Vermicomposting: an effective liquid fertilizer and biopesticide [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: William Akwanyi
- Editores: George Onyango, Innocent Faith, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
technologies_6685 - Quênia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Mururi Wamunga Job
Welthungerhilfe farmer
Quênia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Farmers who have used vermicompost and vermijuice have recorded good harvests and there are no adverse impacts on their farms.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [Quênia]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- Compilador/a: William Akwanyi
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Vermicomposting is an on-farm waste management strategy where worms are used for biodecomposition of wastes to produce a natural liquid fertilizer and pesticide.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
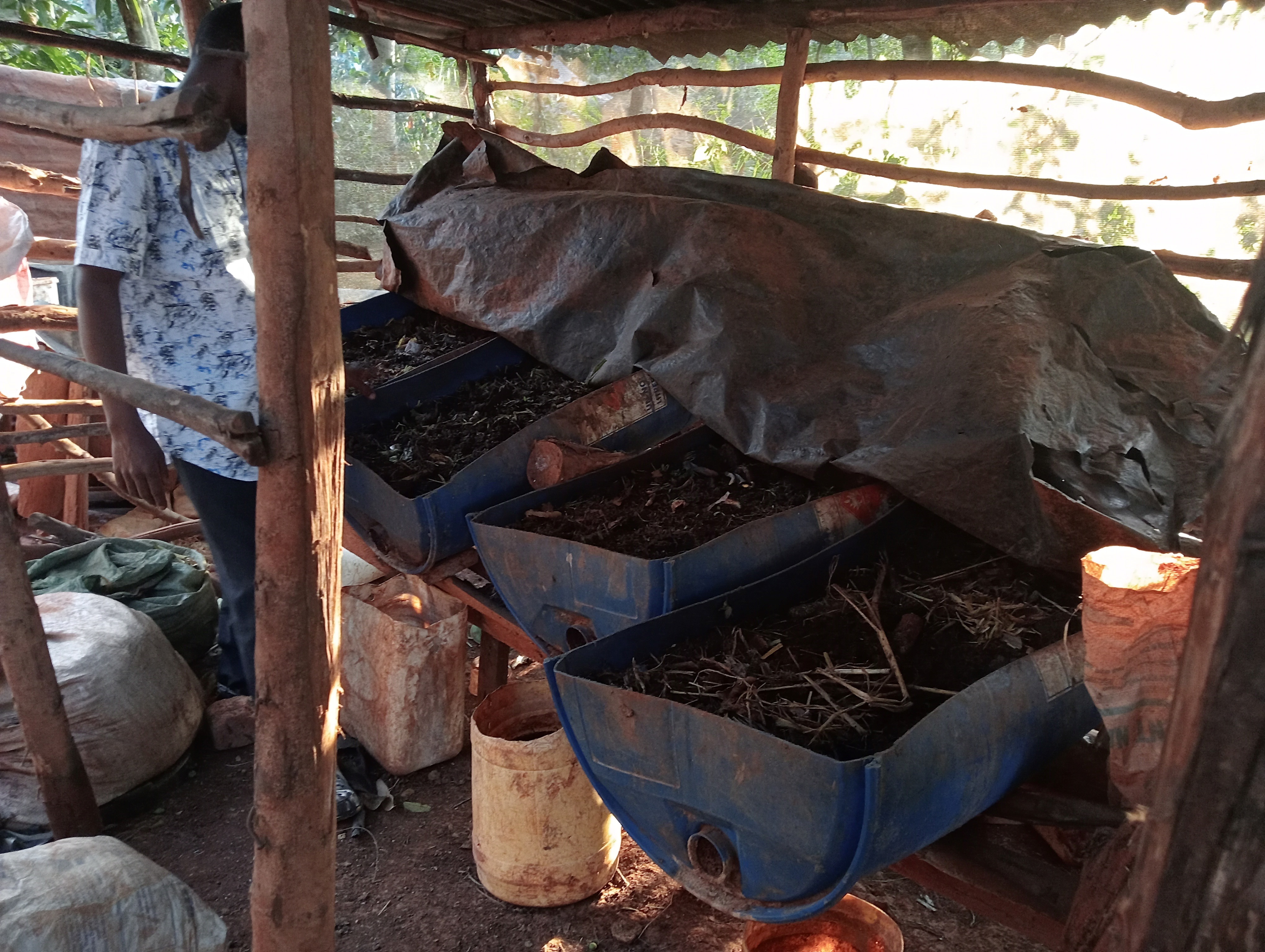
Vermitechnology is biodecomposition of wastes using worms such as red wigglers. It includes vermicomposting (production of compost) and vermiculture (production of worms to ensure sustainability of the enterprise).
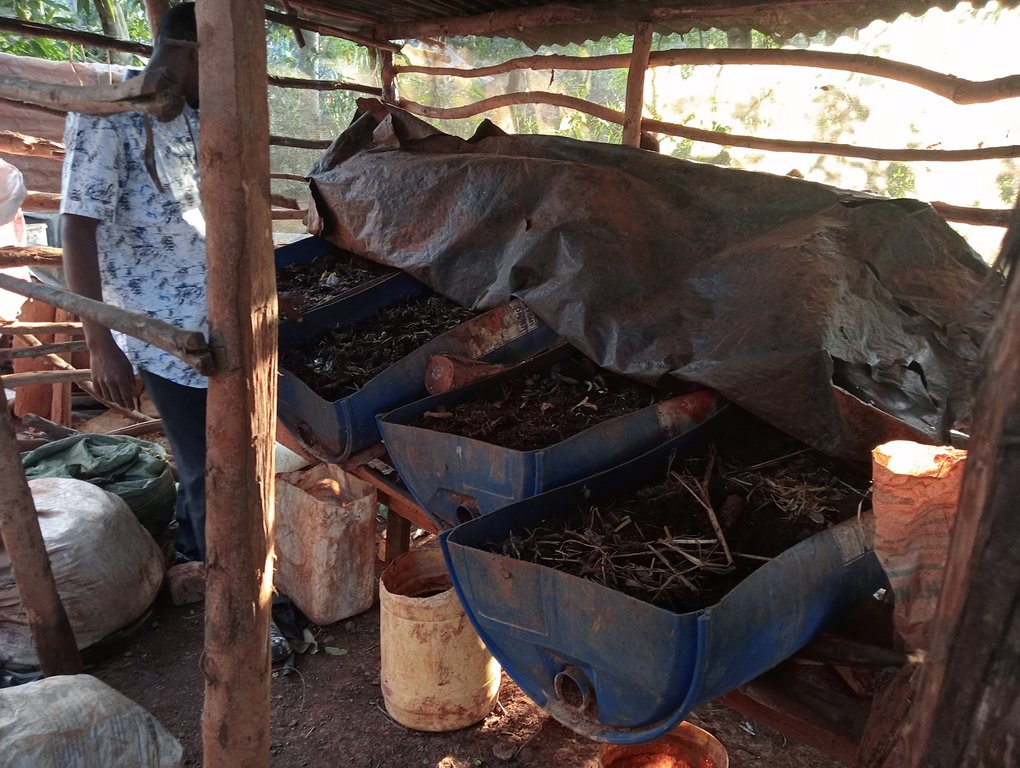
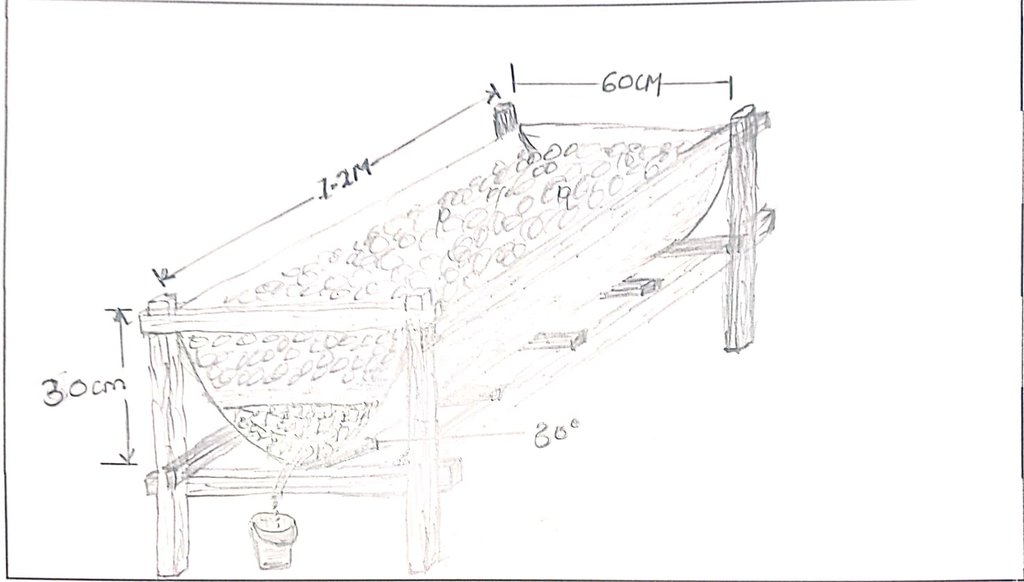
A vermicomposting structure is installed under shade and covered with a black polythene sheet to protect worms from the heat of the sun, and to prevent volatilization of nitrogen. The structure itself can be made by cutting a 60 cm radius and 120 cm height drum into two halves lengthwise. The half to be used must be thoroughly cleaned of oil or chemical residue. A hole is drilled at one end of the half drum for the installation of a tap. A base is made using wooden rails fastened on wooden posts using nails. The container is angled at 30° with the outlet pipe or tap on the lower side to allow free flow of leachate/ vermijuice. Materials are introduced in the half drum, including a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum, a 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food (kitchen and/ or animal wastes) on the bedding material. 20 litres of water are evenly sprinkled on the worm food. The worms and casts are introduced and evenly spread on the food. A bucket is placed at the outlet to collect drops of vermijuice.
Bedding materials include maize cobs, chopped maize straw, agroforestry tree bark, husks, old cartons and paper, and sugarcane bagasse. Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively. However, temperature can be checked by hand also. It is advisable that food (waste) is decomposed before being added onto the bedding material to maintain the temperature within the desired range of 15 - 20°C. Worms coil at the top of the material whenever temperatures go higher. Humidity is often higher in culture bins than in composting beds. Hence, more leachate in culture bins than in composting beds. However, humidity content in both culture bins and composting beds should not exceed 60% since the worms can take in a lot of water and die.
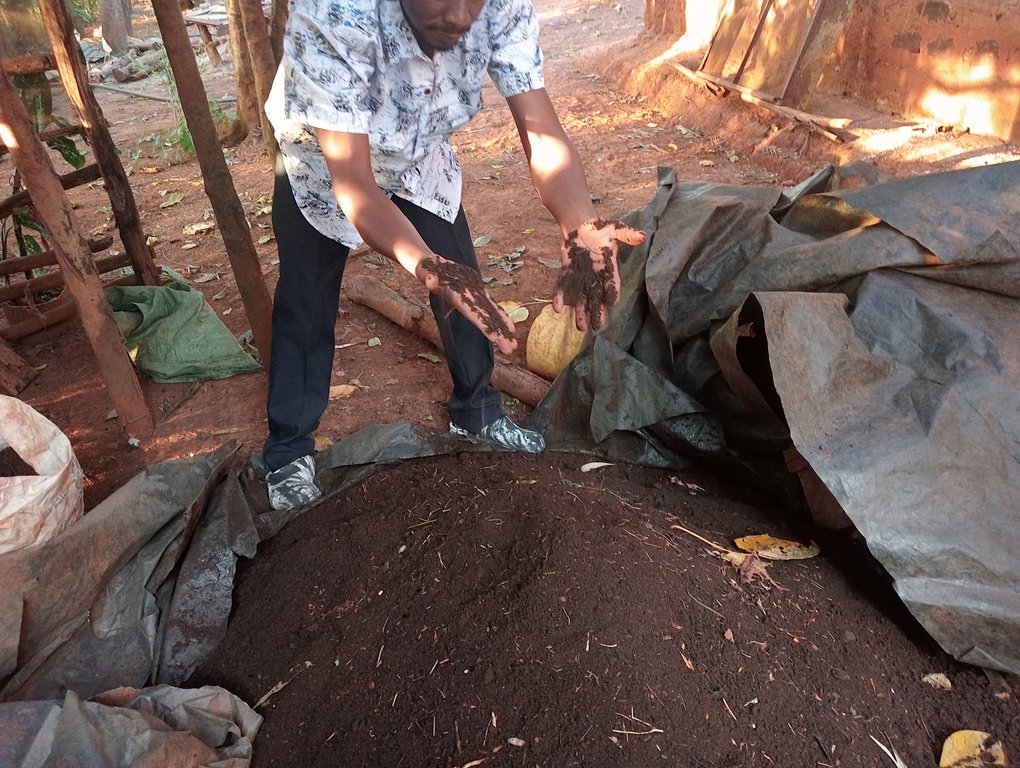
Feeding of the worms is done every 2 weeks where a mixture of 1 kg of chopped fresh tithonia, 3 kg of fresh cow dung, and 3 kg of cooked maize meal (“ugali”) is added and evenly spread on the decomposing material. Collected juice is returned to the system every 2 weeks for a period of 2 months. After the 2 months, the juice will be ready for use as folia fertilizer and pesticide. The casts become ready manure after about 2.5 - 3 weeks. It is harvested by dividing the container into 2 equal halves widthwise and not introducing food to the upper half to make the worms concentrate on materials on the lower half. The worm-free compost on the upper part is completely removed to be used as manure. The remaining material containing the worms is spread uniformly in the half drum. Worm food is then added evenly spread on top.
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. Provided that all inputs are available, a farmer can produce vermicompost and vermijuice 4 times from the same system in a year i.e., 40 litres of vermijuice and 120 kgs of ready-to-use compost in a year. Normally, a one-acre (0.4ha) farm requires about 20 tonnes of compost for planting maize. Vermijuice is mixed with water in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 10 parts of water when required as a folia fertilizer and in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 5 parts of water when required as a pesticide. 20 – 30 litres of vermijuice can be applied to a 0.4 ha farm. However, the amount required for fertilizer varies from farm to farm depending on the conditions of the soil and the crop(s) to be grown. It is important that soil testing is done to determine the conditions of the soil to ensure that the compost is added at the correct rate.
Vermicomposting requires less space and less maintenance labour compared to normal composting. It takes a shorter time to get compost from vermicomposting than from normal composting. On the other hand, large farms would require the installation of several vermicomposting units in order to meet the farm demand. The choice of either technology or both depends on a number of factors, including the size of the farm, the amount of compost required, the time required to produce the compost, etc.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kakamega County in western Kenya
Especificação adicional de localização:
Matora A Village, Ebukuti Sub-location, Manyala Location, Marama South Ward, Butere Sub-county
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The are no protected areas within the area i.e., sub-county
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2017
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
ProSoil project under WHH as the implementing partner
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrossilvipecuária

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- legumes - outros
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
- Legumes e leguminosas - feijão
- culturas de raízes/tubos - batata doce, inhame, taro/cocoyam, outros
Sistema de cultivo anual:
Milho/sorgo/painço entremeado com legumes
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
- culturas forrageiras - gramíneas
- passiflora - maracujá
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- abacate
- frutas, outros
- manga, mangostão, goiaba
- mamão
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Crops planted during long and short rain seasons.
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Maize and beans
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- caprinos
- gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
- aves
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Cattle dung and poultry droppings are used as inputs in vermicomposting. Compost is applied on soil where livestock fodder is planted.
Produtos e serviços:
- segurança econômica, prestígio dos investimentos
- leite
- ovos
- carne
Espécie:
gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
Contagem:
2
Espécie:
caprinos
Contagem:
3
Espécie:
aves
Contagem:
4
Comentários:
There are assorted trees on the farm, and these provide litter that is an input in composting.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Crops are planted all year round due to availability of irrigation water from Eshiatukha and Luanda streams which supplement rain water.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada de fertilidade do solo
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
- Gestão de resíduos/gestão de águas residuais
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A6: Gerenciamento de resíduos
A6: Especificar o gerenciamento de resíduos:
A 6.3: coletado
Comentários:
Some plant residues, especially leaves are collected and used as input in vermicomposting.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
- Ca: acidificação
- Cp: poluição do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Degradação biológica
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
Compost and vermijuice stabilize soil pH and have potential to suppress some soil-born plant pathogens that would have caused plant diseases.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Prevents pathogens
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
The drawing above is of a half drum; 60 cm radius and 120 cm height.
The half drum is supported on rails fastened on wooden posts using nails.
The half drum is positioned in a slanting manner at 30° to the horizontal level to enable free flow of the juice.
The outlet of the vermijuice is on the lower side.
Materials introduced in the half drum include the following: a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum; 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food on the bedding material. The worm food material are determined by the required soil nutrients e.g., banana trunk for potassium (K)-rich manure and/ or vermijuice, crushed eggs for calcium (Ca)-rich, and tithonia for nitrogen (N)-rich.
The worms and cast are introduced and evenly spread on the food.
A bucket is placed at the outlet to receive dropping vermijuice.
Autor:
William Akwanyi
Data:
30/01/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
A half drum vermicomposting unit as described in 2.2
Especificar as dimensões da unidade (se for relevante):
0.17 cubic metres
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
KES
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
122,95
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
300
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of vermicomposting unit, inclusive shed | Before procuring worms |
| 2. | Adding materials | Before procuring worms |
| 3. | Introduction of worms | After completion of construction |
Comentários:
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. The farmer should have the structure ready with all materials except food for the worms before procuring the worms.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of shade over the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| Equipamento | Hammer | |||||
| Equipamento | Hand saw | |||||
| Equipamento | Tape measure | |||||
| Material vegetal | Bedding material | |||||
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Worms in cast | |||||
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Kitchen or animal wastes | |||||
| Material de construção | Half drum | |||||
| Material de construção | Gunny sheet | |||||
| Material de construção | Nails | |||||
| Material de construção | Iron sheets | |||||
| Outros | Gravel | |||||
| Outros | Sand | |||||
| Outros | Water |
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
7000,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The ProSoil project provided the worms
Comentários:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The costs refer to the equipment described in 2.2. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 56.93 USD.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring humidity and temperature | Daily |
| 2. | Feeding | Biweekly |
| 3. | Watering | Biweekly |
| 4. | Predator control | Daily |
| 5. | Harvesting compost | Every 2.5 - 3 months |
| 6. | Collection of vermijuice | Daily |
Comentários:
Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia:
2000,0
Comentários:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 16.27 USD.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another. It is not easy to attach monetary value to some of the input e.g., wastes and water.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1300,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Kakamega Meteorological Station
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
The climate in the area favours most agricultural activities.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The farm is located at an area that is lower in altitude compared to other areas in the larger area. The altitude of the farm is 1,319 meters above sea level.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil pH of most farms in the area ranges from moderately acid (4) to moderately alkaline (7).
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
The area has high agrobiodiversity since most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
- idosos
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Especifique:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
Comentários:
The farmer has an official title deed for his piece of land. He also leases other people's pieces of land for farming. Water in the streams such as Eshiatukha and Luanda and springs is freely accessed without restrictions. There is a borehole in the neighbourhood, and the managers of this borehole have set rules for accessing the water thereat.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Comentários:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
8
Comentários/especificar:
Number of 90Kg bags of maize harvested per acre of land. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Not easy to quantify by the farmer. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Produção de forragens
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5
Comentários/especificar:
Number of harvesting cycles in one season. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2
Quantidade posterior à GST:
6
Comentários/especificar:
Amount of milk in litres from one cow. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
70
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the probability of crops failing to do well in any season.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Land management has been eased because use of manure from vermicomposting improves the soil structure making it easier to plough.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10,000
Quantidade posterior à GST:
0
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the amount of money in KES spend on fertilizers. The farmer no longer purchases fertilizers.
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2,000
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50,000
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the amount of money earned from sell of farm produce. Currently, he sells manure, worms, and vermijuice and also offers services in construction of vermicomposting structures.
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the number of farm products that the farmer sells to earn income. Based on estimate by the farmer.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the number of months when there in no food in the house and the household has to purchase all food required in the house.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the percentage of moisture content in the soil during the dry season.
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40
Quantidade posterior à GST:
80
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimation of soil cover on his farm.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2
Quantidade posterior à GST:
4
Comentários/especificar:
Soil organic matter has increased due to use of manure.
Acidez
Comentários/especificar:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
20
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated vegetation cover at his farm.
Diversidade vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
8
Comentários/especificar:
Quantity refers to the number of crops that the farmer establishes on his farm.
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
There are earthworms at the farm.
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Not easy to quantify. Compost improves carbon sequestration in the soil.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | muito bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Use of vermicompost and vermijuice reduces the farmer's dependence on inorganic fertilizers and pesticides.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
The project was implemented in the entire ward. Very few farmers have vermicomposting structures.
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Most farmers are not implementing yet they were taken through the vermicomposting training by the ProSoil project.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Outros (especificar):
Design
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
The farmer does not fit taps on the composting structures as outlets for the vermijuice since someone can accidentally close the tap and forget to open, especially during humidity checking leading to high humidity which can cause the death of the worms.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| It is an agribusiness venture. |
| It is a source of manure and pesticide. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Compost and vermijuice can be sold to earn income. |
| Structures can be made from locally available material. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Not effective for large scale farming. | Establishment of many bigger structures. |
| The technology is not common among many farmers. | Need for increased awareness creation among farmers, especially on proper knowledge on composting. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Possible death of worms due to unfavourable temperature and humidity. | Ensure regular checking of temperature and humidity. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
One visit at one farm
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up on phone.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
30/01/2023
Comentários:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Free download at https://kakamega.go.ke/public-participation-county-development-plans/
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Vermicompost Suppression of Pythium Aphanidermatum Seedling Disease: Practical Applications and an Exploration of The Mechanisms of Disease Suppression
URL:
https://ecommons.cornell.edu/bitstream/handle/1813/31195/alh54.pdf;sequence=1
7.4 Comentários gerais
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Community Resource Persons (CRP) in agricultural extension [Quênia]
Community Resource Persons (CRP) form a farmer-to-farmer learning approach that bridges the gap in agricultural extension, increases farmers' access to agricultural information (SLM knowledge), and increases the adoption of SLM practices.
- Compilador/a: William Akwanyi
Módulos
Não há módulos