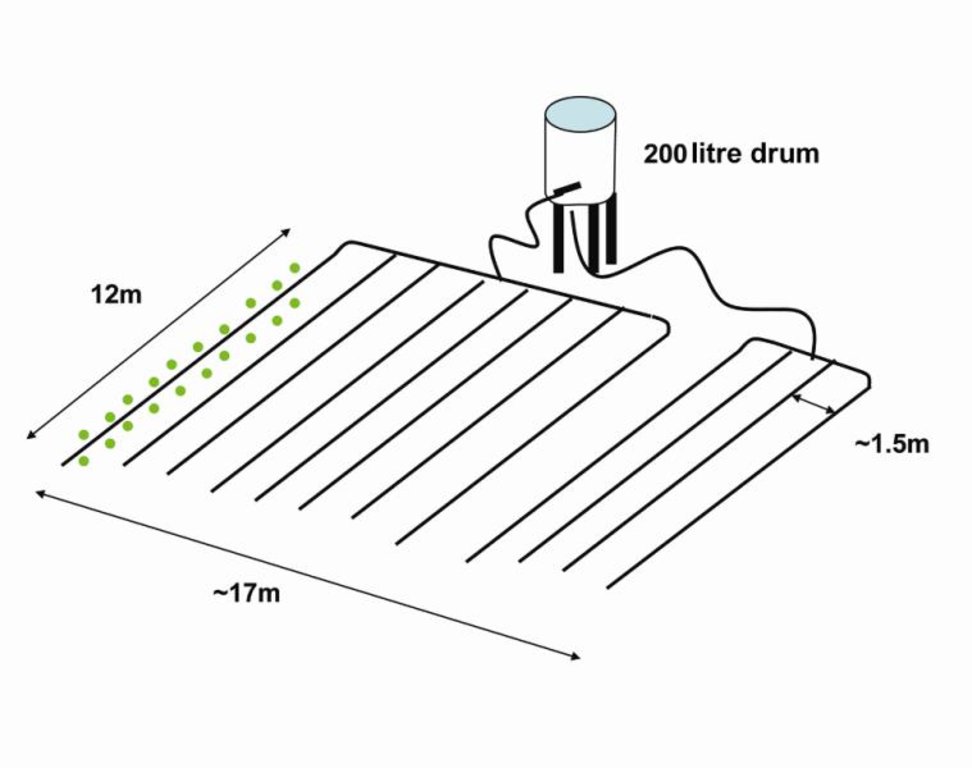
The following setup was used in Iman Singh Basnet’s fi eld:
- two drip irrigation sets: one set with
8 lines, one with 4 lines
- a 200 l plastic drum
- 20 bitter gourd plants per line with
1.5m spacing between lines
- approximate area covered: 200m2
Note that the drum was not delivered with the drip irrigation set. Mr Basnet uses the same drum for irrigating other crops where drip irrigation is not feasible, in which case he connects a pipe with a rose to the drum.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: supplementary irrigation, constant and slow supply of nutrients, increase in soil fertility & increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: pest control
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
Drip irrigation system
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
200 l plastic drum; 20 bitter gourd plants per line with 1.5m spacing between lines
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare and place stakes | |
| 2. | Collect urine (see WOCAT fact sheet ‘Improved cattle shed for improved urine collection – QT NEP1) | |
| 3. | Grow bitter gourd seedlings | |
| 4. | Set up drip irrigation set and prepare field | |
| 5. | Transplant seedlings |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Collect urine and prepare irrigation system | persons/unit | 2,0 | 2,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Drip set | unit | 1,0 | 36,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Drum | unit | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Stakes | unit | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 50,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 50,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear drip holes | |
| 2. | Double filter the urine – once when taking out of the collection tank, and again when pouring into the drip irrigation tank | |
| 3. | Irrigate every alternate day with 160 l water and 40 l urine. | |
| 4. | Fix shoots to the stakes | |
| 5. | Raise ridges for better irrigation efficiency | |
| 6. | Harvest the crop |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Maintain drip irrigatio nsystem and apply urine | persons/unit | 15,0 | 2,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 30,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 30,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Cost calculated in January 2007.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Comercial/mercado
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
reduced expenses for agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Allows organic production of high value crops
establishment costs
Impactos socioculturais
social prestige as a progressive farmer
requires handling of dung and urine
Impactos ecológicos
Outros impactos ecológicos
application of agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
eutrophication, nitrification of water bodies due to uncontrolled outflow of urine
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
reduced influx of nutrients into water bodies
dependence on costly external inputs
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser and the high price that bitter gourd fetches means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, a major reduction in fertiliser costs and improved income leads to increased benefits.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some farmers in Surkhet district started to use the technology in 2006, after seeing Iman Singh Basnet's innovation of applying urine through drip irrigation in 2005.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Urine as a liquid manure is applied at the same time as irrigation (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation or other forms of small scale irrigation needs to be promoted |
|
The on-farm use of collected urine reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing cash expenditure and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the technology to increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less acceptable How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the use of urine and show that there is no problem with using human urine |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The initial establishment costs for a drip irrigation set may hinder adoption |
Prepare a business plan and calculate the cost-benefi t to convince farmers of the technology’s benefi ts |
| Lack of availability of urine may inhibit the commercial application of urine with drip irrigation | Urine needs to be established as a tradeable good produced by livestock farmers and bought by vegetable farmers to apply to their crops |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Nepal]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Compilador/a: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Nepal]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Compilador/a: Richard Allen
Módulos
Não há módulos