Afforestation for firewood production [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Editores: Miajan Maroofi, Hekmatullah Sharifzai, Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov, Aqila Haidery
- Revisor: William Critchley
Bunyodi jangal baroi tavlidi chubi sukht
technologies_668 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Sari Joy Village, Rustaq District
Afeganistão
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Researcher:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
27/10/2016
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
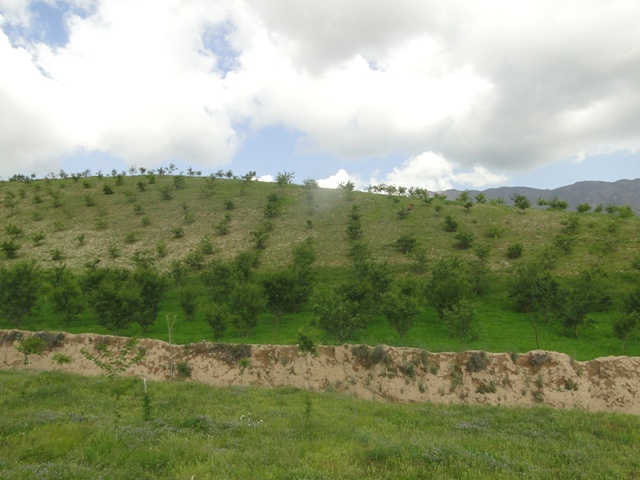
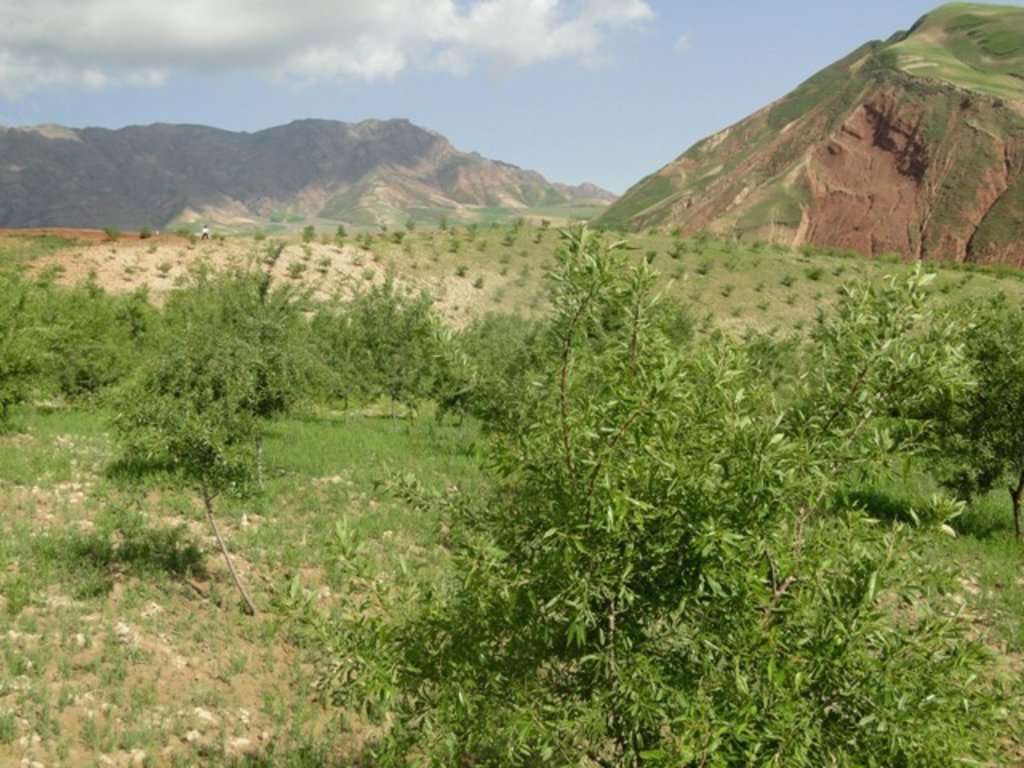
Non-fruit and fruit trees are planted on heavily degraded forest land to protect the land from erosion and further degradation and provide fuelwood for the local community.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Project supported implementation of afforestation has taken place in the villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 and 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter, and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580 mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use, and includes low levels of vegetation cover, severe water erosion of topsoil, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting the socio-economic well-being of local communities, as well as contributing to the risk of being adversely affected by drought - and landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology are based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zones of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions
Despite the low forest cover in Rustaq, Afghanistan, local communities strongly rely on fuelwood and animal dung for cooking and heating throughout the whole year. Forests are mainly found on community land with open access to all, and there are no protection measures in place. The high demand on fuelwood for household needs places strong pressure on the remaining patches of forests and bushes, which are currently threatened by eradication. Such high demand in the area is likely to remain as there are no other alternative energy sources. The mass destruction of local forests is one of the main causes of intensive erosion, aridification, loss of topsoil and formation of gullies. Low forest cover increases vulnerability to severe rainfall and risks of landslides.
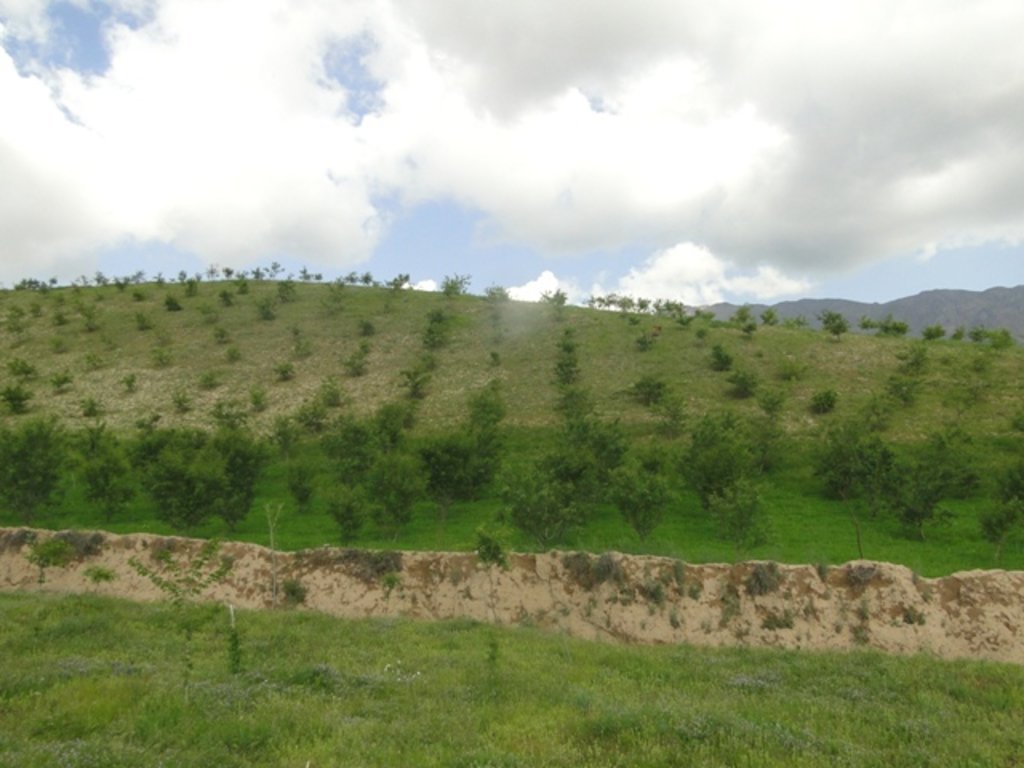
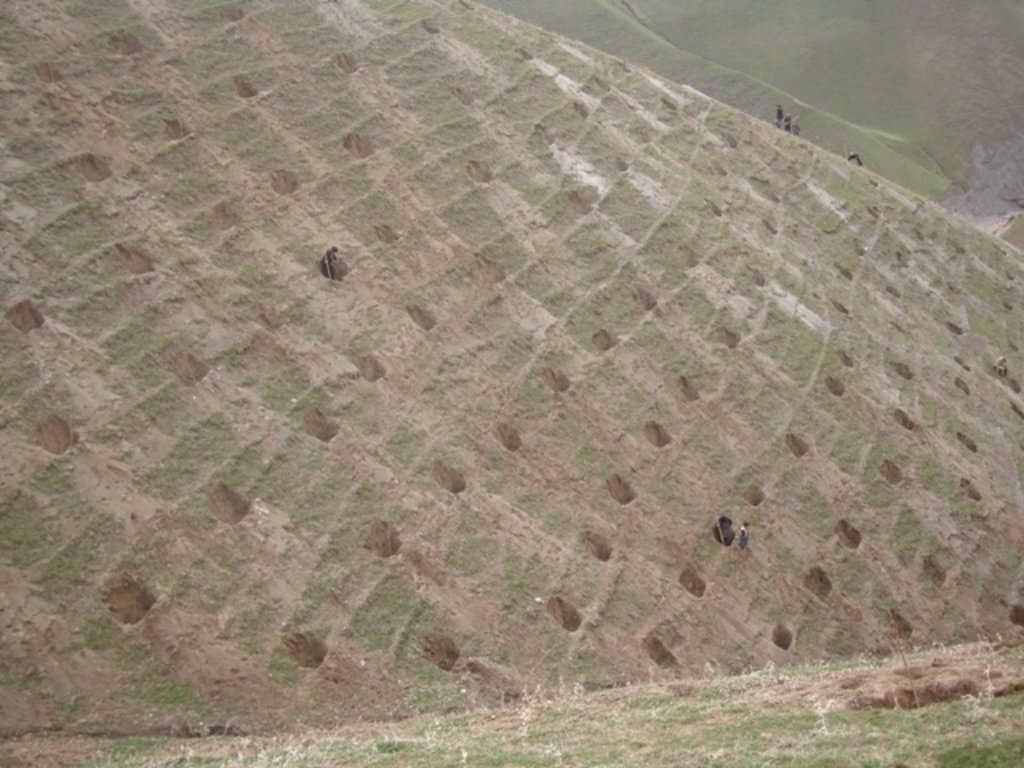
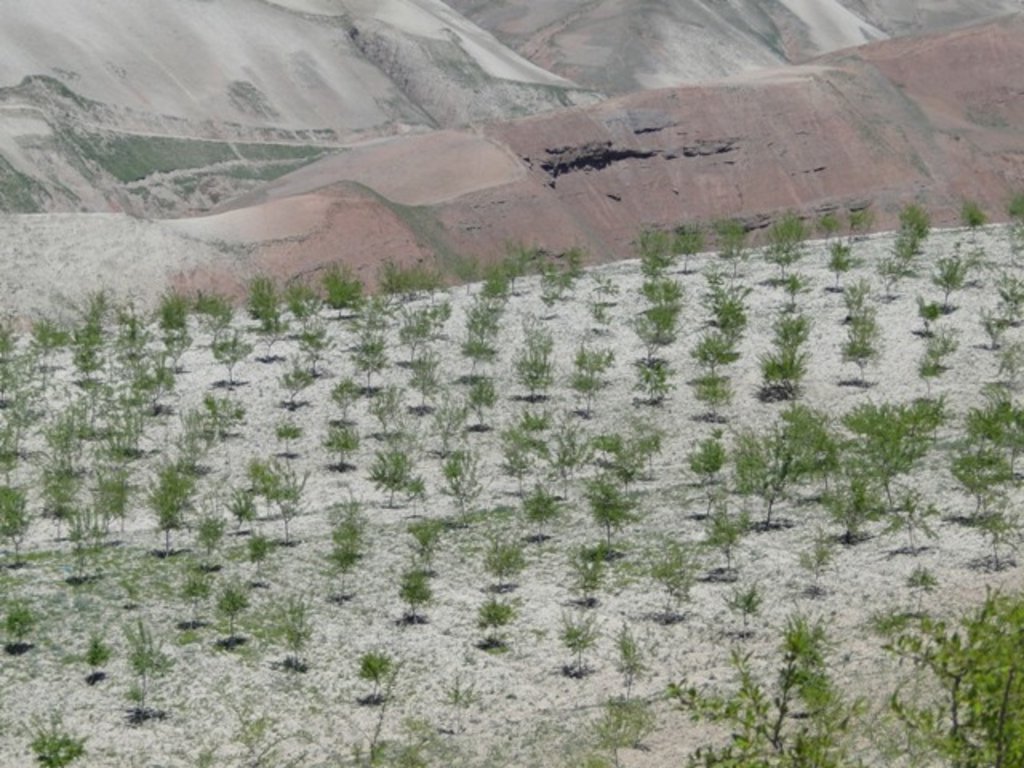
Afforestation measures in the three villages were initiated to halt the land degradation and provide sustainable firewood. The reforestation sites are largely on community land with a small share on private land. The area is characterized by hilly (16-30%) and steep (31-60%) slopes. Planting and maintaining forest in such conditions requires close support in the appropriate design of forest plots, and relevant maintenance recommendations, which can then ensure the survival of the plantation. A plot of 0.2 ha is divided into 4 m x 3 m sections. Each tree is placed in a pit of 50 cm x 30 cm with rich soil around the roots. Once the tree is planted, it is watered and covered with lime. Russian willow, acacia, mulberry and almond are the most common tree species used for afforestation purposes.
Most of the newly established forest sites are located at walking distance of the nearby villages: this is important to help provide protection of the plot from animal intrusion and ensure proper maintenance of the trees. The forest plot is watered for three years in a row. The Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) pays 