Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd production [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Richard Allen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Karela kheti ma thopa sinchai ko satha ma pasu mutra ko prayog (Nepali)
technologies_1751 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
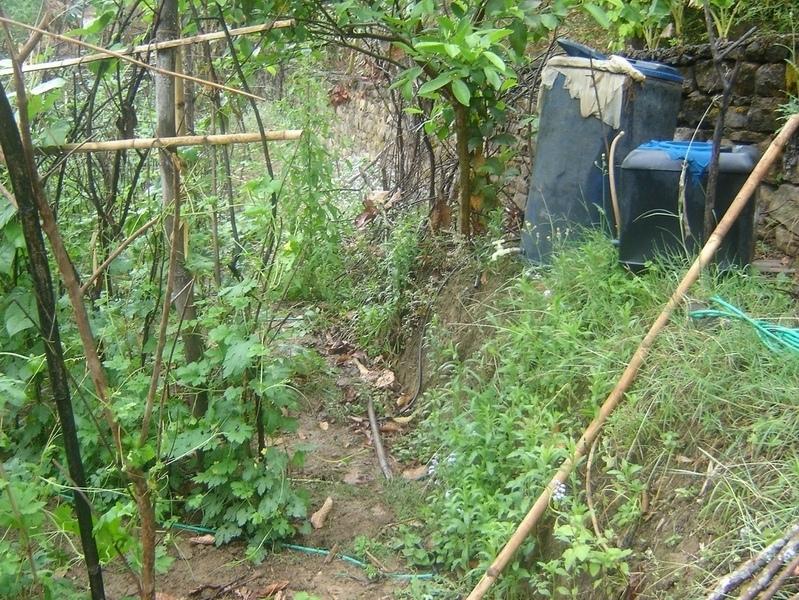
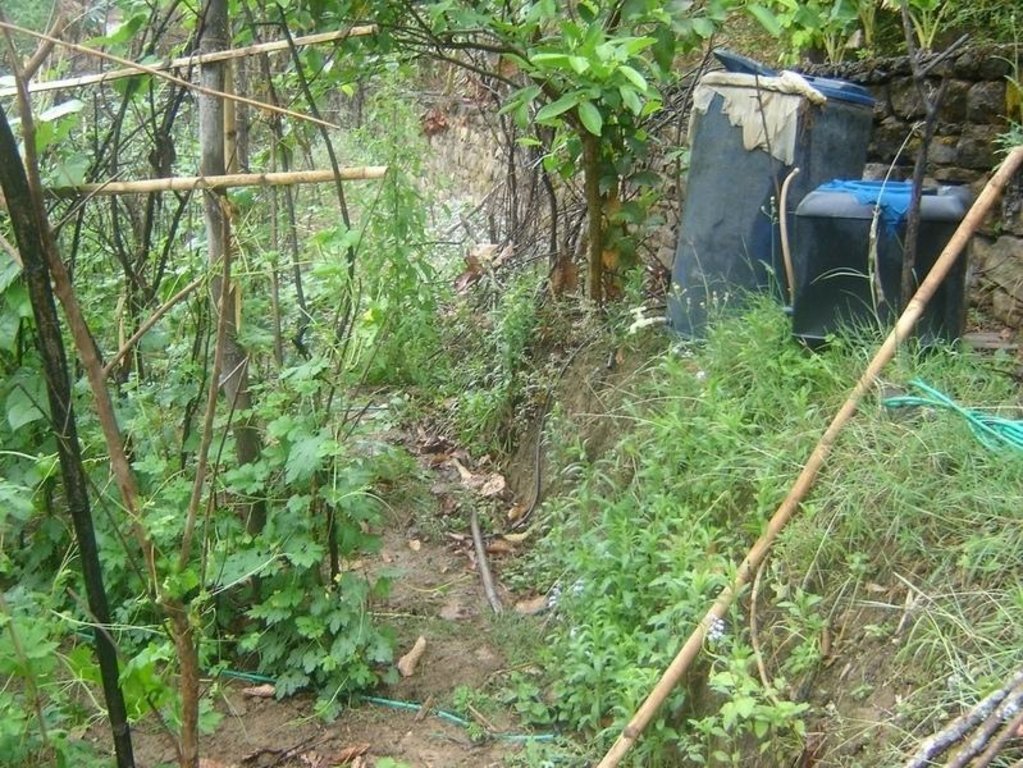
Bitter gourd vegetables fetch a high price in the off-season and respond well if grown with drip irrigation. This crop is planted in December/January and harvested from May through to July/August. The growing period mainly falls in the driest period of the year and therefore requires irrigation.
In addition to water, the plants need fertiliser to ensure healthy growth and good production. Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants and high crop productivity can only be achieved if sufficient nitrogen is available. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in most areas of Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure; but in many places this is being supplemented or entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser, mainly urea. However, fertiliser prices have increased substantially in recent years and this type of fertiliser is often not available in sufficient quantities in areas away from the roadheads. At the same time cultivation practices are intensifying with greater cropping intensities and more nutrient demanding crops as local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are introduced. This can easily lead to nutrient mining and soil fertility decline unless there is an equivalent increase in inorganic or mineral fertilisation.
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser; it is nitrogen rich. The urine is collected in improved cattle sheds (fact sheet on urine collection QT NEP1). For constant fertiliser application and to reduce the water requirement, the collected urine can be added to the irrigation water in the drip irrigation tanks (fertigation). Farmers who have tried this say it has increased the yield of bitter gourd and other cash crops, in some cases by as much as 100%. Other crops that can be grown using drip irrigation with a water-urine mixture are cauliflower, cucumber, and other types of gourd.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Midhills districts of Nepal
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 香瓜、南瓜、南瓜或葫芦
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater. Also, irrigation water is in short supply during 6 to 8 months of the year. Fertigation allows about 20 to 30% of the irrigation water to be replaced by urine.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
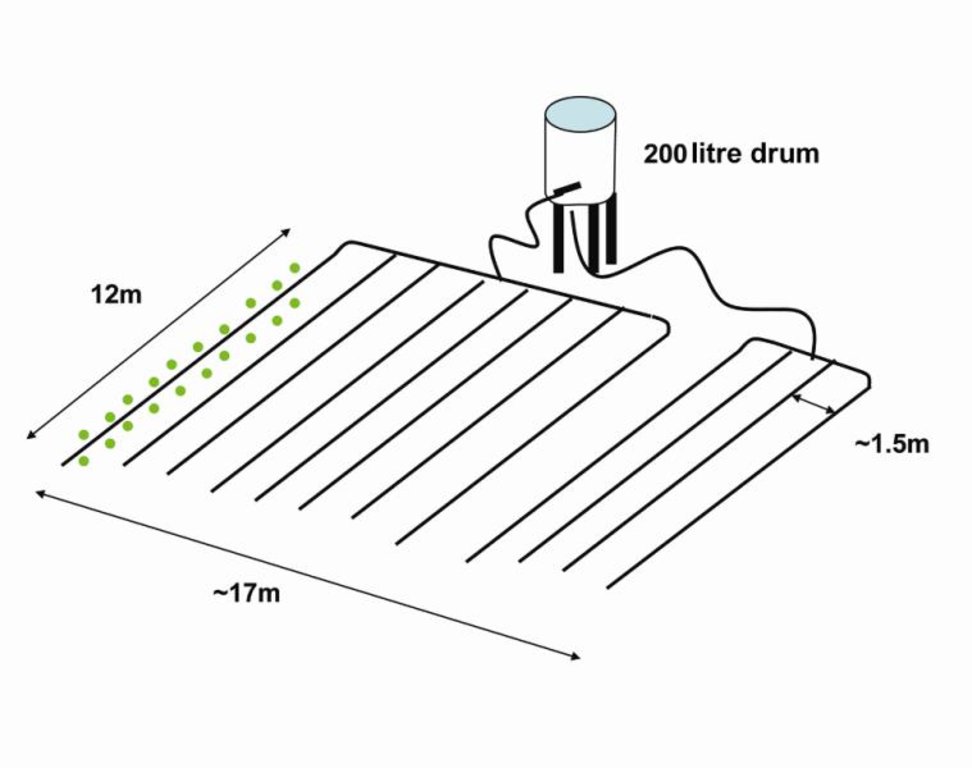
The following setup was used in Iman Singh Basnet’s fi eld:
- two drip irrigation sets: one set with
8 lines, one with 4 lines
- a 200 l plastic drum
- 20 bitter gourd plants per line with
1.5m spacing between lines
- approximate area covered: 200m2
Note that the drum was not delivered with the drip irrigation set. Mr Basnet uses the same drum for irrigating other crops where drip irrigation is not feasible, in which case he connects a pipe with a rose to the drum.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: supplementary irrigation, constant and slow supply of nutrients, increase in soil fertility & increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: pest control
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Drip irrigation system
指定单位面积(如相关):
200 l plastic drum; 20 bitter gourd plants per line with 1.5m spacing between lines
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare and place stakes | |
| 2. | Collect urine (see WOCAT fact sheet ‘Improved cattle shed for improved urine collection – QT NEP1) | |
| 3. | Grow bitter gourd seedlings | |
| 4. | Set up drip irrigation set and prepare field | |
| 5. | Transplant seedlings |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collect urine and prepare irrigation system | persons/unit | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Drip set | unit | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Drum | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stakes | unit | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 50.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 50.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear drip holes | |
| 2. | Double filter the urine – once when taking out of the collection tank, and again when pouring into the drip irrigation tank | |
| 3. | Irrigate every alternate day with 160 l water and 40 l urine. | |
| 4. | Fix shoots to the stakes | |
| 5. | Raise ridges for better irrigation efficiency | |
| 6. | Harvest the crop |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintain drip irrigatio nsystem and apply urine | persons/unit | 15.0 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 30.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 30.0 | |||||
注释:
Cost calculated in January 2007.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
reduced expenses for agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
其它社会经济效应
Allows organic production of high value crops
establishment costs
社会文化影响
social prestige as a progressive farmer
requires handling of dung and urine
生态影响
其它生态影响
application of agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
eutrophication, nitrification of water bodies due to uncontrolled outflow of urine
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
reduced influx of nutrients into water bodies
dependence on costly external inputs
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser and the high price that bitter gourd fetches means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, a major reduction in fertiliser costs and improved income leads to increased benefits.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some farmers in Surkhet district started to use the technology in 2006, after seeing Iman Singh Basnet's innovation of applying urine through drip irrigation in 2005.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Urine as a liquid manure is applied at the same time as irrigation (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation or other forms of small scale irrigation needs to be promoted |
|
The on-farm use of collected urine reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing cash expenditure and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the technology to increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less acceptable How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the use of urine and show that there is no problem with using human urine |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The initial establishment costs for a drip irrigation set may hinder adoption |
Prepare a business plan and calculate the cost-benefi t to convince farmers of the technology’s benefi ts |
| Lack of availability of urine may inhibit the commercial application of urine with drip irrigation | Urine needs to be established as a tradeable good produced by livestock farmers and bought by vegetable farmers to apply to their crops |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
模块
无模块