Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Ahmad Khalid Wiyar
- Editores: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy, Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د ځنګل رغونی او کرنیزی ځنګلداری لپاره د پمپ په واسطه د ابه خور سیستم
technologies_7473 - Afeganistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 5 de Março de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 24 de Março de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 18 de Maio de 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 9 de Julho de 2025 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Safi Sharifullah
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Afeganistão
usuário de terra:
Safi Mohammad Afzal
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afeganistão
usuário de terra:
Safi Qiamuddin
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afeganistão
usuário de terra:
Safi Farhad
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
Afeganistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in AfghanistanNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Afeganistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
No, the technology described here is not problematic with regard to land degradation. In fact, it promotes sustainable land management by enhancing soil health, preventing erosion, and supporting afforestation efforts. This technology contributes to the restoration and conservation of forest ecosystems.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
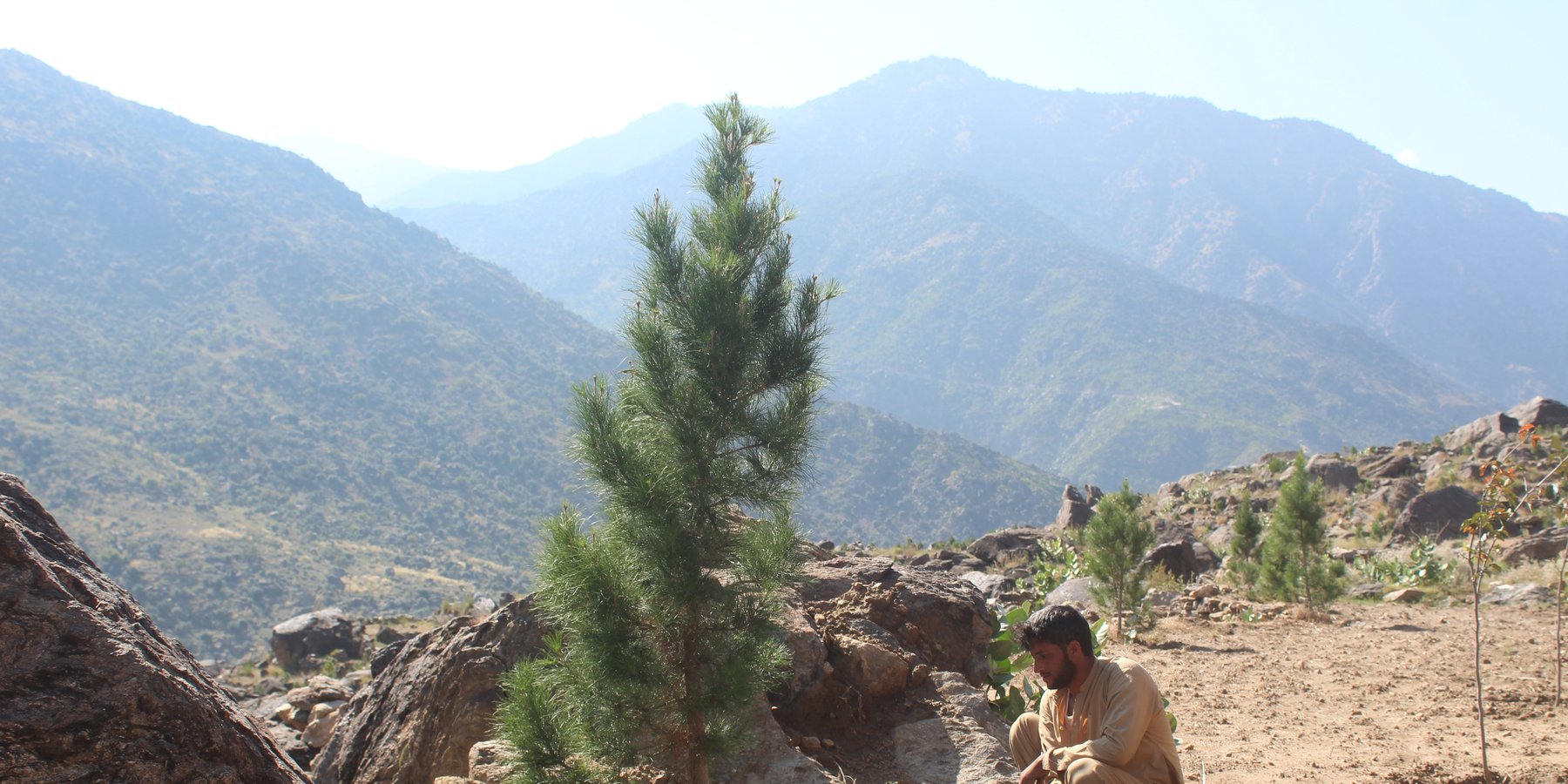
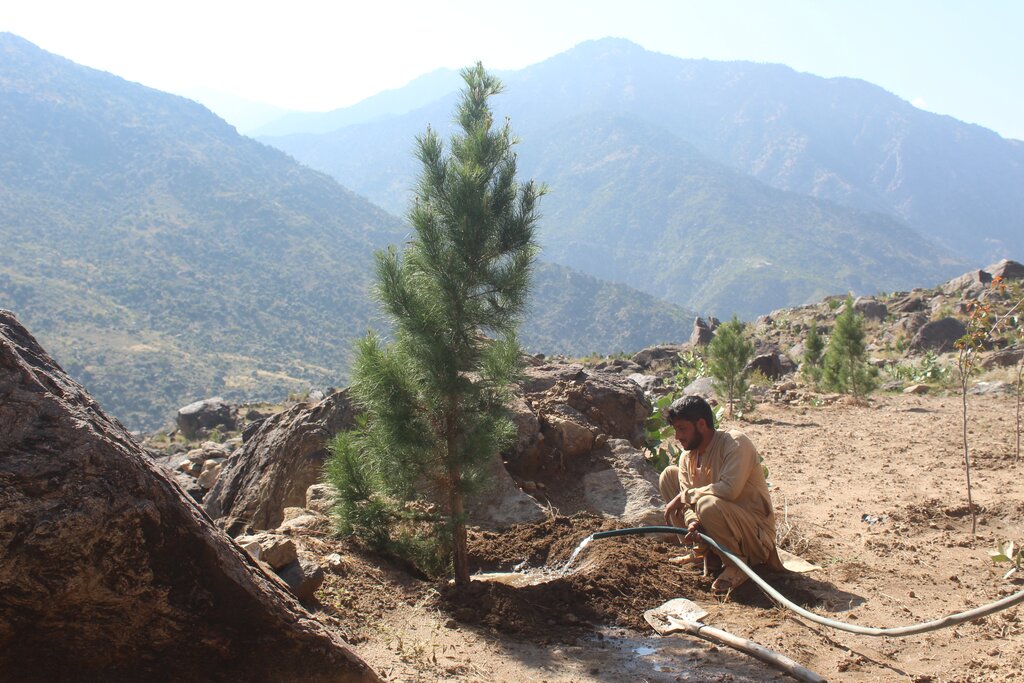
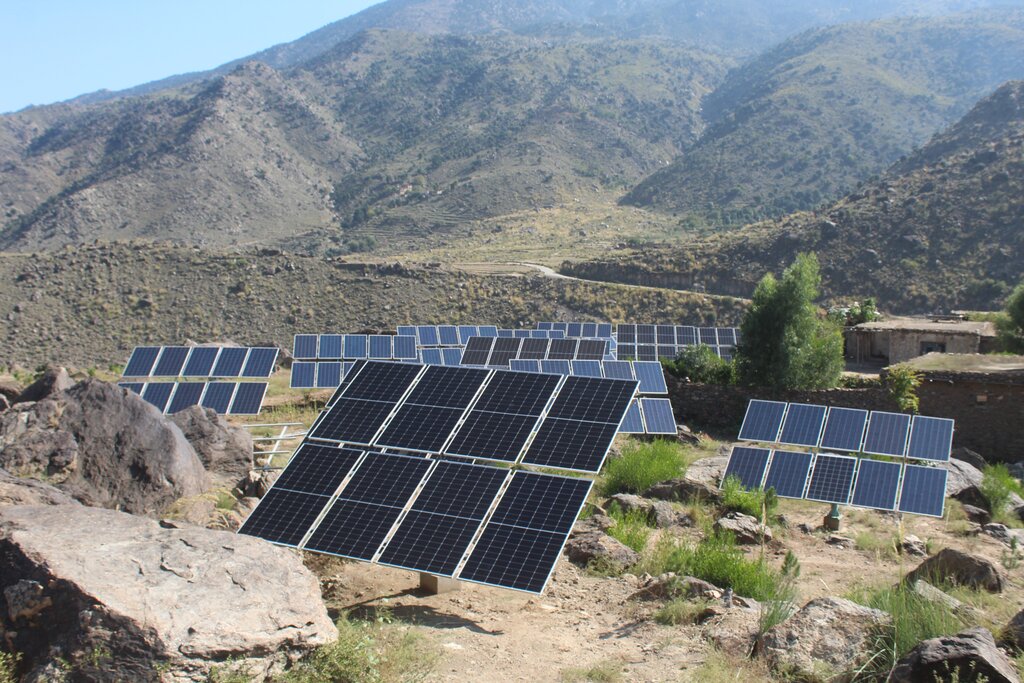
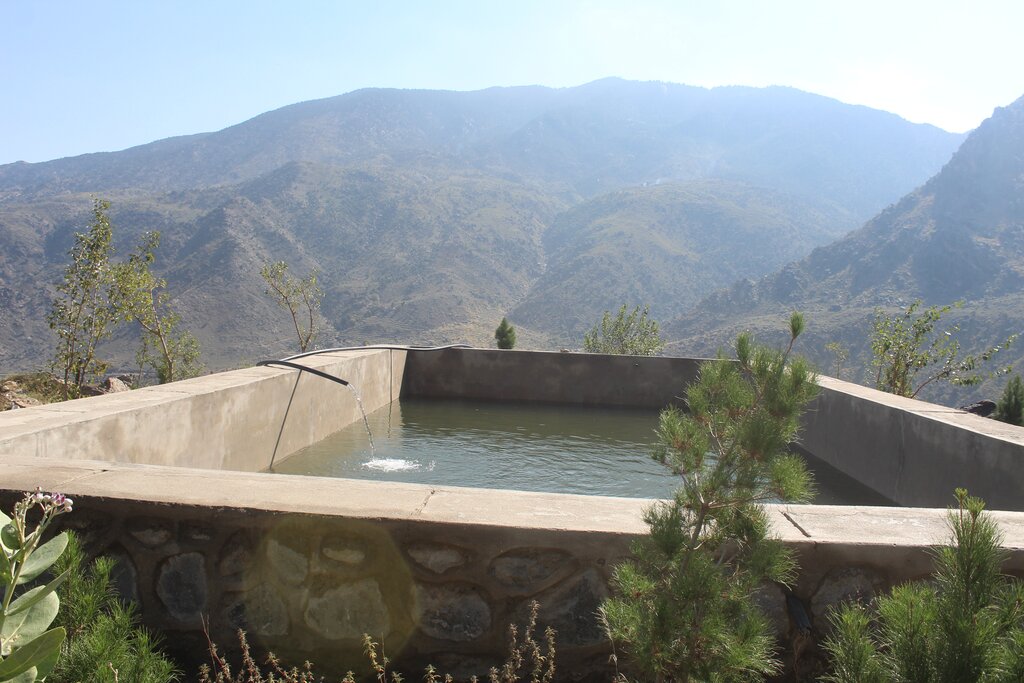
Water exploitation is a major issue in Afghanistan. The lift irrigation technology helps to irrigate an afforestation/agroforestry area (demonstration plot) using surface water (rivers) and solar-powered submersible pump. The construction of reservoirs at the demo plot ensures efficient water storage and use for irrigation purposes without relying on groundwater. A well-designed pipe irrigation scheme is implemented to distribute water evenly across the site, supporting plant irrigation and growth.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
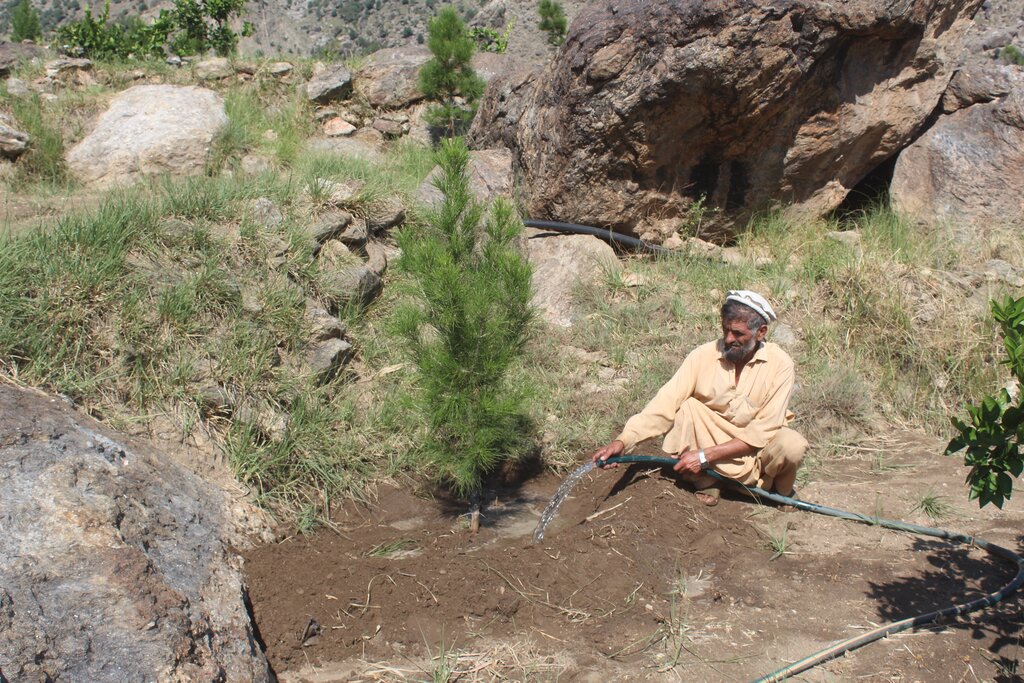
Water exploitation is a critical issue in Afghanistan, and the project aims to address this challenge through innovative and sustainable technology. The technology involves the use of solar panels and submersible water pumps to efficiently lift water from a nearby river to reservoirs constructed uphill, which is then distributed by gravity with the help of a pipe system to irrigate planted saplings in the afforested and agroforestry area. For afforestation, Pinus eldarica (Afghan pine) was planted due to its adaptability and soil stabilization properties. Additionally, citrus and persimmon trees are introduced for agroforestry, combining tree cultivation with agricultural benefits. This integrated technology promotes biodiversity, soil health, and sustainable land use, making the site a model/ demonstration site for afforestation and agroforestry practices. This is a significant advancement in the local area, utilizing clean energy to promote sustainable land and forest management and environmental restoration. The project is implemented on communal land, covering 50.25 hectares of land.
The primary purpose of this technology is to create an efficient irrigation system that extracts and transports water to support afforestation and agroforestry activities. By doing so, it aims to restore forest cover, mitigate environmental challenges such as land degradation, and promote long-term ecological and socio-economic sustainability. The technology includes key components such as solar panels, water pumps (submersible), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, water reservoirs, and saplings. Additionally, it requires labor, technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and construction materials for its establishment and maintenance.
The benefits of this technology are substantial. It has successfully irrigated previously barren land, achieving an impressive 85% survival rate for the saplings that were planted in the plot, while preventing land degradation and improving soil health. Without this technology, survival rates would drop to zero due to the arid conditions. Furthermore, the project has enhanced the capacities of local farmers/community members, enabling them to replicate and demonstrate the technology within their community. This has fostered a sense of ownership and empowerment among land users.
Land users have expressed both appreciation and concerns regarding the technology. On the positive side, they value its efficiency and reliability, as the solar panels provide a consistent water supply, especially during the hot/sunny season, leading to increased greenery and healthier trees. The cost-effectiveness of solar energy, with its low operational costs compared to traditional diesel pumps, has also been a significant advantage. Additionally, the environmentally friendly nature of the technology aligns with their desire for sustainable practices. The capacity-building programs provided by organizations like FAO have further empowered users to manage the system effectively.
However, some challenges have been noted. The initial investment costs for purchasing, installing and construction of the technology are high, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to replicate. Technical issues, such as inverter failures or battery malfunctions during extreme weather conditions (e.g., cloudy weather), can disrupt operations. Additionally, not all community members are equally informed about the technology’s benefits, highlighting the need for increased outreach and engagement efforts to ensure broader adoption and understanding.