0.60 US cents per tree per year to sustain the survival of the plantation within the first year. The funding for the irrigation is provided by the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT). LIPT supported the afforestation activities through the provision of technical and financial support. The tree seedlings were supplied by the project, and financial incentives were provided to engage the community in tree-planting.
The plantations are still very young: however, the land users express support for the new forest in their villages, and have observed localized stabilization of the soil and improvement in vegetation cover. There are high expectations of the new forest, which promises access to sustainable fuelwood and non-forest products, such as almonds and mulberry. The grass and tree leaves from the forest plots are already used for animal fodder.
Women and children under 15 years old are expected to be the direct beneficiaries of the new forest. They will no longer spend long hours to collect and deliver fuelwood, bushes and dung. A small portion of women reported involvement in forest establishment activities, while the majority are taking part in protecting the forests from livestock.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Especificação adicional de localização:
Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai
Comentários:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM impementers from Sari Joy (5 plots), Jawaz Khana, (4 plots), and Dashti Mirzai (3 plots) as compiled during focus group discussions. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in all three villages on farmers experiences and observations of afforestation plots, with both SLM implementers (20) and observers (10).
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Silvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
Acacia, Russian willow, mulberry. almond, grass and leaves for fodder
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Some of the forest land has been heavily degraded and was used as grazing land for an extensive period. Most of the land is forest land.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
During the first three years the forest requires irrigation due to aridity. The first year of irrigation is supported by the project, and the rest of the irrigation measures are implemented by the local community with the support of the NRMC.
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
23.6 ha
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Autor:
Aslam Qadamov; Roziya Kirgizbekova
Data:
03/04/2017
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The establishment activities begin with selecting the area for reforestation. Most of the reforestation sites are on slopes above 6% steepness . A plot of 0.2 ha is divided into 4 m x 3 m sections. Planting pits of 50 cm x 30 cm are prepared for planting the trees. Each tree is placed in a pit and good soil is added to the roots. Most popular species used for reforestation are: Russian willow, acacia and mulberry. The newly planted tree is watered and the trunk is covered with a lime and water solution for protection and better growth.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1 ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
67,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Design of the forest plot | Gestão | Winter |
| 2. | Digging pits 50 cmx 30 cm for tree plantation | Estrutural | End of winter |
| 3. | Planting tree seedlings 3m x 4m | Vegetativo | Spring/Rainy season |
| 4. | Watering the tree after planting | Vegetativo | Spring |
| 5. | Covering the tree with lime | Outras medidas | Spring |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Design of the forest | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Digging pits/holes for the trees | person-day | 22,0 | 5,3 | 116,6 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting tree seedlings and watering | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Fertilizer and lime application | person-day | 8,0 | 5,3 | 42,4 | |
| Equipamento | Meter | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Equipamento | Shovel | piece | 2,0 | 3,8 | 7,6 | |
| Equipamento | Pickaxe | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Equipamento | Rope | meter | 500,0 | 0,07 | 35,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Accacia seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| Material vegetal | Russian willow seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| Material vegetal | Mulberry seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | DAP | kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Lime | kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 998,85 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
Comentários:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protecting the trees from livestock | Gestão | Spring/Summer |
| 2. | Pest and disease control | Vegetativo | Spring |
| 3. | Irrigation | Agronômico | Summer/First three years |
| 4. | Replanting dead trees | Vegetativo | Spring |
| 5. | Pruning | Agronômico | Spring |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Pest and disease control | person day | 7,5 | 5,3 | 39,75 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Replanting dead trees | person day | 7,5 | 5,3 | 39,75 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Irrigating the trees | person day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Pruning | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 159,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
564,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 564 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Derived from the publicly available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Local land users refer to the soil type where reforestation is implemented as:
Dark soil is characterized as: moderately deep; topsoil texture medium, below surface texture medium; and medium topsoil organic matter.
Light soil is characterized as: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water varies in the three study villages. Sari Joy and Dashti Mirzai have good surface water availability, which is also food for drinking. Jawaz Khana has poor water both in quality and availability. Water has to be fetched from a distant stream.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq. Although the men are generally the main land users, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for water. The payment is made either in kind or in cash to Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Produção florestal não madeireira
Diversidade de produtos
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Land users learned new methods of planting trees based on the local conditions.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
The established forest is expected to become a reliable source for firewood, which will decrease the burden of women and children under 15 years, who spend long hours to collect firewood.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários relativos à avaliação de impacto:
Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits for their Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all SLM implementers are reflected here.
Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | muito bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Comentários:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: During the FGD with SLM implementers, a multi-criteria matrix was elaborated, and different SLM practices were rated. In the framework of this exercise, SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) returns. As the SLM technology was only implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technology. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
23.6 ha have been afforested with LIPT support
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%".
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The tree plantations protect the soil from erosion. The land is less vulnerable to heavy rainfall, which washes off the topsoil |
| There are very high expectations about production of firewood. Availability of firewood in local forest will make it much easier to access firewood for cooking and heating by local households. |
| Apart from firewood and wood production, other non-timber products are provided by the afforestation plots, such as fodder for livestock from grass (alfalfa, sainfoin) and tree leaves during autumn. Also some plots are planted with almond and mulberry, which can be collected for own use or for selling. |
| Local people value the recreational benefit of the forest, which make their villages greener and provide green spaces for the local people. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The afforestation measures in the village including establishing the forest and protecting it, mobilizing the community around a common goal, and this has a positive impact on the village as a whole. |
| The planted trees and grass under the trees improve the vegetation cover and increase soil quality, which is then less prone to erosion |
| Improved varieties of fruit and non-fruit tree species used for afforestation help to diversify the tree species in the village and make the soil less resistant to dry spells |
| The expected combined benefits of wood and non-wood products, especially when the harvesting period starts, may have positive impact on households' income and food security. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The establishment costs for afforestation measures are very high | |
| The young trees are vulnerability to droughts | |
| During maintenance some plots require irrigation | |
| Afforestation plots, which are established on former grazing land, reduces the grazing land in the village and deprives animals from grazing land |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Community provides weak or no protection of the afforestation site, which results in low tree survival | |
| Weak funding sources for irrigation of the afforestation plots, particularly during the first three years when the trees are young, might compromise the new plantations | |
| Afforestation is established mostly on community land, where unclear land tenure rights persist, which may cause conflict in the community over forest vs grazing land |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
No field visits were conducted
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 15 land users who have implemented afforestation, participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 30 persons interested in afforestation implementation, of which 20 persons are from households that already have implemented afforestation.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Information provided in the reports of the LIPT project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos