Multistorey agroforestry [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Julia Doldt, Noel Templer, Kidist Yilma, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Mitikarsamino Ersha
technologies_6621 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Gabiba Afra
A farmer
Etiópia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Agroforestry is the best technology/practice to sustainably manage the land. It has multiple economic, environmental and social benefits.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Integrated Agroforestry System [Etiópia]
The integrated agroforestry system is a self-initiated approach by a land user to implement agroforestry as part of an indigenous practice and has evolved over the years through technical support, training, and supplies of coffee and tree seedlings by the Office of Agriculture and Coffee Improvement Project. Had there been …
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops, pastures, and livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
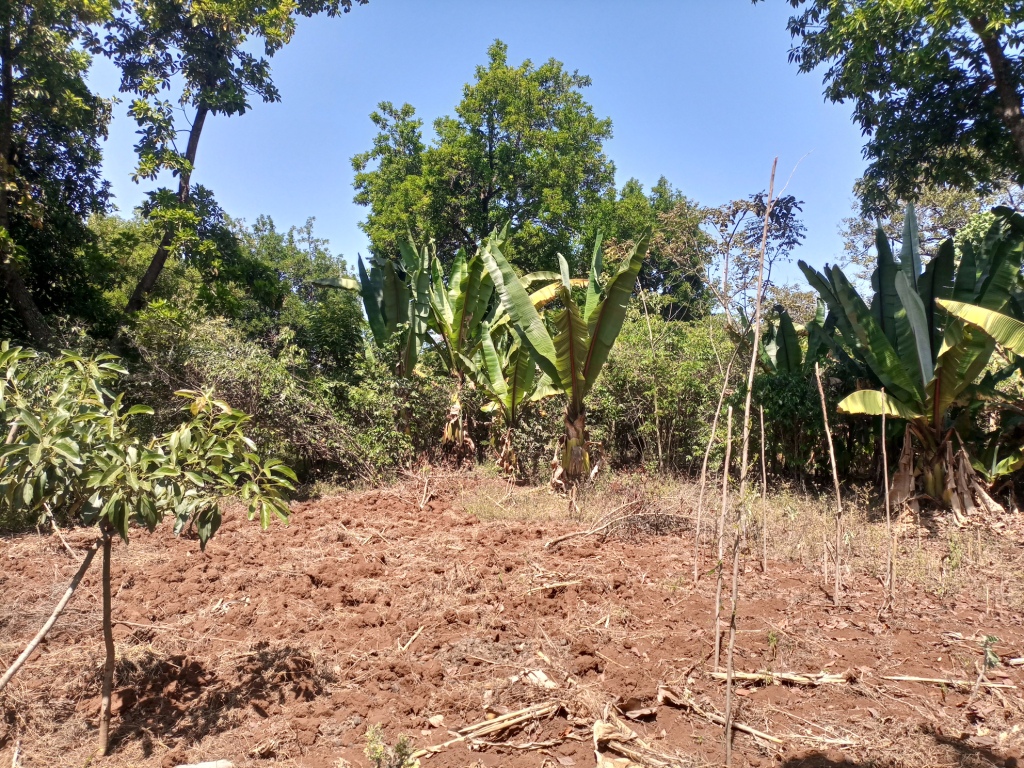
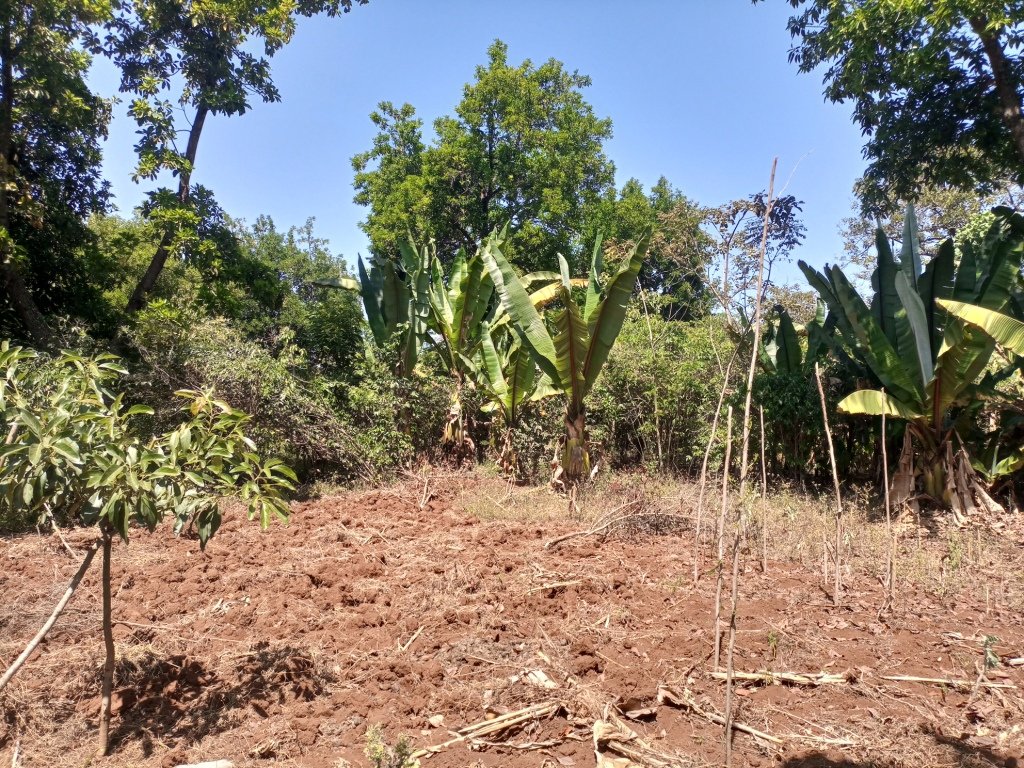
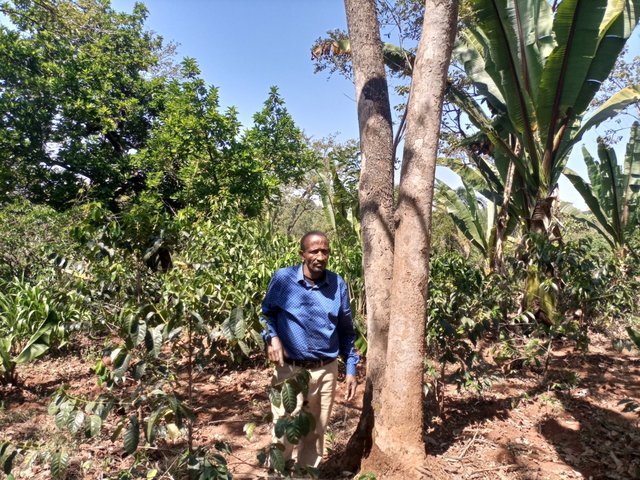
Multistorey agroforestry is the intentional mixing of trees/shrubs with crops and pasture at different levels ("storeys" or heights) and the livestock. The practice creates environmental, economic, and social benefits for the end users. Agroforestry practices provide opportunities to integrate productivity and profitability with environmental stewardship resulting in healthy and sustainable agricultural systems that can be passed on to future generations. Tree litter increases soil organic matter and reduces soil chemical and biological degradation. Tree cover can reduce soil erosion and evaporation from the soil surface. The technology is applied close to the homestead as it demands close follow-up and steady management practices, and that is where tree-crop-livestock integration can be best applied. The farmer whose practice is described here used to be very poor four decades ago. He has planted coffee gradually over the years under shade trees. As a staple perennial food crop, enset was planted also in the mixture. Livestock were also integrated. Eventually, numerous multipurpose tree species, food and fodder crops, and physical structures with productive barriers were integrated into the farming system. As a consequence, a multistorey agroforestry system has been established over years.
The purpose of the technology is to ensure ecological, economic, and social benefits. The rolling landscape of the area necessitates permanent ground cover to reduce the effect of erosive rainfall that degrades the soil. Once established, the technology needs management practices including pruning/stumping of coffee trees, managing other trees, weed control, enrichment planting with coffee and enset, and fertilization of annual and perennial crops. The livelihood of the respondent farmer has been completely changed. He has made a significant accumulation of wealth from producing and sale of tons of unprocessed coffee, avocado fruits and some indigenous bananas. This form of agroforestry creates year-round employment opportunities for proactive farmers. However, subsistence farmers with small parcels give priority entirely to the mono-cropping of cereals and other fast-maturing crops to meet their urgent demand for food. Shortage of land, capital, and a general lack of awareness about the sustainable benefits of the technology are reasons for lack of adoption of the technology.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
Observações gerais sobre as fotos:
The farmer has integrated several crops and tree species. Over years, he noted some tree species are not the best fit for the multi-storey system. He tends to remove some of them. The high-yielding avocado fruit per se was found as an inappropriate mix for the agroforestry system as it has a complete shading effect over the undergrowth. Several other tree species such as Podocarpus species, Olea, Euphorbia, Misana (Croton macrostachyus), Doqima (Syzygium guineense), Tiqur enchet (Pygeum africanum), Pulm tree (Phonex species), Birbira (Millettia ferruginea), Wanza (Cordia africana), Sesa (Albizia species), Sesbania species, Girawa (Vernonia amygdlina) and some fodder grass species such as Napier and Guatemala grass…are all part of the system but the farmer’s choices are the latter five to seven species. Despite his views of the characteristic feature of the different trees in relation to the undergrowth such as coffee, enset, beans, pumpkins and so on, they have immense ecological benefits as well as supply food, bee forages and construction materials.
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Comentários, breve descrição:
The video of this technology is not documented.
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Sidama
Especificação adicional de localização:
Shoye kebele (Kebele - lower administrative level)
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
It is located on farm around the resident area or in homegarden.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
1980
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The farmer started to implement the technology by himself but gradually managed to access support and inputs such as coffee and tree seedling, training, and visits from the agriculture and coffee development office through the extension workers. Farm visit and mentoring services from the district experts were also commendable to inspire the farmer. The visit to the farm by researchers, local development and other actors add knowledge and motivation to the farmer.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- Legumes - Haricot beans and other climbing species, Pumpkin and root crops/tuber potato and yam.
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
- culturas forrageiras - gramíneas
- ervas, pimentão, capsicum
- Enset/false banana
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- abacate
- café, sombra cultivada
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Belg, short rain (March to April) and Meher, long rain (June to September).
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Haricot beans intercropped within maize and under coffee. Actually, maize grow in the buffer zone of the agroforestry farm.
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Cereal maize farm rotate to legume such as haricot beans.
Comentários:
Adjacent small plots of land are used to grow maize to complement Enset/false banana - a staple crop for the household. Also, beans and vegetables such as local kale are integrated into the farming system.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Pastagem
- Open/free grazing
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
- gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
- mulas e jumentos
- aves
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
In an integrated crop-livestock system, crops and livestock interact to create a synergy, with recycling allowing the maximum use of available resources. Crop residues can be used for animal feed, while livestock and livestock by-product production and processing can enhance agricultural productivity by intensifying the use of nutrients that improve soil fertility and reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Apparently, crop residues are a valuable, low-cost feed resource for animal production, and are consequently the major source of nutrients for livestock.