In summary, this solar-powered irrigation technology represents a groundbreaking innovation in the area, combining clean energy with sustainable land management practices. While it has demonstrated significant environmental and agricultural benefits, addressing the challenges of initial costs, technical reliability, and community engagement will be crucial for its long-term success and scalability.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.4 Vídeos da tecnologia
Localização:
N/A
Nome do cinegrafista:
N/A
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Kunar
Especificação adicional de localização:
Managi village of Manogi district
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
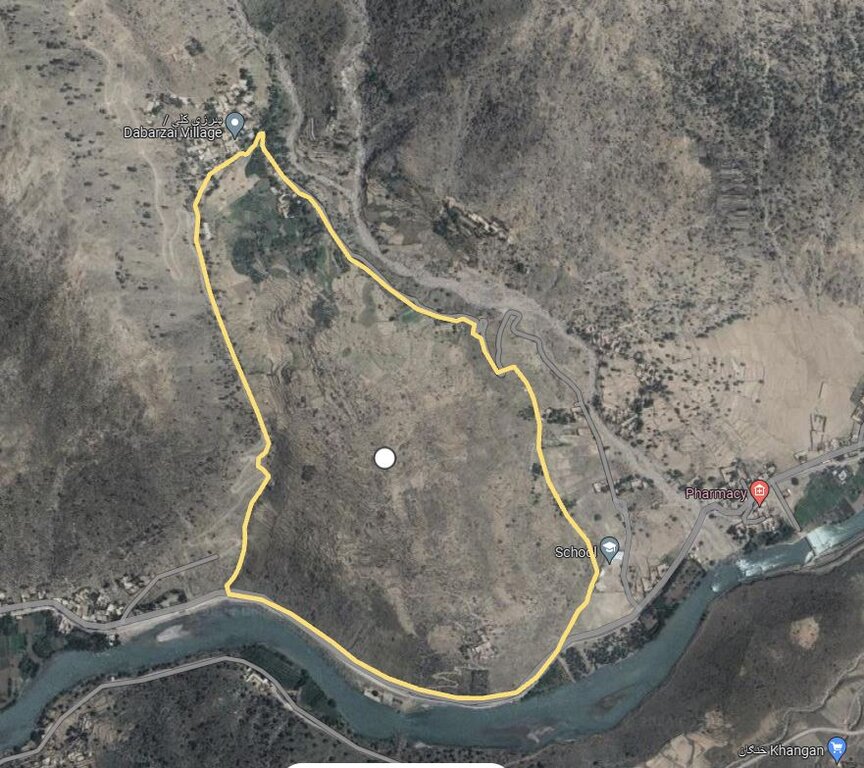
The area is about 50.25 ha, and the coordinate has been taken from the center of the site, where technology has been implemented:
34.9419930°N71.0119714°E
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2022
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
GEF-06 Community based Sustainable Land and Forest Management in Afghanistan
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- cítrico
- Persimmon
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não

Floresta/bosques
- Plantação de árvores, reflorestamento
Plantação de árvores, florestamento: Especificar a origem e composição das espécies:
- Monocultura de variedade local
Tipo de plantação de árvores, florestamento:
- plantação de floresta seca subtropical - Pinus spp.
Tipo de árvore:
- Espécies de pinus (pinheiro)
As árvores especificadas acima são decíduas ou perenes?
- perene
Produtos e serviços:
- Conservação/proteção da natureza
- Lazer/turismo
- Proteção contra desastres naturais
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
5 decades ago, the area was a forest area, but due to war, smuggling and drought the area become barren land.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
The saplings planted in the area have been supplementary irrigated. Prior to the implementation of this technology, the land was barren, and seasonal rains led to soil erosion.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de plantação florestal
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Tecnologias de eficiência energética
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação
- S10: medidas de economia de energia

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M3: Disposição de acordo com o ambiente natural e humano
Comentários:
The project has successfully implemented afforestation by planting trees and promoting agroforestry through the cultivation of fruit trees. To improve irrigation management, the project installed a 1-inch underground pipeline system with connected taps, enabling the attachment of flexible hoses. This efficient setup ensures optimal watering of saplings while significantly reducing water waste. By implementing this approach, the project has enhanced vegetative cover and successfully planted approximately 32,000 saplings. Additionally, the project constructed 14 rotating mounting structures for solar panels, installed 134 solar panels, established pipe schemes for manual irrigation of saplings, and constructed 6 water reservoirs with different capacities. The integration of trees at optimal spacing, combined with regular cultural practices, has further supported the project's goals.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bl: perda da vida do solo

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários:
The planting pits are specially designed for planting of saplings. Additionally, farmers construct small barriers near plants (eye-brows and trenches), known as micro-catchments, to collect and retain water. It is important to note that these micro-catchments are distinct structures, separate from pits and reservoirs, and are specifically built to support water retention for plants. The enhanced vegetation cover and the establishment of micro-catchments for water collection significantly reduce soil erosion. Soil improvement and enrichment, as well as habitat enhancement, are supported through these practices. Additionally, they contribute to groundwater recharge and help control runoff.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The human-induced causes of land degradation include deforestation, overgrazing of livestock, and unsustainable agricultural practices. In response, following the implementation of a specific technology, local communities established regulations rooted in their customs and traditions to protect the site, which is quarantined for five years. These regulations prohibit herders from grazing animals, cutting trees, engaging in unsustainable agricultural practices, and uprooting bushes for fuelwood. Additionally, the community has constructed rainwater harvesting structures, such as eyebrows and trenches, across the site to address natural causes of land degradation through runoff by enhancing water infiltration. As a result, the site is now effectively protected from both human-induced and natural land degradation.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
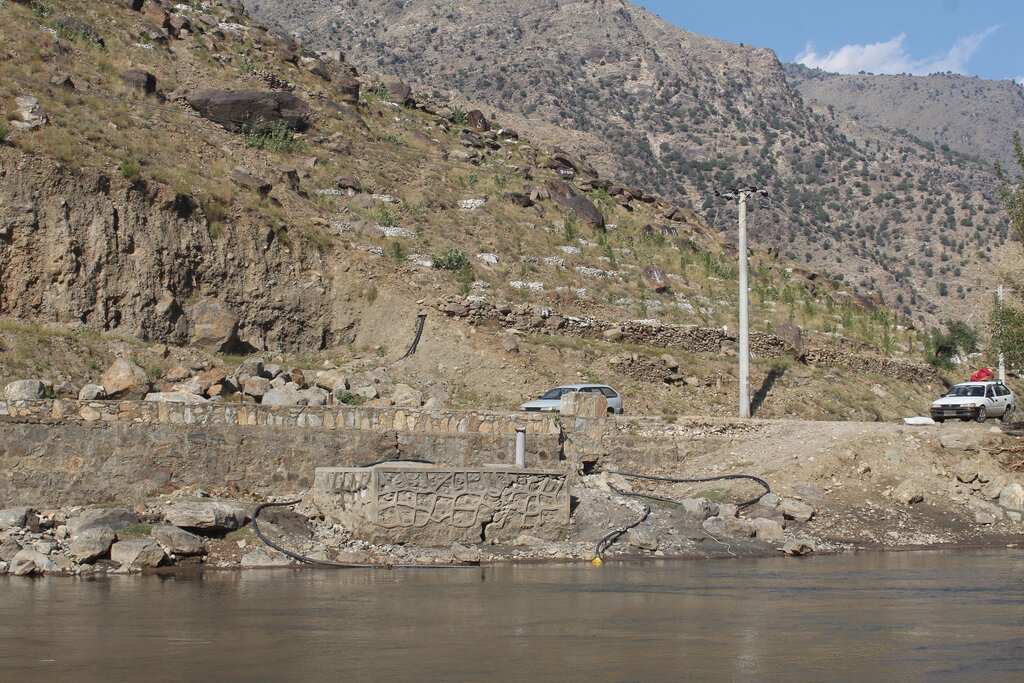
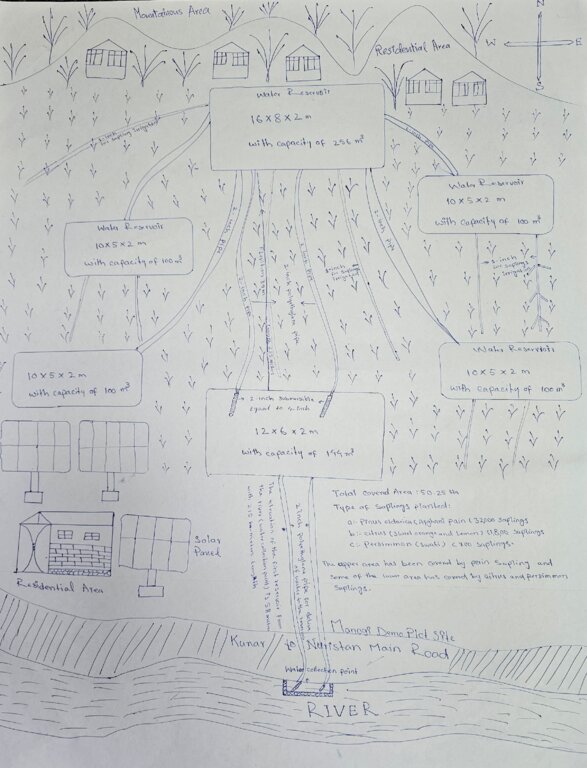
According to the technical specifications from the project engineer, 6 reservoirs have been constructed with varying dimensions and water holding capacities as follows:
1.First reservoir: Dimension of 12x6x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 144 m³.
2.Central reservoir: Dimensions of 16x8x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 256 m³.
3.Four additional reservoirs: Each measuring 10x5x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 100 m³
In total, the reservoirs will hold 800 m³ of water, ensuring a reliable water supply for irrigation of the area. Two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs by gravity.
Furthermore, excavation and backfilling for 2-inch polyethylene pipes should be done to a depth of 80 cm with a width of 50 cm. For 1.5-inch pipes, excavation and backfilling should be 40 cm deep. The installation of 1.5-inch polyethylene pipes, including all elbows, joints, connectors, and valves, should be carried out every 30 meters on both sides, connecting to 1-inch pipes, in accordance with specifications and to satisfaction.
Additionally, 32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghan Pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings were planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. The saplings are spaced 5 meters apart, both plant-to-plant and row-to-row, as part of afforestation and agroforestry initiatives. This effort aims to restore ecosystems, enhance biodiversity, and improve soil conservation.
Autor:
Hafizullah Naeemy
Data:
01/03/2022
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
50.25 Hectares
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5 USD
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Awareness and mobilization of the community | Aug-2021 |
| 2. | Survey and site selection followed by feasibility study | Sep to Oct-2021 |
| 3. | Stakeholder consultation | Aug-2021 till Sep-2022 |
| 4. | Preparation of technical design, drawings, and Bill of Quantities (BoQ). | Nov to Dec-2021 |
| 5. | Initiation of procurement process for required tools and equipment | Jan to Feb-2022 |
| 6. | Excavation and construction of water reservoirs, setting up pipe system and installation of solar panels for irrigation. | Mar to Sep-2022 |
| 7. | Capacity building of the target communities | Aug- 2021 till date |
| 8. | Practical interventions: production or purchase of saplings, digging planting pits, transplatation and irrigation of saplings and establishment of micro-catchments | Feb to Mar-2023 |
Comentários:
The awareness-raising session on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) was successfully held to improve understanding of land and forest management practices and conservation efforts. Community members were actively mobilized to support the project, aiding in the completion of construction and installation work.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Unskilled labor for planting of saplings | Man/day | 450,0 | 5,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Skilled labor for installation of irrigation system and constuction of reservoirs | Man/day | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | |
| Equipamento | Water Pump 2 inch - 10HP/7500w | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Equipamento | Solar Panel minimum size 400W and 270W | Number | 132,0 | 82,0 | 10824,0 | |
| Equipamento | DC to AC Inverter 7.5-11KW | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| Equipamento | Polyethylene Pipes 2 Inch and 1.5 Inch with all elbows, joints, connectors and valves after 30 meter for both sides to connect pipes. | Meter | 4300,0 | 2,75 | 11825,0 | |
| Equipamento | Rotating PV panels mounting structure (manual) | Number | 28,0 | 270,0 | 7560,0 | |
| Equipamento | DC and AC current wire | Meter | 1800,0 | 2,5 | 4500,0 | |
| Equipamento | Distribution board | Number | 2,0 | 70,0 | 140,0 | |
| Equipamento | Flexon 1 inch rubberize pipes | Meter | 5500,0 | 1,4 | 7700,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Saplings procured & transported | Sapling | 32000,0 | 0,775 | 24800,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Planting tools | lump sum | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Organic fertilizers for transplanted saplings added through community | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | 6 reservoirs constructed by a construction company (cement, stone, sand excavation, etc.. | lump sum | 1,0 | 35000,0 | 35000,0 | |
| Outros | Patrolling, irrigating and quarantine of the site | lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 111799,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 111799,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The remining cost were covered by the project.
Comentários:
The first two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs through gravity.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Patrolling | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump (submersible) | Ad hoc /Annually |
| 4. | Plot maintenance (Pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding,). | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacement of failed saplings | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing micro-catchments | Spring/annually |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labor for cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Man/day | 60,0 | 5,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labor for patrolling | Man/day | 360,0 | 5,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labor for repairing micro-catchments | Man/day | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Manage the solar system operations | Man/day | 360,0 | 2,77 | 997,2 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Labor for weeding and mulching | Man/day | 30,0 | 5,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Pump submersible, PVC pipe, fittings | lumpsum | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Shovels | lumpsum | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | saplings | Sapling | 2000,0 | 0,6 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Organic fertilizers (cows dungs) | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 7787,2 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 7787,2 | |||||
Comentários:
The community has hired an individual to manage the solar system operations. This person is responsible for both operating the solar system for lifting water and overseeing the distribution of water for irrigation purposes among community members.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
All equipment are imported and has resulted into higher cost.
Natural hazards, floods and windstorms will increase the costs of repairs and replacement
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
300,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Most of rain occur in the months of Feb, Mar, Apr, July and Aug.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
The data has been collected based on the farmers observation and local practices.
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Frequentemente
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The area where the technology is applied covers 50.25 hectares and is managed by 112 land users.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
In Afghanistan, the traditional land use system involves the equitable distribution of deserts and barren land among the local residents. The decisions made by the elders are respected and adhered to by all members of the community.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
fruit production (citrus and persimmon)
Comentários/especificar:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as part of the agroforestry system and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people. Based on the production, the socio-economic status of the community members is expected to improve.
Produção de madeira
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
A total of 32,000 forest saplings (Pinus species) were successfully planted
Comentários/especificar:
32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghani pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. Following agronomic practices, the four Ds—dead, diseased, damaged, and dying—branches will be pruned and utilized for shelter and fuel.
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0 fruit trees
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Approximately 1,200 fruit trees, including sweet orange and persimmon species, have been planted
Comentários/especificar:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as a agroforestry and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
The area was once barren and occasionally used for rainfed cultivation, where most farmers grew wheat. Now, with the introduction and implementation of the technology farmers can also intercrop beans, mung beans, and others. Farmers who have more than 1 hectare of land hire labor for agronomical practices.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
100%
Comentários/especificar:
With the adoption of this technology, irrigation for planted saplings is now available 100% throughout all seasons of the year.
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Timber Production, Non-Timber Forest Products, Ecotourism, Agroforestry, Wildlife Conservation and Fuelwood and Biomass
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
Recreational opportunities that benefit both local communities and visitors such as nature trails allowed individuals to engage with nature, promoting physical activity and wellness. The reforestation efforts have led to the restoration of habitats for various wildlife species, this provides opportunities for wildlife observation and photography, and contributing to local ecotourism.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Improved due to workshops and on job trainings
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil coverage by plantation of saplings and micro-catchment structures
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to the availability of irrigation water and the establishment of micro-catchments to harvest water and enhance water infiltaration soil moisture for sapling growth has increased
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to natural regeneration and plantation of saplings and intercrops
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil coverage and less water runoff
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
better soil cover reduced water runoff and ultimately flooding
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Comentários/especificar:
Soil erosion was reduced and has been better controlled
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Due to plantation
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | aumento | moderadamente | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | primavera | aumento | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de vento local | moderadamente |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
The community economic condition is not good. So, without receiving incentives they are not able to adopt such technology easily.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Improved water availability with minimized fuel cost and decreased pollution as well as minimum operational cost |
| Opportunities/ potential for upscaling of the technology |
| Use of clean energy to contribute to mitigate climate change |
| Reduce greenhouse emission through carbon sequestration |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The technology is highly efficient and suitable for adoption by land users. It promotes clean energy, reduces greenhouse gas emissions through carbon sequestration, and contributes to climate change adaptation. |
| The area has been successfully afforested, restoring its natural beauty and original landscape. |
| The vegetation cover on the previously degraded land has been significantly enhanced. |
| This technology with its approach for implementation represents an effective solution for the restoration of degraded soils. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Inadequate maintenance and repair services of the technology | Linkage to the service provider and maintenance services. Nation wide technology transfer |
| Solar water lifting relies on fully sunny days for operation, which can sometimes be a limitation, especially when weather conditions are cloudy or during periods of low sunlight. This can result in insufficient water being lifted to meet the irrigation needs of the site. | Backup charging system/battery system |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Solar water lifting depends on sunny days for operation, which can sometimes fall short of meeting irrigation needs during cloudy periods. | Combining solar power with backup energy (like batteries or grid connection) |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
10
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
15
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
2
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
28/11/2024
Comentários:
The data has been collected during Oct and Nov 2024
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos