Using shallow wells for crops and lowering the saline groundwater table [Tailândia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Kaewjai Oechaiyaphum
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Pitayakon Limtong, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Samran Sombatpanit, Joana Eichenberger
shallow well
technologies_4391 - Tailândia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
SooPho Boonchu
Land user
Tailândia
co-compiler:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Prawanna Prasit
Technical for Land Development Group , Land Development Regional Office 3 , Land Development Department.
Tailândia
National consultant:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - Tailândia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Through this technology, farmers can pump water from shallow wells for agriculture throughout the year: it can lower the groundwater table and reduce salinity. This technology has resulted in reduction salinity in surrounding low land areas. Hence, shallow wells have been accepted by land users.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Pumping groundwater from shallow wells for agriculture can control the groundwater table in recharge areas. It helps to manage saline aquifers and reduce soil salinity. Such shallow wells range from 25 to 30 meters deep. This technology is very well-accepted by the land users.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
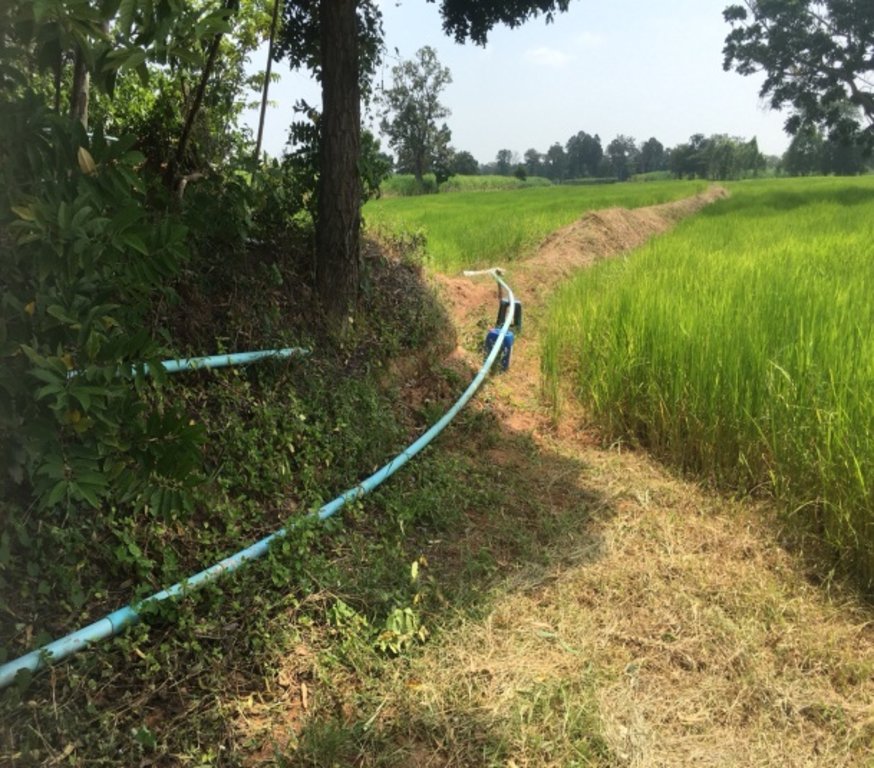
The shallow well is a structure created in the ground by digging or drilling to access water resources. This example of shallow wells is their use in recharge areas to lower groundwater tables. The technology is a subproject of a larger LDD initiative. The technology has been promoted by the Land Development Department at Bua Yai district Nakhon Ratchasima province since 2014. The objectives of the main project are (1) to provide water resources in recharge areas for agriculture: (2) to reduce the amount of saline groundwater and (3) to set up positive economic impact measures.
The process of technology establishment comprises 1) a recharge area survey in salt-affected areas, 2) drilling shallow wells to 25-30 meters depth, 3) installing 5.5 hp gasoline pumps and testing water quality, 4) pumping groundwater and distributing it to the cultivated areas.