Produtos e serviços:
- estrume como fertilizante/ produção de energia
Espécie:
gado - lácteo
Contagem:
10
Espécie:
caprinos
Contagem:
4
Espécie:
aves
Contagem:
3
Espécie:
mulas e jumentos
Contagem:
1
Comentários:
Four decades back or before the conversion of the land into the agroforestry, it was partly wetland and the grazing land used by free roaming animals.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Agriculture is entirely rainfed that rely on bimodal rainfall intercepted twice a year.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Diverse SLM practices are integrated over the farmland.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
- Ca: acidificação

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pw: estagnação hídrica
- Ps: Subsidência de solos orgânico, sedimentação do solo

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
The bare land that was subjected to soil erosion is arrested and reversed. Frequent cultivation, a threat to degradation has been entirely changed. Diverse types of degradation to the farmland have been mitigated.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Agroforestry practice helps to conserve soil and water as a barrier and via covering the ground. Tree species also serve as wind break to reduce wind velocity and wind erosion. Integrating tree species with grasses/forage not only reduces soil and water loss but also supply feed to the livestock. It also maintain soil organic matter and improve physical properties, fix nitrogen and promote efficient nutrient cycling. Furthermore, the twigs and leaves serve as mulch, green manure, etc. Integration of diverse trees/shrubs also break the impermeable layer and facilitate nutrient cycling from deep layer in certain soils, and reduce the development of soil acidity.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
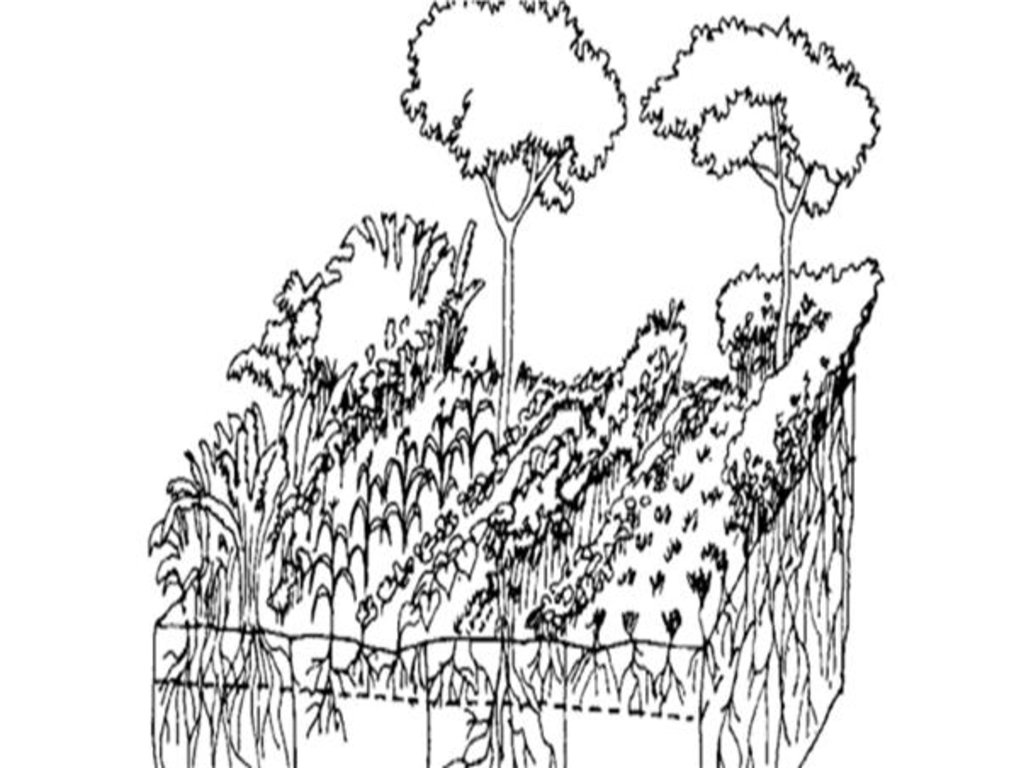
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
An adopted technical drawing/specification of the classification of tree-crop arrangement in the multistorey agroforestry system.
Autor:
Xu J, Mercado A, He J., Dawson I (eds.) (2013); ISBN 978-92-9059-333-1
Data:
20/01/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
4Timad
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
4 Timad = 1 ha
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ethiopian Birr
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
53,12
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
In rural area wage rate vary by type of work: coffee harvest-80 ETB/day, weeding 60 ETB/day. About 70 birr/day, on average.
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | Before and during Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain) season. |
| 2. | Enset and Coffee planting | In Belg and Meher season, respectively. |
| 3. | Planting beans (annual crops) | In Belg season |
| 4. | Fodder and other Multipurpose trees planting | In Meher (main rainy season). |
Comentários:
Farmer start small and keep on enriching and managing the farm with inputs and technology components. This is for a single year but two seasons with short and long rain. Actually, perennial crops such as coffee and enset are not planted every year.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land preparation | Oxen plow | 16,0 | 200,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting annual crops | Oxen plow | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting perennial crops | PDs | 20,0 | 70,0 | 1400,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting fodder crops and trees | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Spade | Number | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Hoe | Number | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Digging fork | Number | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Coffee seedling | number | 2500,0 | 10,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Enset seedling | number | 6000,0 | 5,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Tree seedling | number | 1500,0 | 2,0 | 3000,0 | 50,0 |
| Material vegetal | Beans seed | kg | 50,0 | 42,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | NSP fertilizer | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Urea fertilizer | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 73950,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1392,13 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
In the past, coffee seedling was freely supplied to the farmer by the Ministry of Agriculture. The trend has changed recently. Apart from some tree seedlings that are freely supplied through government nurseries, virtually all costs for the establishment of Agroforestry are covered by the farmer themselves.
Comentários:
Commodity price in Ethiopia is frequently changing because of inflation and economic crisis. Therefore, it is impossible to confidently estimate the price of inputs, farm tools, and labor costs.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inputs | Before the onset of short/long rain. |
| 2. | Management | Throughout the year depending on the management types. |
| 3. | Farm tools | During off-season. |
Comentários:
A farmer estimate maintenance costs of about 40,000 ETB per hectare of land. However, my calculation in the following section reduces it a bit lower by excluding the cost of plant protection, and by boosting the contribution of family labor in the household. Apart for the general calculation, as the average land holding in Sidama region is less than 0.25 ha, a farmer may not go for adopting the technology on 1 ha.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Enrichment/replacement planting | PDs | 5,0 | 70,0 | 350,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Fertilization | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Weeding | PDs | 40,0 | 70,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Hoes | number | 4,0 | 600,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Digging fork | number | 4,0 | 500,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Spade | number | 4,0 | 400,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Coffee seedling for replacement | number | 250,0 | 10,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | NSP | kg | 100,0 | 44,0 | 4400,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Urea | kg | 50,0 | 44,0 | 2200,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 21050,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 396,27 | |||||
Comentários:
Frequently changing prices of inputs, labor, and farm tools disable someone to give an estimate for the establishment and maintenance costs in the future. Essentially, maintenance cost demands lower investment than the establishment cost. Unlike in the past years, agroforestry doesn't start from scratch but can be built up on the existing initiative. Therefore, it would be rather an intensification of agroforestry than just establishing.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Economic crisis and the prevailing inflation in the country, and global changes in price of petroleum and other commodities such as chemical fertilizers.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The area receive adequate rainfall.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Awassa Meteorology center
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
The climate is virtually consistent except during the season of El Nino and cyclical shortage that happens once in years.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The topography feature is changing from moderate to bit slopy. However, the steepness of the farmland is not more than 15%.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Not available.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Surface water is available year-round with fluctuation of the volume with the season. Besides, pollution is high during the rainy season because of soil erosion from the upstream.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The applied technology/practices comprise diverse species of tree crops. It can be characterized as a practice highly rich in agrobiodiversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
He is also engaged in fuel wood business. Of course, the business does not focus on indigenous tree species but the most commonly marketable trees for construction and fuel wood in Ethiopia i.e. eucalyptus species.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
He possesses 4.5 hectares of land. However, it is much higher than the regional average, and could be still less than a few farmers.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Especifique:
Land use right is issued by the state. Of course, the land is inherited in the parent line. He also accessed more parcel during land redistribution of the Derg regime. As a rule, the land belongs to the state but the user has usufructs.
Comentários:
Farmers are certified based on the usufructs right issued by the government via the land administration policy enshrined in the country's constitution.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
Tap water is accessible some distance away. The deep well the farmer has is not clean for drinking by the household but for cattle and cleaning goods and clothes.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
It is difficult to guess the increment by weight of perennial crops such as Enset. Of course, the performance is much better in the agroforestry system with intensive management and application of organic fertilizers. The integration also ameliorates the microclimate of the area and makes the situation ideal for the crops.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
In the agroforestry system, a combination of livestock manure, tree litter, and a mixed cropping system contributes to soil fertility and soil health which improves crop quality.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Increased with improved soil fertility and soil healthy.
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
Livestock access to feed during the dry spell when communal grazing land is denuded of grass. Furthermore, agroforestry promotes a cut-and-carry feeding system that strengthens reliance on one's feed reserves at disposal. This goes with the intensification of livestock production.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The practices rather improve the resilience of the crop as it creates an ambient environment.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
The integration increase product diversity.
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Cattle manure is used for the production of heat and light energy through the application of biogas technology.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
Agroforestry's contribution to drinking water availability and water quality was not measured and was beyond the scope of respondents to comprehend and address the questions except the merely conceptual reflection. Of course, the technology reduces runoff and recharges the ground water which directly contributes to the availability of surface water for livestock.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
Fertilizer supply changed more to organic than chemical fertilizer. The foliage of tree litter and in situ decomposition of organic matter added substantial value to the restoration of soil fertility.
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Increased management demand with gradual increase of the integration of tree crops and the overall size of the land is remarked by the farmer.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Land users generate reasonable income from the integration of different perennial and annual crops as well as livestock.
Estado de saúde
Direitos do uso da terra/à água
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
The technology immensely contributed to SLM by covering the farmland with perennial trees and crops and by incorporating the physical structure into the practice.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
The groundwater table is estimated to increase as the ground cover promotes the infiltration and vertical movement of the intercepted rain on a gradual basis.
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
As some tree species such as avocados consume large amounts of water for transpiration needs, the degree of evaporation reduction of the practices is counterbalanced by the integration of the high-consumers with low-consumer species. Overall, agroforestry has a positive impact on evaporation reduction.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Acumulação de solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Nutrient cycling is highly improved because different tree species may penetrate the impervious soil layer and bring the nutrient to the surface via tree litter, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and add to the soil.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Highly increase, though not measured for this particular farm.
Acidez
Comentários/especificar:
The cause of soil acidity can be diverse including the soil parent materials. However, agroforestry has positive acidity-reducing factors by improving soil fertility and soil health.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Highly increased because of the combination of trees/shrubs with food crops and fodder crops.
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Agroforestry hosts the predators and prey and creates balanced food chains that reduce the degrees of pest development.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
It is a climate-smart agriculture by its virtue that increase carbon sequestration as a regenerative agriculture.
Velocidade do vento
Microclima
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
The practices ameliorate the prevailing adverse climatic conditions and land degradation.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
Even if the impact of agroforestry plays a positive reduction role in pollution, the overall impact is compromised by the total farmland covered by a combination of tree crops.
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
Agroforestry has a filtering capacity of polluted air with dust and adverse temperature such as during dry and hot days.
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
Intercepted by leaves of trees and shrubs.
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
It highly contributes to carbon absorption and storage above and below the ground.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
Agroforestry has beneficial ecological and economic functions.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | muito bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | estação seca | aumento | muito bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
About 30% of resident farmers have adopted the technology. The prevailing farming system necessitate change in the approach, and outshined farmers motivated the others to follow suit.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mercados dinâmicos
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Raising coffee prices motivated farmers to refocus on the crop which years back discouraged to shift of the coffee farm to eucalyptus plantation.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Increase production per unit of land and improve livelihoods of family farmers. |
| Reduce land/soil degradation because of permanent soil cover. |
| Ensure sustainable production, reduce risks and improve the biodiversity. Also, increase the family farmers income and their status in the society. It enables them to feel as valuable elite in the community. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Agroforestry improves total production earned from a farmland and improve the wellbeing of the adopted farmers. Implies, it has substantial economic benefits. |
| It reduces soil erosion and land degradation. Also has immense ecological benefits and improves the microclimate of the surrounding. |
| It reduces risks of crop failure owing to climate variability. Also, boost the biodiversity of trees, crops, and habitat diversity that host various living creature in the biosphere as well pedosphere. This is related to carbon sequestration, emission reduction, proper ecosystem function, and overall ecological contribution. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Demand intensive management, and there is shortage of labor. | Identify and established trees and crops that requires minimum labor for planting, maintenance & propagation. |
| Incompatible tree species to the essence of proper integration in Agroforestry. | Select and adopt trees and crops with desirable characteristics to be integrated in the technology and responsive to management practices. |
| Inconsistent product prices for the farm products such as coffee beans and avocado fruits on the local market. | Link farmers to free and fair market which is consistent and sustainable. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Failure to select tree species with desirable characteristics |
Trees/shrubs with the following desirable characteristics need to be considered: - Deep root system to draw water & nutrients. - Easy to propagate, & high biomass producers, palatable, provide more green manure, & high survival percentage. - Adaptable to close spacing like in hedgerows. - Good sprouting & positive response to pruning. - High coppicing and pollarding capacity. |
| Highly dense in some areas and slightly sparse in some part of the farm. | Try to maintain the spacing and distribution of suitable species composition. |
| Trees and shrubs less used as livestock feed except during the shortage period | Promote feeding the diverse fodder trees to the livestock to ensure their access and benefited from trees/shrubs as well than rely only on grass family. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
An intensified agroforestry system visited.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Only one farmer interviewed.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Land users, regional bureau of agriculture natural resource management expert and GIZ regional advisor consulted.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
13/01/2023
Comentários:
Extensive field visits and interviews were conducted with Land users, Regional NRM expert, and ISFM + regional advisor.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
World Agroforestry Centre. 2008. Annual Report 2007-2008: Agroforestry for food security and healthy ecosystems. Nairobi, Kenya: World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF). ISSN 1995-6851
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www.worldagroforestry.org
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Agroforestry System for Ecological Restoration: How to reconcile conservation and production options for Brazil's Cerrado and Caatinga Biomes. Miccolis, Peneiveirok Marques et al. 2016. ISBN: 978-85-63288-18-9
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://apps.worldagroforestry.org/downloads/Publications/PDFS/B19034.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Indigenous Agroforestry Practices and their Implications on Sustainable Land Use and Natural Resources Management: The Case of Wonago Woreda. Sustainable Land Use Forum (SURF), 2006. Research Report No 1, Addis Ababa
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www. devinet.org/sluf
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
The Center for Subtropical Agroforestry (CSTAF)
URL:
http://www. cstaf.ifas.ufl.edu/
Título/ descrição:
World Agroforestry (ICRAF)
URL:
https://www.worldagroforestry.org; https://www.cgiar.org/research/center/world-agroforestry-centre/
7.4 Comentários gerais
The questionnaire is comprehensive and give the opportunity to add additional techniques/approaches via the "other" options. However, it is demanding as it requires for videography and sketching skills for every technology.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Integrated Agroforestry System [Etiópia]
The integrated agroforestry system is a self-initiated approach by a land user to implement agroforestry as part of an indigenous practice and has evolved over the years through technical support, training, and supplies of coffee and tree seedlings by the Office of Agriculture and Coffee Improvement Project. Had there been …
- Compilador/a: GERBA LETA
Módulos
Não há módulos