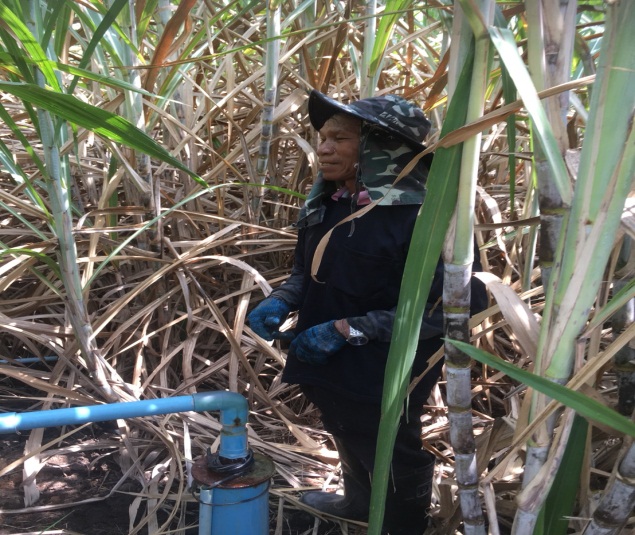
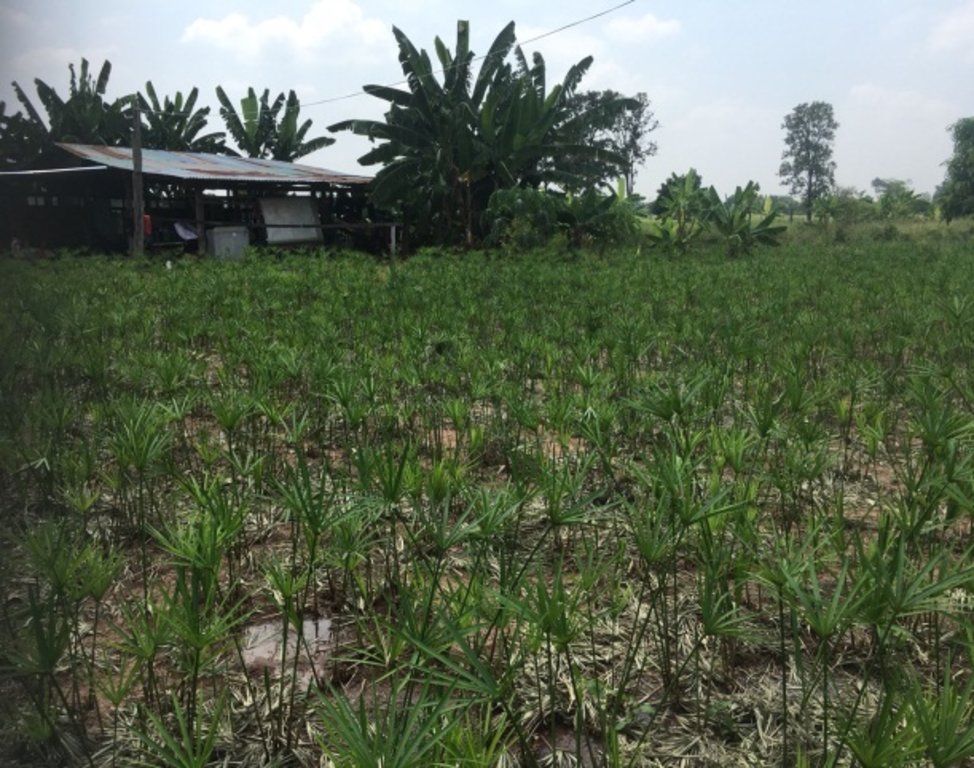
Shallow well technology has been implemented on the fields of Mr. Boonchu Supho, Ban Nong Mek, Moo 9, T.Dan Chang, A. Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima Province. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 21 rai (approx. 3.4 hectares), undulating area with a 2-5% slope, situated at approx. 200 meters above sea level, with a tropical climate, and soil which is classified as being in the series of Kula Ronghai (Ki). This area is upland, and located in the recharge area. Mr. Boonchu Supho has 13 rai (approx. 2 hectares) of lowland rice fields and one shallow well.
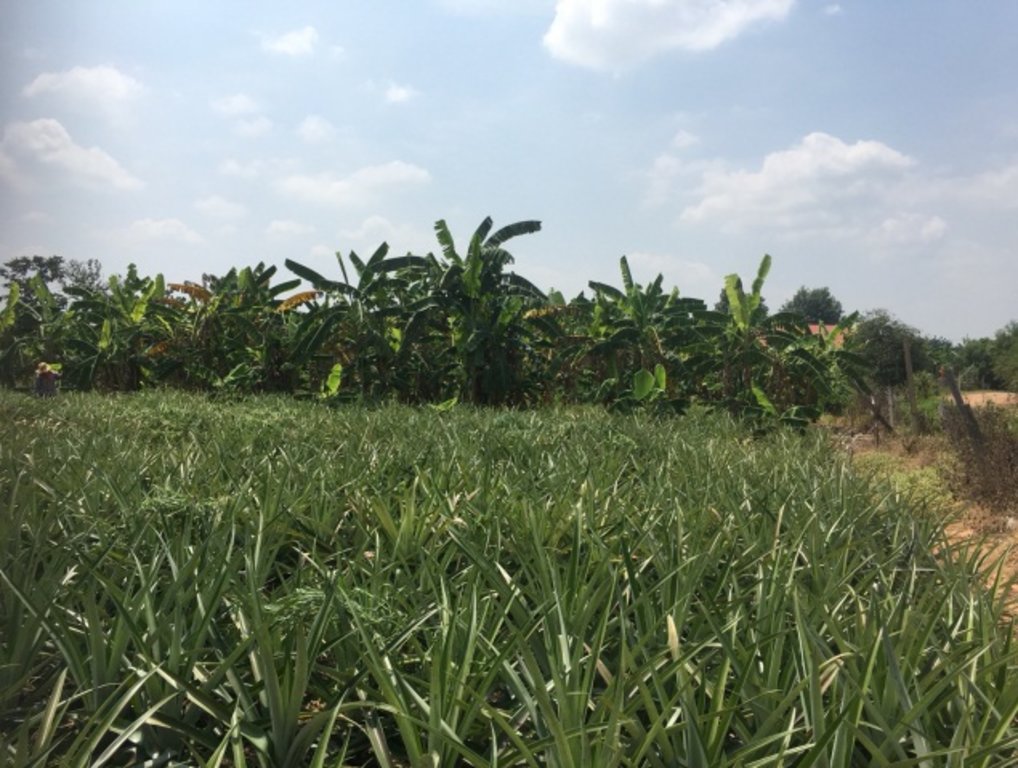
In the past, water scarcity was the main issue with his land. Droughts resulted in water scarcity and low productivity. After excavating a shallow well in 2014, groundwater was used for 19 rai of cultivation. Due to soil salinity reduction, rice yields increased to 590 kg/rai (approx. 3700 kg/ha: an increase of approx. 47.4%). Sugar cane yield increased to 30 ton/rai. Moreover, land users can use land more efficiently with mixed plantations of banana, pineapples, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal and lemongrass to generate income. Even with a drought in 2018, his land had enough water for cultivation, while rice fields in the surrounding area faced water scarcity problem.
In conclusion, the benefits of the shallow well are 1) lowering the groundwater table and reducing salinity, 2) enhancing rice and sugar cane yields, 3) ability to cultivate throughout the year and 4) better soil properties and a better environment. However, the disadvantage of the shallow well is that farmers have to pay for electricity (around 1,200 THB/ 9 months or 10,800 THB/year).
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
Using shallow well for planting in the recharge area
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
To interview Mr. Boonchu Supho
Data:
09/10/2017
Localização:
Ban Koksa-ard Moo 9 T.Danchanget, A.Buayai, Nakhon-Ratchasima
Nome do cinegrafista:
.Jilayus Sommutram
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tailândia
Região/Estado/Província:
Nakhon Ratchasima
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ban Koksa-ard Moo 10 T.Danchang, A.Buayai
Comentários:
Mr. Boonchu Supho has in total 21 rai, divided into 1) Recharge area, which is located in the upland zone. Land utilization comprises 2 rai of residence and shallow well, 1.5 rai of the sugar cane field, 1 rai of a banana field, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of pineapple and 0.5 rai of chillies, galangal, and lemongrass. 2) Discharge area, which is located in a low land area. This area has 13 rai of in-season rice
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2014
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The Land Development Department and local authorities created a demonstration plot to solve the saline soil problem under the LDD project (on preventing soil salinity and to lower the groundwater table in the recharge area) in Bua Yai district. Nakhon Ratchasima Province, since 2014
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- prevents soil salinity and to lower the groundwater table on recharge area
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- vegetable
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
- legumes - outros
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
- abacaxi
- cana-de-açúcar
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Land user growing rice 1 time/year, growing sugar cane 2 times/3 years and using of water punping for vegetable growing during rain delay season/ drought situation
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
Principais produtos/serviços:
shallow well
Comentários:
An excavating shallow well on recharge area was to lower groundwater table and prevent soil salinity in recharge area. Groundwater was used for rice, sugar cane, banana, pineapple and vegetable growing. This technology has increased productivity up to 47.4% in rice: sugar cane has more than doubled its yields.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- vegetable
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
- legumes - outros
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- abacaxi
- cana-de-açúcar
- sweet bamboo
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não
Comentários:
An excavated shallow well in the recharge area was to lower groundwater table and prevents soil salinity in the recharge area. Groundwater was used for rice, sugar cane, banana, pineapple, and vegetable growing. This technology has increased productivity up to 47.4% in rice: sugar cane has more than doubled its yields.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Outros (p. ex. pós-inundação):
- shallow well
Comentários:
Land users know how drought or rain can delay affect productivity. Hence, land users have decided to engage in this project
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Gestão do lençol freático
- desalination
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Groundwater from the shallow well was used for 19 rai of plantation area. The result shows that this technology can increase soil moisture; make a better environment, crop residue from post-harvest can enhance soil organic matter and soil fertility
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bl: perda da vida do solo

Degradação da água
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
There is not much organic fertilizing in 19 rai of land. Most organic fertilizer has been used in vegetable growing while other plantations are usually chemical fertilizing. Hence, increasing crop production needs more chemical fertilizing.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Adaptar à degradação do solo
Comentários:
The land user has used shallow well technology during drought and rain delay situation since 2014-2018. They found that using shallow wells can reduce groundwater table which might dissolve saline aquifer and spread salinity. Hence, shallow well technology can reduce salinity in lower lying land. With less salt in the topsoil, rice yield has increased to 5-10%
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
21 rai own by one selected land user....(e.g. 24 acres, 4.5 hectares)
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 hectare =…6.25 rai
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
THB
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
300 THB
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | To drilling shallow well with 25-30 meters depth | January 2014 |
| 2. | Sugar fields | May 2014, 2016, 2018 |
| 3. | Pineapple fields | May 2018 |
| 4. | Banana fields | May 2014 |
| 5. | Reed fields | May 2015 |
| 6. | Sweet bamboo fields | May 2015 |
| 7. | Chillies, galangal and lemon grass fields | May 2014-2018 |
| 8. | Rice fields | June 2014-2018 |
Comentários:
No irrigation water therefore planting time depends directly upon the period of the early rainy season, which will be May to July
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Costs of labor for sugarcane cultivation | puddle | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Costs of labor for rice cultivation. | rai | 13,0 | 1150,0 | 14950,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Costs of labor for sugar cane cultivation. | rai | 1,5 | 1200,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Costs of labor for pineapple cultivation. | rai | 1,0 | 1200,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Equipamento | Costs of labor for Banana cultivation | rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Equipamento | Costs of labor for Papyrus cultivation. | rai | 0,5 | 900,0 | 450,0 | |
| Equipamento | Costs of labor for Sweet bamboo cultivation. | rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| Equipamento | Costs of labor for Chilli, galangal, lemon grass cultivation | rai | 1,0 | 900,0 | 900,0 | |
| Equipamento | Cost of shallow water well drilling equipment | puddle | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Bud seedling sugarcane | seedling | 2250,0 | 0,9 | 2025,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Bud seedling Pineapple | seedling | 2500,0 | 2,0 | 5000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Bud seedling Banana | seedling | 100,0 | 10,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Bud seedling Papyrus | seedling | 3000,0 | 0,2 | 600,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Bud seedling sweet bamboo | seedling | 25,0 | 80,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Bud seedling Chilli, galangal, lemon grass | seedling | 2000,0 | 1,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Seedling rice KDML105 | seedling | 65,0 | 25,0 | 1625,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Chemical fertilizer 15-15-15 | kg | 300,0 | 13,0 | 3900,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Chicken manure | kg | 2000,0 | 2,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Outros | Electricity charge | hr | 240,0 | 5,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Outros | Machinery | rai | 19,0 | 500,0 | 9500,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 155850,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 155850,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The Land Development Department supports expenses for drilling shallow wells approximately 100,000 THB. The land users are involved in the maintenance of shallow wells at the 2nd year about 2,000 THB and pay for cost of maintenance and electricity bills about 1,200 baht per month for 9 months. Moreover, land users have to paid for farm pond construction under farm pond project of LDD about 2,500 THB.
Comentários:
Nong Mek Village, Moo 9, Dan Chang Subdistrict, Bua Yai District, Nakhon Ratchasima Province located on the recharge area which has totally 1,000 rai. Recharge area is a type of upland where use for cassava and sugar cane planting. Most land users have not much knowledge and motivation on shallow well drilling. Hence, Land Development Department comes to train, solution on salt-affected soil with the project on prevents soil salinity, and to lower the groundwater table on recharge area since 2014. The shallow well technology has been implemented through the demonstration plot, which is the first learning center of salt-affected soil management on the recharge area
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance | 1 Times/year |
| 2. | Electricity charge | 1 Times/month |
Comentários:
Shallow well which supported by LDD is a type of 5.5 hp gasoline pump then, land users try to use the electric water pump instead. The use of electrical water pump can increases yield productivity and enhance land users’ income. This is resulting in a better life.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | electricity charge,5 baht per unit 8 hours per day, 360 days / year | time | 2880,0 | 5,0 | 14400,0 | |
| Equipamento | Machinery | time | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 16400,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 16400,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Land users do maintenance this technology by themselves, without hiring labor. There has only cost of modifying.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Cost of shallow wells implementation at the 1st year consists of 100,000 THB of labor hiring, equipment, and installation. Besides, land users have to pay 2,500 THB for farm pond construction
The expenditure at the 1st year in 2014, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields. The expenditure at the 1st year with 19 rai is 42,050 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB. Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 52,850 THB.
The income from crop production at 1st year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 2,000 THB/month or 24,000 THB/year from chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 173,700 THB and net income is 120,850 THB
Cost and income at 2nd year in 2015 are described as following;
The expenditure at 2nd year in 2015, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 0.5 rai of reed fields. The expenditure at the 2nd year is 40,475 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 51,275 THB.
The income from crop production at the 2nd year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galanga, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 140,425 THB
The expenditure at the 3rd year in 2016, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 1 rai of reed fields and 0.5 rai of reed. The expenditure at the 3rd year is 40,800 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 51,600 THB.
The income from crop production at 3rd year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 140,100 THB
The expenditure at the 4th year in 2017, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields and 1 rai of reed fields and 0.5 rai of reed. The expenditure at the 4th year is 37,125 THB combine with electricity charge 10,800 THB and 2,000 THB of water pump modifying fee Thus, the grand total of expenditure is 47,925 THB.
The income from crop production at 4th year, land users sold rice yield and got 109,200 THB (the average amount of yield is 560 kg/rai, totally gain yield is 7,280 kg, price of rice yield is 15 THB/kg). Land users got 40,500 THB from sugar cane production (the average amount of yield is 30 ton/rai, totally gain yield is 45 ton, price of sugar cane yield is 900 THB/ton). Moreover, land users also got 3,500 THB/month or 42,000 THB/year from reed, sweet bamboo, chilies, galangal, and lemongrass production. Thus, the grand total of income is 191,700 THB and net income is 143,775 THB
The expenditure at the 5th year in 2018, pumping groundwater needs to use electricity 8 hours/ 270 day. The amount of water pumping has distributed to 13 rai of rice fields, 1.5 rai of sugar cane fields, 1 rai of sweet bamboo, 1 rai of banana, 1 rai of chilies, galangal and lemongrass fields,1 rai of reed
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1084,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average annual rainfall from 2008-2013
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Meteorological Department
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Temperatures average 13-39 degrees Celsius, average relative humidity 55-89.%
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Geography The Bua Yai district is located in the north of Nakhon Ratchasima. On the Korat Plateau
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
The surface soil is sandy loam. The bottom soil is sandy loam soil. The pH is between 7.5 - 8.5. Salinity is at a salty level. Have salt stains on the surface throughout the year and have very low P and K.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Especifique:
Slightly saline
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
saline groundwater
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Before drilling shallow wells there were very few animals living in this area. After 1 year of shallow well being implemented, there is an increase in food and plant sources, the habitat of living things. To implement the technology resulting in more organisms such as fish, birds, rats, earthworms, and insects
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users are diligent in their work and patient. They carried out crop rotation throughout the year. The, they get more revenue daily, monthly and yearly.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Land users drill a shallow well on the recharge area in order to pump groundwater for planting throughout the year to reduce expenses and increase family income
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
- Rainfed.
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Comentários:
Land users can decide to use the land by themselves. They did crop rotation by using water pumped from shallow wells. The Land users could be an example for the other that could be shown by surrounding farmer want to engage in this project.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Qualidade da safra
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Qualidade da água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Acumulação de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Salinidade
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Acidez
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Impactos da seca
Impactos de ciclones, temporais
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Risco de incêndio
Velocidade do vento
Microclima
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Comentários:
An opinion of the land user, there are many situations such as rain delay during 2014-2016, drought during December – April 201 and flood in rainy season while rain delay in 2018 can lead to water scarcity problem. However, that situation cannot impact farmland with shallow wells.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Land users to pay a 2,000 baht machinery as a long-term investment to operate for several years and pay the electric fee for water pumping but land users can have 10,800 THB and the revenue daily, monthly and annually and reduce costs in the household
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Land user and other farmer have knowledge and understanding on an advantage of shallow well technology implemented. Some of them drill water well by themselves.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
changing practice
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Land users have modified water pump machine by use electric pump instead of a gasoline pump
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Reduce soil salinity |
| Save money by bringing rice and vegetables grown into household food. |
| Increase sales revenue, rice, sugarcane, pineapple, Papyrus, banana, lemongrass, galangal, chili, and sweet bamboo. |
| Save money by bringing rice and vegetables grown into household food. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Pumping water from shallow wells for agricultural use, can reduce groundwater table and prevent salinity that is a great measure on land degradation mitigation |
| The land user can have food from plant production from their farms. The land user can reduce household expenses. Left to sell, resulting in a daily, monthly and annual income and make a better life. |
| Biodiversity enhancement, there are many plants and living things such as earthworms, birds, fish, frogs, and insects. This is resulting in a balanced ecosystem. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| After one year of shallow wells implemented, land users must take care and maintain shallow wells as usual. | Make an agreement on taking care of shallow wells after implemented. |
| To inform LDD when something is wrong |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Other land users who are not participating. will not get knowledge about the use of shallow well to reduce the level of underground water. | LDD staff / Land users participating in the project to advise or educate other farmers on how to join the project. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
Visit 1 farmer/user's land
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Interview with 1 farmer.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
The Land Development Department officers and planners (7)
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
03/09/2018
Comentários:
To be clear on the result of the technology implementation there should be soil sampling as well.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Evaluate the project using water from shallow wells to prevent. Distribution of saline soil as farmers participate in Bua Yai District,Nakhon Ratchasima Province (Kamolthip Sasithorn: 2017
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.ldd.go.th
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Study of groundwater level changes to rice production in an integrated saline soil development project area, Bua Yai District, Nakhon Ratchasima Province (Bowon Buakhao: 2017)
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.ldd.go.th
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/27/
7.4 Comentários gerais
Some part of the questionnaire is very complex such as the cost of input
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos